Antimicrobials and Antimicrobial Resistance
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
We don’t ______ antibiotic resistant bacteria- bacteria are constantly mutating and we _______ growth of bacteria with mutations that enhance survival in the presence of that antibiotic.
induce; selectively encourage
What is constitutive resistance?
bacteria are resistant to antibiotic because they lack the uptake system or targets of the antibiotic
What type of resistance is unrelated to previous antibiotic exposure?
constitutive
What is acquired resistance?
bacteria become resistant to antibiotics by mutation resulting in alteration of uptake systems or targets of antibiotics
What type of resistance is dependent on prior exposure?
acquired
What are the three basic mechanisms of acquired resistance?
Alter the target of the drug
Alter uptake of drug
Inactive the drug
What are ways a bacteria could alter the target of the drug?
modify the target site
reduce significance of the target site
How could a bacteria alter uptake of a drug?
inhibit uptake (decrease pore size)
increase excretion (tetracyclines)
How could bacteria inactivate a drug?
synthesis of inactivating enzymes
some bacteria produce beta-lactamase enzyme that destroys or deactivates the beta-lactam antimicrobials
What is the difference between multi-antibiotic resistant and cross-resistance?
multi-antibiotic: multiple DIFFERENT resistance mechanisms = different classes
cross-resistance: resistance due to a COMMON mechanism - so that resistance to one antibiotic implies resistance to others = same class
What are two ways multi-antibiotic resistance could occur?
common when R-plasmids exchanged (conjugation)
constant use of drugs eliminates sensitive cells
True or false: cross-resistance is unidirectional.
true
How could an organisms be resistant to several Beta-lactams?
production of Beta-lactamase
What are the two basic mechanisms by which bacteria ACQUIRE resistance?
changes in DNA via MUTATION
Acquisition of DNA
What form of acquired resistance is lethal?
mutations
What is selective advantage?
mutations that are not lethal, but increase in population until they may become dominant type
What is selective pressure?
antibiotic resistance only confers selective advantage IF antibiotics are present
What mechanism of acquired resistance generates genetic diversity?
genetic transfer (acquisition of DNA)
What is genetic transfer a critical mechanism for?
bacterial adaptation to changing environments and host conditions
What are the two relevant mechanisms of genetic transfer?
transduction and conjugation
What is transduction?
transfer of DNA following bacteriophage infection → bacteriophage DNA is integrated into bacterial chromosome
What is conjugation?
inter-bacterial DNA transfer through sex pilus
What can plasmids encode?
pili genes
exotoxins
MULTIPLE antibiotic resistance genes (R plasmids)
True or false: plasmids usually encode factors not ESSENTIAL for growth and replication.
true
How are plasmids transferred?
transferred vertically during bacterial division and horizontally during conjugation
What is the basis for selecting antibiotic that is effective against the bacteria?
gram related spectra
historical data
in vitro sensitivity and antibiotic sensitivity testing
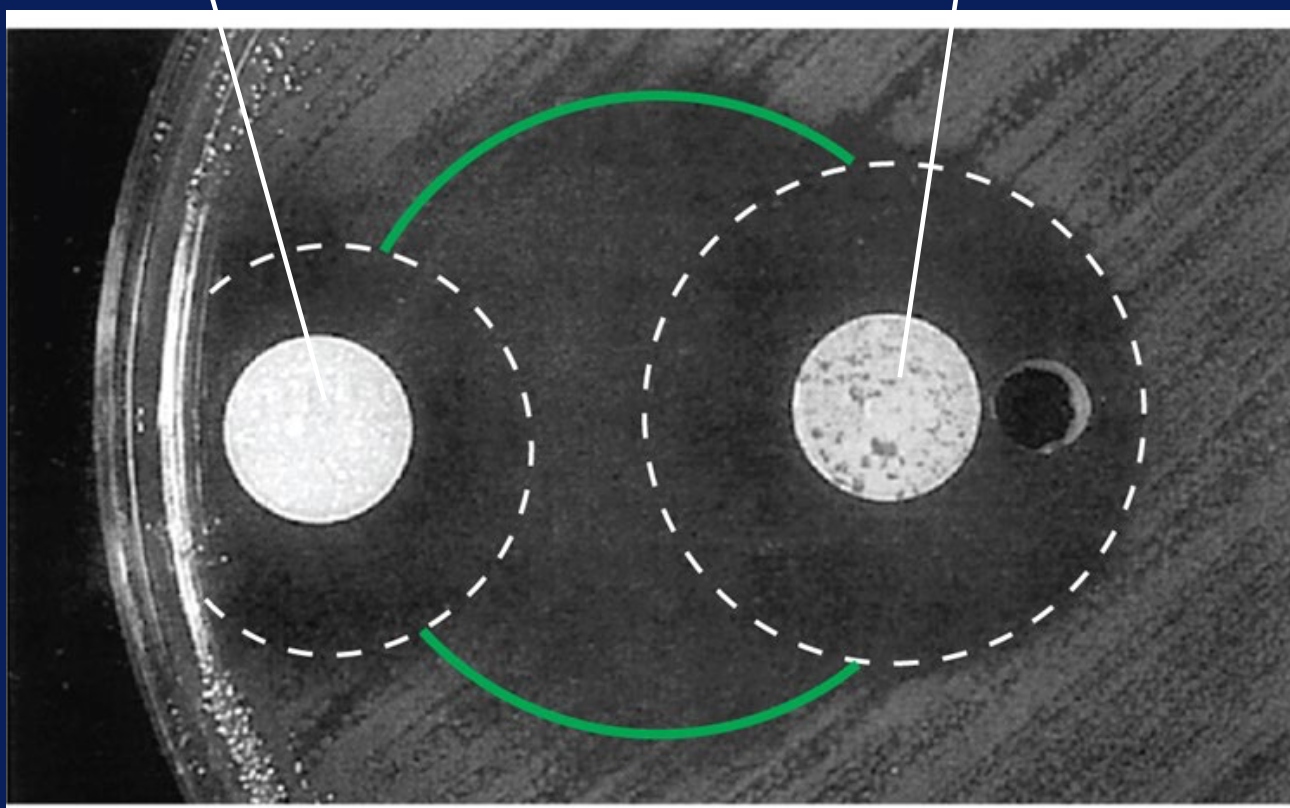
What is this an example of?
synergism between two antimicrobial agents
What are strategies for limiting antibacterial resistance?
• Effective surveillance systems for the collection of data at the local and national level and monitor
• Ideally treatment should be based on antimicrobial susceptibility test results
• Strict adherence to drug withdrawal periods in food-producing animals
• Maintain high concentration of drug in patient for sufficient time
• Use antimicrobials only when necessary
• Use antimicrobial agents in combination
What are the routes of administration in prescribing antimicrobial drugs?
topical
oral route
IM
IV
What are safety and side effect considerations when prescribing antimicrobial drugs?
toxicity and allergies