midterm practice
1/585
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
586 Terms
Where is the blind spot located?
where the optic nerve passes out of the eye
What fluid is found in the anterior chamber?
aqueous
labeled a
vestibule
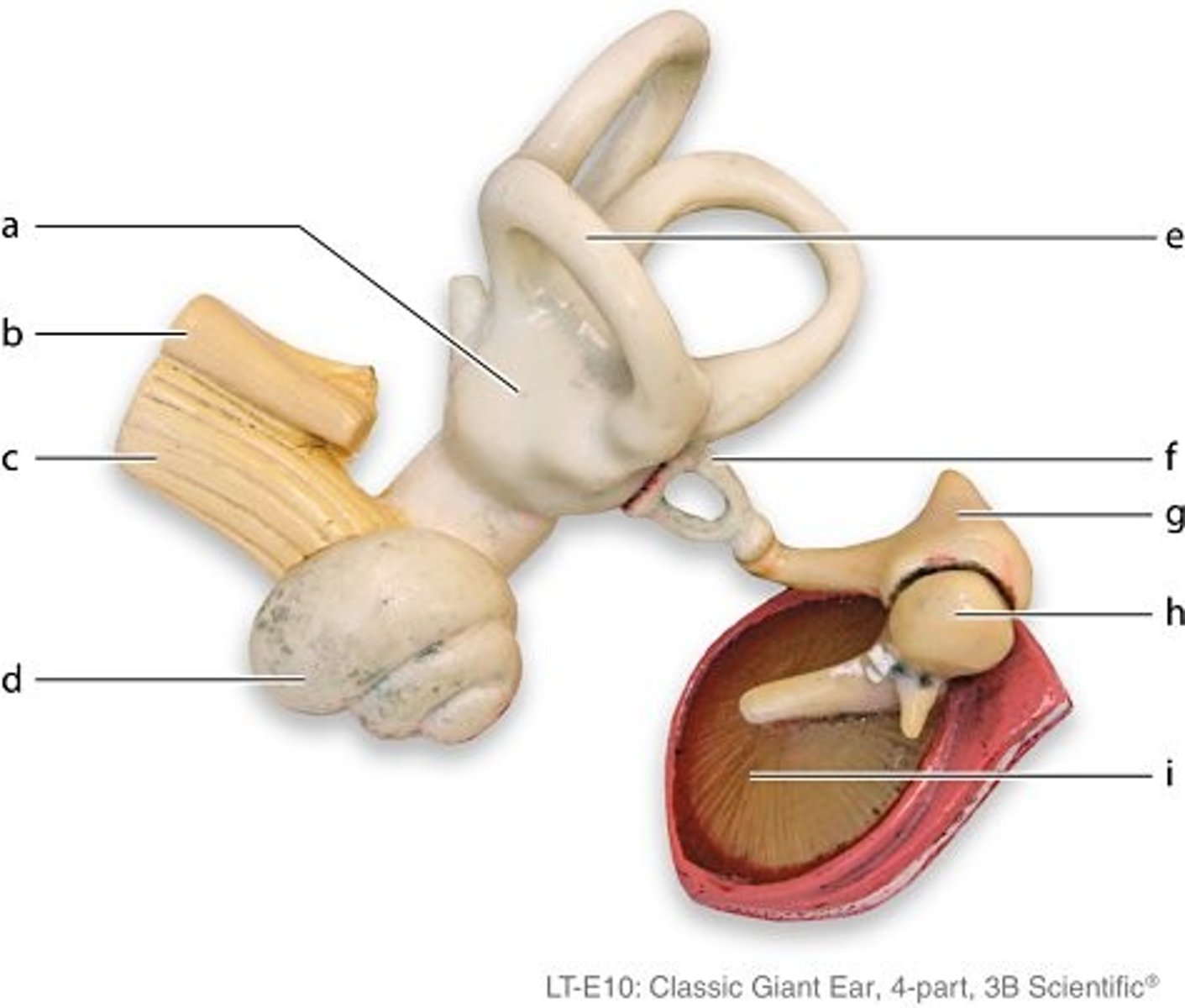
labeled b
cornea
What is the cause of color blindness?
missing or abnormal cones
Which cranial nerve does NOT innervate the extrinsic eye muscles?
facial nerve
