lab exam
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
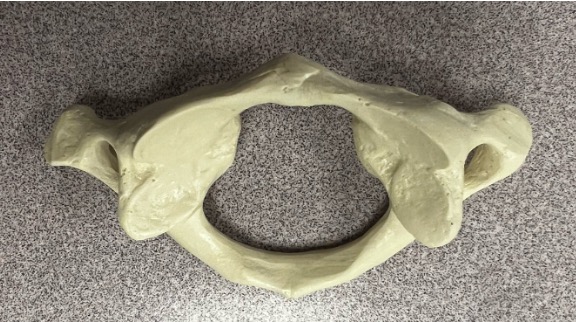
what type of vertebrae is this
atlas

what type of vertebrae is this
axis
What do the superior articulating facets articulate with and what motion does that joint allow our heads to do?
skull, allow the “yes” motion.
What does the Odontoid process articulate with and what motion does that joint allow our heads to do
anterior arch of atlas vertebrae, allows the “no” motion
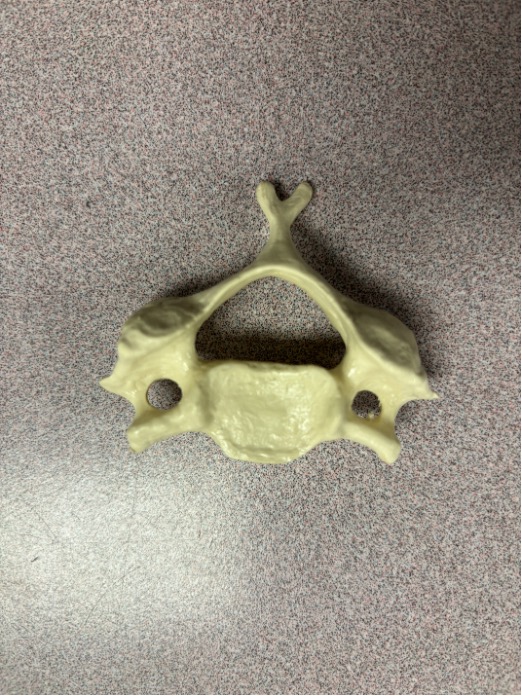
what vertebrae is this
cervical
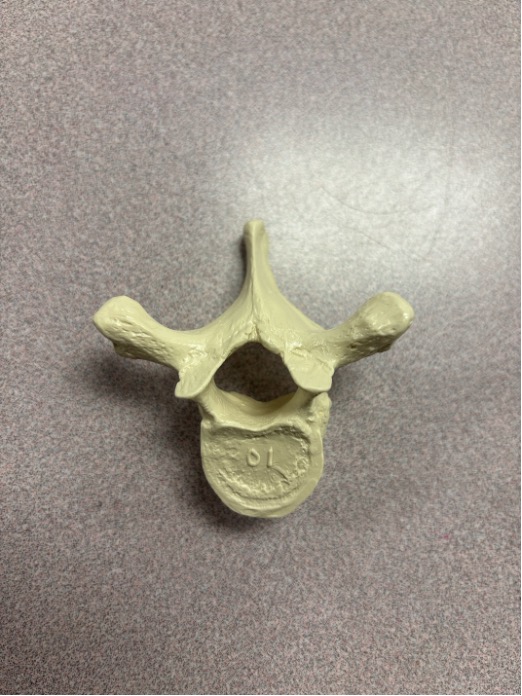
what vertebrae is this
thoracic
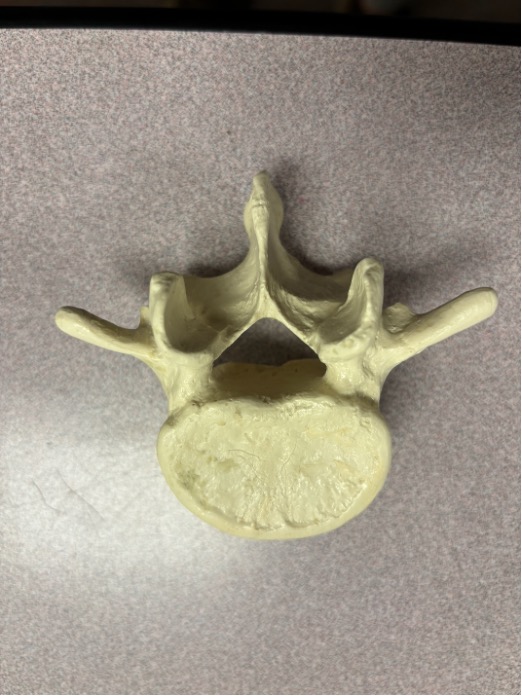
what vertebrae is this
lumbar
