BIOLOGY MOD 6
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Mutations definition (2)
a permanent change that occurs in our DNA sequence, either due to mistakes when the DNA is copied or as the result of environmental factors.
the new source of alleles in organisms
Mutagen defintion
-An environmental agent which can permanently damage DNA.
3 different types of mutagens and examples
-Naturally occurring mutagens (e.g. HPV (STD), transposons)
-Ionising electromagnetic radiation (e.g. UV rays, X-rays)
-Chemicals (e.g. asbestos, barbecuing food causes mutagenic chemicals)
What mutagens do (2)
-Mutagens dramatically increase the rate of mutations and may be natural or artificial.
-In some cases, mutagens act as carcinogens (cancer causing agents).
Different types of mutations: (3)
-Neutral: No effect on survival
-Beneficial: Increases likelihood of survival
-Harmful: Decreased likelihood of survival.
How mutations are repaired
- They are detected and repaired by enzymes.
Effect of mutations (2)
-Mutations can have no effect on the polypeptide or a significant effect.
-If the amino acid is greatly changed and it is important in the protein, it can affect the individual greatly.
How does ionising radiation cause mutations?
Ionising radiation causes mutations by removing electrons from atoms/molecules, thus forming ions.
What type of ionising radiation is bad? (2)
Short term, high exposure
How does UV radiation cause a mutation? (5 steps)
a thymine dimer is produced
The dimer is detected and the surrounding DNA opens to form a bubble.
Enzymes cut out the damaged region from the bubble.
DNA polymerase replaces the cut out and ligase seals it.
If the dimer is not cut properly, problems like skin cancer can occur.
How do radioactive elements cause mutations? (2)
-Radioactive elements like Uranium-236 are another source of EM radiation.
-These elements release gamma rays as they decay
What are chemical mutagens?
Chemical mutations are a substance that can cause mutation (change to DNA)
Different types of chemical mutagens:
intercalating agents, base analogues and/or DNA reactive chemicals.
How do intercalating agents cause chemical mutations? (2)
a chemical mutagen inserts itself into the bonds between the base pairs and alter the shape of DNA.
can cause deletion or insertion which can lead to subsequent errors in DNA replication.
Specific example of an intercalating agent:
Ethidium Bromide- a labraotory stain used to visualise DNA
What is a base analogue
A chemical mutagen where the substance is structurally similar to the nitrogenous base in the DNA.
How do base analogues cause chemical DNA mutation?
- it incorporates into the DNA sequence instead of the usual bases. ➡ ️ The DNA no longer functions.
Example of a base analogue:
5-Bromouracil
What is a naturally occuring mutagen?
A naturally occurring (biological) factor that can cause a mutation (a change in DNA).
How do viruses cause (naturally occuring) DNA mutation?
- they insert their genetic information into the chromosomes of the host cell.
Example of a (natrually occuring) virus which causes DNA mutation:
HPV (AKA genital warts) is responsible for the majority of cervical cancers
What are transponsons and how do they cause DNA mutation (naturally occuring) (2)
-Short DNA sequences that can move around the genome.
-They are extremely common in eukaryotic genomes (over 45% of the genome.)
Define mutation
A mutation is a permanent change in the sequence of DNA that can be beneficial, neutral or harmful due to mistakes when the DNA is copied or from the environment.
What is a point mutation?
Point mutations are a change in the DNA or RNA sequence that alters, adds or removes only one or very few nucleotides.
What is a silent mutation? (point mutation)
When a new codon still codes for the same amino acid.
-Neutral mutation
-No effect on the polypeptide
What is a missense mutation? (point mutation) (3)
When the new codon results in a replacement amino acid.
-Polypeptide chain has a new amino acid
-Polypeptide chain is still formed
-Effect of the altered polypeptide chain depends on the importance of the amino acid that was replaced.
What is a nonsense mutation (point mutation)
When the new codon results in the creation of a stop codon.
-Polypeptide chain terminates due to stop codon.
-Polypeptide chain is incomplete and the protein is non-functional.
What is a frameshift mutation? (point mutation)
When one or two nucleotides are added or removed from the DNA sequence, which alters every codon from that point onwards.
