Chapter 6 - Anatomy and Physiology (Part 1)
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
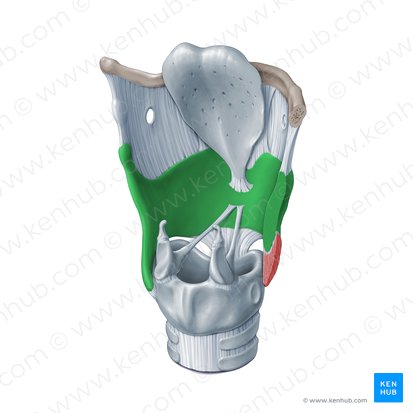
thyroid cartilage
What is the wing-shaped plate of cartilage that sits anterior to the larynx and forms the Adam's apple?
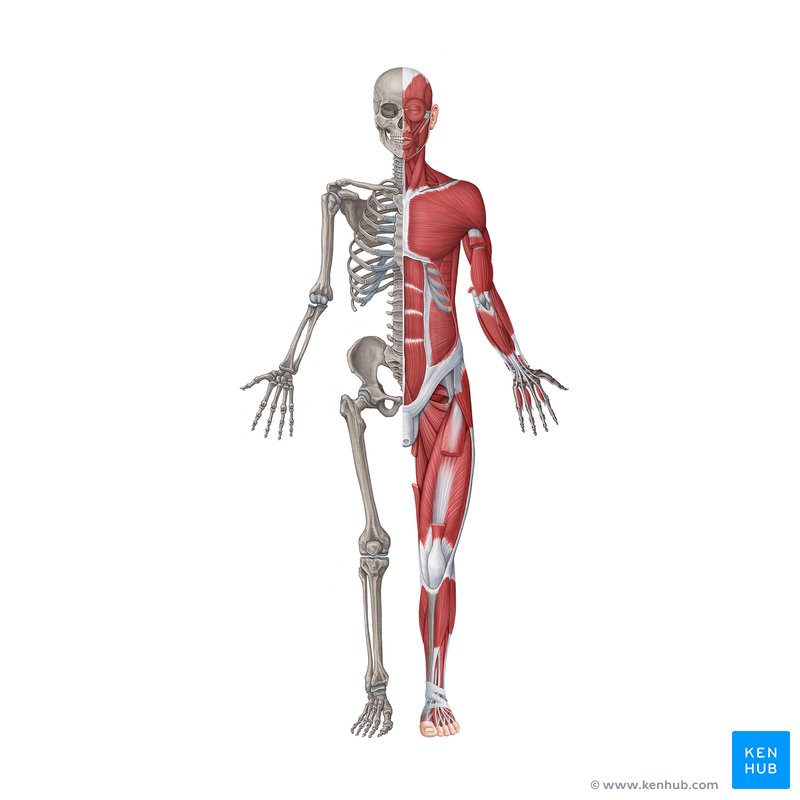
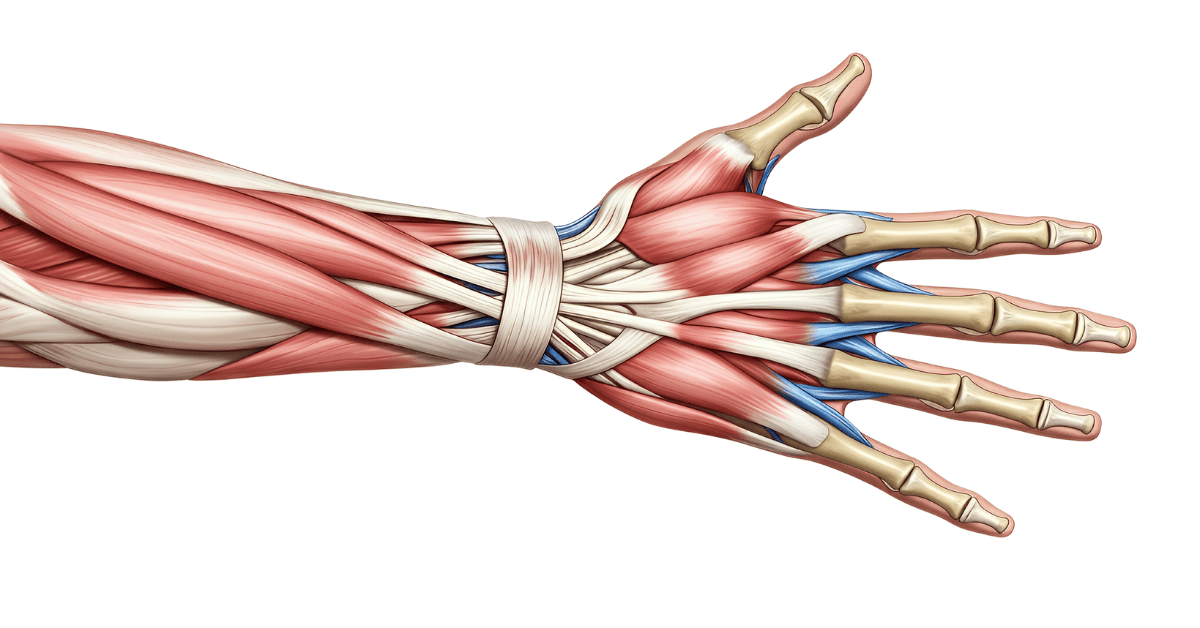
musculoskeletal system
What is the system of bones and skeletal muscles that support and protect the body and permit movement?
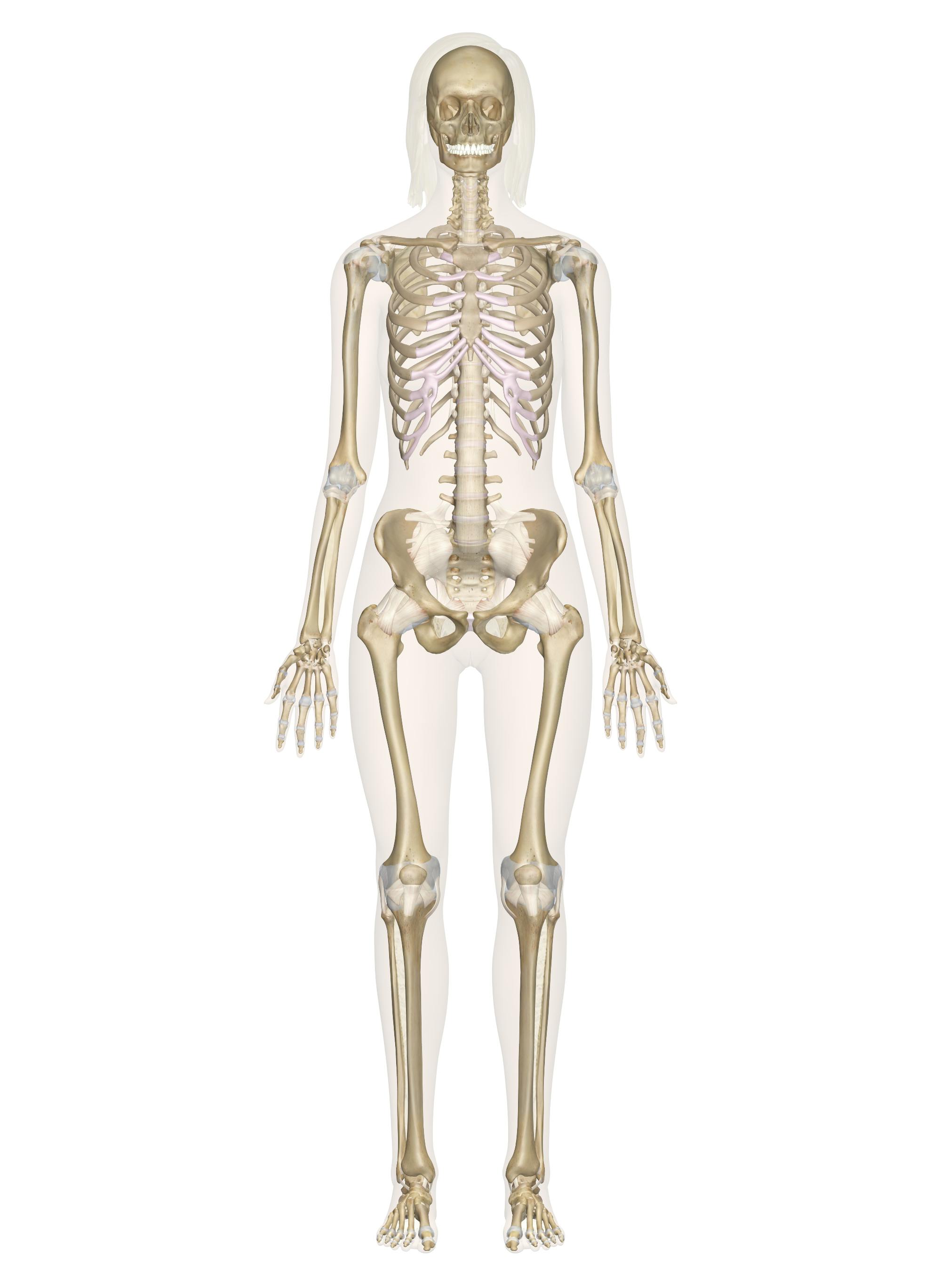
skeleton
What are the bones of the body?
muscles
What are tissues that can contract to allow movement of a body part?
ligaments
What are tissues that connect bone to bone?
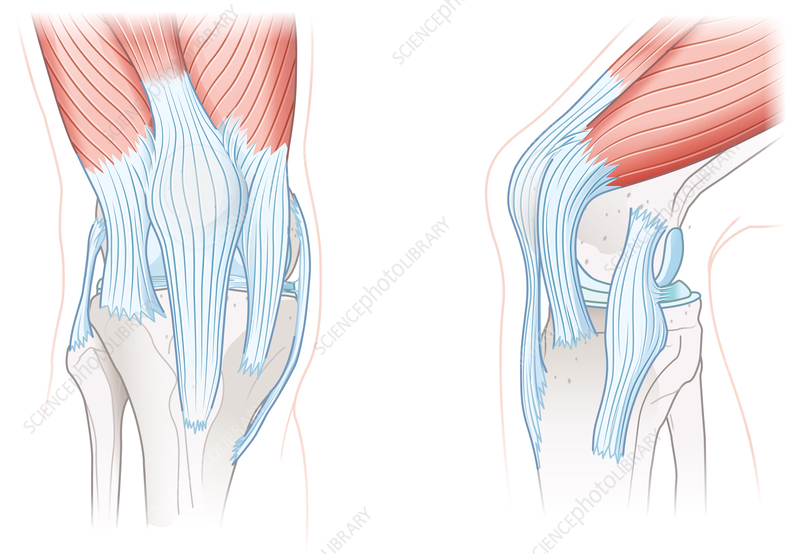
tendons
What are tissues that connect muscle to bone?
(1) give the body shape (2) protect vital organs (3) provide body movement
What are the three main functions of the musculosketal system?
marrow
What is found inside a bone?
produce blood cells and store certain nutrients
What is the purpose of bone marrow?
skull
What is the bony structure of the head?
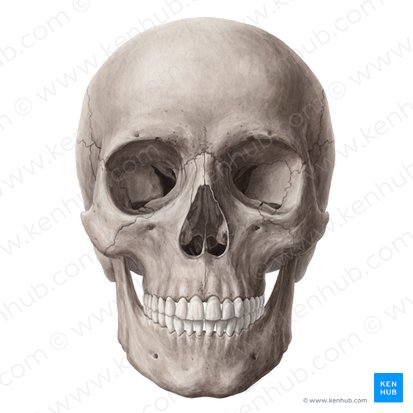
enclose and protect the brain
What is the main function of the skull?
cranium
What is the top, back, and sides of the skull?
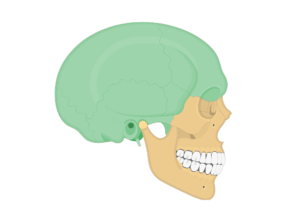
face
What is the front of the skull?
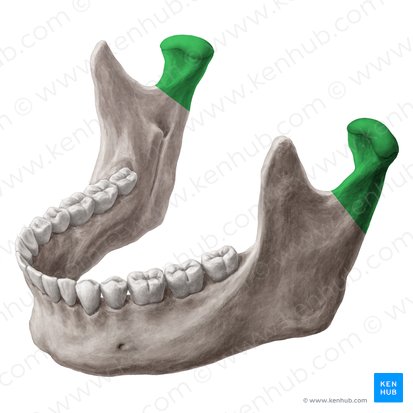
mandible
What is the lower jawbone?