diploids
2n, full set of chromosomes
Haploids
n, half set of chromosomes,
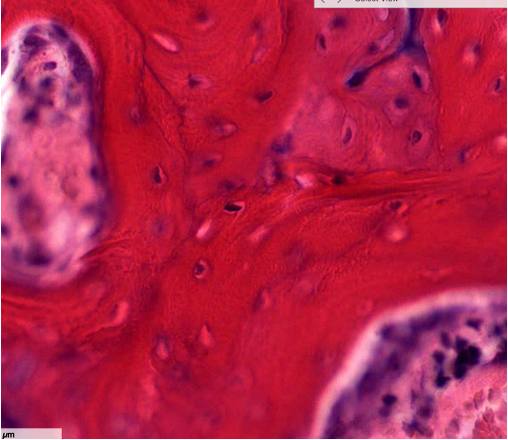
what stage of endochondrial ossification is this showing
resting
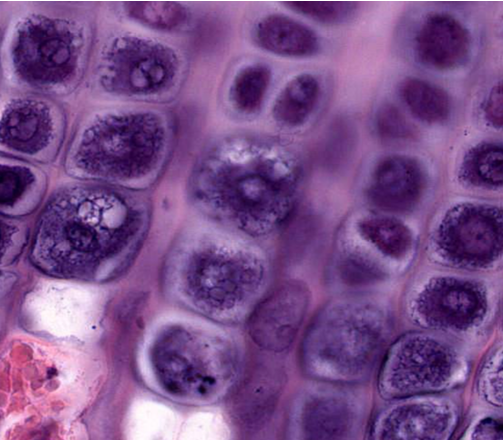
what stage of endochondrial ossification is this showing
hypertrophy
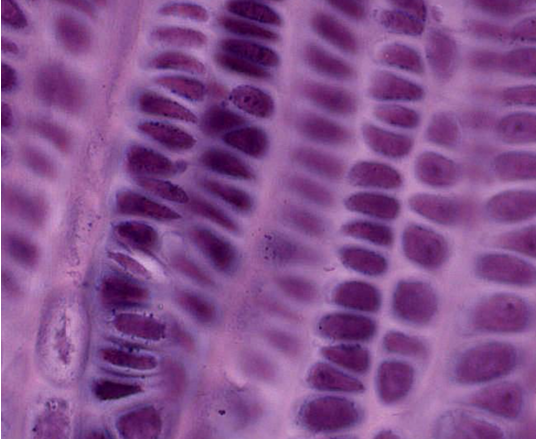
what stage of endochondrial ossification is this showing
proliferative
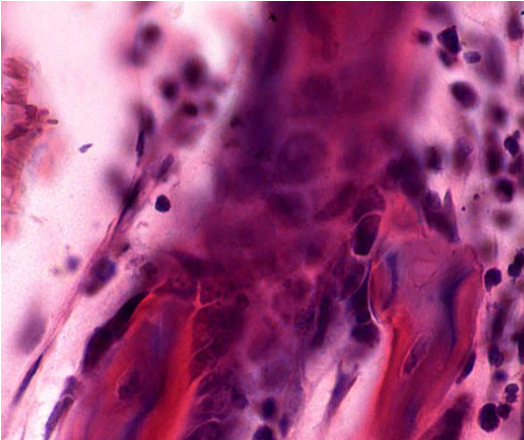
what stage of endochondrial ossification is this showing
calcification
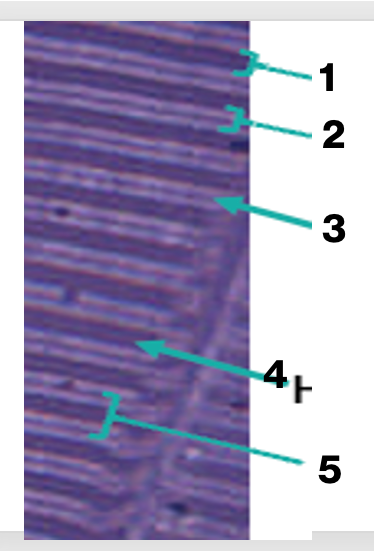
sarcomere of skeletal muscles, what is “1”
A band
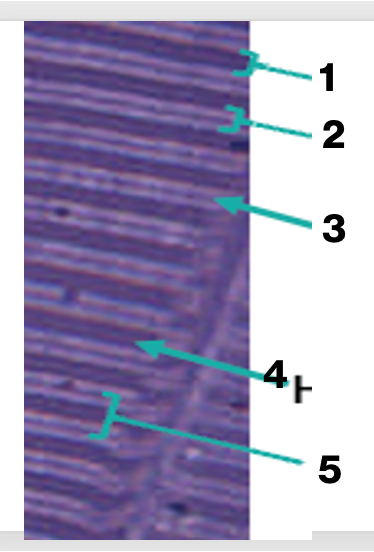
sarcomere of skeletal muscles, what is “2”
I band