-Polypeptide chain has significant changes as every codon is changed.
-Loss of functional protein and different polypeptides is formed.
-A stop codon may form, which shortens the polypeptide.
What are the 2 types of frameshift mutation?
Nucleotide insertion: one or two nucleotides are added to the DNA sequence.
Nucleotide deletion: one or two nucleotides are removed from the DNA sequence. E.g. turner syndrome
What is a chromosomal mutation? What is a nondisjunction
The change in structure or number of chromosomes in a cell, which can significantly affect many genes at once.
A nondisjunction is the faliure of homologous sister chromatids to separate properly
What is a duplication mutation? (chromosomal mutation)
A replication of a section of a chromosome.
-Multiple copies of the same genes on the chromosome.
-Often leads to increased gene expression.
-Can be harmful depending on the gene involved.
What is an inversion mutation? (chromosomal mutation)
Genes present in reverse order
-May involve as few as two bases or several genres.
usually harmless
What is a deletion mutation? (chromosomal mutation)
Removal of sections of a chromosome.
-Deletions can cause disrupted or missing genes, which can have serious effects on growth and development.
-Chromosomal deletions are often fatal
What is an insertion mutation? (chromosomal mutation)
A section of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to a different chromosome.
What is a translocation chromosome? (chromosomal mutation)
A whole chromosome or a segment of a chromosome becomes attached to or exchanged with another chromosome of segment.
What is Aneuploidy? (chromosomal mutation)
-The presence of an abnormal number of a particular chromosome
-E.g. an extra chromosome (trisomy) or a missing chromosome.
What is a polyploidy? (chromosomal mutation)
Entire genome duplication- individual has an extra complete set of chromosomes.
fatal to human embryos
common among plants, e.g. strawberries
What are somatic cells?
Somatic cells are body cells (non-reproductive cells) which contain two sets of chromosomes.
-These cells are not inherited
What are germ line cells?
Germ-line cells are gametes (reproductive cells) produced in the gonads.
-Any mutations in these gametes can be inherited.
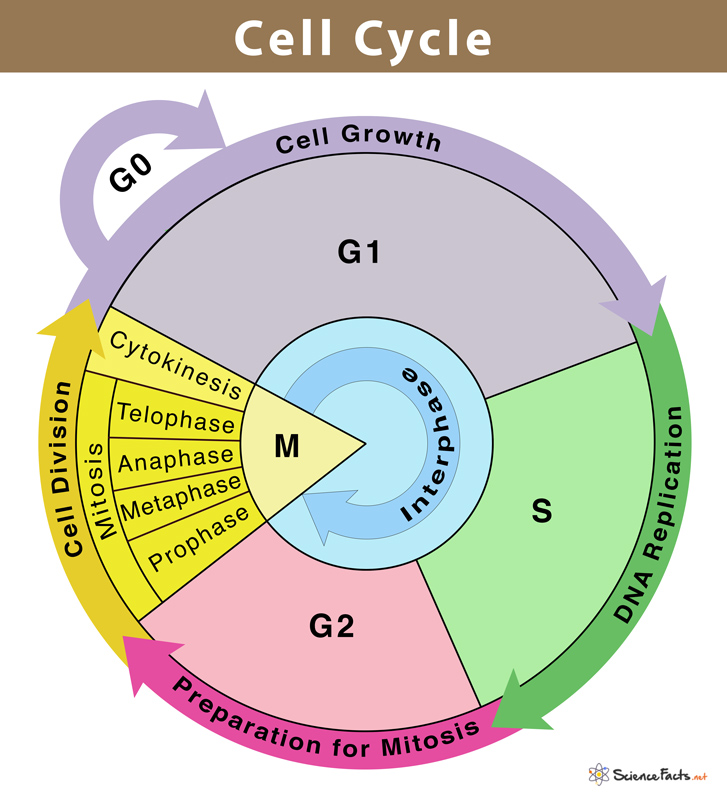
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
G0- cell cycle resets
G1- Cellular contents, excluding chromosomes, are duplicated.