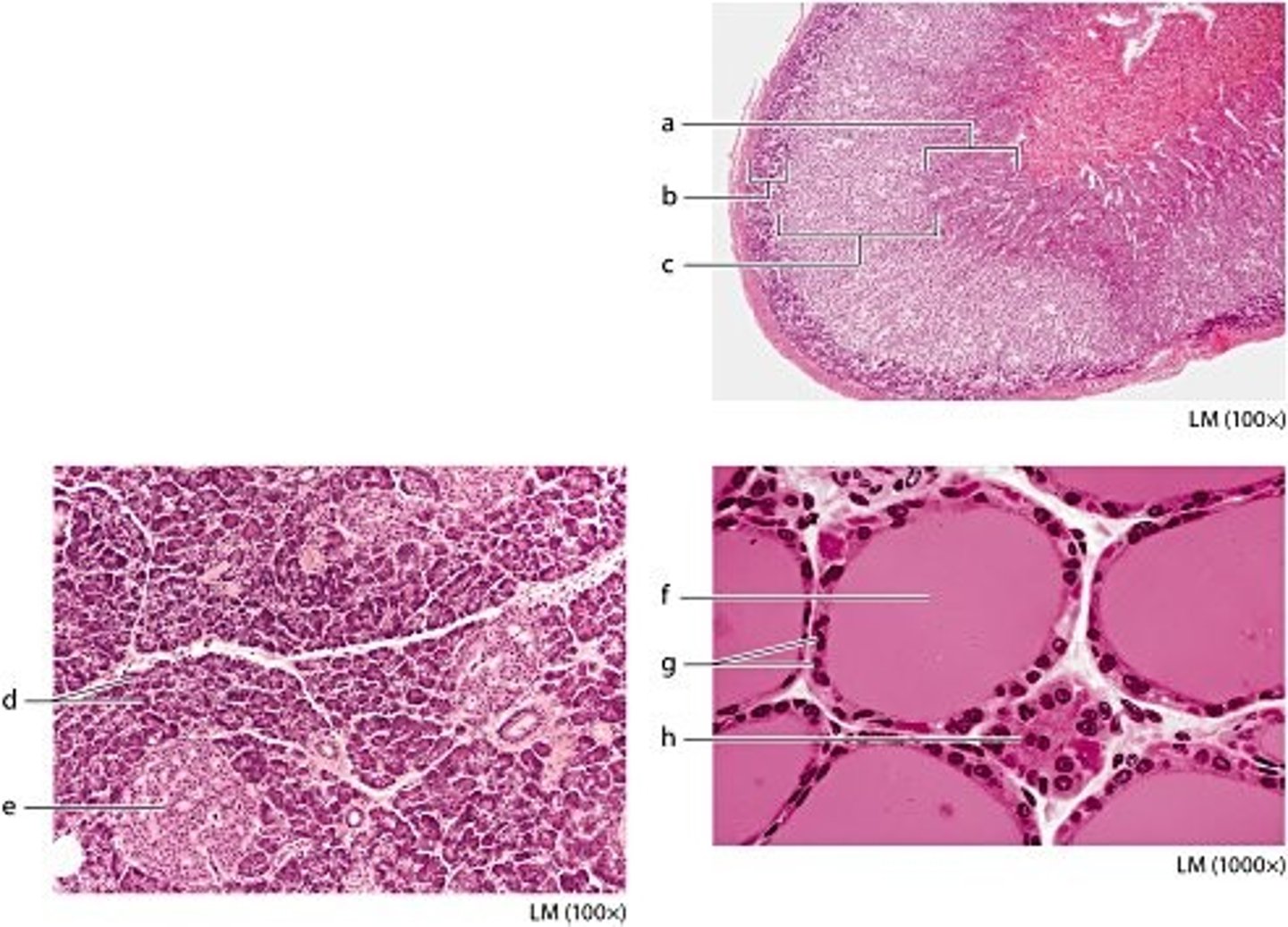
labeled a
zona reticularis
Which gland produces prolactin?
pituitary gland
Which cells produce oxytocin?
neuroendocrine cells
labeled c
anterior pituitary
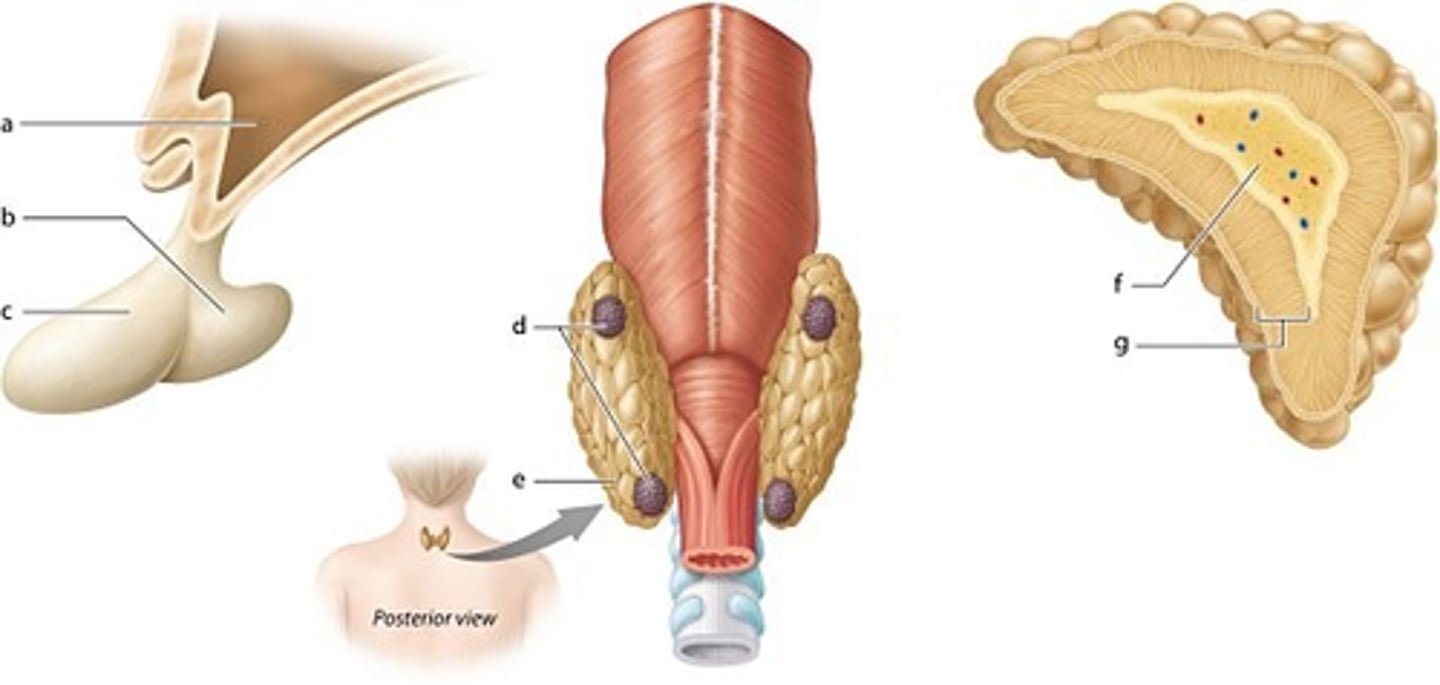
labeled f
adrenal medulla
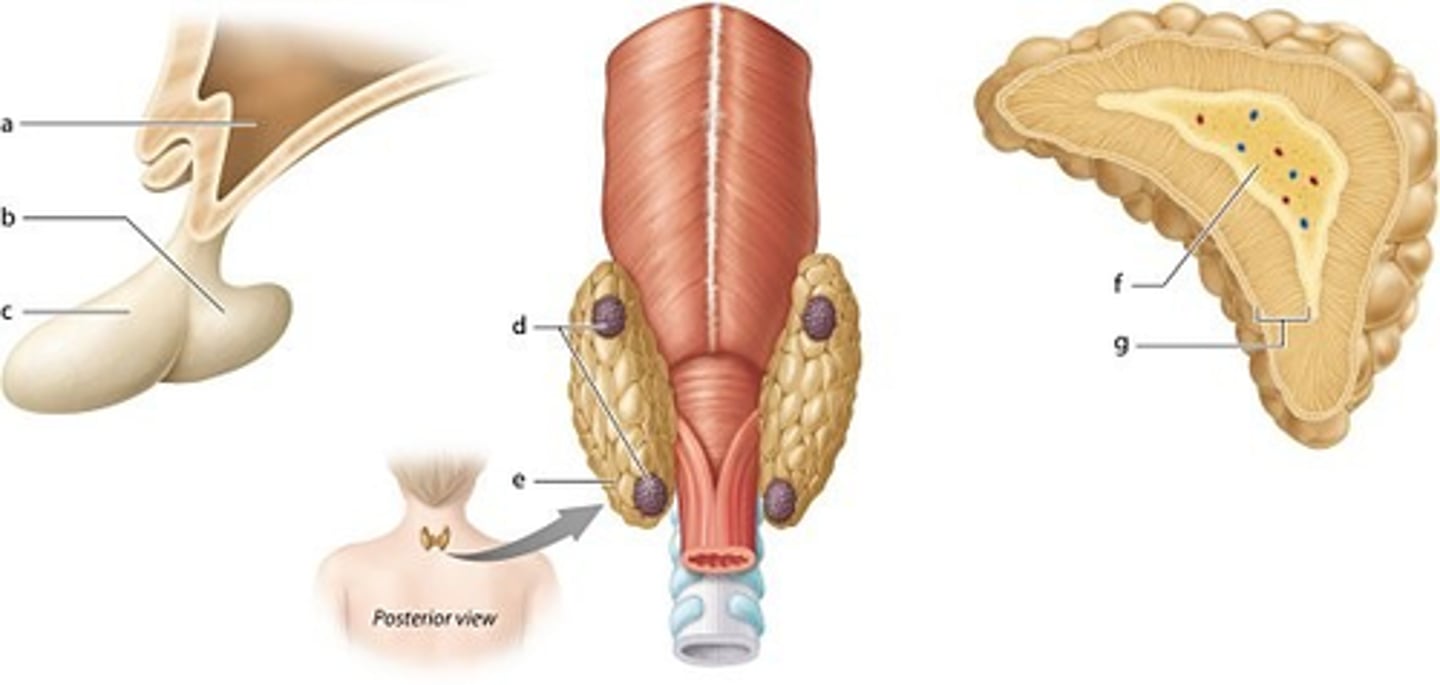
Which hormone is produced in the hypothalamus?
oxytocin
What antigen is present on the surface of B+ erythrocyte?
B antigen and +Rh antigen