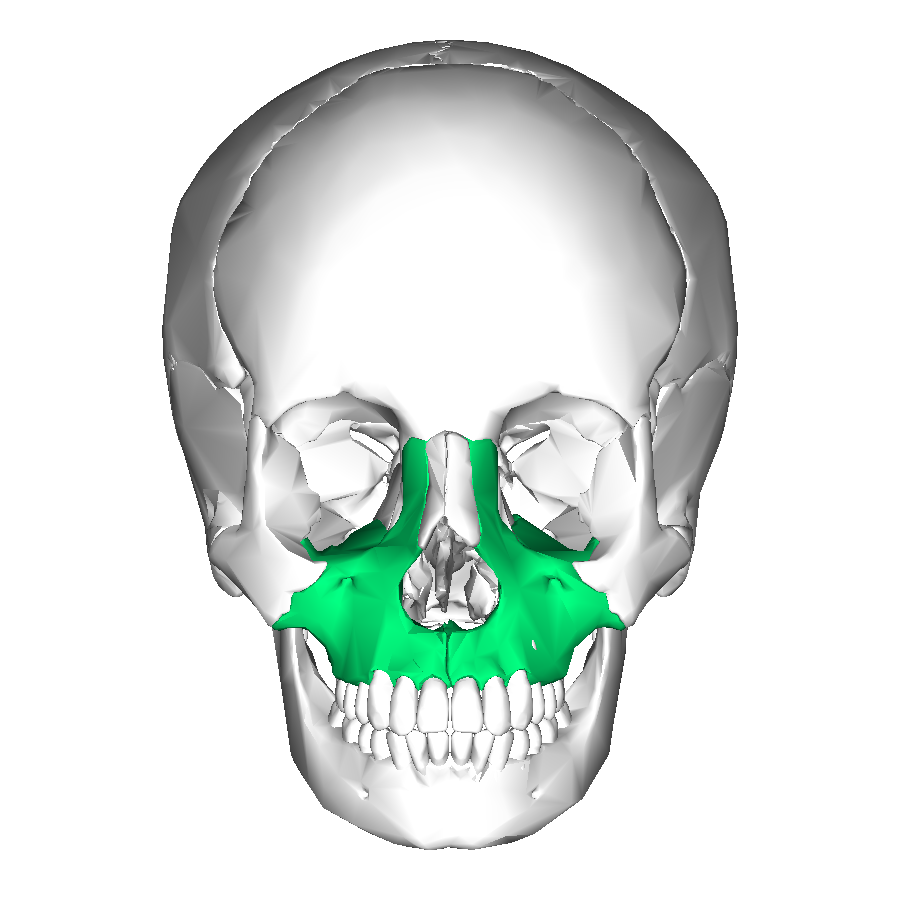
maxillae
What are the two fused bones forming the upper jaw?
nasal bones
What are the nose bones?
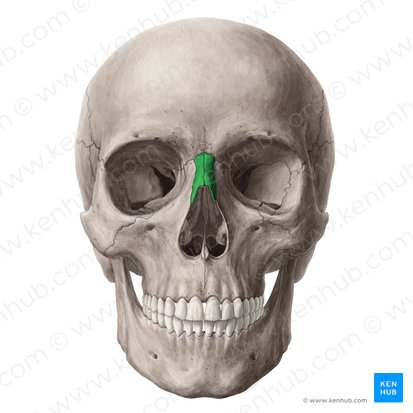
orbits
What are the bony structures around the eyes; the eye sockets?
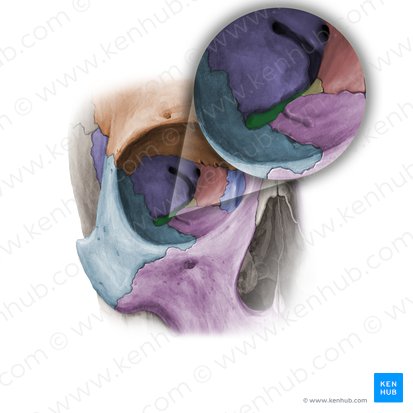
zygomatic arches
What are the bones that form the structure of the cheeks?
spinal column
What provides structure and support for the body and houses and protects the spinal cord?
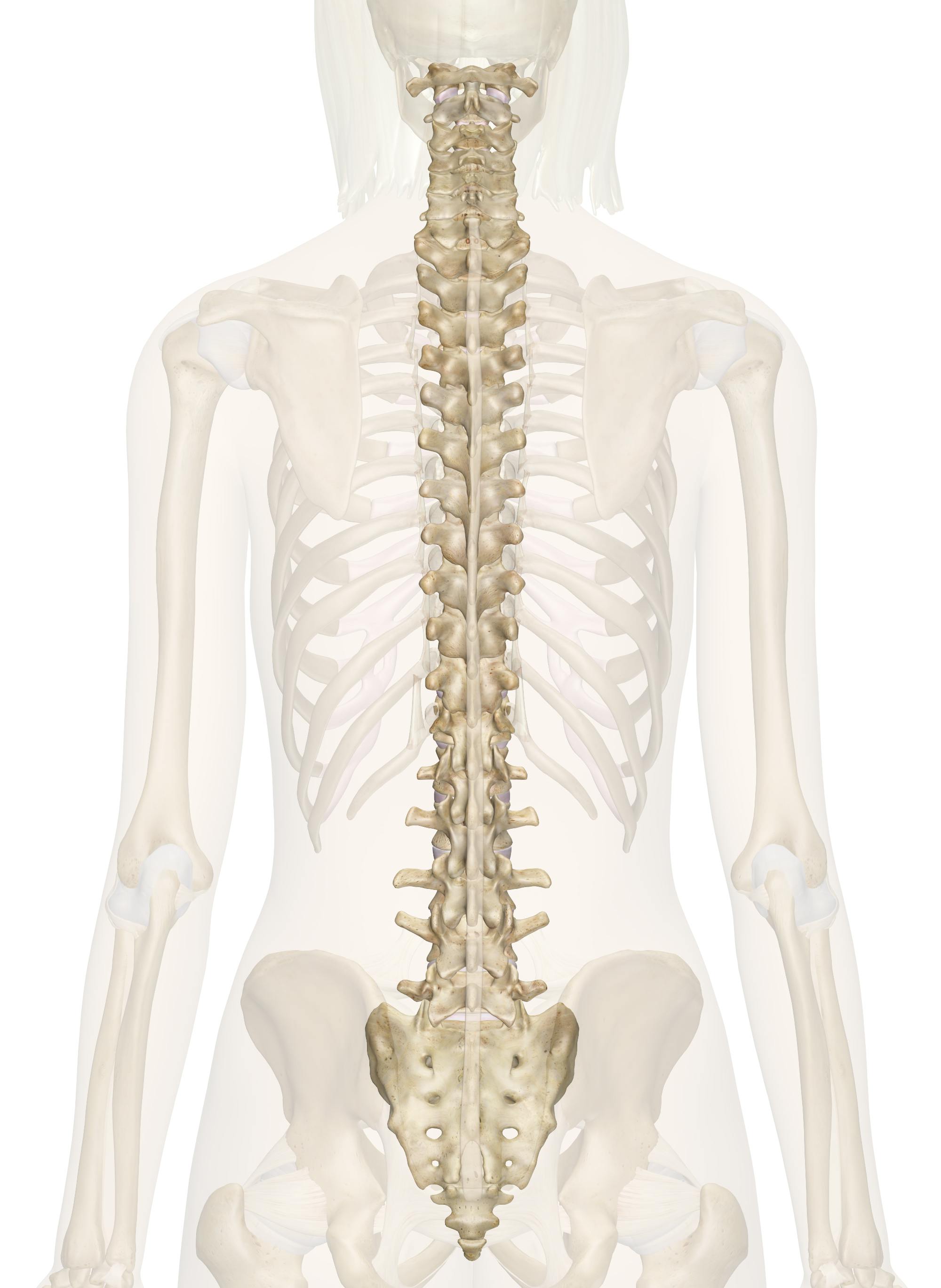
vertebrae
What are the 33 bones of the spinal column?
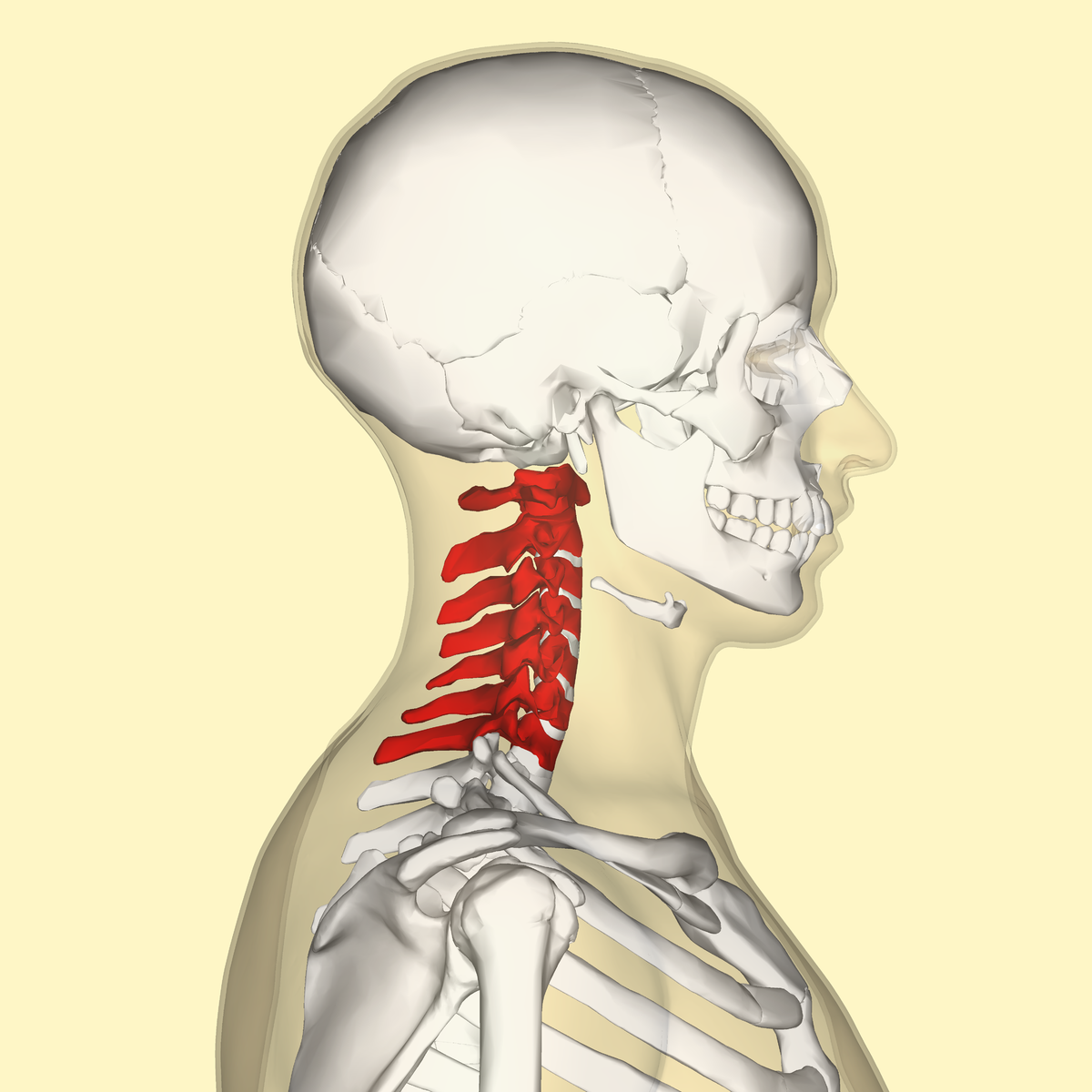
cervical
What division of the spinal column corresponds to the neck?
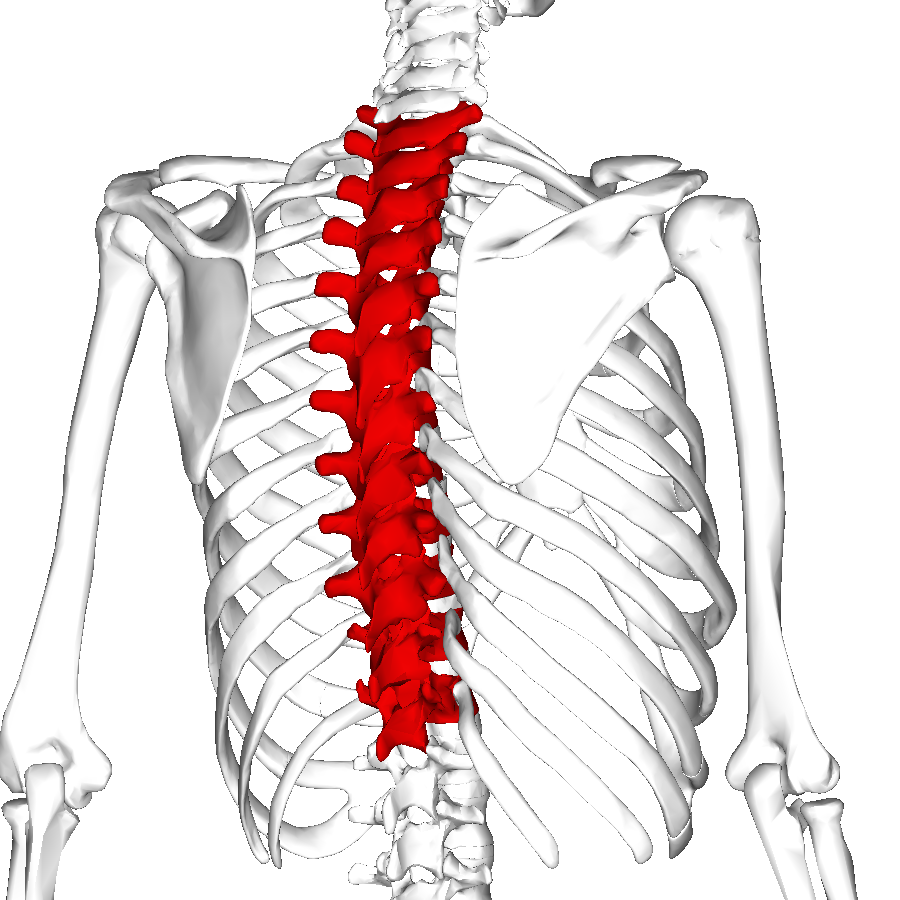
thoracic
What division of the spinal column corresponds to the thorax, ribs, and upper back?
