OB II Unit 6 Fetal Skeleton 119- 142
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What does the fetal skeleton look like?
Skeleton appears as cartilaginous structures that undergo ossification.
What anomalies result from the fetal skeleton?
Anomalies result from genetic factors, unknown causes, or environmental factors
What is skeletal dysplasia?
•Describes abnormal growth & density of cartilage & bone
What is dwarfism?
Disproportionately short stature (occurs secondary to a skeletal dysplasia)
What is the lethal form of skeletal dysplasia?
Lethal forms = extremely severe prenatal appearance
Severe Micromelia – shortening of limbs
What is the nonlethal form of skeletal dysplasia?
•- Nonlethal forms = manifest milder form
What is the process of evaluating the skeletal system of a fetus?
Assess limb shortening – measure all long bones
Assess bone contour
Estimate degree of ossification
Evaluate thoracic shape & circumference
Coexistent hand & foot anomalies
Evaluate face & profile
Survey for other anomalies
Manifestation of skeletal dysplasias varies
What are the segmental patterns of long bones?
Rhizomelia
Mesomelia
What is the non-segmental pattern of long bones?
Micromelia
What is Rhizomelia?
Shortening of proximal segment
Humerus and Femur
What is Mesomelia?
Shortening of distal segments
Radius/Ulna and Tibia/Fibula
What is Micromelia?
Shortening of ENTIRE Extremity
What is the most common LETHAL skeletal dysplasia?
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
What are the 2 subdivisions of thanatophoric dysplasia?
Type I: short, curved femurs, flat vertebral bodies
Type II: short, straight femurs, flat vertebral bodies, cloverleaf skull
What type of thanatophoric dysplasia may be an autosomal recessive inherited trait?
Type 2
What is the prognosis of thanatophoric dysplasia?
Extremely grim due to pulmonary hypoplasia
What are the US findings for thanatophoric dysplasia?
•Severe micromelia
•Cloverleaf deformity
•Narrow thorax with shortened ribs
•Protuberant abdomen
•Frontal Bossing – bulging forehead
•Hypertelorism
•Flat vertebral bodies
What are extra US findings for thanatophoric dysplasia?
•Severe Polyhydramnios
•Hydrocephalus
•Nonimmune hydrops
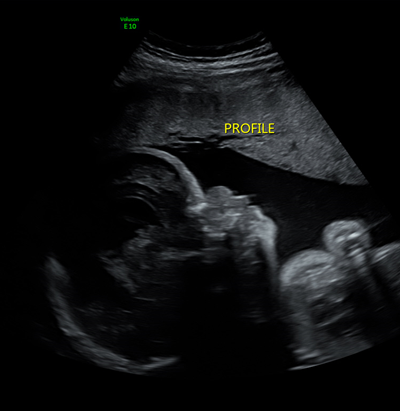
What is this image showing?
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
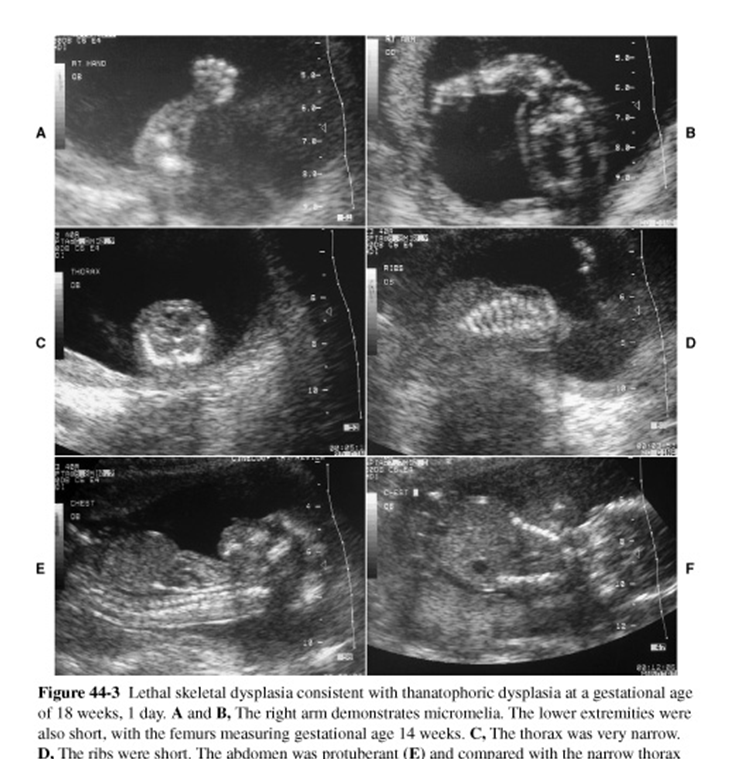
What are these images showing?