What is a hematocrit?
percentage of erythrocytes in a blood sample
Which formed element functions in blood clotting?
thrombocyte
Which formed element contains hemoglobin?
erythrocyte
labeled e
platelet
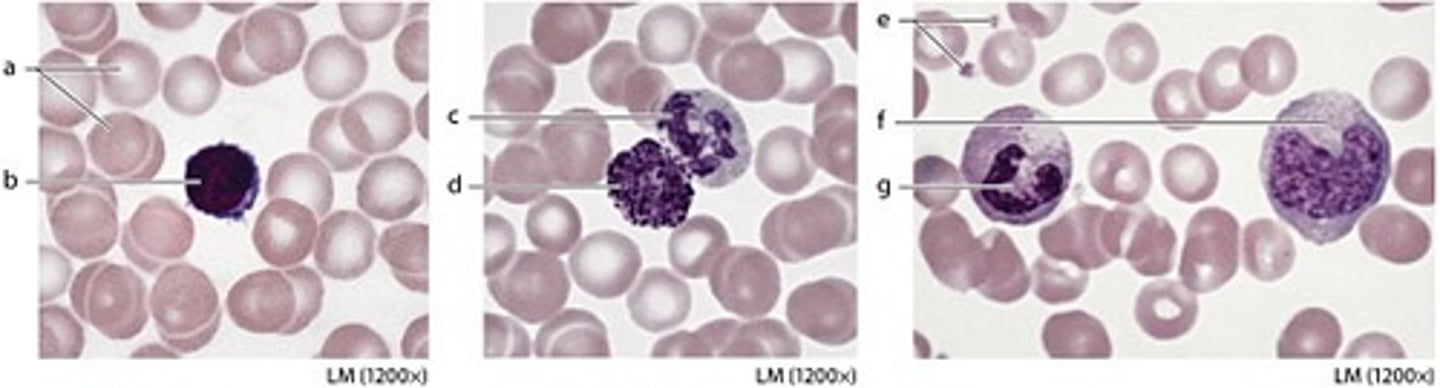
Which best describes coagulation?
It is a positive feedback mechanism.
How is the base of the heart different from the apex of the heart?
The great vessels are located on the base.