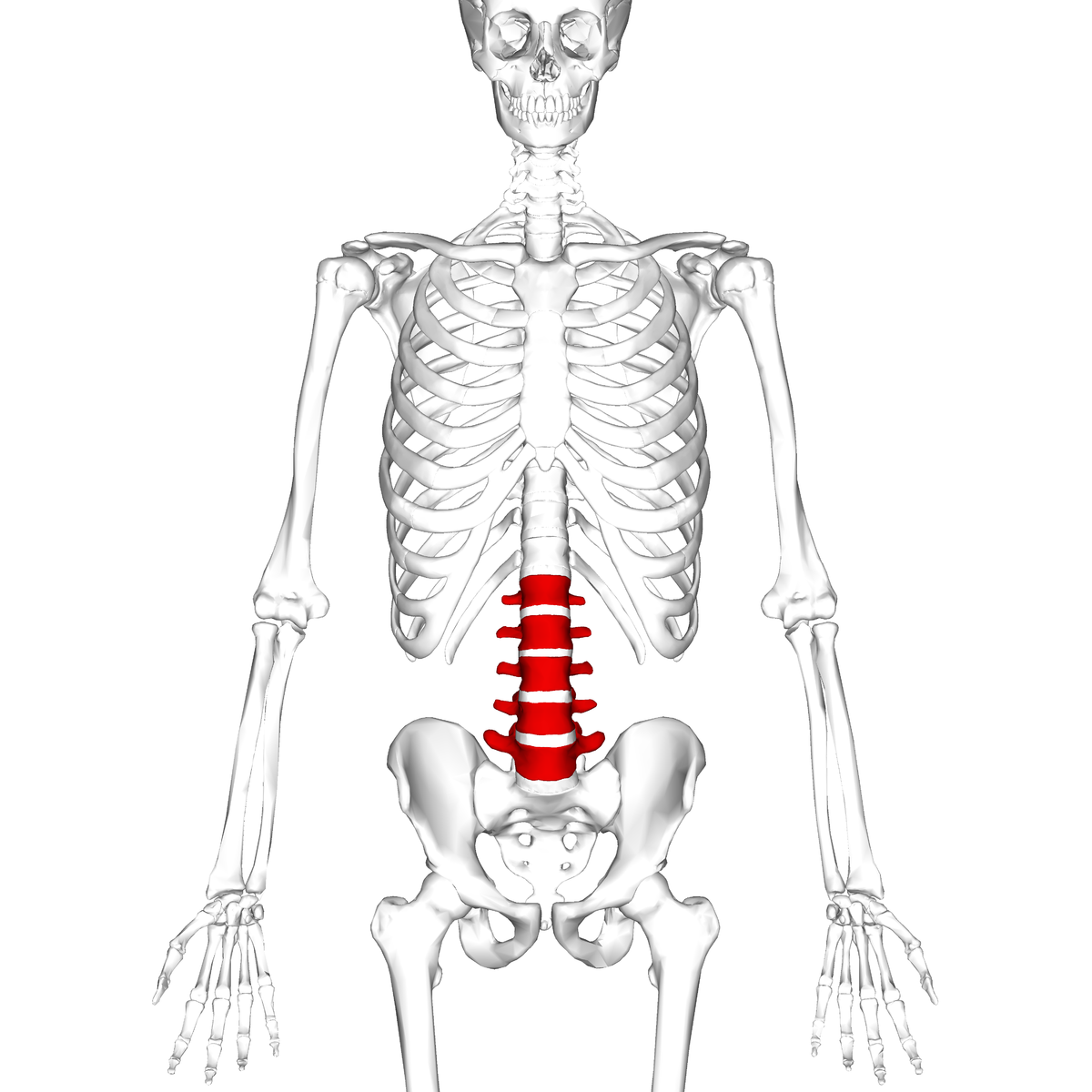
lumbar
What division of the spinal column corresponds to the lower back?
sacral
What division of the spinal column corresponds to the back wall of the pelvis?
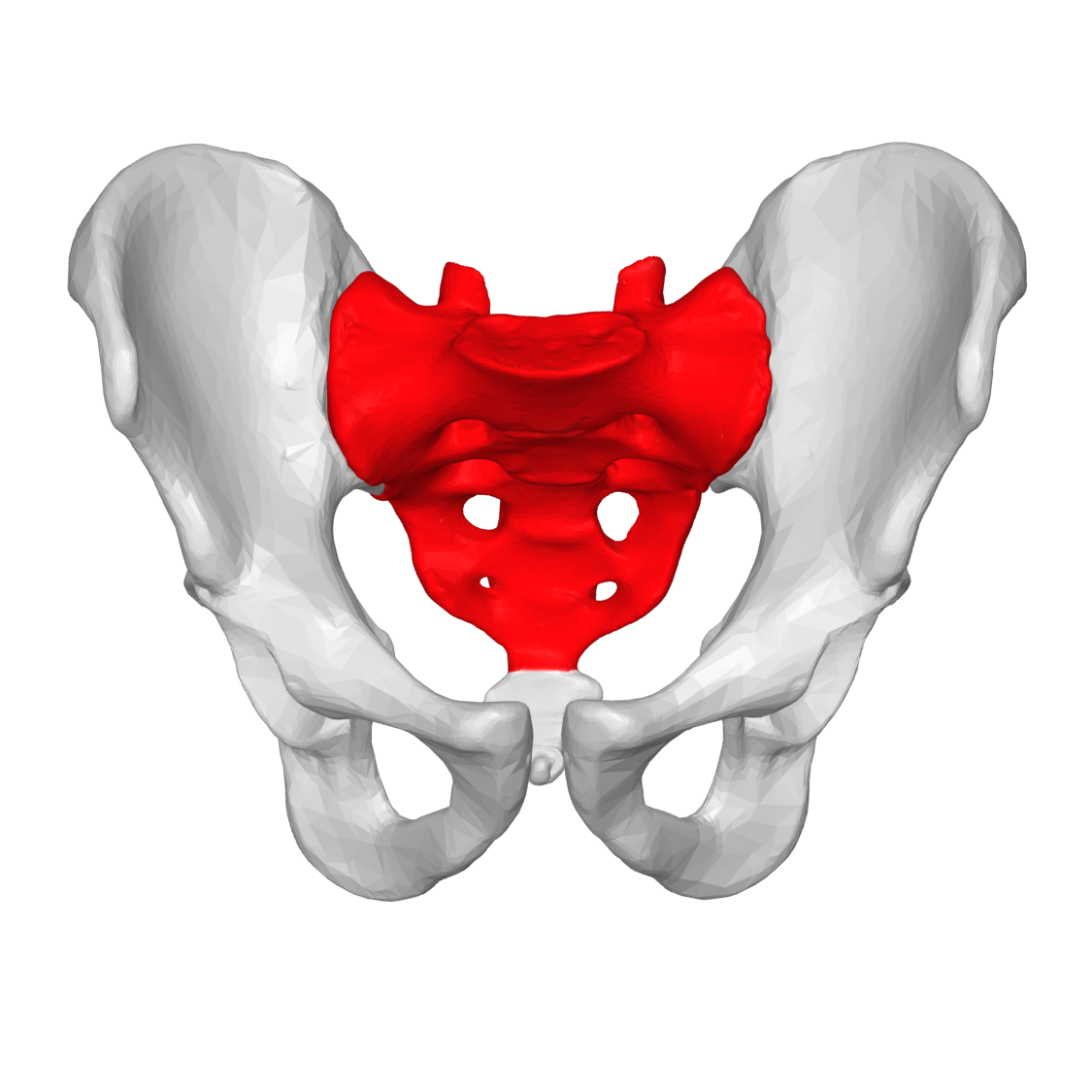
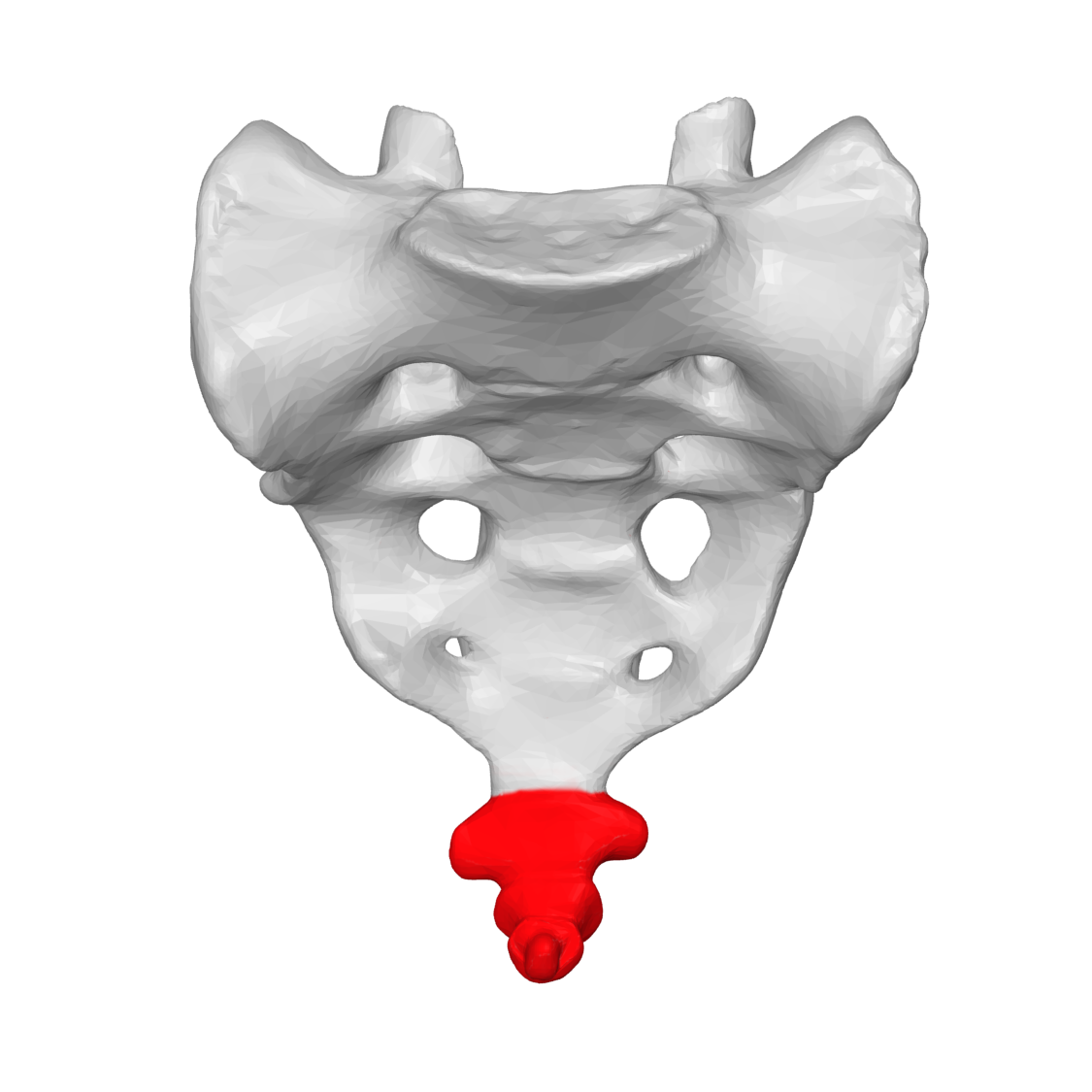
coccyx
What division of the spinal column corresponds to the tailbone?
thorax
What is the chest?
thoracic cavity
What is the internal space formed by the bones of the thorax?
heart, lungs, major blood vessels
What is contained in the thoracic cavity?
sternum
What is the breastbone?
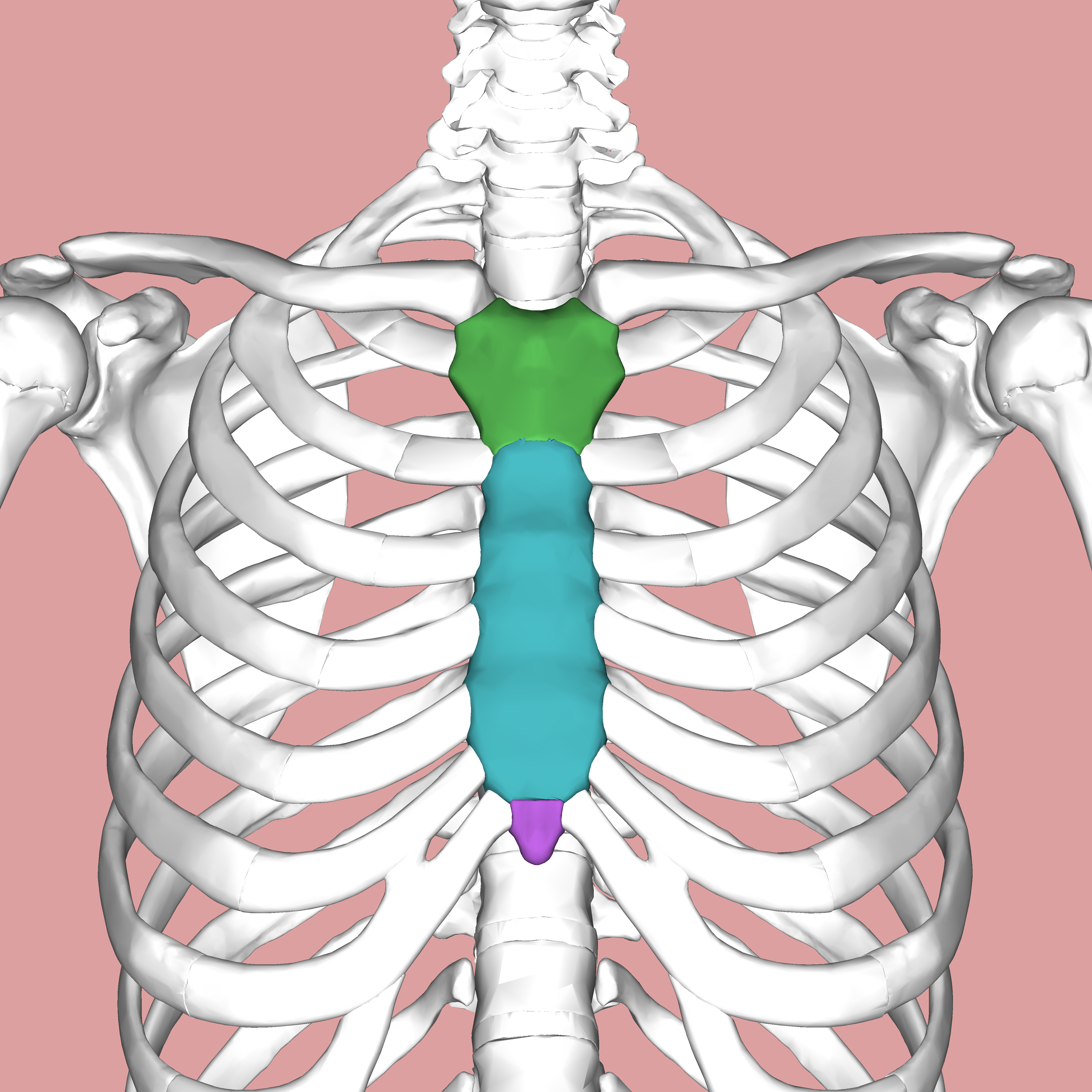
12
How many pairs of ribs are there?