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
What is another name for dwarfism?
Achondroplasia
What is the most common NON-lethal dysplasia?
Achondroplasia/ Dwarfism
What is achondroplasia?
Decreased endochondral bone formation, producing SHORT, SQUAT BONES
Achondroplasia may not be evident until after ____ weeks when biometry becomes abnormal.
22 weeks
What is the heterogeneous form of achondroplasia?
Good survival rate with normal intelligence & life span
What is the homozygous form of achondroplasia?
LETHAL, with most infants dying from respiratory problems
What are the US findings for achondroplasia?
Rhizomelia
Macrocephaly
Trident hands
Short prox. & middle phalanges
Depressed nasal bridge
Frontal bossing
Mild ventriculomegaly
What is a rare lethal skeletal dysplasia?
Achondrogenesis
What are the cartilage abnormalities of achondrogenesis?
Cartilage abnormalities = abnormal bone formation & hypomineralization
What are the 2 types of achondrogensis?
Type 1 = Parenti-Fraccaro
Type 2 = Langer-Saldino (89% of cases)
What is the prognosis of achondrogenesis?
Grim due to pulmonary hypoplasia
What are the US findings for achondrogenesis?
•Severe micromelia
•Decreased or absent ossification of spine
•Macrocephaly
•Short trunk
•Short thorax & ribs
•Micrognathia
•Polyhydramnios
•Hydrops is possible
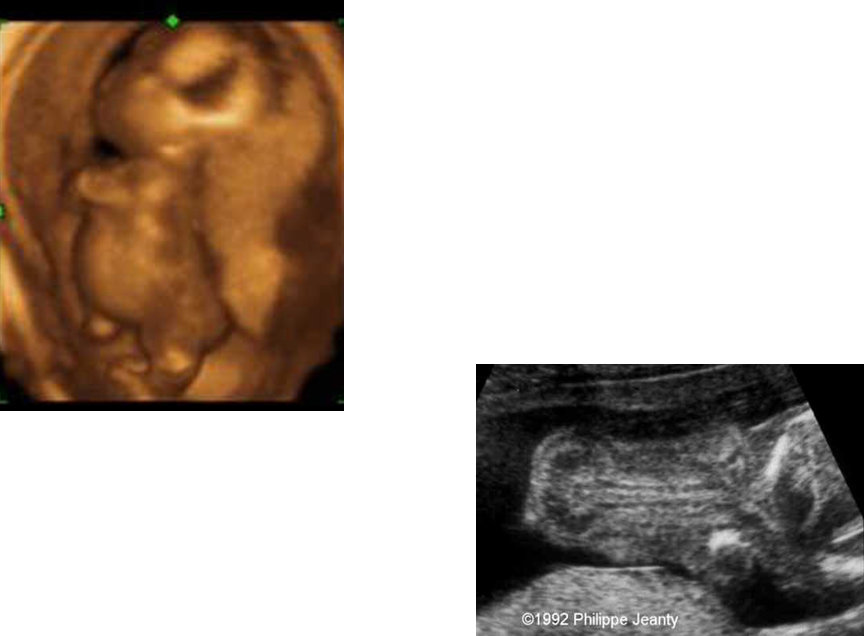
What are these images showing?
Achondrogenesis
What is osteogenesis imperfecta?
Collagen production problem which = Brittle Bones
Where does osteogenesis imperfecta manifest?
•Manifests in the teeth, skin, ligaments & blue sclera
What are the 4 types of osteogenesis imperfecta?
•Types 1 & 4 = mildest forms
•Type 3 = severe form
•Type 2 = MOST SEVERE –LETHAL
Osteogenesis imperfecta has an increased translucency in what trimester?
1st trimester
what are the US findings for osteogenesis imperfecta?
Generalized Hypomineralization of bones especially cranium
Skull = allows brain structures to be clearly visualized; compressible
Multiple fractures of long bones, ribs, & spine
May leave bones bowed, thickened, & sharply angulated
Narrow thorax
Micromelia
Polyhydramnios
What type is similar to type 2 but less severe?