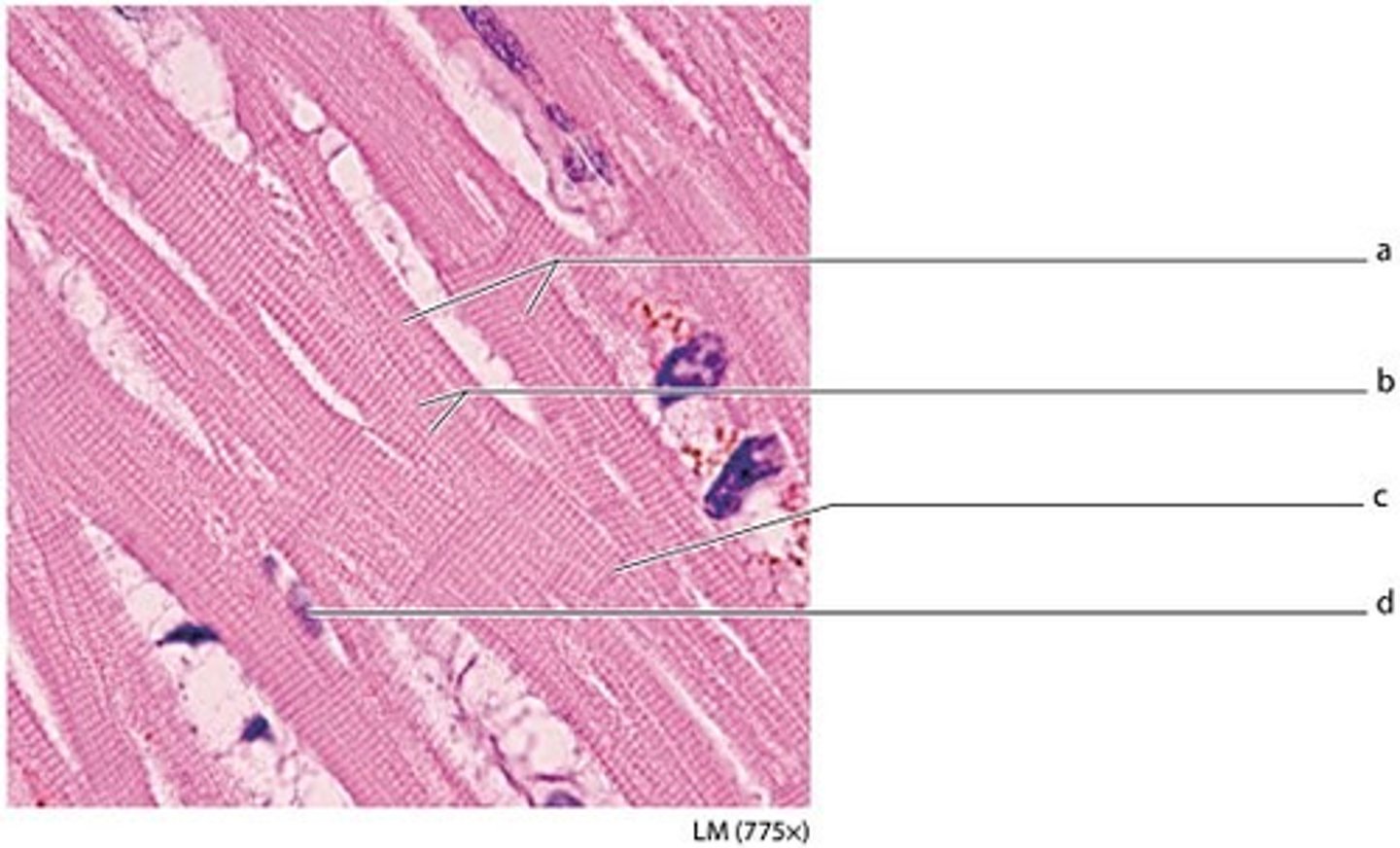
labeled a
cardiac muscle fibers
Which structure separates the right and left ventricles?
interventricular septum
labeled g
left ventricle
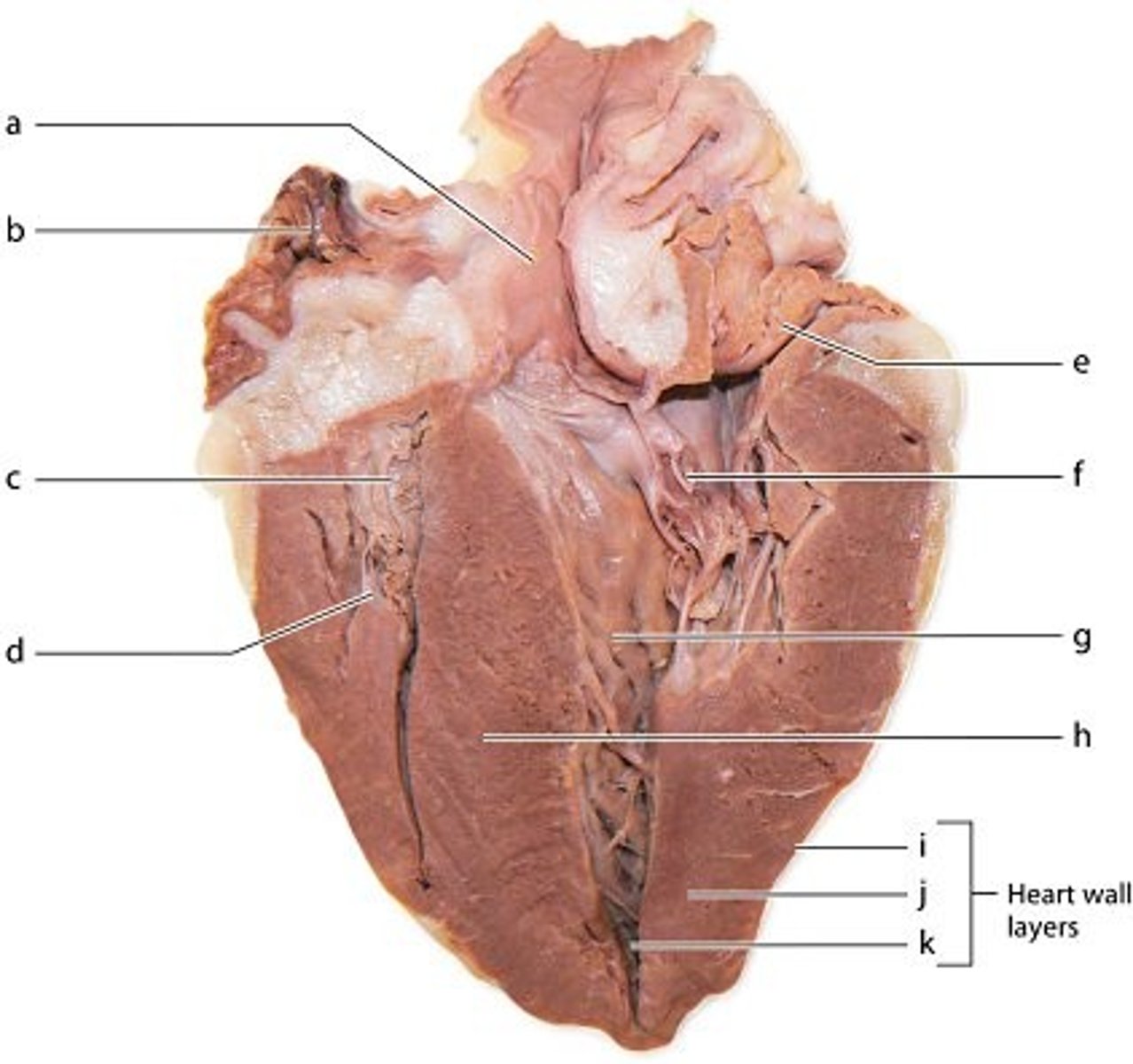
How is backflow of blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium prevented?
tricuspid valve
What is the anatomical term for the "pacemaker" of the heart?