10
How many pairs of ribs are attached to the sternum?
2
How many pairs of ribs are "floating" and have no anterior attachment?
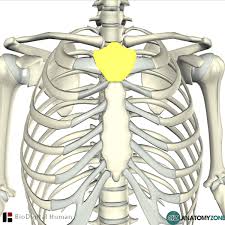
manubrium
What is the superior portion of the sternum?
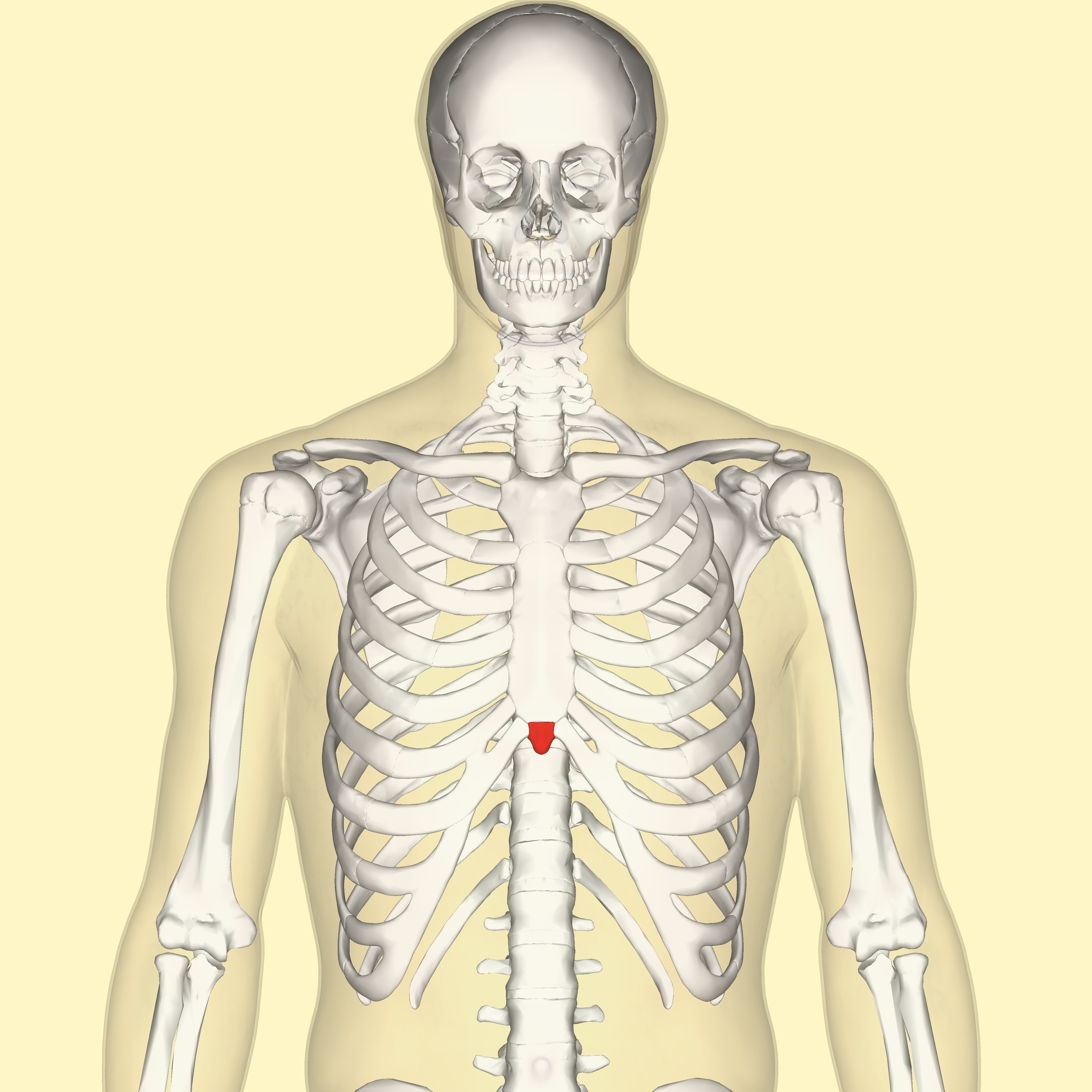
xiphoid process
What is the inferior portion of the sternum?
pelvis
What is the basin-shaped bony structure that supports the spine and is the point of proximal attachment for the lower extremities?
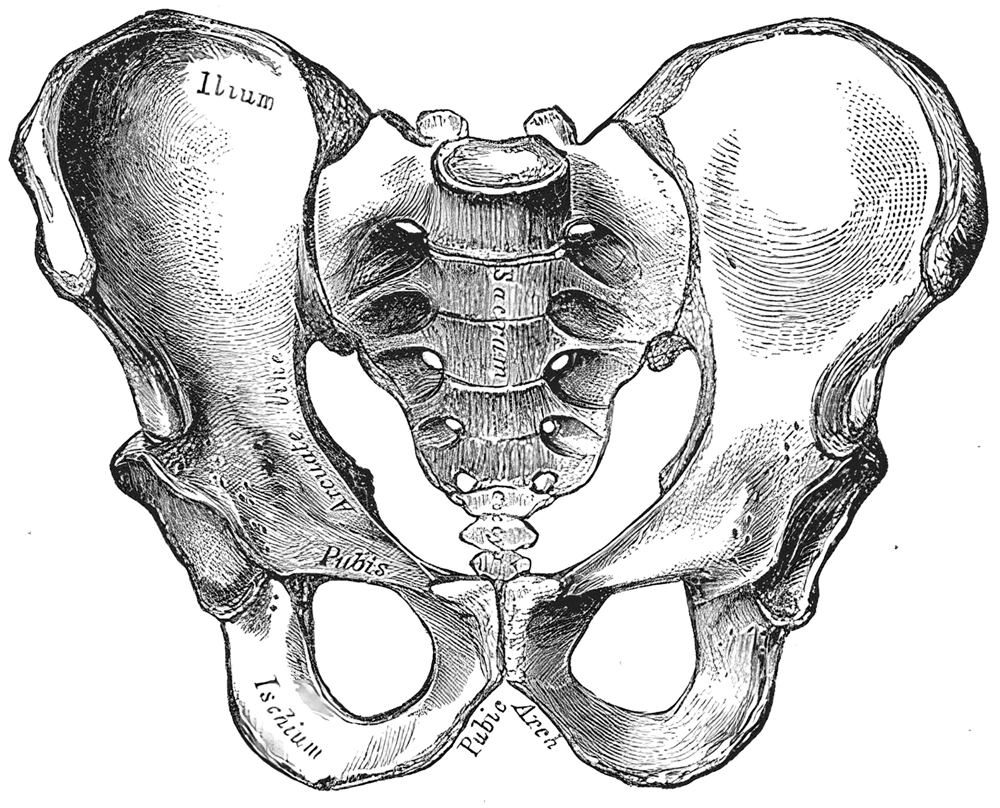
ilium
What is the superior and widest portion of the pelvis?
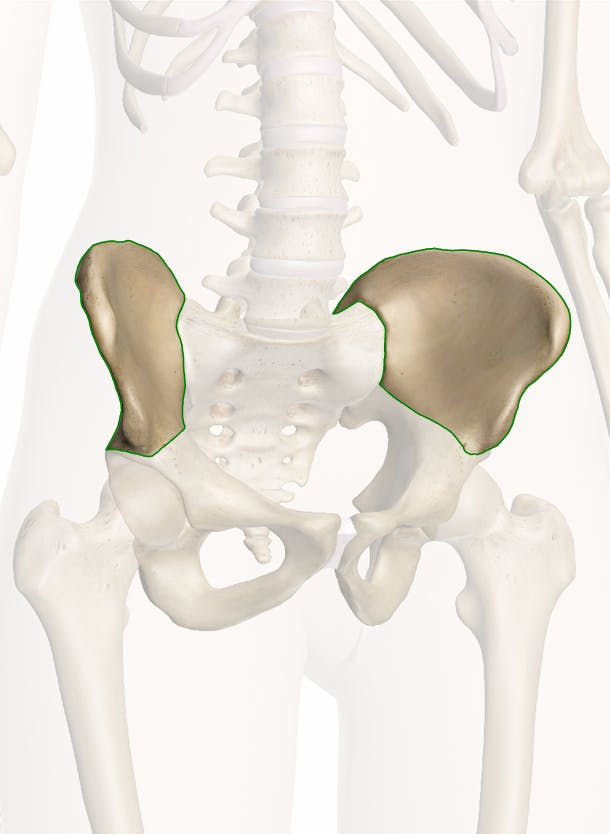
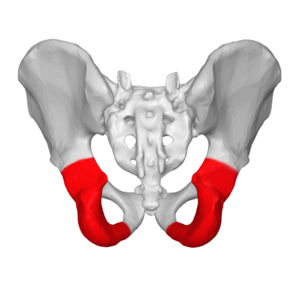
ischium
What is the lower, posterior portion of the pelvis?
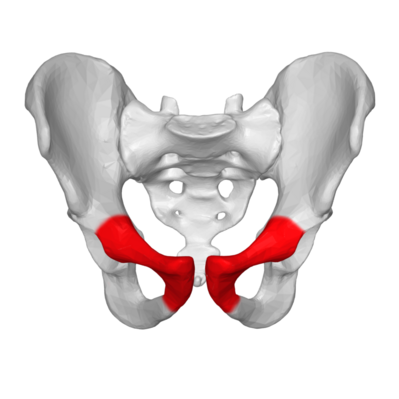
pubis
What is the medial anterior portion of the pelvis?
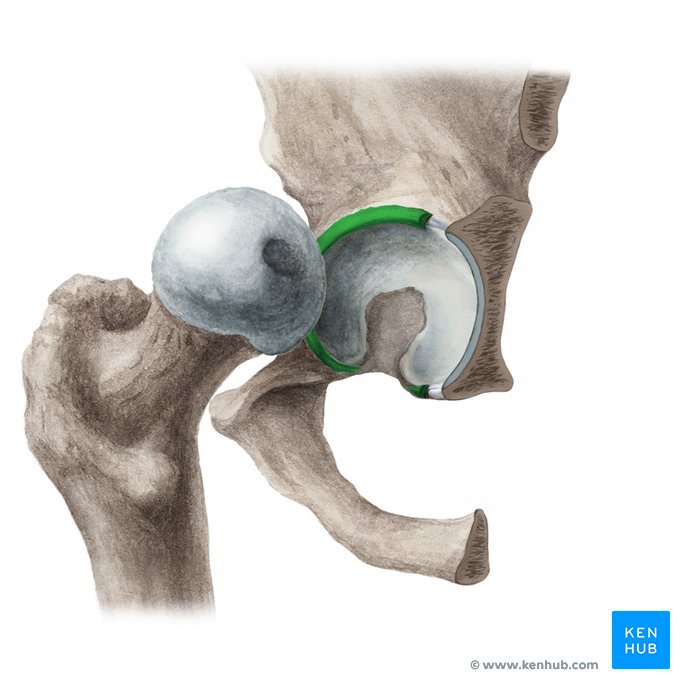
acetabulum
What is the pelvic socket into which the ball at the proximal end of the femur fits to form the hip joint?
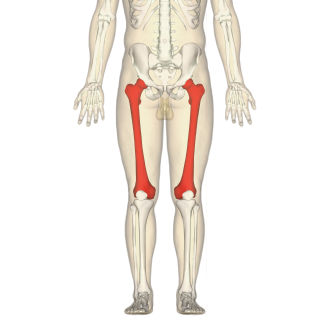
femur
What is the large bone of the thigh?
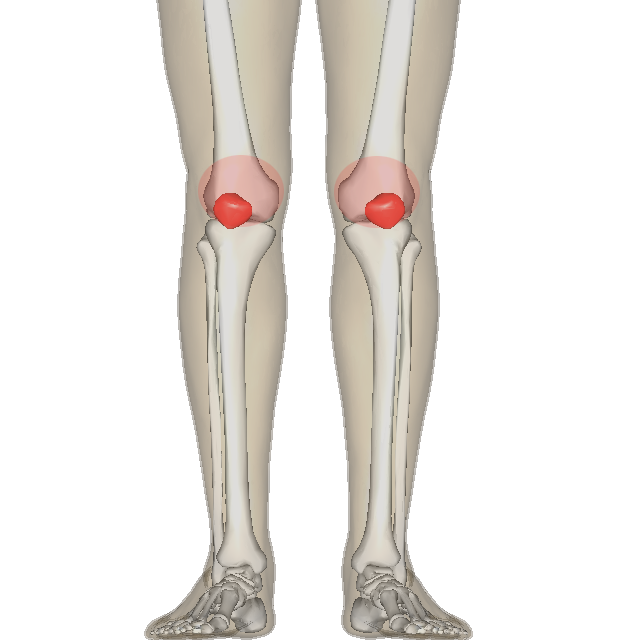
patella
What is the kneecap?