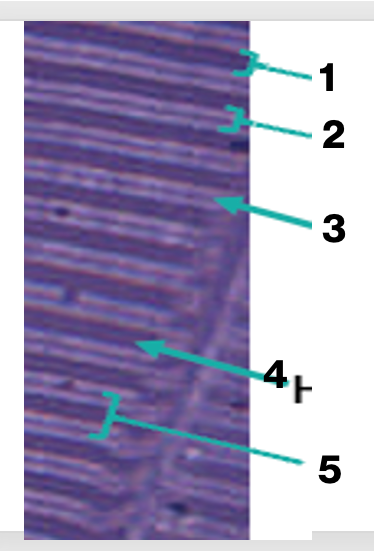
sarcomere of skeletal muscles, what is “3'“
Z line
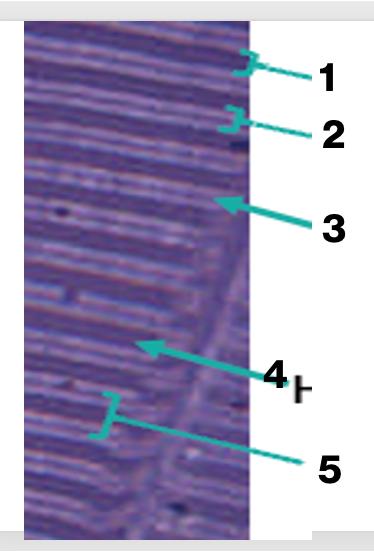
sarcomere of skeletal muscles, what is “4”
H band
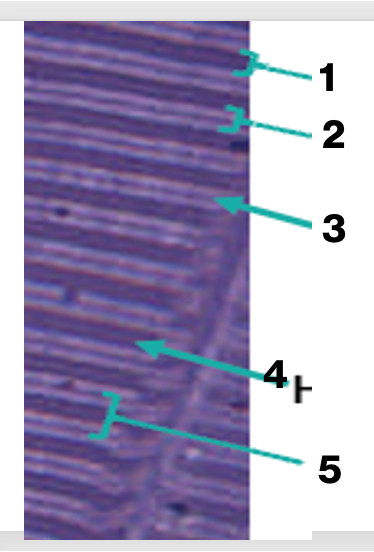
sarcomere of skeletal muscles, what is “5”
sarcomere
What type of protein filament(s) are found in the A band?
myosin and actin filaments
What type of protein filament(s) are found in the H band?
myosin filaments
What type of protein filament(s) are found in the I band?
thin actin filaments
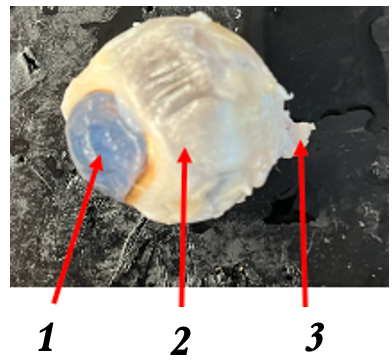
what is 1
cornea
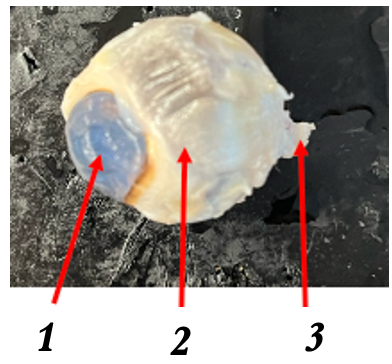
what is 2
sclera
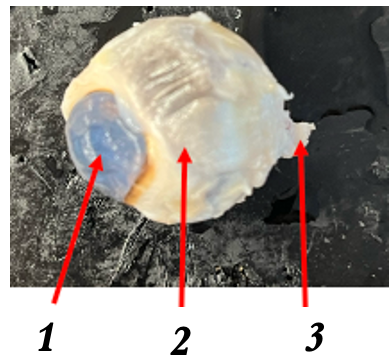
what is 3
optic nerve