SA node
Which component of the ECG represents the depolarization of the ventricles?
QRS complex
How many electrodes should be attached to the left forearm to record a 3 lead ECG?
0
Which component of the cardiac conduction system extends through the interventricular septum toward the apex of the heart?
right and left bundle branches
What is the direct source of the heart sounds in a heartbeat?
snapping shut of valves
labeled d
basilic vein
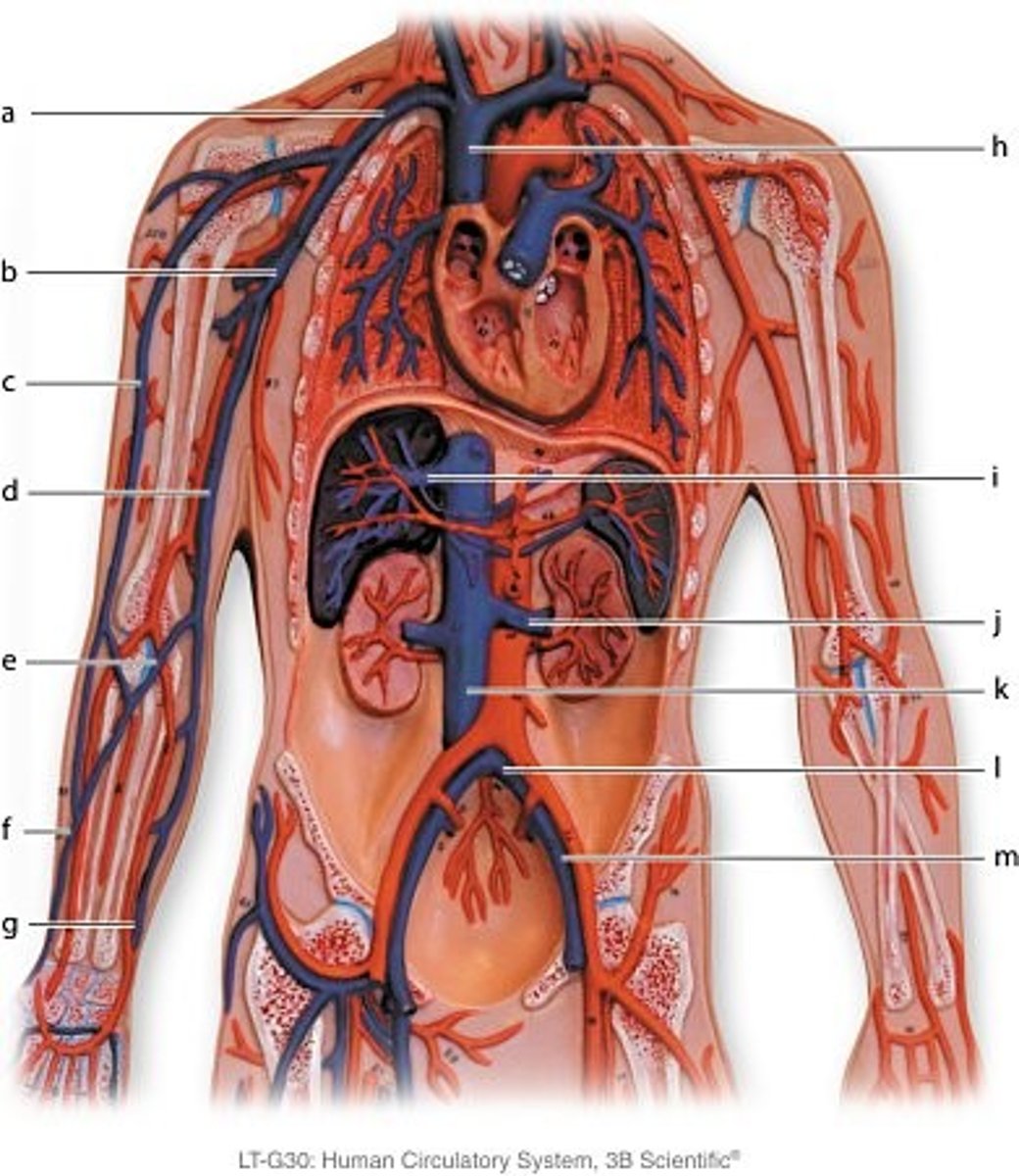
Which blood vessel connects the basilic and cephalic veins?