Type 3
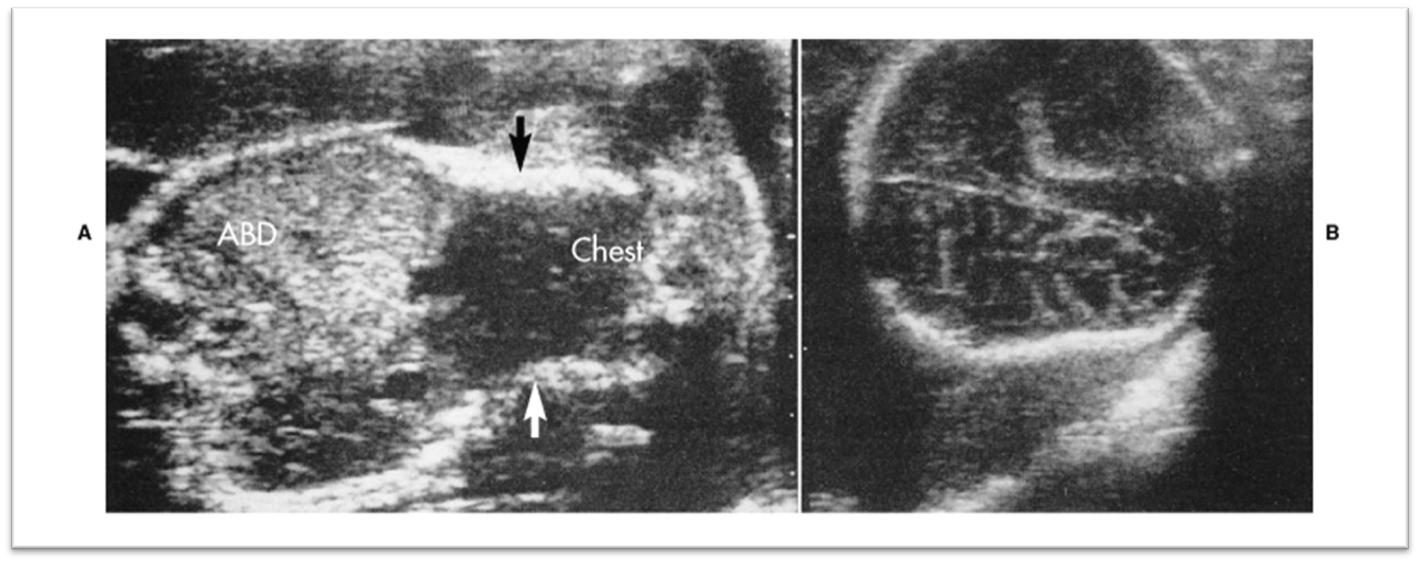
what is this image showing?
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
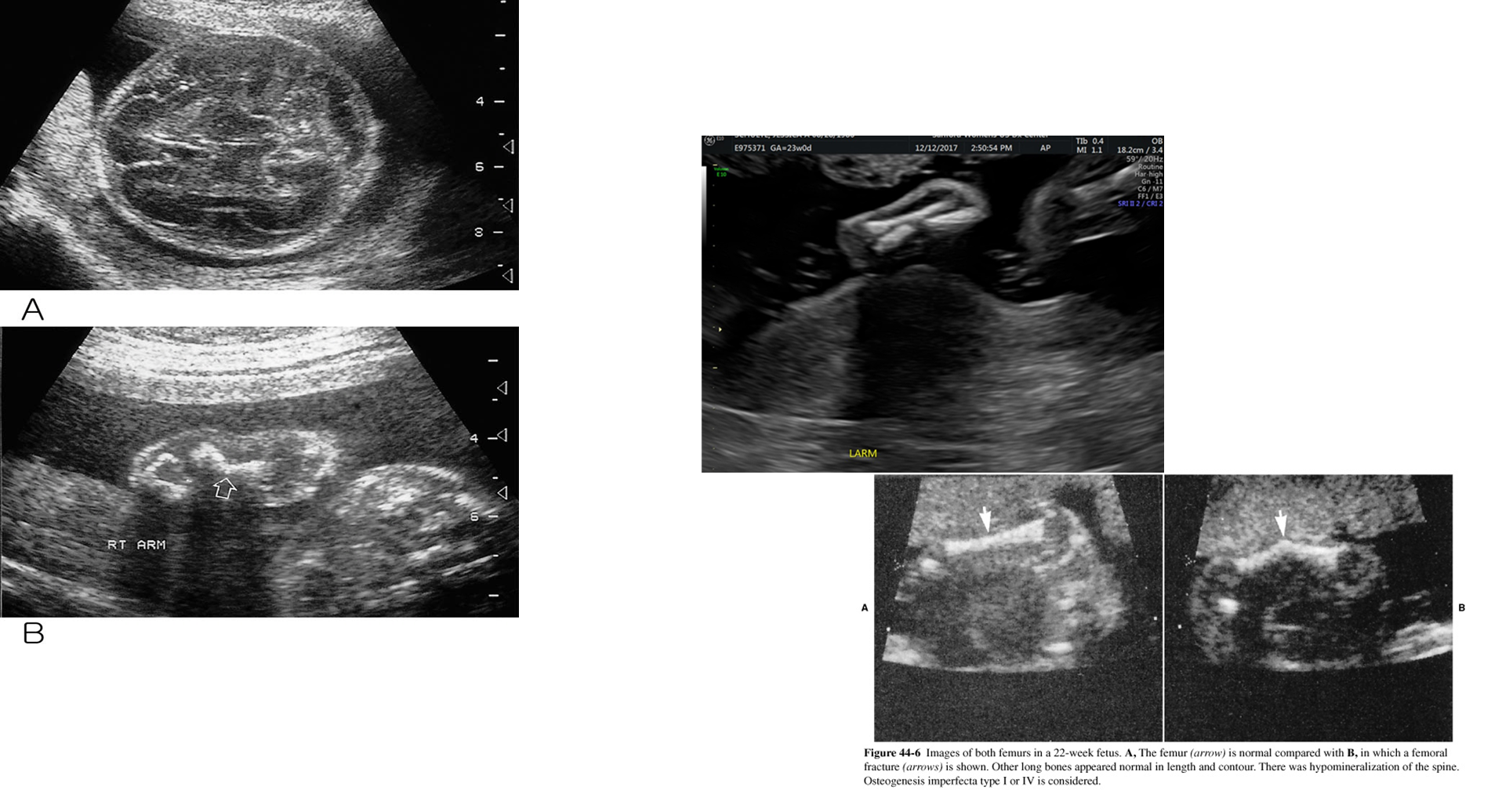
What are these images showing?
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
What is congenital hypophosphatasia?
Lethal disorder of diffuse hypomineralization caused by alkaline phosphatase deficiency
What is the US features of congenital hypophosphatasia?