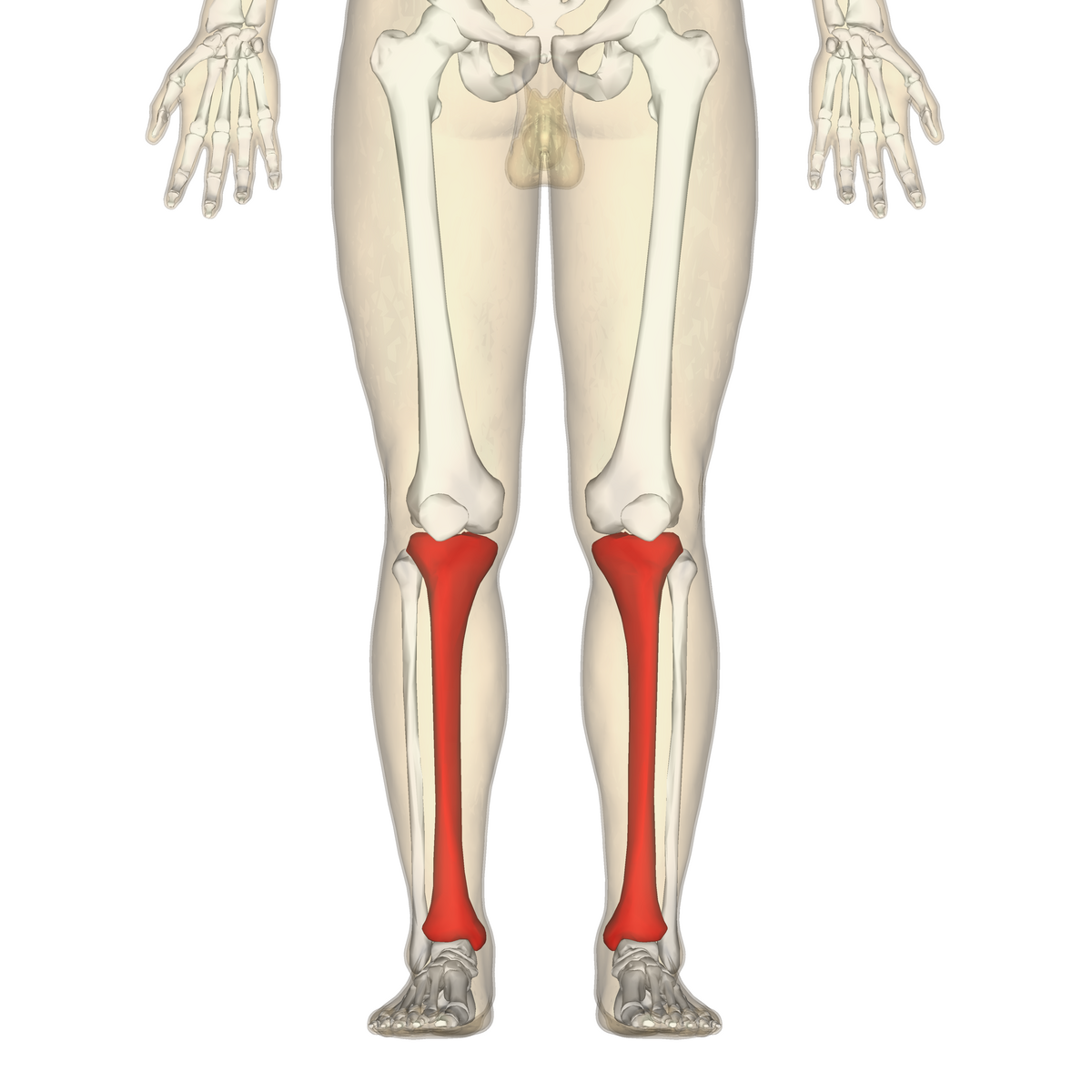
tibia
What is the medial and larger bone of the lower leg?
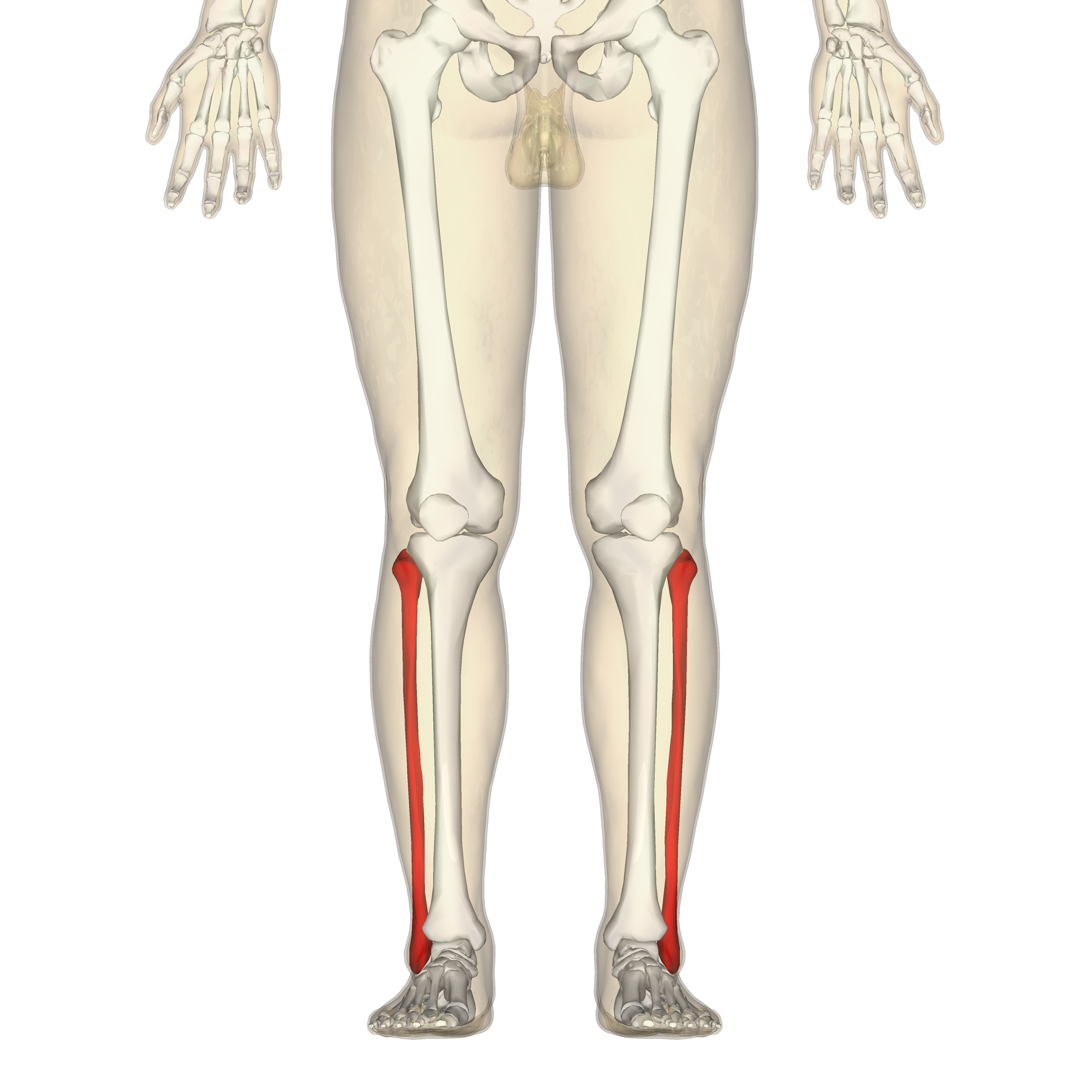
fibula
What is the lateral and smaller bone of the lower leg?
malleolus
What is the protrusion on the side of the ankle?
tarsals
What are the ankle bones?
metatarsals
What are the foot bones?
calcaneus
What is the heel bone?
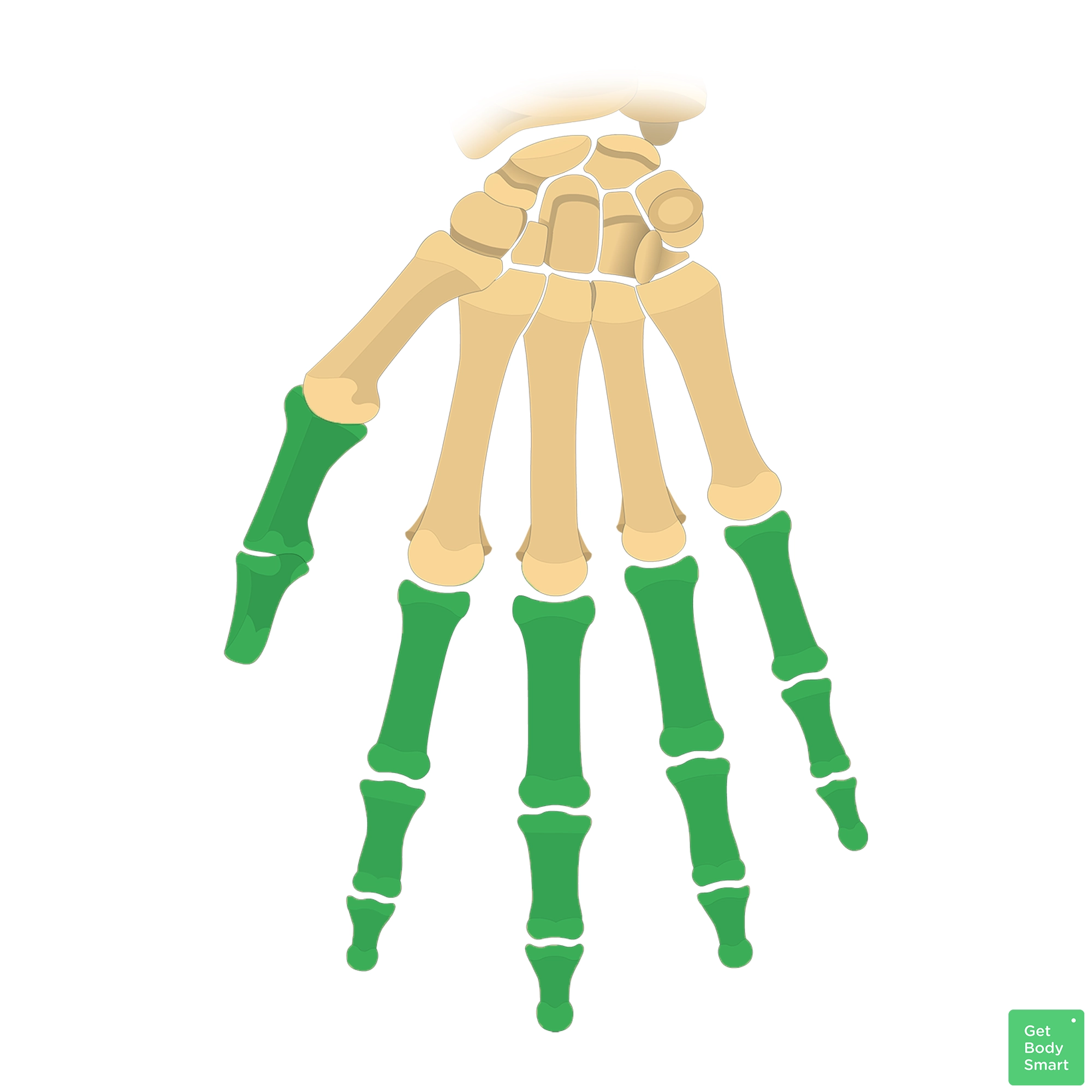
phalanges
What are the toe (and finger) bones?
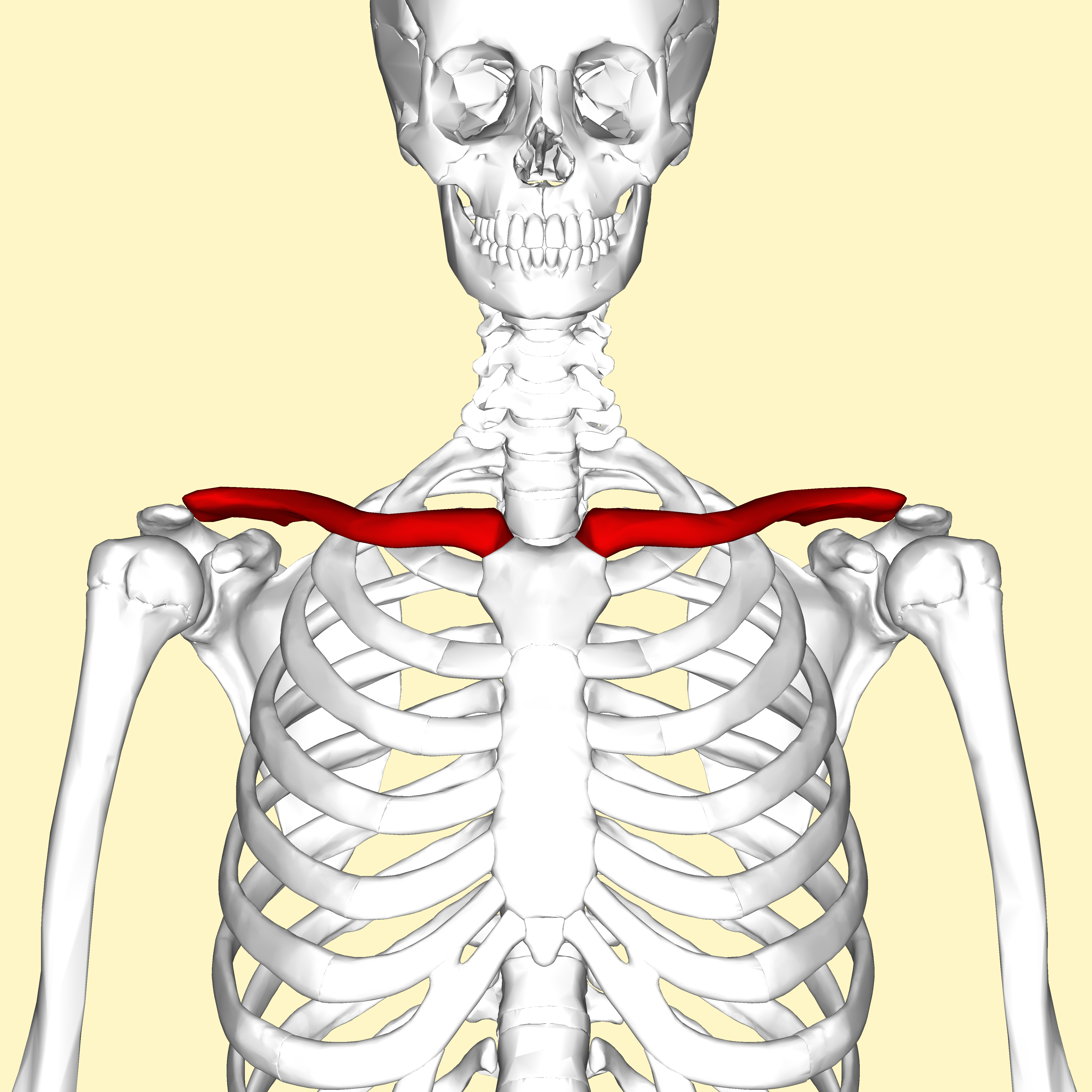
clavicle
What is the collarbone?
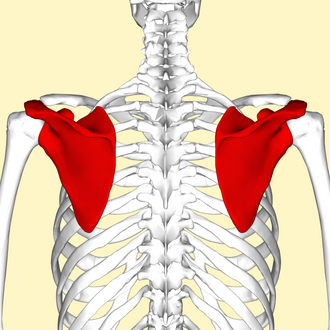
scapula
What is the shoulder blade?
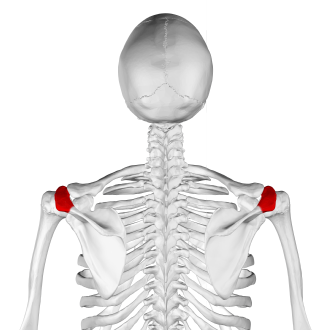
acromion process
What is the highest portion of the shoulder?
acromioclavicular joint
What is the joint where the acromion and the clavicle meet?
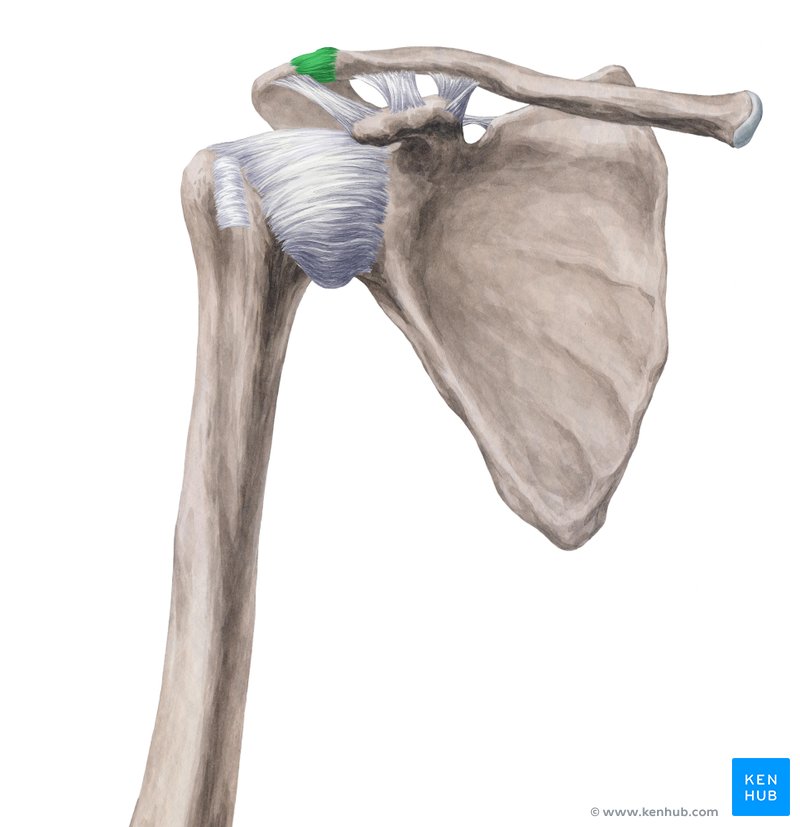
humerus
What is the bone of the upper arm, between the shoulder and the elbow?
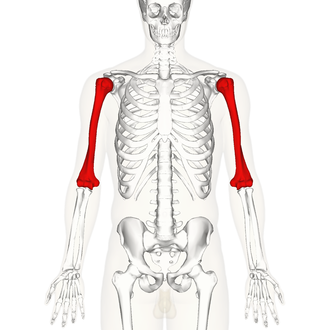
radius
What is the lateral bone of the forearm?
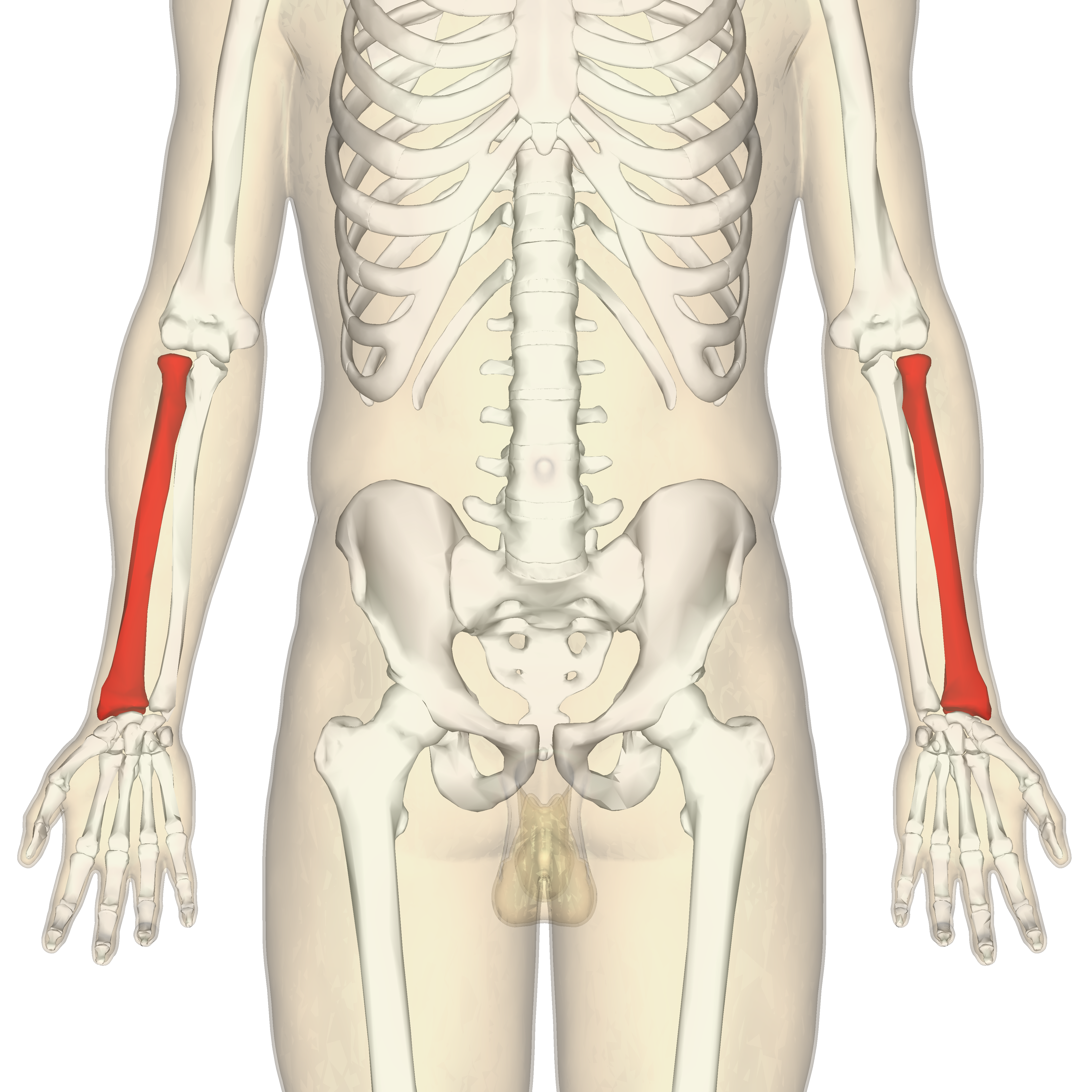
ulna
What is the medial bone of the forearm?
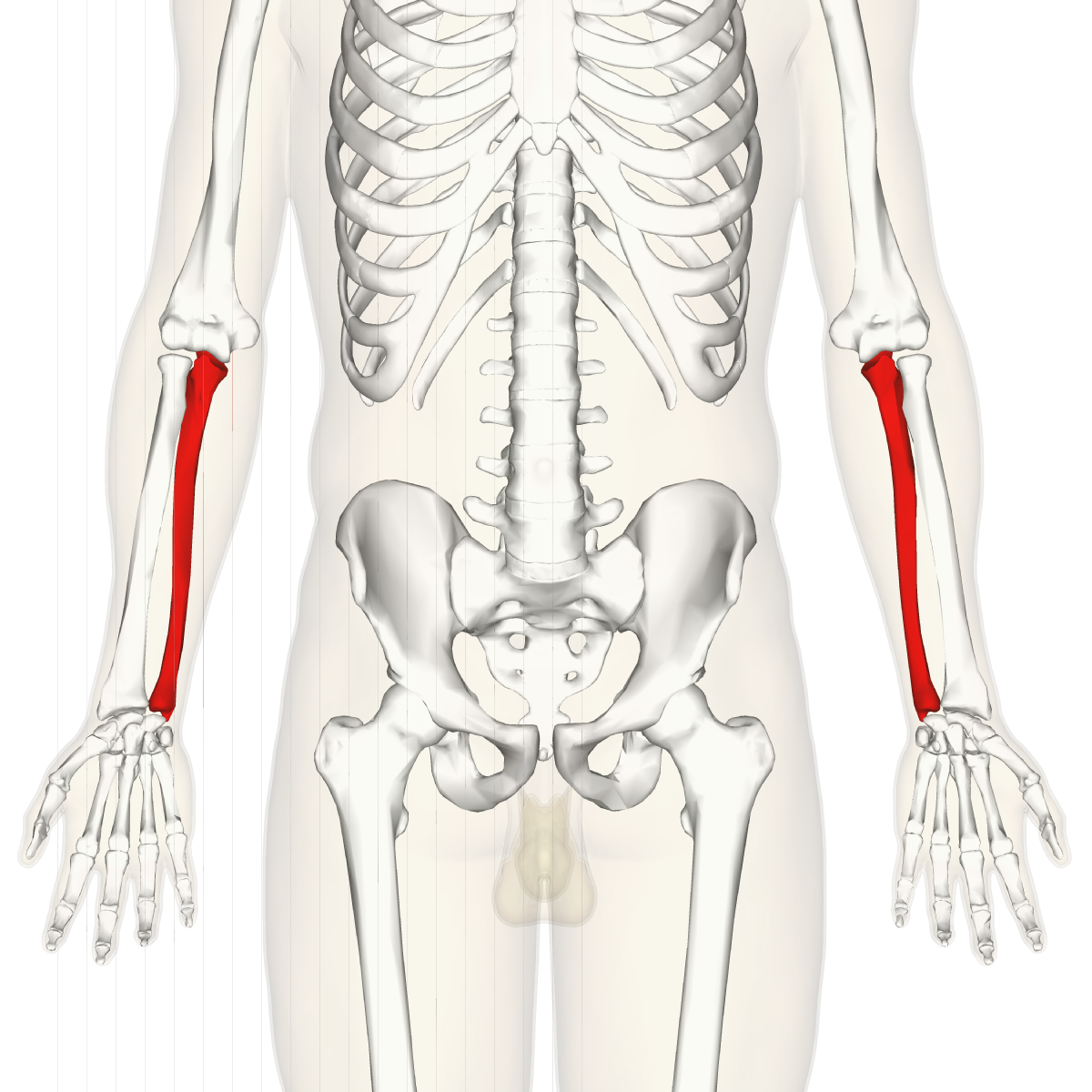
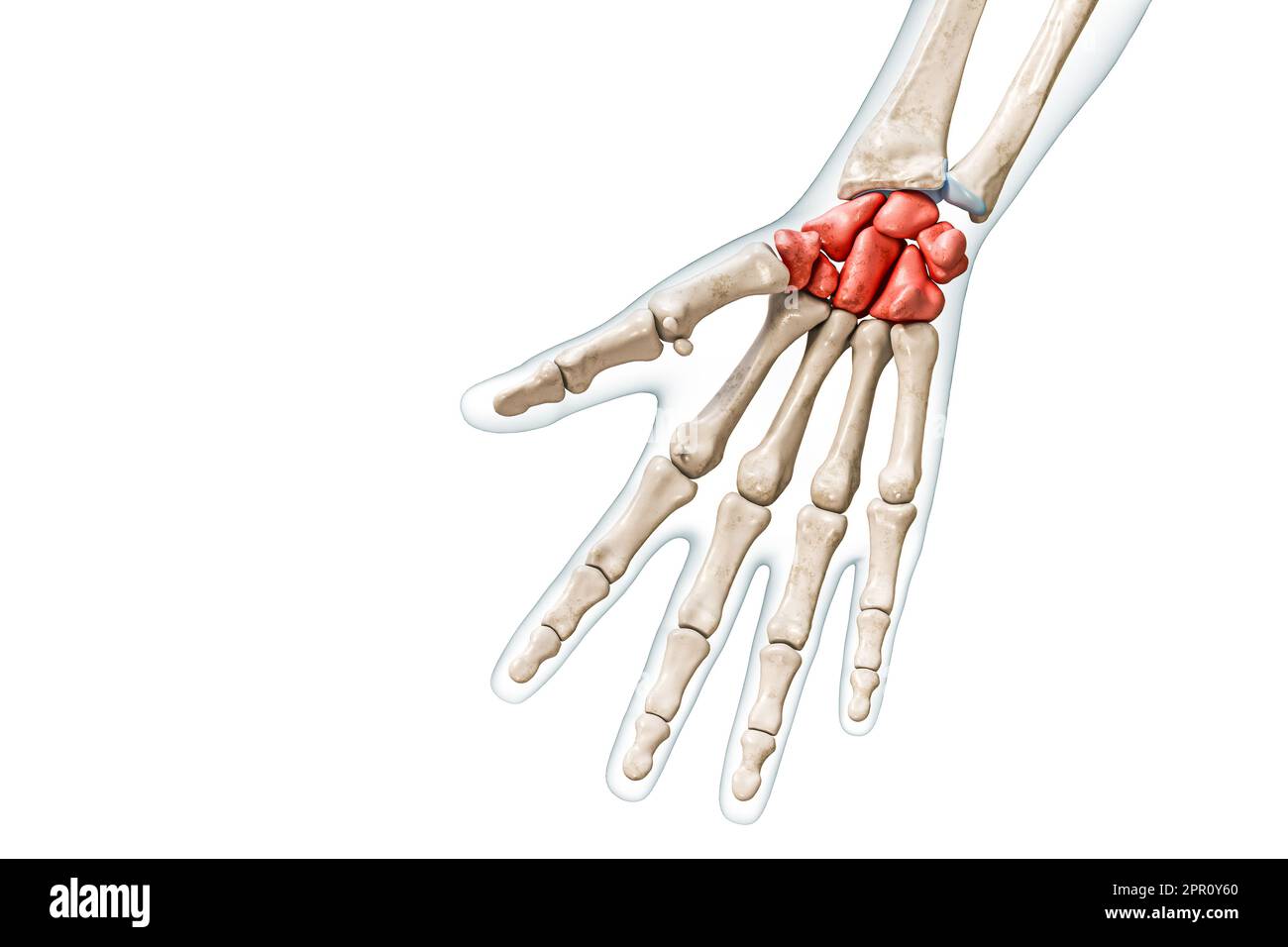
carpals
What are the wrist bones?