median cubital vein
labeled e
median cubital vein
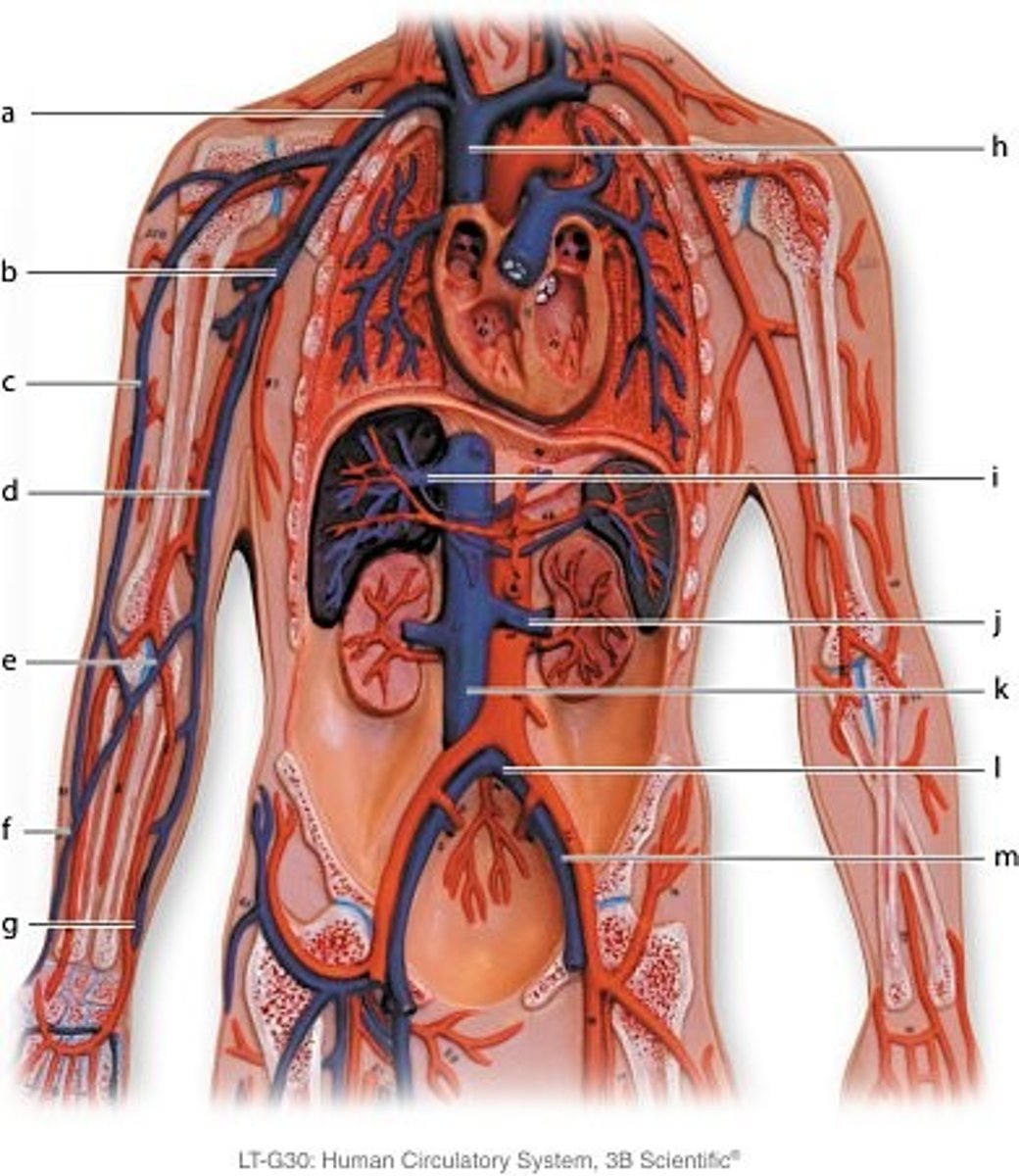
Which blood vessel has the thickest layer of smooth muscle?
artery
Which blood vessel branches from the brachial artery?
radial artery
Which vessel empties directly into the superior vena cava?
brachiocephalic vein
Which lymphoid organ filters lymph?
lymph nodes
In an ELISA, which statement is true of the substrate?
It is the last molecule added.
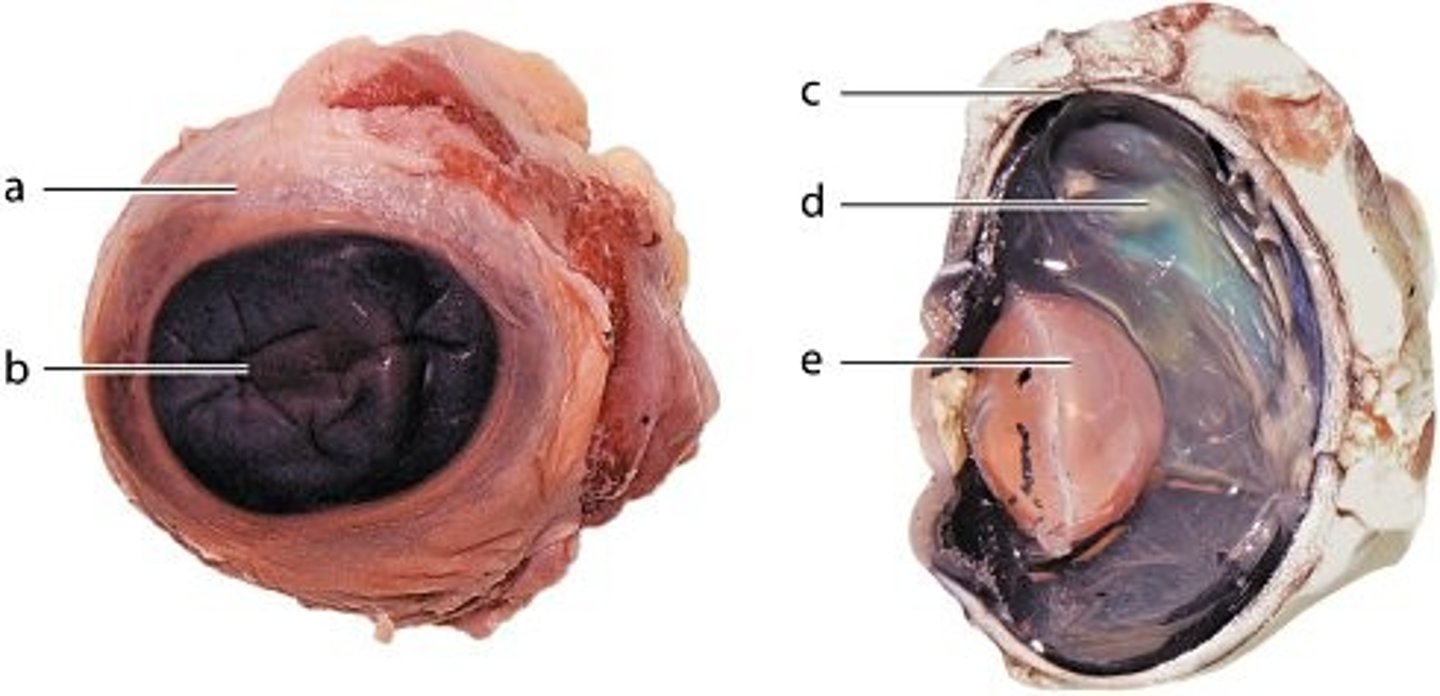
An examination of a micrograph shows that there are more afferent vessels than efferent vessels entering a particular structure. What lymphoid organ is the micrograph?
lymph node
Which statement describes the thymus?
It atrophies with age.
Where does the thoracic duct begin?
at the cisterna chyli
Why does a positive pregnancy test have two pink stripes?
One stripe binds to the hormone, the other stripe is a control zone.