Diffuse hypomineralization of bone
Moderate to severe micromelia
Extremities may be bowed, fractured, or absent
Poorly ossified cranium with well-visualized brain structures
Small thoracic cavity
What is diastrophic dysplasia?
•Rare disorder with micromelia, talipes, cleft palate, micrognathia, scoliosis, short stature, earlobe & hand deformities, (fixed abducted thumb = hitchhiker thumb)
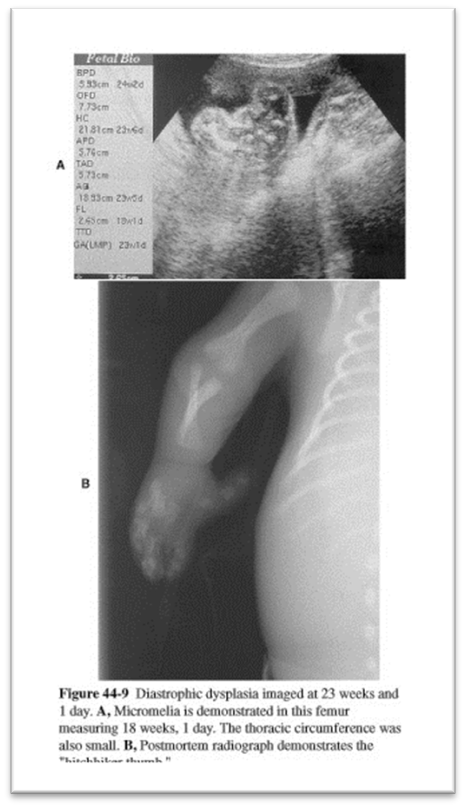
What is this image showing?