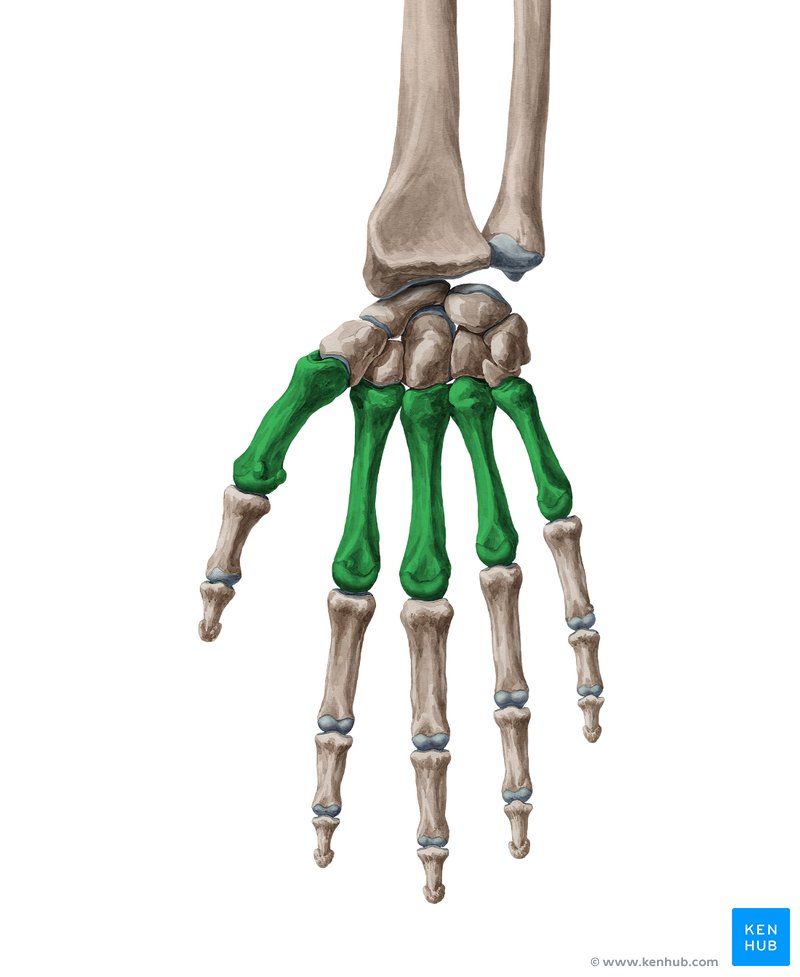
metacarpals
What are the bones of the hand?
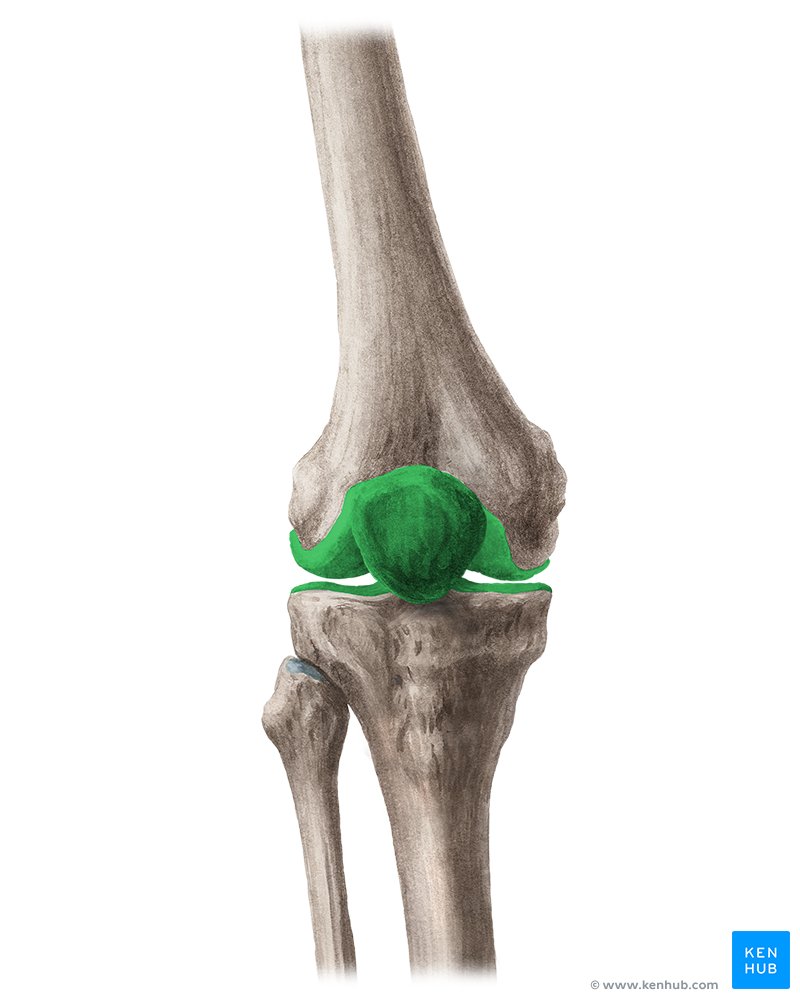
joint
What is the point where two bones come together?
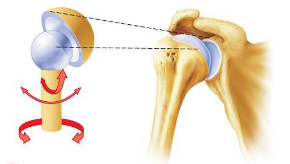
ball-and-socket joint
What type of joint rotates in a round socket?
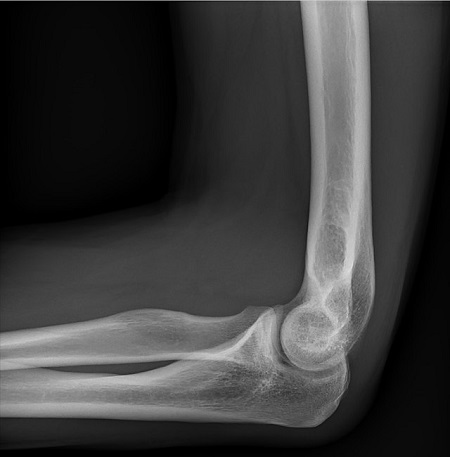
hinge joint
What type of joint bends and straightens?
voluntary muscle (or skeletal muscle)
What is a muscle that can be consciously controlled?
involuntary muscle (or smooth muscle)
What is a muscle that responds automatically to brain signals but cannot be consciously controlled?
cardiac muscle
What is a specialized involuntary musle found only in the heart?
automaticity
What is the ability of the heart to generate and conduct electrical impulses on its own?
heartbeat (contraction)
What is controlled by the electrical impulses of the heart?
respiratory (or pulmonary) system
What is the system of nose, mouth, throat, lungs, and muscles that brings oxygen into the body and expels carbon dioxide?
oxygen (O2)
What is moved into the bloodstream through inhalation?
carbon dioxide (CO2)
What is picked up by the blood and excreted from the body through exhalation?
mouth and nose
Where does air enter the body?
oropharynx
What is the area directly posterior to the mouth?
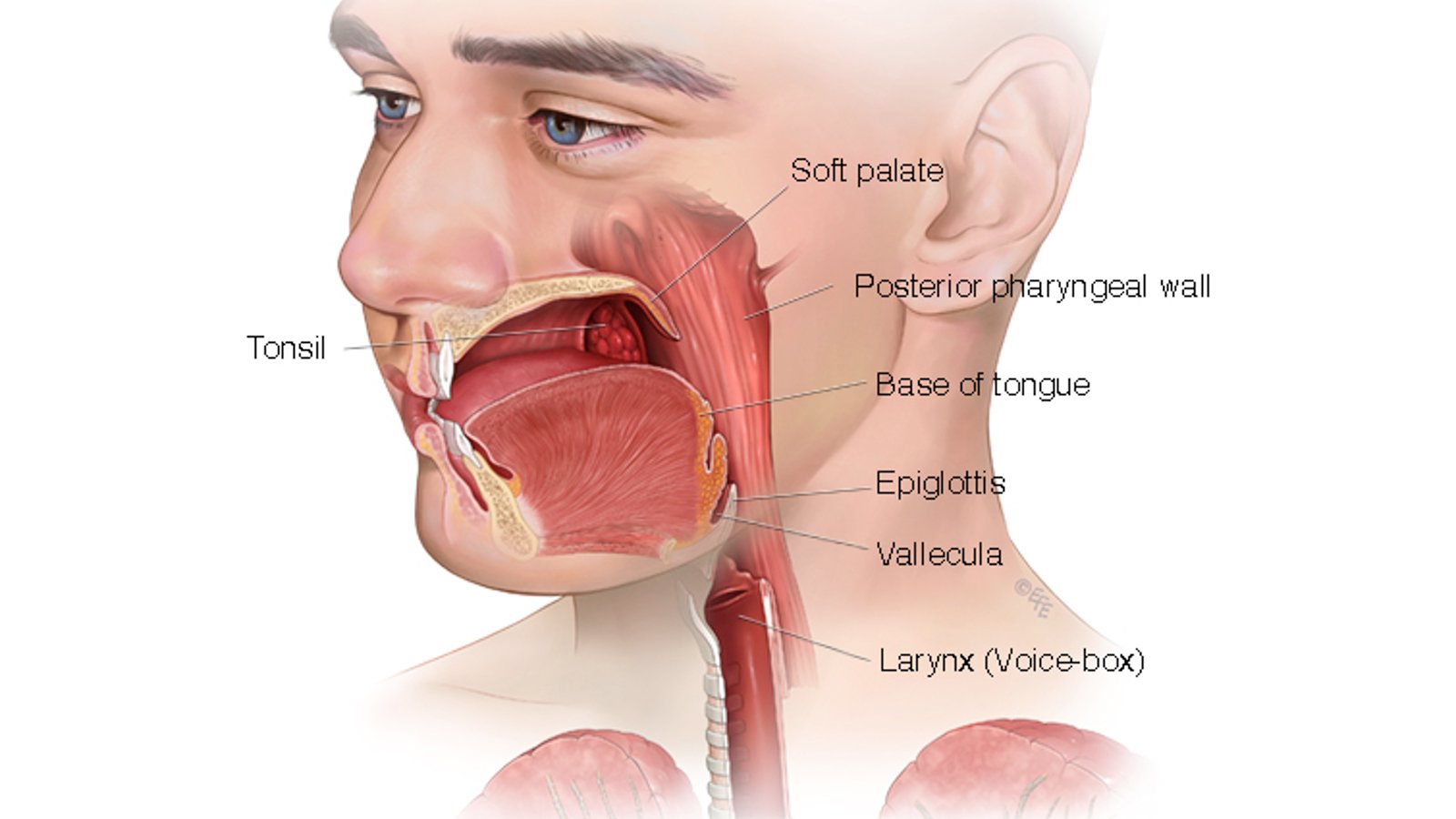
nasopharynx
What is the area directly posterior to the nose?
pharynx
What is the area that directly posterior to the mouth and nose, made up of the oropharynx and the nasopharynx?
epiglottis
What is a leaf-shaped structure that prevents food and foreign matter from entering the trachea?
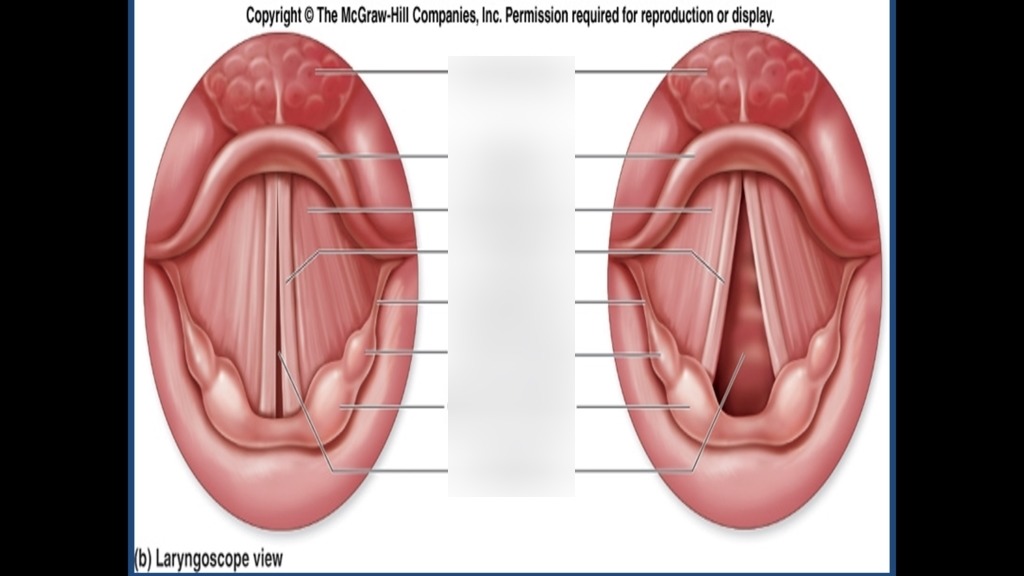
glottis
What is the opening to the trachea?
larynx
What is the voice box?
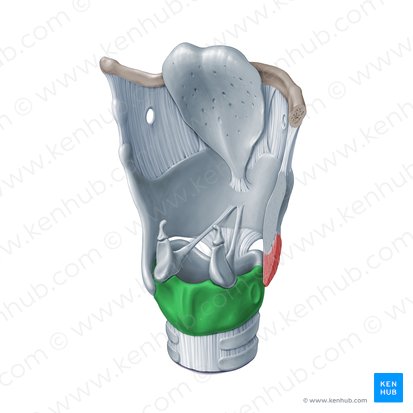
cricoid cartilage
What is a ring-shaped structure that forms the lower portion of the larynx?
trachea
What is the "windpipe"; the structure that connects the pharynx to the lungs?
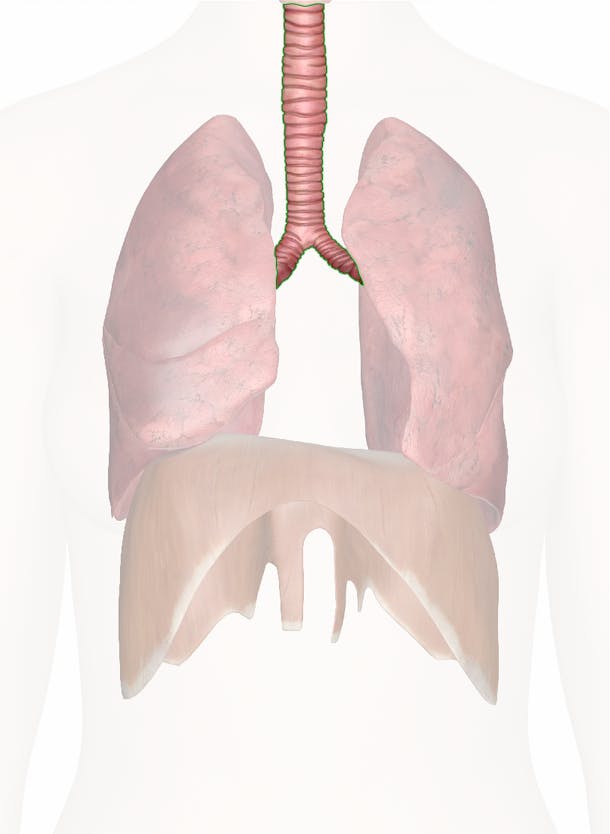
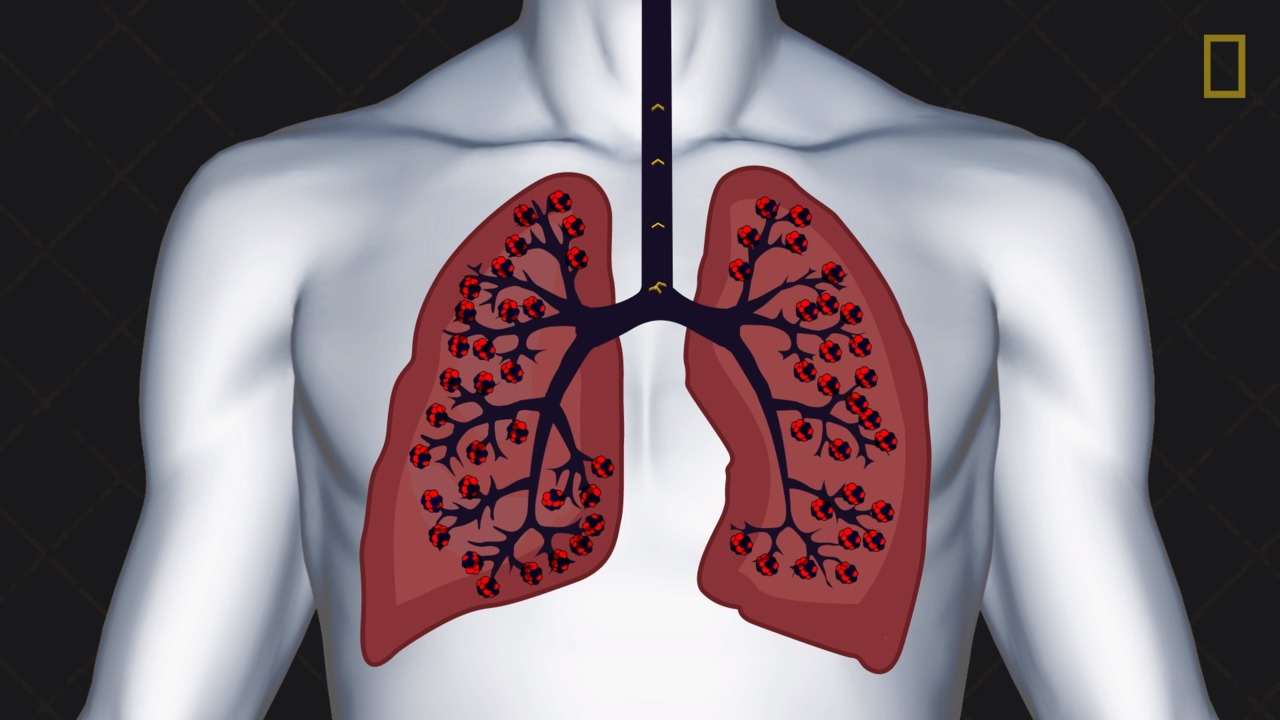
lungs
What are the organs where exchange of atmospheric oxygen and waste carbon dioxide takes place?
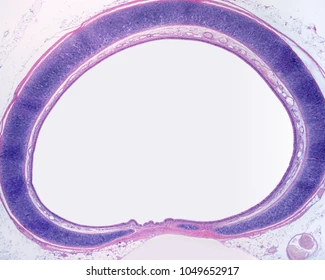
16 C-shaped rings of cartilage
What are the lungs formed and protected by?
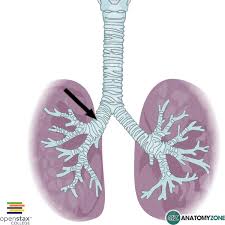
bifurcate
What means to 'divide or fork into two channels or branches'?
bronchi
What are the two large sets of branches that come off the trachea and enter the lungs; consisting of a right and left _ ?
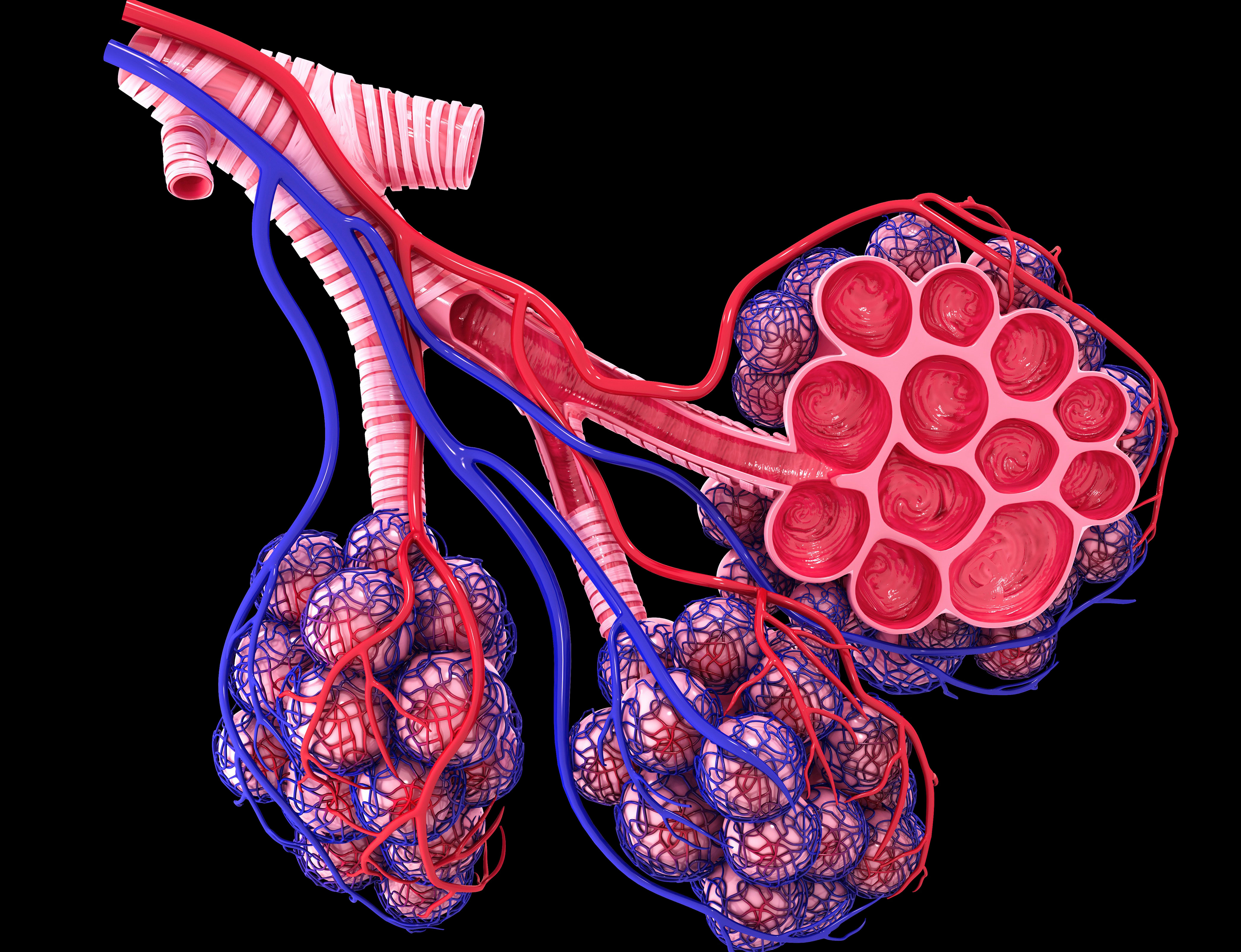
bronchioles
What are the branches of the bronchi?
alveoli
What are the microscopic sacs of the lungs where gas exchange with the bloodstream takes place?
diaphragm
What is the muscular structure that divides the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity; a major muscle of respiration?
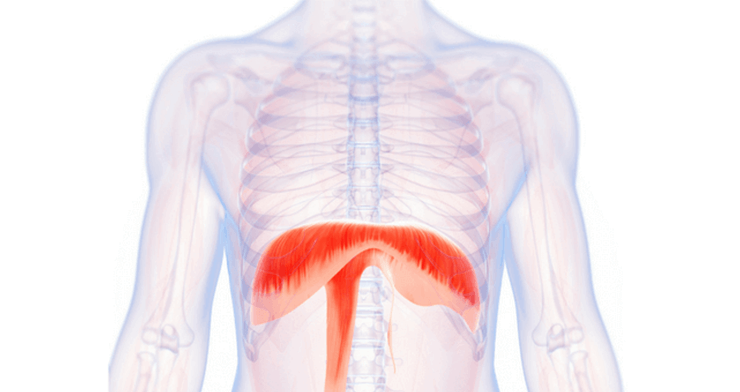
phrenic nerve
What is the diaphragm largely controlled by?
intercostal muscles
What are the rib muscles?
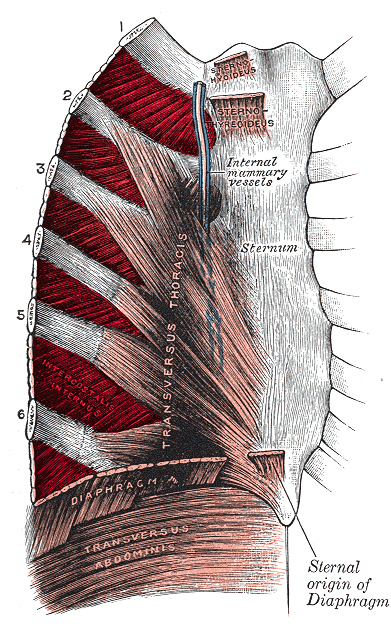
inhalation
What is an active process in which the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm contract, expanding the size of the chest cavity and causing air to flow into the lungs?
exhalation
What is a passive process in which the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm relax, causing the chest cavity to decrease in size and air to flow out of the lungs?
ventilation
What is the process of moving gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between inhaled air and the pulmonary circulation of blood?
respiration
What is the process of moving oxygen and carbon dioxide between circulating blood and cells?
buffer system
What is a system that helps manage the pH of the body to maintain it at a normal level?
adequate breathing
What is breathing that is sufficient to support life?
inadequate breathing
What is breathing that is insufficient to support life?