S- Each of the 46 chromosomes are duplicated by the cell.
G2- The cell double checks duplicated chromosomes for error, and makes repairs.
Mitosis
Cytokenesis
What are somatic mutations? (4)
These mutations are often due to replication errors prior to mitosis.
Somatic mutations may have no effect on the individual at all, depending on the gene that is changed.
E.g. if the gene that is changed is a tumor suppressor gene, then it may result in cancer.
Mutations in some somatic cells will not be passed onto the next generation and therefore do not affect the gene pool, only the individual.
When do spontaneous mutations occur? (2)
These occur in the S phase of the cell cycle, and if it's not repaired during proofreading during the G2 phase, then it will be passed on to the daughter cells.
When the mutated cell continues to divide by mitosis, the mutation is amplified within the tissue- which may result in phenotypic changes.
Example of a phenotypic change in organs:
Cancer
How do germline mutations affect the gene pool? + example
When a gamete carrying a mutation fuses with another gamete, an embryo forms.
The mutation is replicated in every cell of the embryo as it undergoes mitosis and grows into a child.
For example: cystic fibrosis.
What is coding DNA? (exons)
the sequence of bases used for the production of polypeptides or proteins.
What does coding DNA affect? (3)
Mutations in coding DNA usually affect the type or sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide or protein produced, and therefore the phenotype of the individual.
Example: mutations in tumor suppressor genes can result in cancer.
can affect the phenotype of the individual
What does non-coding DNA affect? (6)
affect gene expression and cell functioning.
some have no effect.
‘switch on' genes or 'switch off' genes.
Coding for end products, e.g. rRNA and RNA.
linked to birth defects
associated with having a predisposition to a disease, or developmental abnormalities.
What are the 3 causes of genetic variation?
fertilisation, meiosis and mutation.
How does fertilisation increase genetic variation? (3)
Fertilisation creates genetic variation by bringing together two unique sets of genetic material from different parents.
Random fusion of gametes (each gamete carries a random combination of alleles due to meiosis)
Genetic mixing: (offspring inherit half their genes from each parent)
How does meiosis increase genetic variation? (2)
Independent assortment: The random separation of homologous chromosome pairs during meiosis I leads to millions of possible chromosome combinations in gametes.
Crossing over (recombination): Homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, creating new allele combinations that are different from the parents.
How does mutation increase genetic variation? (4)
by altering DNA sequences
Spontaneous DNA replication errors: creates new alleles.
Environmental factors: Cause mutations, e.g. electromagnetic radiation or chemicals.
Chromosomal mutations: Large DNA segments are deleted, duplicated or rearranged, further increasing genetic diversity.
Advantages of genetic variability: (2)
Greater variability improves the ability of the population to adapt to changes in the environment.
Little or no variability means a population is more likely to be wiped out.
How can mutations affect a gene pool (4)
Mutations are the original source of introducing genetic variations to a gene pool
They can confer advantageous traits that enhance an organisms fitness
An accumulation of beneficial mutations over generations can lead to evolutionary adaptations
Overall imact of mutations on the gene pool is gradual, as mutation rates are low
What is gene flow
Gene flow, or migration, involves the transfer of alleles between populations, through the movement of individuals or their gametes.
How does gene flow affect a population? (4)
This process can introduce new genetic material into a population's gene pool, increasing genetic diversity.
For example, when individuals from one population migrate and breed with members of another, they can introduce new alleles.
Gene flow tends to homogenise (make similar) differences between populations, reducing the likelihood of divergence and speciation.
Restricted gene flow can lead to increased differentiation and potentially the formation of a new species.
What is genetic drift? (2)
random fluctuations in allele frequencies within a population
significant in smaller populations
What causes genetic drift? (2 named effects)
Natural disasters (bottleneck effect)
founder effect: geographical isolation
The establishment of a new population by a small number of individuals (founder effect)
How does genetic drift affect a gene pool?
Genetic drift can lead to the loss of genetic variation, as alleles may be randomly fixed or lost over time.
This reduction in genetic diversity can decrease a population's ability to adapt to environmental changes and increase the risk of extinction.
