Ecology lecture 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
ecology
science of complex interactions
30 degrees North
hot deserts
30 degrees south
tropical deserts
Above 0 degrees Kelvin emits?
electromagnetic radiation
^max = 2897000/T
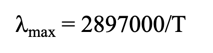
Wien’s Law
shorter wavelength (greater or lower energy)
greater energy
0-3000 nm
short wavelength
3000 - 100,000 nm
long wavelength
6000 degrees, wavelength max: 480 nm
the sun
288 degrees (255 w/o atmosphere); wavelength max: 10200 nm
the earth
CO2 (greenhouse gas)
carbon dioxide
CH4 (greenhouse gas)
methane
CFCs (greenhouse gas)
chlorofluorocarbons
N2O (greenhouse gas)
nitrous oxide
O3 (greenhouse gas)
ozone
the earth is..? (degrees celcius)
15 degrees C
what would the Earth’s temp be without greenhouse gases?
-18 degrees C
a = 1
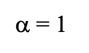
complete absorption at a given wavelength
does the earth primarily take in short or long waves?
short
does the earth primarily emit long or short waves?
long
what causes differential heating?
At higher latitudes, light strikes the Earth’s surface at a lower angle and gets spread over a greater area. At the equator, the sun is closer to what is perpendicular from it so its shining directly on the earth’s surface.
adiabatic lapse rate
The rate at which an air parcel changes temperature as it rises or sinks in the atmosphere without gaining or losing heat to its surroundings.
adiabatic cooling (4-7 degrees C of cooling for every 1KM of altitude)
As air is pushed upwards the pressure decreases and it
expands
which two months are equinox?
march and septemeber
which two months are solstice?
december and june
characteristics of water
high specific heat, amount of energy required for phase change, less dense when solid, high tensile/surface strength, an excellent solvent, an abundant greenhouse gas
ea
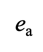
the ambient partial pressure of water in air (how much gaseous water is in the air right now)
ea/esat x 100
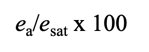
relative humidity
what does the ITCZ stand for
intertropical convergence zone
what is the ITCZ?
a belt around the Earth near the equator where the winds from the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere meet.
hadley cell
a giant loop of moving air: hot air rises at the equator, moves away, sinks at 30°, and returns back to the equator.
does the northern hemisphere have low or high pressure?
higher pressure
does the southern hemisphere have low or high pressure?
lower pressure
Water climate diagrams
left y axis: mean monthly temp
water climate diagrams
right y axis: mean monthly precipitation
what is always in the middle for water climate diagrams?
summer
water climate diagrams (blue means?)
precipitation
water climate diagrams (red means?)
temperature
water climate diagrams (dots means?)
potential evaporation exceeds preciptation
water climate diagrams (straight vertical lines mean?)
precipitation exceeds