DNA Structure and Replication
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

39 Terms
Both DNA and RNA are types of...
Nucleic acids
A botanist is extracting DNA from an apple tree. Where in the cells should she look?
In the nucleus
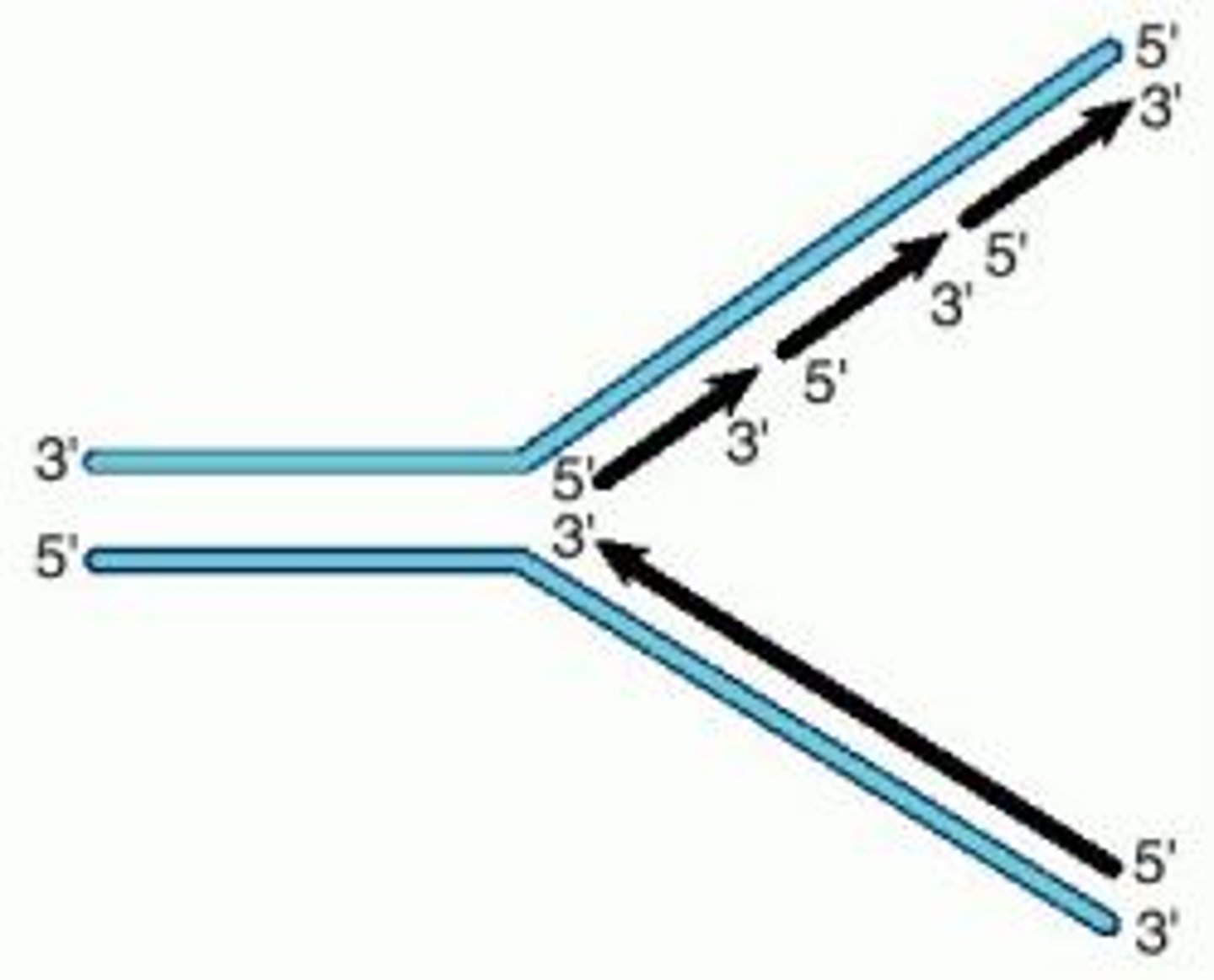
The DNA double helix strand is anti-parallel. This means that...
Both strands go in different directions
Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine are...
Nitrogenous bases
After examining the DNA of different organisms, what did Chargaff conclude about the four bases?
A=T and C=G
What holds base pairs together?
Hydrogen bonds
If the percentage of Adenine in a DNA sample is 40%, what is the percentage of Guanine?
10
Which of the following features of DNA is most important in determining traits of an organism?
The sequence of nitrogenous bases
DNA molecules consist of...
One old strand and one new strand
Which of the following events occurs directly after a DNA molecule is unzipped?
Free-floating nucleotides pair up with exposed bases.
What do the dotted lines represent between nitrogen bases ?