Area of retina specialized for detailed vision
H
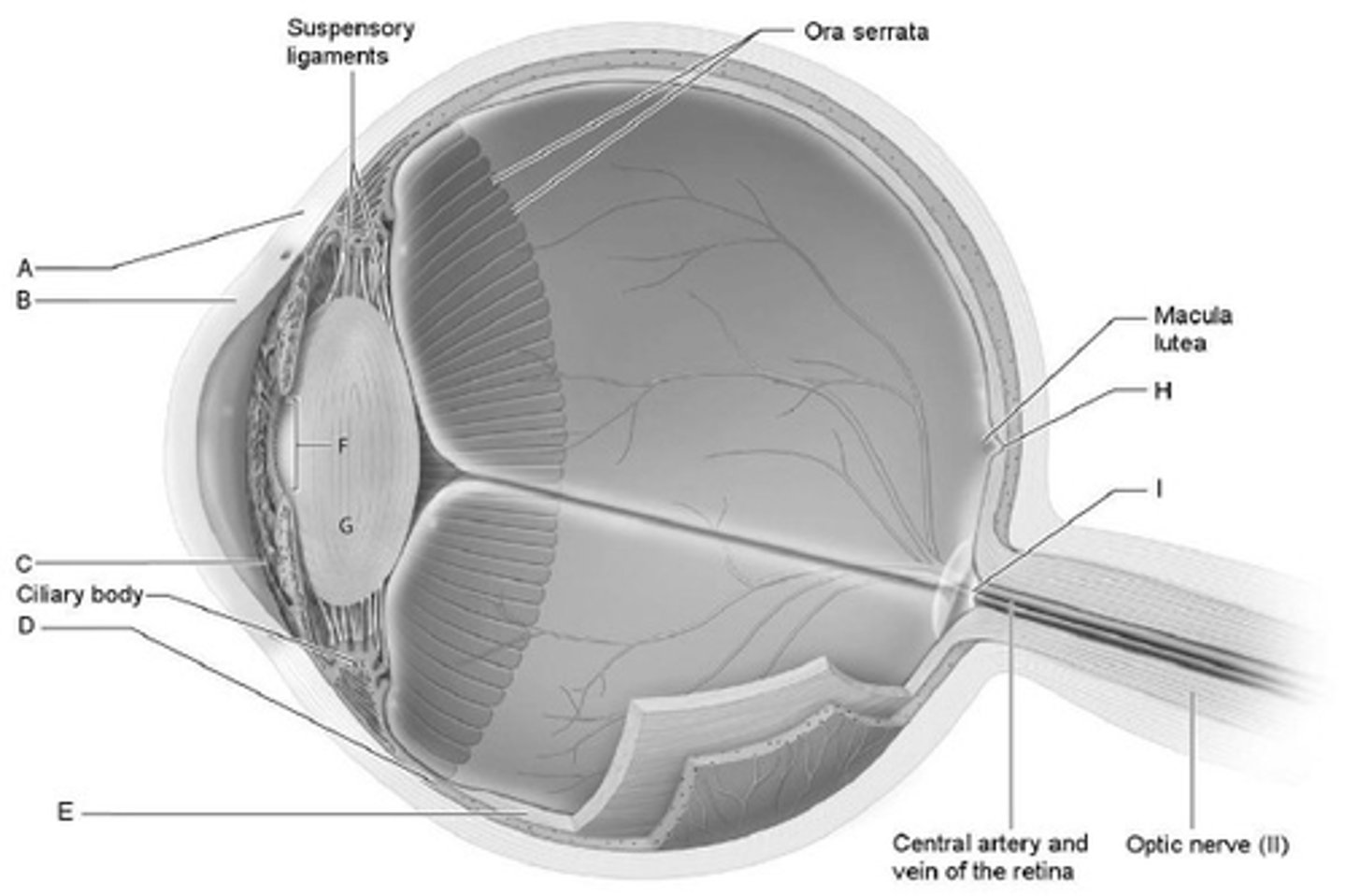
The receptor cells for static equilibrium are located in the:
maculae of the utricle and saccule of the vestibule.
What equalizes pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane?
pharyngotympanic tube (auditory tube)
Where is the primary gustatory cortex located?
frontal lobe
The startle reflex occurs when unexpected sounds reach the:
midbrain
What cranial nerve carries information about hearing and head movement to the brain?
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Olfaction is the sense of:
smell
The activation of olfactory receptors requires that the odorant become immersed in:
mucus
tympanic membrane
c
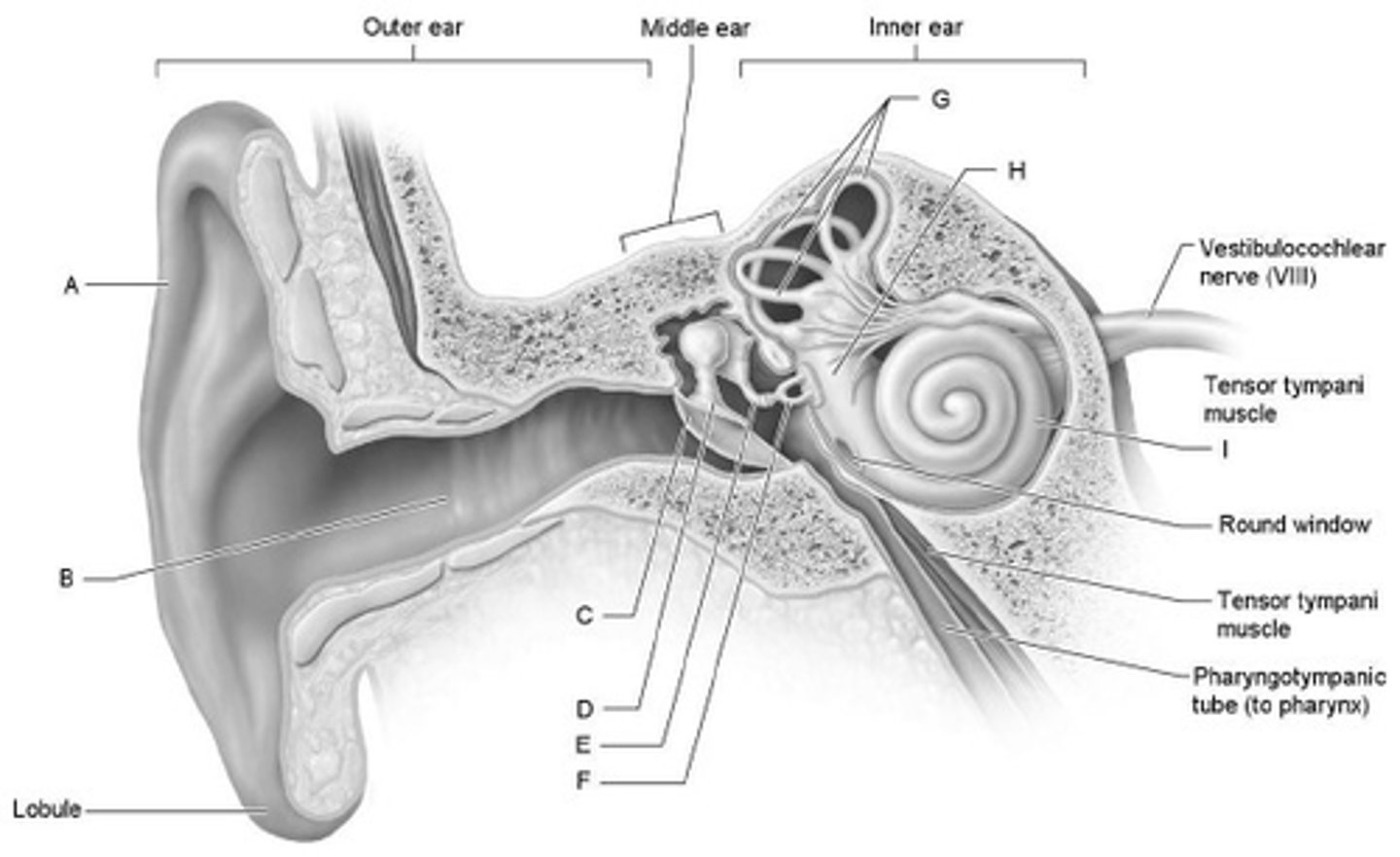
Where does the conscious awareness of sound begin, along with the analysis of its pitch, location, and loudness?
temporal lobe
How are the nervous system and endocrine system similar?
Cells of both the nervous system and the endocrine system release chemicals to communicate with cells.
What hormone is the primary antagonist of glucagon?
insulin
Place the following hormones in the correct order of their control, from first tier to third tier.
thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), production of T3 and T4
A short-term effect of growth hormone is:
fat breakdown
Chemical messengers released by endocrine glands to regulate some functions of other cells are known as:
hormoens
All target cells:
have receptors to which hormones bind.
What hormones are released by the posterior pituitary?
antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin
Avery has high blood pressure and hypernatremia (excess blood sodium ion concentration). The hypersecretion of which hormone could lead to his condition?
aldosterone
Upon binding to a receptor to form a hormone-receptor complex, steroid hormones may cause:
an increase in protein synthesis.
Increasing levels of blood glucose stimulate the release of insulin. This type of stimulation is known as:
humoral stimulation
Which valve is situated between the left atrium and left ventricle?
bicuspid (mitral) valve
Blood in the right ventricle arrived from the:
right atrium
What is the function of the valves in the heart?
prevent backflow of blood through the heart
Which two arteries arise from the right coronary artery?
the right marginal artery and the right posterior interventricular artery
Which of the following does NOT return blood to the right atrium of the heart?
pulmonary vein
Which vessel supplies the systemic circuit with oxygenated blood?
aorta
The sinoatrial (SA) node fires more rapidly at higher body temperatures, increasing cardiac output.
true
Generally, coronary veins empty into a vessel known as the:
coronary sinus.
What activity is occurring in the heart during the Q-T interval on an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