Unlike natural selection, genetic drift does not necessarily favour alleles that confer a selective advantage.
What is an intron
segment of DNA/RNA that does not code for proteins
What is ancient biotechnology and an example
Was in practice without fully understanding the biological & biochemical processes involved.
Example: fermentation using yeast
Classical biotechnology def and example
Movement of biotechnology from farmyard/garden into laboratory.
Emerged with contributions of scientists such as Louis Pasteur & Gregor Mendel.
Example: Medicine production
Modern biotechnology def and example
Manipulation at a molecular level, dince the discovery of DNA
transgenic organisms
Future biotechnology example and def
Will come with greater understanding of genomics and protein function.
green chemistry
Medical (current) biotechnology
Pharmaceuticals: Vaccines, antibiotics
Stem cell treatments
Bio-inspired materials: spray on skin
Diagnostics: biosensors
Enviornmental (current) biotechnology in agirculture (3)
Agriculture:
Genetically modified crops
Artificial insemination/pollination
Selective breeding
Industrial (current) biotechnology def and example
Biodegradable plastics | Biopolymers created from plant and bacterial systems. |
Industrial efficiency | Enzymes can be isolated and (sometimes) genetically modified to speed up industrial chemical processes. |
Energy sources | Biofuels: Fuel can be extracted from biomass. |
Agriculture in biotechnology application (3)
Improving plant and animal production by increasing yield, nutritional value and resistance to disease.
Aims to enhance the quality of, and economic returns from, commercial crops.
Animal conservation.
Industrial biotechnology application
Promote the transformation of unsustainable systems into a biotechnology based sustainable economic system.
- Improve efficiency and maximise yield.
- Clean up pollution and spillages.
Medical biotechnology application
Improve health outcomes.
- Treat/cure disease.
- Improve quality of life.
- Diagnosis.
Social implications of biotechnology
Considerations: politics, patenting, privacy, equity in access and cost.
Positives: better disease treatment, improved quality of life, biodiversity, economic growth.
Negatives: privacy concerns, limited accessibility, risk of monopolies and high costs.
Ethical implications of biotechnology
Considerations: balance benefits/harms, justice, equity, and respect for beliefs/culture.
Support: moral duty to research, right to quality of life, informed knowledge of potential suffering.
Concerns: risk of eugenics, “playing God,” discrimination, environmental harm, profit-driven patents, widened inequality, and animal exploitation.
Impact on biodiversity due to genetic techniques
Biodiversity: supports healthy, resilient ecosystems and sustains life.
Decreasing: monocultures and horizontal gene transfer reduce variation.
Increasing: recombinant technologies and new genetic combinations boost diversity.
Inducing genetic change, fill in the table
Technology | Genetic change |
Technology | Genetic change |
Hybridisation | Introduction of new species |
Selective breeding | All individuals have similar alleles which reduces genetic variation. |
Artificial pollination | Reduction of genetic diversity. Favourable alleles become increasingly common. |
Artificial insemination | Favourable alleles passed down to many offspring. |
Transgenic species | Introduction of new, genetically modified species. |
Gene cloning | Increases the frequency of a particular gene. |
Whole-organism cloning | The gene pool of an entire population of cloned organisms would have very little to no variation. |
Artifical insemination
→ deliberate insertion of semen through the cervix into the uterus without sexual intercourse for the purpose of achieving fertilisation.
Allows for animals with desired characteristics to produce offspring.
Artifical pollination
→ dusting of pollen by hand, from the anthers to stigma of same/different plants.
Enables plant breeder to control the characteristics of the plants being bred.
IVF process (in-vitro fertilisation) and definition
When an egg is fertilised by sperm outside the body in an artificially created environment; usually in a test tube or petri dish.
Semen extracted from male by mechanical stimulation or through the use of an artificial vagina.
Hormone treatments stimulate egg production.
Eggs are taken from the ovaries.
The eggs are mixed with the sperm to become fertilised.
Fertilised eggs are placed in an incubator for approximately 48 hours.
Embryos are implanted into the uterus, or frozen.
Selective breeding
Humans selectively develop particular phenotypic traits by choosing which males and female will sexually reproduce and have offspring together.
