8.1 & 8.2 - Fossil Fuels
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
8.1 - Energy and the Enviornment
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Name the 3 fossil fuels
oil (petroleum
coal
natural gas
Facts about fossil fuels
most fossil fuels formed long before dinosaurs, extinction = 65 million years ago
they’re easy, cheap, reliable
80% of energy used in the US comes from burning fossil fuels
nonrenewable carbon-based resources formed between 150-300 million years ago from remains of dead organisms
Photosynthesis
process of turning light into energy
only done by plants/producers
consumers eat the plants and consume their energy
Energy in the US
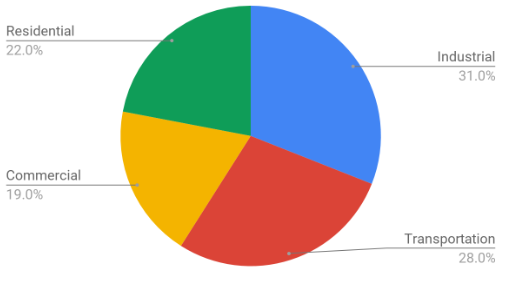
% of fossil fuel usage in US

Combustion Reaction
when carbon and hydrogen atoms from a fossil fuel combine with oxygen from the air to form carbon dioxide and water
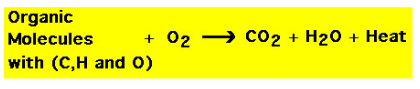
converts chemical potential energy stored within bonds of fossil fuel into thermal energy
Oil (Petroleum)
partially decomposed ancient marine microorganisms sunk to ocean floor and over time, were buried under layers of sediment and rock
made up of a mixture of hydrocarbons
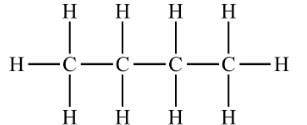
C₄H₁₀
What does most oil and natural gas start life as?
microscopic plants and animals that live in the ocean
plant plankton
animal plankton
How does oil form?
sea creatures died, sediment built up, the trapped oil is in between layers
scientists don’t really know what it is
What are some popular oil sites?
Middle East
east South America
Russia
scientists are debating whether to dig in Antarctica
Wyoming
West Virginia
Kentucky
Pennsylvania
Oil Transportation
once extracted, oil and gas must be sent to a refinery for processing
pipelines transport most of the world’s oil from refinery
massive oil tankers also play an important role in distribution
supertanker, train, truck, or pipeline
How is oil extracted?
drilling, on land or at sea
strip mining in the case of tar sands oil and shale
Oil’s Uses
transportation fuels (gasoline)
electrical generation
asphalt
plastic
Natural Gas (formation and composition)
formed in the same way that oil forms
due to density differences, natural gas is found trapped on top of petroleum deposits
composed of mostly methane, but could also contain butane or propane
Natural Gas (sustainability)
contains more chemical potential energy per kg than coal or oil = more efficient
produces less CO2 (pollutants) than oil or coal when burned
Uses of Natural Gas
cooking
heating
homes
manufacturing
it is federally mandated to add sulfer to prevent it from not smelling, which may lead to people not noticing gas leaks
what is the difference between conventional and unconventional natural gas?
conventional - located in porous and permeable rock beds or mixed into oil reservoirs and can be accessed via standard drilling
unconventional - any form of gas that is too difficult or expensive to extract via regular drilling, requiring a special stimulation technique, such as fracking
Hydroulic Fracturing “Fracking”
uses chemically treated high pressure water to break apart rock containing natural gas
risks include contamination of ground water and air pollution from methane release
Coal
decomposing swamp plants buried under mud with no oxygen, these remains produced peat
peat = partially decayed vegetation
over time, increased pressure and heat transformed this peat into the coal we use
Why do we use coal?
safer to ship, cheaper to extract, abundant in US
Wyoming, Appalachian Mountains hold majority of US coal
inexpensive
Cost of coal
more air pollution than any other fossil fuel
CO2 released into the atmosphere leads to global warming
Extraction = lots of environmental damage
many hazards associated with mining
how does a coal power plant work?
coal is burned in a furnace- converted to thermal energy
thermal energy heats water to make steam
steam turns turbine
turbine blades spin an electric generator
electrical current transmitted along power lines
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using fossil fuels to generate electricity?
they convert chemical potential energy to thermal energy, which is then converted into other useful forms
they are nonrenewable and bad for the environment
how does a nuclear power plant work?
fission takes place in the reactor vessel, control rods are used to control the chain reaction
it is encased in a concrete container/containment structure to cool the process
water from the ocean is used to cool the very intense heat caused from the reaction
the cooling creates steam which spins a turbine, which powers a generator, which powers other things, like telephone poles
In what ways do people use energy resources daily?
charging cell phones
logging onto the internet
stoves
furnaces
air conditioners
vehicles
How does the law of conservation of energy apply to the burning of fossil fuels?
it isn’t created, since it comes from the energy of dead plants and animals
it isn’t destroyed because when it burns, the energy is converted into a new form, like thermal energy
Why are fossil fuels considered to be a nonrenewable resource?
they take millions and millions of years to form
they are being burned and used a much faster rate, which will lead to them eventually running out
What are the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear power plants and those that burn fossil fuels?
they transform nuclear/chemical energy into electrical energy
they aren’t renewable
What is nuclear fission? Example? Why does it release energy?
an atom splits apart
causes a tremendous amount of thermal energy to be formed from a small amount of mass
concrete towers encase these processes, cooling it down by releasing waste heat
doesn’t take as much energy to create as fusion, less cost
ex: the energy from the sun
releases energy because the smaller atoms don’t need as much energy as the bigger atoms, so they emit thermal energy
What is nuclear fusion?
atoms combine at very high temperatures
a small amount of mass creates a tremendous amount of thermal energy
using this method as an energy source is problematic because their reactants require great amounts of energy and their high temperatures aren’t easy to contain
What is a chain reaction (fission)?
when a neutron strikes the nucleus of a uranium atom
causes it to split into two smaller atoms
two or three neutrons are emitted
the process continues
What are the different classifications of nuclear waste and what do they mean?
low-level waste - low levels of radioactive material
half-life = the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay into a different element or isotope
high-level waste - high levels of radioactive material
What are some indicators that our climate is changing?
polar ice is melting
shifts in animal locations/migrating (season’s timing)
global temp is rising
less snow
hurricane season is longer
ocean temp/level is rising
less ozone
traces of more green house gases
pH is decreasing, more acidic oceans
Balance the chemical reaction for photosynthesis:
CO₂ + H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + O₂ = carbon dioxide + water →glucose + oxygen
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂6O₆ = photosynthesis
Where does nuclear energy come from?
U₂₃₅ in the ground
What type of energy is the product of nuclear energy?
thermal energy
is nuclear energy a fossil fuel?
no
is nuclear energy organic
no, it does not contain carbon
is nuclear energy renewable?
no
where are nuclear power plants?
located in 32 countries
about 440 nuclear reactors in total
60 new power plants under construction
lots on east coast of the us
lots in europe
few in other places
not built near seismic zones
how many kg of coal is equal to 1 kg of uranium?
3 million
overall efficiency of a nuclear power plant = 35%
Pros of nuclear energy output
does not produce air pollutants that burning fossil fuels does
no release of CO₂
large amount of energy produced from small amount of uranium
cons of nuclear energy output
disposing of nuclear waste is difficult
uranium is not renewable
power plants expensive to build, takes 10+ years
radioactive material harmful to living organisms and the environment