The ventricular cells are undergoing action potentials.
Which chamber experiences a maximum pressure of around 118 mm Hg during contraction?
left ventricle
Which of the following arteries gives rise to all others listed?
axillary artery
The outward force that blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels is:
blood pressure
The union of the radial and ulnar veins forms the:
brachial vein.
Which blood vessels experience the sharpest decrease in blood pressure?
systemic arterioles
Which mechanism allows lipid-soluble substances to move through the membranes of endothelial cells of capillaries?
diffusion
Which artery supplies the small intestine with blood?
superior mesenteric artery
What name does the femoral artery take as it emerges in the posterior thigh?
popliteal artery
Cerebrospinal fluid drains into:
dural sinuses
Which of the following arteries has the smallest diameter?
metarteriole
Central chemoreceptors detect a decrease in pH in interstitial fluids in the brain. What is the response of the medulla to maintain delivery of oxygen to cells?
A feedback loop is initiated that indirectly increases sympathetic activity which results in vasoconstriction and a rise in blood pressure.
Carbohydrate groups on the surfaces of erythrocytes determine blood type and are known as:
antigens
When is fibrin produced during the coagulation cascade?
common pathway
What organ secretes most of the plasma proteins?
liver
Select the correct pathway to form a monocyte through the process of leukopoiesis.
HSC, myeloid cell line, monoblast, promonocyte, monocyte
During the common pathway, what turns fibrinogen into fibrin?
thrombin
What is the most common type of leukocyte in a healthy adult?
neutrophill
Which of the following must occur first during hemostasis?
Group of answer choices
formation of thrombin
Where do T lymphocytes mature?
thymus gland
All leukocytes arise from:
hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs).
Platelets are cell fragments formed from:
megakaryocytes.
Which of the following represent the five basic classes of antibodies?
IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM
What are the primary cells of adaptive (specific) immunity?
lymphocytes
Cells that help regulate the immune response are:
helper T (TH) cells.
Which of the following is NOT a surface barrier serving as the first line of defense?
antibody
How many antigen-binding sites for antigens does each IgG antibody possess on its V regions?
2
The clumping of cells that are cross-linked by their attachments to antibodies is known as:
agglutination
Mrs. Sanchez had a great deal of inflammation after her recent surgery. The inflammation was triggered by the antibody known as:
ige
What do lacteals, located in the small intestine, collect?
fat
B cells develop and mature in the:
bone marrow
Which lymph trunks receive lymph from the upper limbs?
subclavian trunks