Diastrophic dysplasia
What is Camptomelic Dysplasia?
•Group of LETHAL skeletal dysplasias
What is Camptomelic dysplasia characterized by?
Characterized by BOWING of the long bones
Bowing of long bones (Legs affected worst)
Small thorax
Hypoplastic fibulas & scapulae
Hypertelorism
Cleft Palate
Micrognathia
Talipes
Hydrocephalus
Polyhydramnios
Hydronephrosis
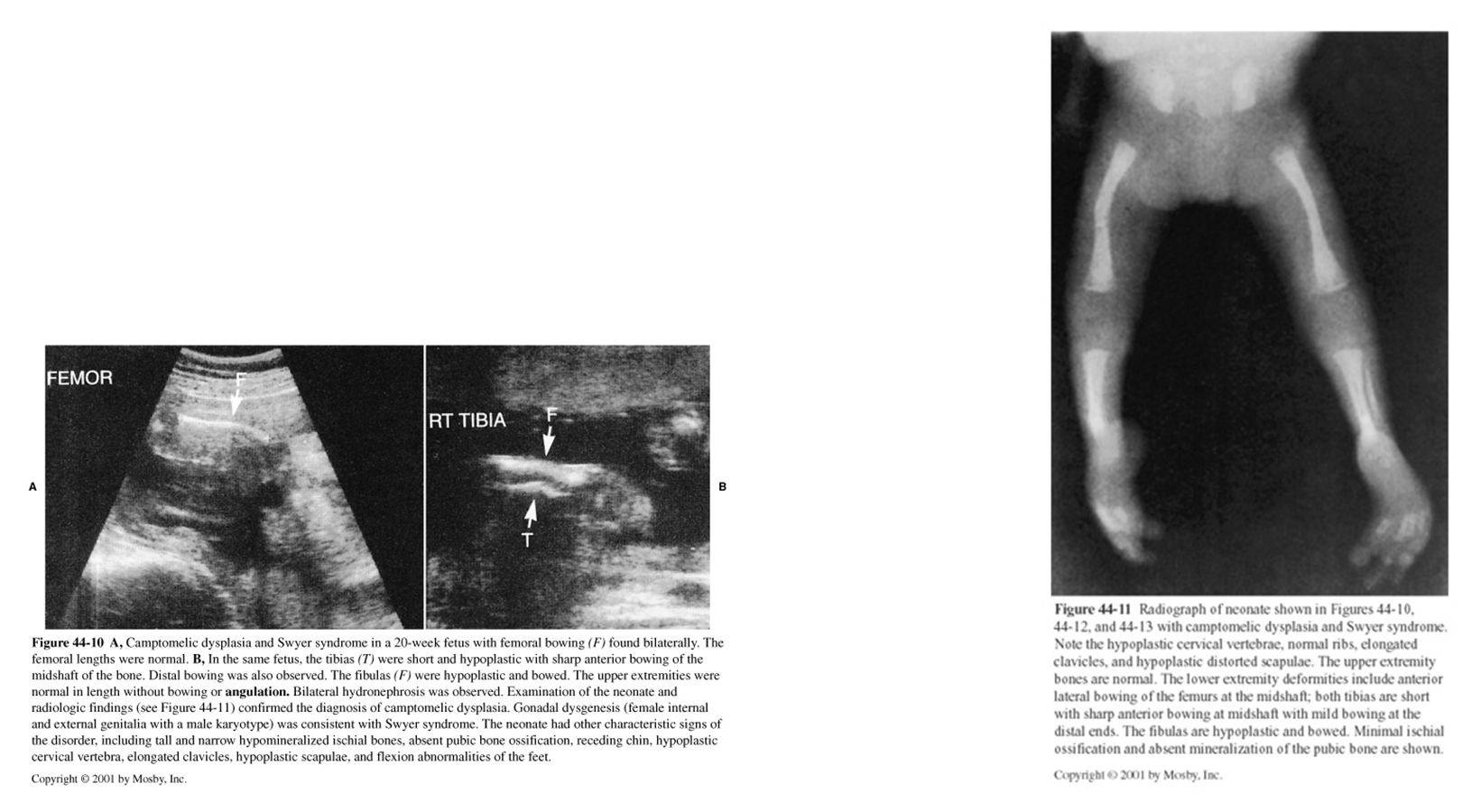
What are these images showing?
Campomelic dysplasia