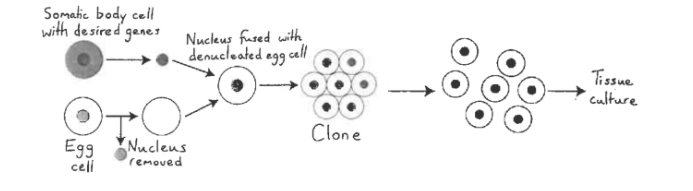
Whole organism cloning def and and process
Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)
Adult somatic cell is removed from the animal to be cloned.
Donor cells are starved and isolated of nutrients to stop cell division.
An unfertilised egg is removed from the donor organism. The DNA is removed using a micropipette.
Transfer somatic cell nucleus into enucleated egg cell.
Electric pulse or chemical treatment stimulates division.
The cell is cultured so that it divides and becomes an embryo.
The embryo is implanted into the uterus of the surrogate mother.
Whole organism cloning advantages and disadvantages
Advantages | Disadvantages |
- Produces genetically uniform organisms with reliable drug responses, which can be used in research. - Human tissues can be ‘grown’ (embryonic stem cell technology), saving lives. - Can produce livestock and crops with desirable characteristics. Genetic uniformity ensures consistent results. - Can be used to save endangered animals. - Tissue culture rapidly produces many copies from a parent plant. | - Expensive. - Resource-consuming. - Ethical concerns. - Reduces genetic diversity. - Risks food security. - Doesn’t guaranteed an identical organism:
|
Cloning in plants (cutting, grafting, tissue culture)
Method | Description |
Cutting | A section of a plant is removed from the parent plant and placed in soil/water. |
Grafting | A cutting from the stem of the plant is bound to the cut stem of another plant with developed roots. The stems fuse. |
Tissue culture | A section of the parent plant is pulverised, releasing individual plant cells. Cells are grown on a nutrient/hormone containing medium to form sprouts. |
Process of theraputic cloning
Cloning techniques developed to produce therapies for disease. Involves the production of stem cells genetically identical to the donor.
Nucleus removed from patient cell.
DNA inserted into a denucleated egg cell.
The cell begins to divide into an embryo.
The embryonic stem cells are removed.
The stem cells are treated so that they remain in their undifferentiated state.
Recombinant DNA process
Isolation: DNA extracted from natural sources.
The required gene is isolated.
Plasmid removed from bacteria.
Digestion: DNA fragments are cut using the same restriction enzyme.
The fragments produced have matching ‘sticky ends’ sections of single-stranded DNA with exposed nucleotide bases at the end of a double-stranded molecule.
Insertion: The target gene is inserted into the scaffold DNA.
The sticky ends join up in a process called annealing.
Ligation: DNA ligase joins fragments.
Bacterial transformation: The process of introducing foreign DNA into bacteria.
The recombinant plasmid is inserted back into a bacterial cell.
Multiple copies of the gene will be produced.
The gene is inserted into an egg cell of another species and becomes part of the newly formed organism’s DNA after fertilisation.
What is a transgenic organism
an organism that develops from a cell that foreign DNA has been inserted into. The organism will express the introduced trait.
Application of transgenic organisms and how it is created
Improvement of crop yields.
Herbicide resistance.
Enhancement of desirable features
Production of human proteins.
Treatment through gene therapy.
Created through Biolistics: a ‘gene gun’ shoots small metal bullets covered in DNA into the nucleus of a cell.
Positives and negatives of biodiversity in agriculture
Positives | Negatives |
- Insect and herbicide resistance = less harmful chemicals. - Increase stress-resistance and productivity.
- Potential to increase genetic diversity in crops through transgenics. | - Can result in soil nutrient loss and a reduction in ecosystem diversity. - Could lead to the establishment of monoculturing practices. - Horizontal gene transfer into native ecosystems.
|
Social, economic and cultrual influences on biotechnology
Social | - The biological techniques available are dictated by:
|
Economic | - Financial costs and benefits.
|
Cultural | - Religious opinion, educational levels, difference of opinion due to location & customs. |