Hydrogen bonds
If the percentage of Cytosine in a DNA sample is 30%, what is the percentage of Thymine?
20
Which of the following steps in DNA replication comes FIRST?
DNA unwinds
What enzyme connects the new nucleotides together and proofreads them?
DNA Polymerase
Why is DNA replication called "semi-conservative"?
DNA consists of one old strand and one new strand
What enzyme unwinds or unzips the DNA strands?
Helicase
DNA is replicated in which phase of the Cell Cycle?
S
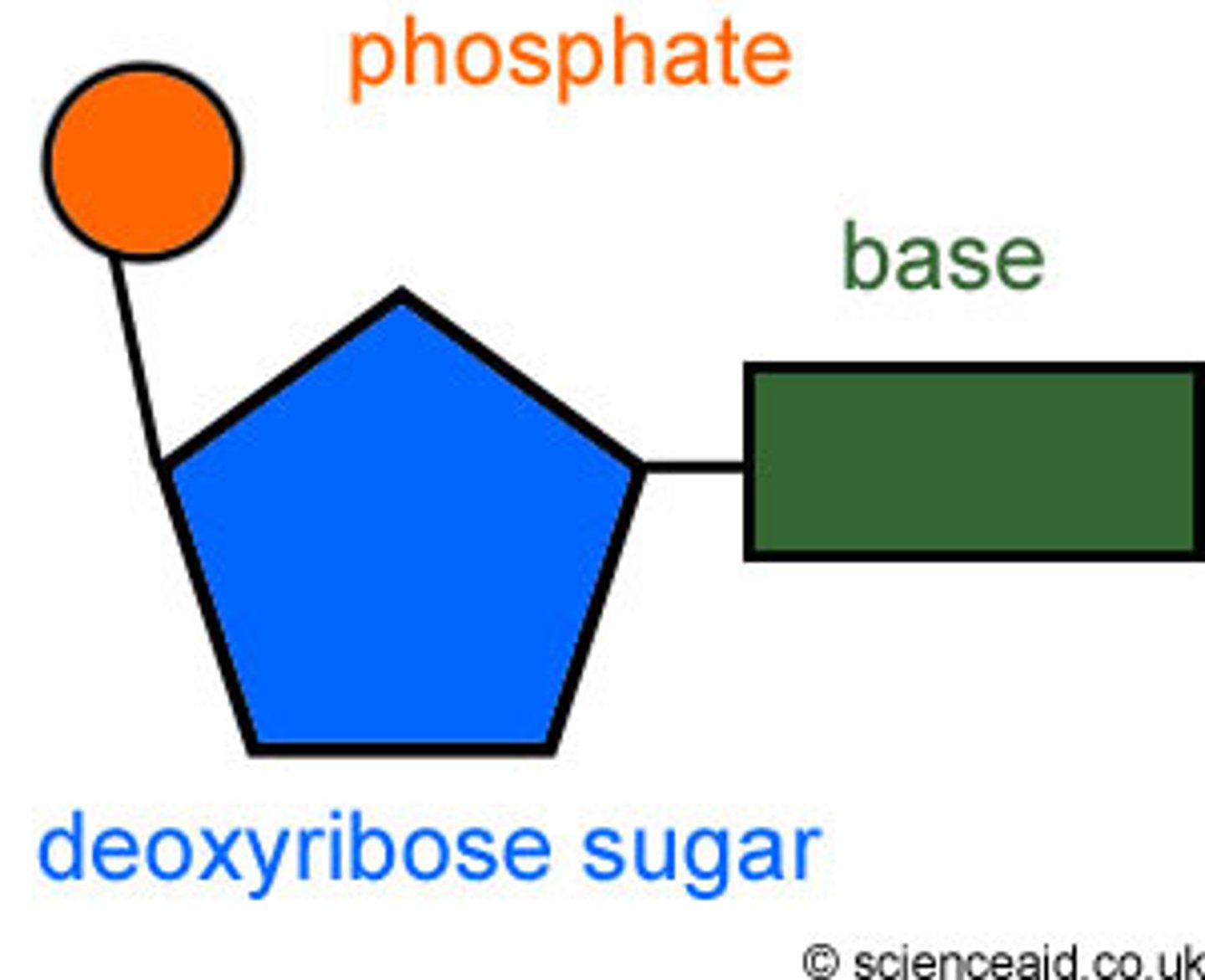
The "sides" of a DNA ladder are made up of what?
Deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups
DNA Polymerase is an enzyme that...
binds free-floating nucleotides to the DNA template strand
The "rungs" of a DNA ladder are made up of what?
Nitrogen-containing bases
Which of the following is the complementary strand to this DNA sequence: GATCTG
CTAGAC
Which of the following is the complementary strand to this DNA sequence: TCAGAC
AGTCTG
Watson and Crick built models of DNA and compared it to a spiral staircase. This illustrates that DNA is...