what is 1
viterous humor

what is 2
lens

what is 1
retina

what is 2
choroid

what is 1
pupil

what is 2
iris
What is a blind spot?
a small area in the retina where the optic nerve exits the eye which is called the optic disc
Why aren’t we normally aware of blind spots
because our brain filters them out. Each eye compensates for the other eyes blind spot when both eyes are open
What is presbyopia?
condition in where the lens of the eye loses flexibility. It usually becomes noticeable around/after the age of 40
What causes presbyopia
the gradual hardening and loss of elasticity of the eye lens. The ciliary muscles struggle to change their shape.
what is another term for nearsightedness
myopia
what is anouther term for farsightedness
hyperopia
where on the body do we find the greatest density of receptor fields
fingertips, face, lips
merkel cells (disks), meissners corpuscles, Krause endbulbs, and the root hair plexus are all
touch receptors
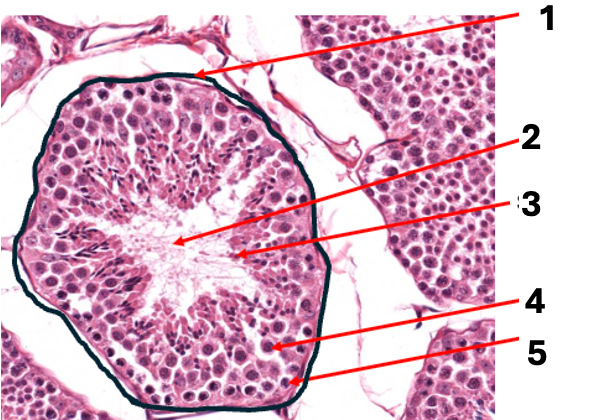
what is 1
basement membrane
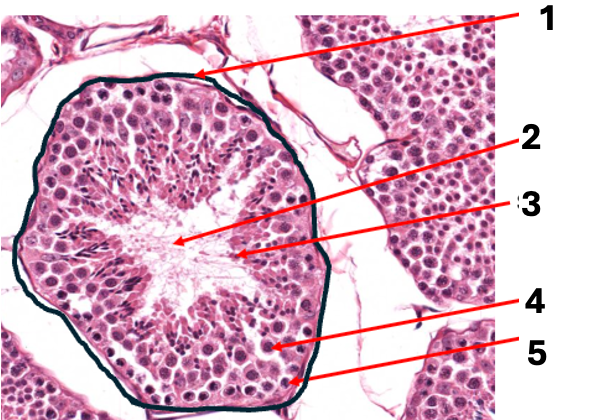
what is 2
sperm cell (n)
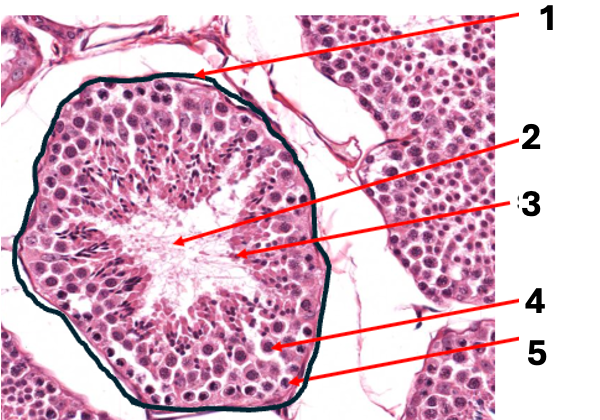
what is 3
spermatid (n)
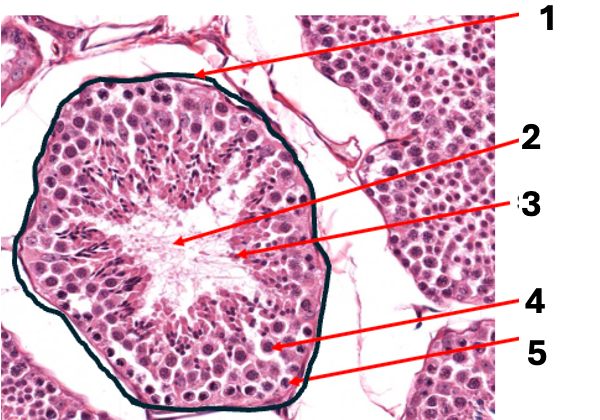
what is 4
primary spermatocyte (2n)
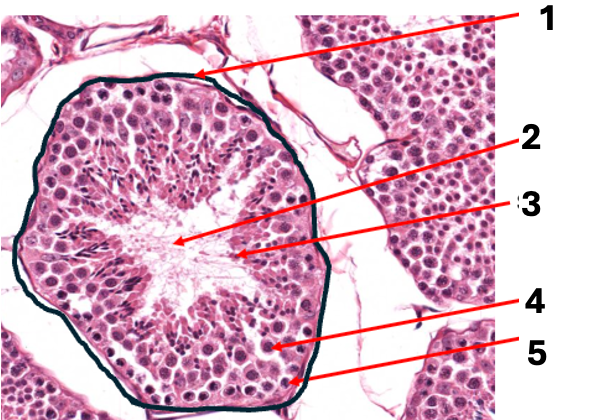
what is 5
spermatogonium cell (2n)