A double helix
What type of bonds connect the bases to each other?
Hydrogen bonds
Chargaff's Rule states that DNA contains equal amounts of _____ and _____, as well as _____ and _____.
A, T; C, G
Prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells in that...
They don't have a nucleus to hold their DNA
Where is DNA stored in a eukaryotic cell?
nucleus
A nucleotide consists of what three parts?
A phosphate group, five carbon sugar, and nitrogenous base
Enzyme that Glues the Okazaki fragments together
ligase
Enzyme that removes primase for the lagging strand and add complementary DNA bases to the template strand
DNA Polymerase I
Enzyme that proofread to confirm that mispairing of bases is not present
DNA polymerase I
DNA polymerase can only add in the ____' to ____' direction
5' to 3' direction
semiconservative replication
Method of DNA replication in which parental strands separate, act as templates, and produce molecules of DNA with one parental DNA strand and one new DNA strand
Leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
Lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
RNA Primase
An enzyme that creates an RNA primer for initiation of DNA replication.
replication bubble
Segment of a DNA molecule that is unwinding and undergoing replication.
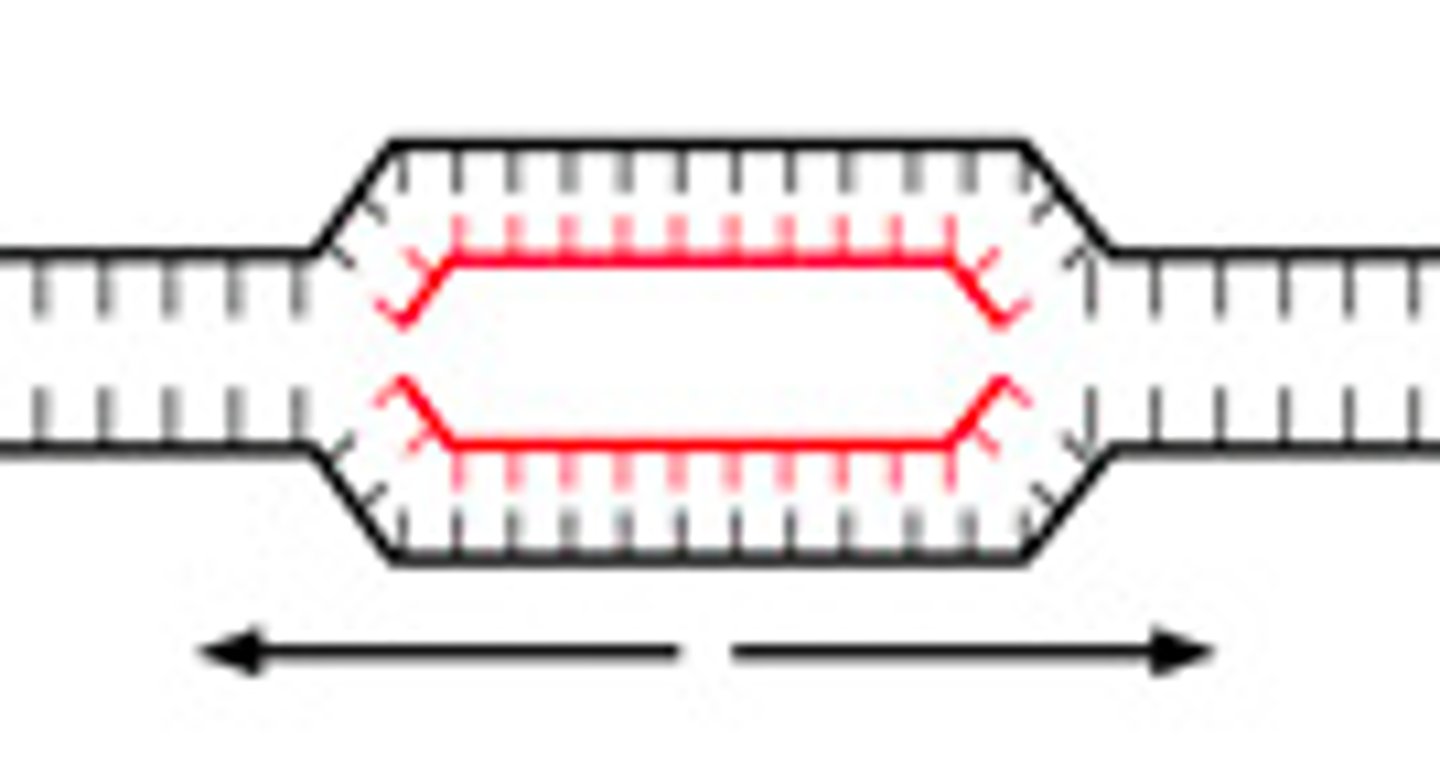
replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing.