U6 - Nervous System
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Nervous system divided into
CNS (brain and spinal cord (includes interneurons))
Peripheral PNS (all nerves including cranial/spinal nerves)
Peripheral nervous system divisions
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (all nerves)
sensory (afferent) (send impulses from the senses to the CNS)
motor (efferent) (sends impulses from CNS to muscles/glands)
Somatic nervous system (voluntary muscle control)
Autonomic nervous system (involuntary muscle control)
Sympathetic (fight or flight, emergencies)
Parasympathetic (calms down sympathetic response, provides resting function e.g. digestion, urination)
!!! Nervous system = master control center for body, works w/ endocrine system
Neurons carry impulses, which pass thru processes and into cell body
action potential moves down the length of axon, when reaches axon terminals causes release of neurotransmitters to travel across synaptic cleft
cutaneous sensations - impulses produced in the skin (ex: touch, pressure, hot/cold, pain) - not equally distributed, some parts more sensitive
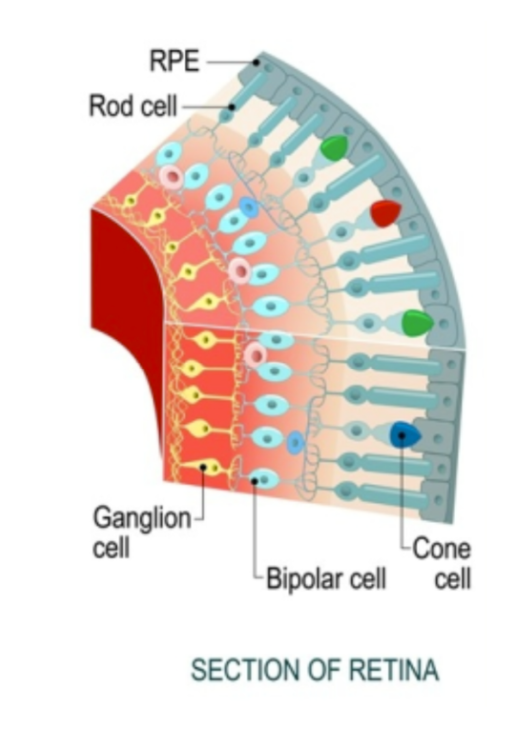
light passes thru eye, hits retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), light causes molecular changes that begin an impulse, impulse travels thru rods/cones → bipolar neurons → ganglion cells → optic nerve
How nervous system does its job
Sensory input - detects changes (stimuli) from inside/outside body w/ PNS
Integration - process/interpret info in CNS
Response - activation of muscles (motor output) or glands thru PNS
Types of nerve cells
Neurons - conduct impulses around the body (10%)
Neuroglia - ‘nerve glue,’ support/protect/insulate neurons (90%)
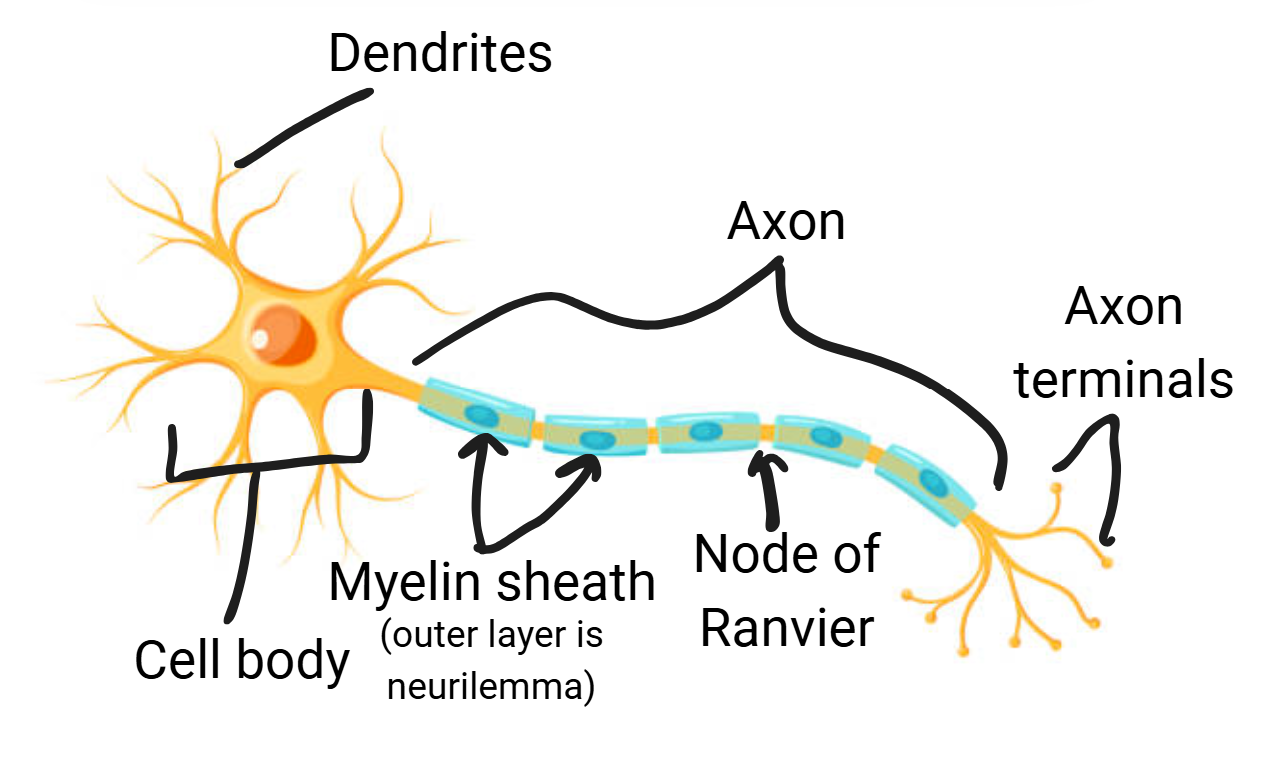
Structure of neuron
cell body (nucleus, cytoplasm, organelles)
Dendrites (bring impulses toward cell body, has receptors)
Axon (send impulses away from cell body)
end in axon terminals which release neurotransmitters to pass the impulse to the next neuron
Myelin sheath
Nodes of Ranvier
Neurilemma (outside layer of myelin)
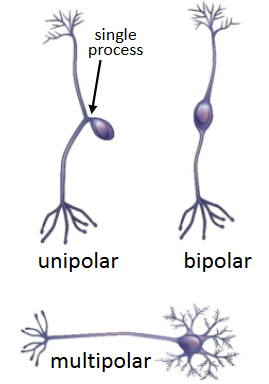
How to classify neurons
By # of processes that extend outwards
unipolar - 1 process
bipolar - 2
multipolar - many
By function
Afferent (sensory) carry impulses toward CNS
Efferent (motor) carry impulses away from CNS
Interneurons connect afferent & efferent neurons (part of CNS)
Myelin sheath
axons wrapped in myelin sheath (acts as waxy insulation & helps nerve impulses travel more quickly)
Schwann cell (type of neuroglia) wraps itself around axon to make myelin
many Schwann cells = myelin sheath
outer layer = neurilemma
gaps btwn myelin = Nodes of Ranvier
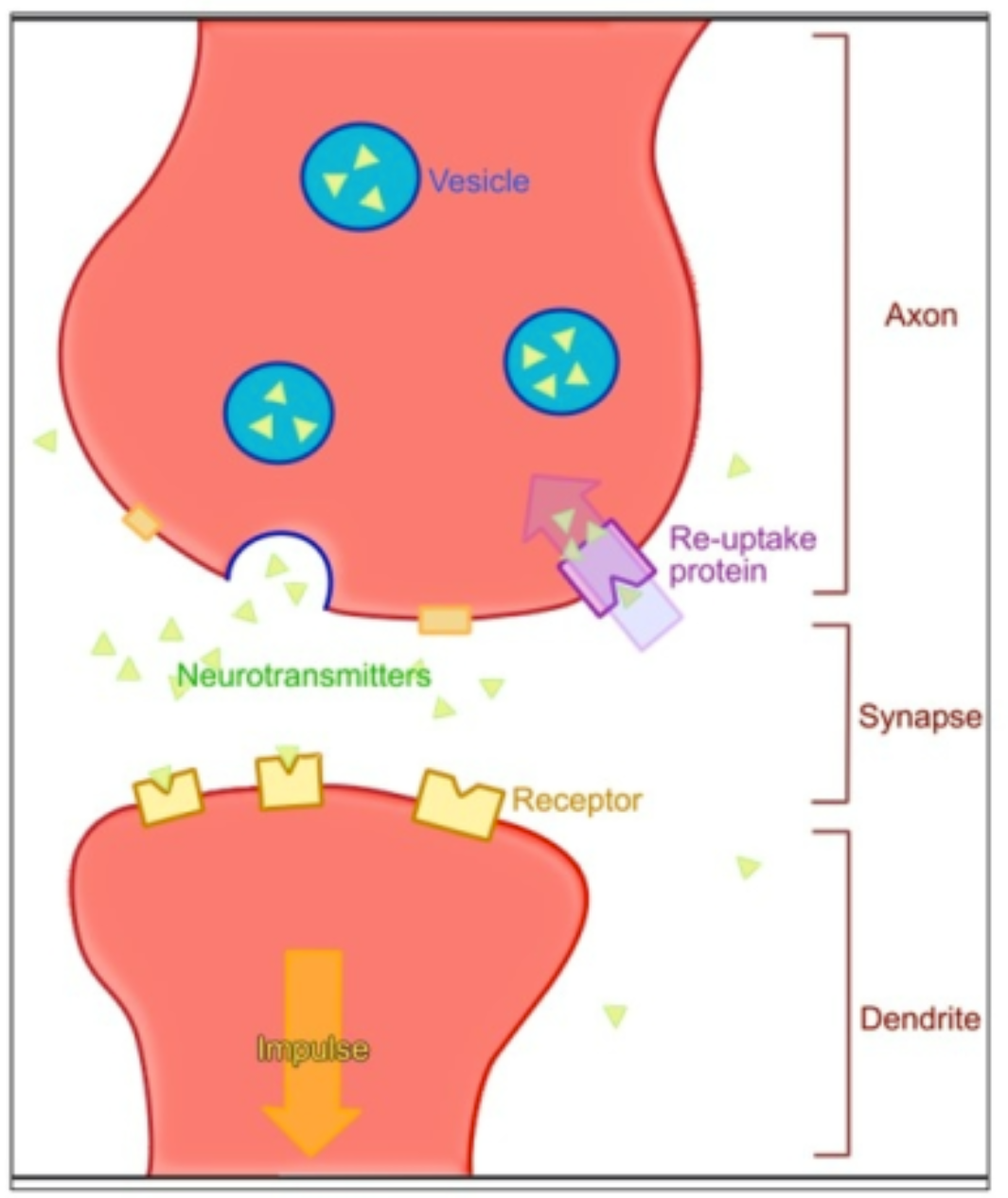
Synapse
where 2 neurons meet (not touch)
space = synaptic cleft
at axon terminal, impulse stimulates vesicles to release neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters open receptors to continue action potential from 1 neuron to next
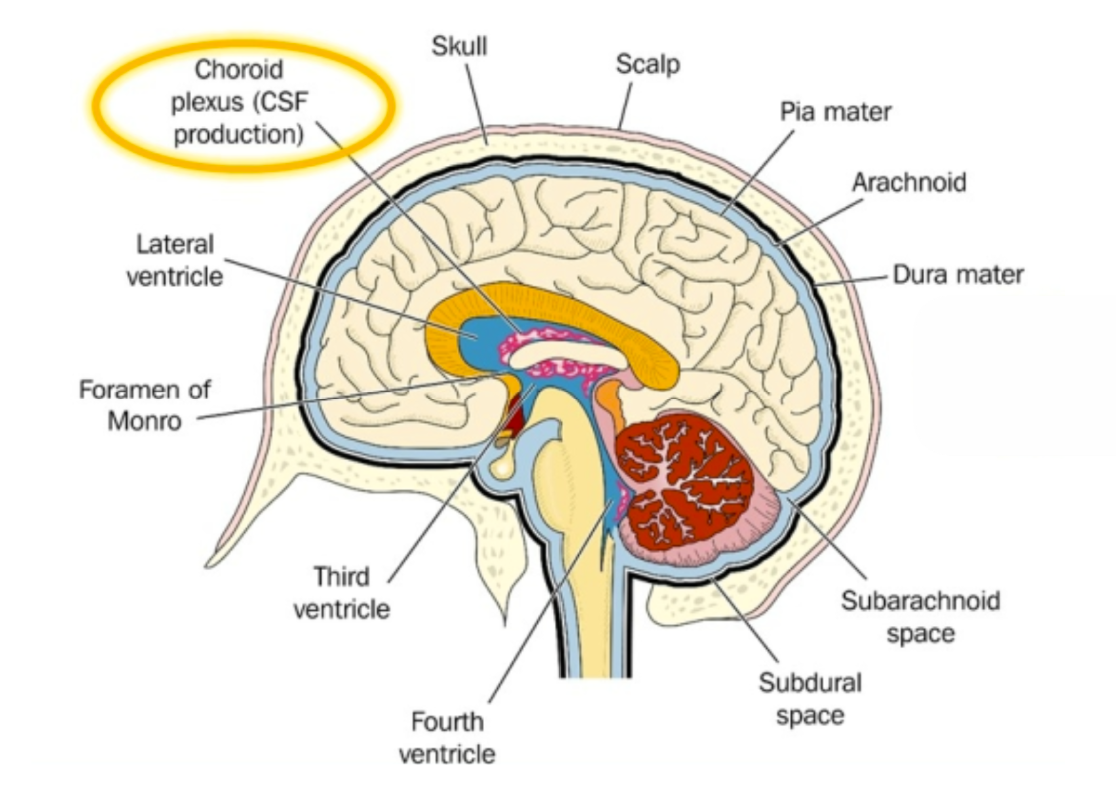
Meninges
3 layers of connective tissue that protect CNS (superficial to deep listed below:)
Dura mater - thick, tough layer
Arachnoid membrane - thin, cobweb-like layer
Pia mater - thin layer containing lots of blood vessels
Cerebrospinal fluid
btwn arachnoid layer and pia mater (subarachnoid space)
protects brain by preventing contact w/ the skull
maintains blood-brain barrier to prevent infection, provide cushioning, & control brain homeostasis
constantly produced/circulated/reabsorbed in ventricles (4)
lateral ventricles (2) (connected to the 3rd ventricle by thin interventricular foramen (foramen of Monro)
3rd & 4th ventricle
flows around ventricles and absorbed by arachnoid granulations (thru dural venous sinuses) into the blood
*if CSF is blocked by tumor/injury, can build up and cause hydrocephalus and lead to brain damage (infant → enlarged head)
Choroid plexuses
clusters of capillaries in the ventricles that produce CSF
Cerebrum
largest part of brain
left and right hemispheres, connected by corpus callosum
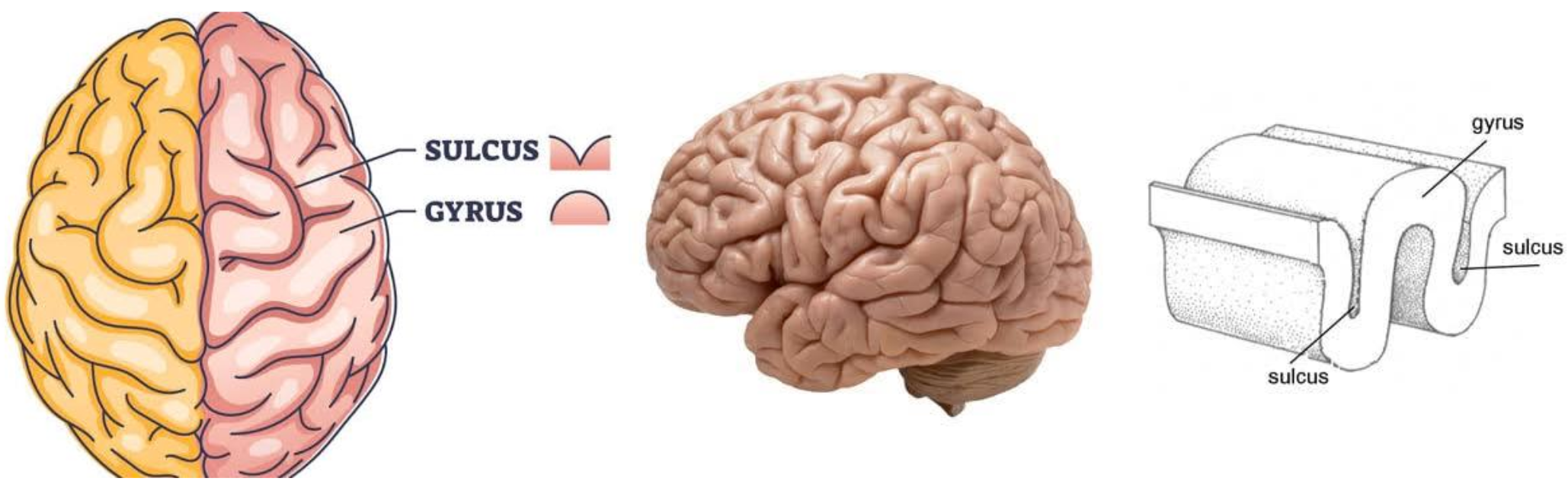
surface covered in ridges (gyri), grooves (sulci), and deeper grooves (fissures) (see pic)
4 lobes (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital) (names from parts of skull protecting them)
3 major layers of the brain (superficial to deep)
Cerebral cortex - ‘gray matter,’ made of dendrites/cell bodies
Cerebral medulla - ‘white matter,’ made of myelinated axons
Basal nuclei - islands of gray matter
Frontal lobe controls:
🏃🏻♀️voluntary movements
🤔reasoning/decision-making
🗣️verbal communication (Broca’s area)
(planning)
(memory)
(ability to predict consequences of actions)
Parietal lobe
separated from frontal lobe by central sulcus
sensations (pain, temp, touch/pressure)
body position
visual-spatial processing
Occipital lobe controls:
visual processing (vision/memory of objects)
Temporal lobes
separated from frontal lobe by lateral sulcus
memory (emotional association of memories)
comprehension/pronunciation of words
(sensations of smell and sound/hearing)
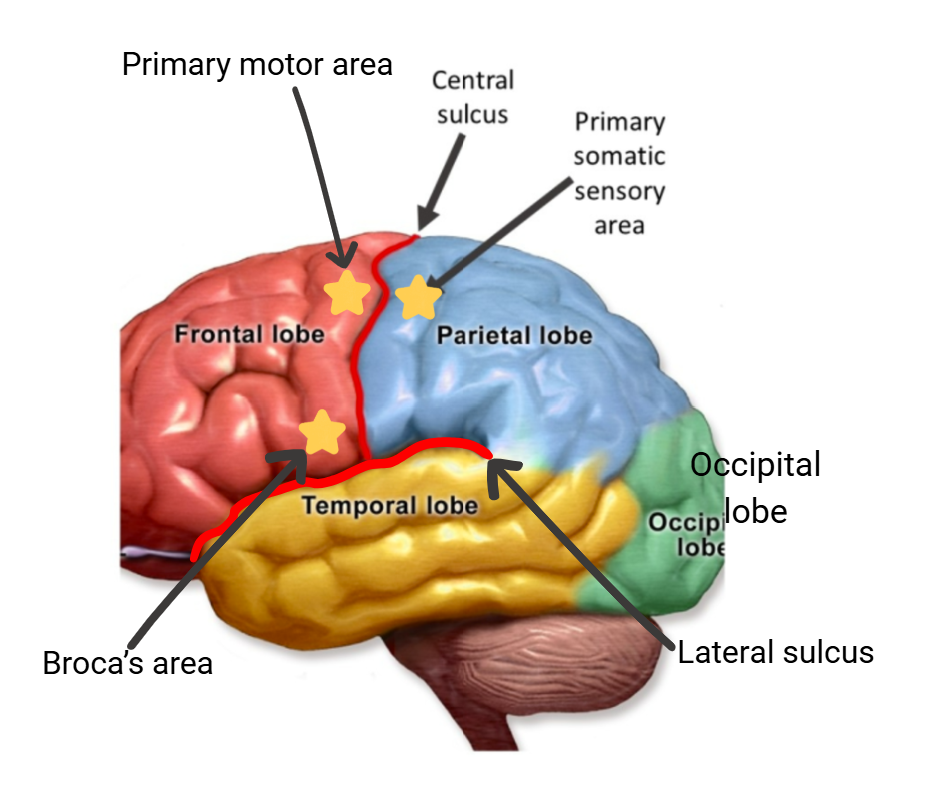
Areas of the Brain
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
temporal lobes
occipital lobe
central sulcus
lateral sulcus
primary somatic sensory area (parietal, near central sulcus)
primary motor area (frontal, near central sulcus)
Broca’s area (frontal, near lateral sulcus)
How senses react to stimuli
5 major types of sensory receptors
Mechano- (touch)
Thermo- (temp. variations)
Pain (aka nociceptors)
Chemo- (chemical)
Photo- (light)
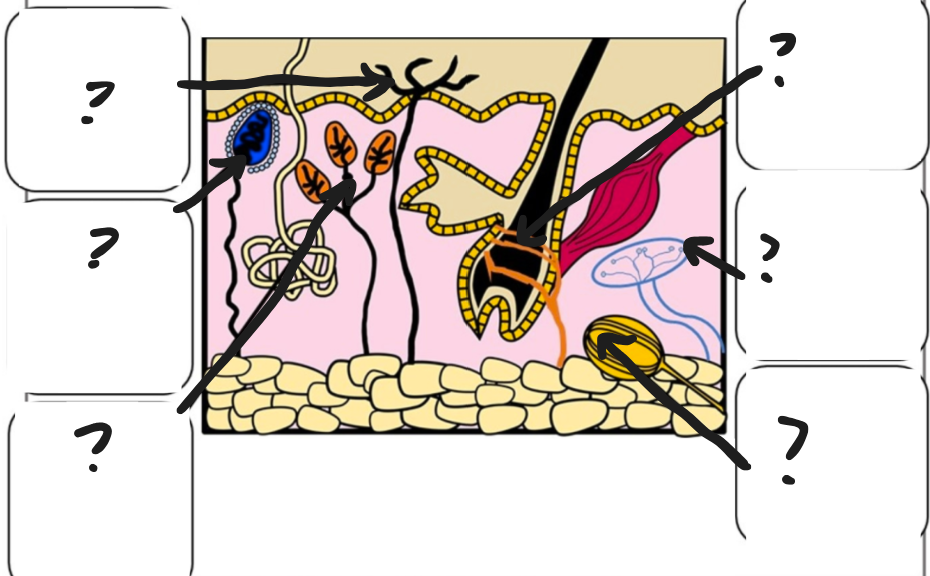
Types of touch receptors
Free nerve endings (sense pain, temp, touch, pressure - cutaneous sensations)
Meissner’s corpuscles (encapsulated nerve endings, found in hairless skin that detect light touch)
Merkel’s disks (detect light touch & pressure w/in epidermis)
Hair follicle receptors (detect movement of hair)
Ruffini’s corpuscles (detect deep pressure and stretching of skin)
Pacinian corpuscles (encapsulated nerve endings that detect deep pressure & vibrations)
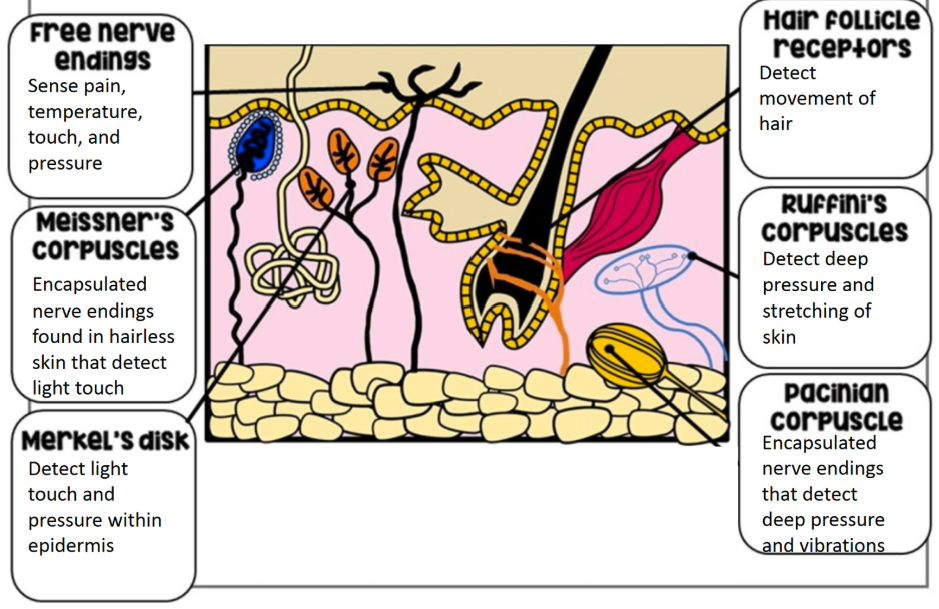
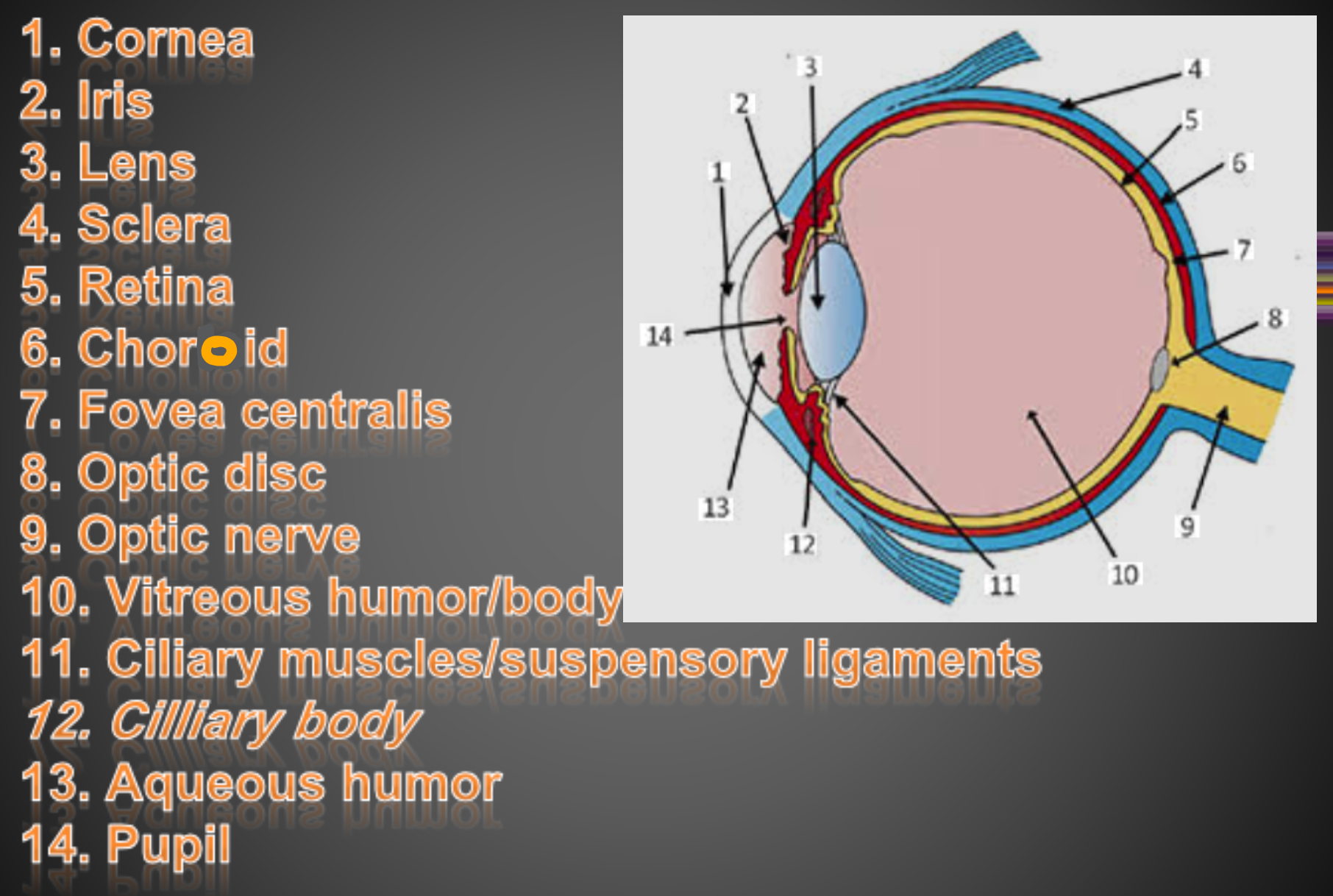
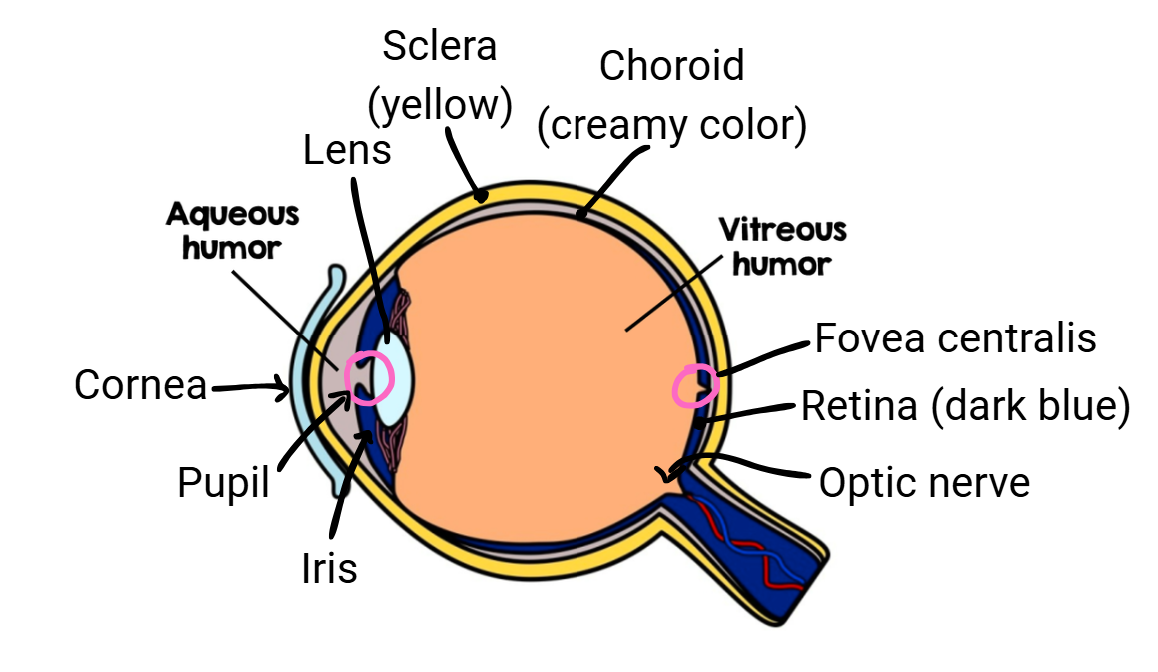
Layers of the eye
Sclera (white of the eye; made of fibrous connective tissue; protects/shapes the eye)
Choroid (pigmented, vascular membrane that includes the iris & pupil)
Retina (contains photoreceptors that turn light energy into nerve impulses)
How light enters the eye
cornea (made of thick transparent tissue) allows light into eye
iris (colored part of eye located behind cornea) works w/ pupil to regulate light entering
pupil (opening in the center of the iris) is where light enters
low light = open (dilated)
high light = closed (constricted)
Lens
semi-solid disc that directs light waves towards the retina
controlled by ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments (bend/flatten lens based on distance of image being viewed)
in front of lens is aqueous humor (thick, jelly like fluid that refracts light and fills the space btwn the lens and cornea)
pic: ciliary body has ciliary muscles, macula part of retina that has fovea
as one ages, the lens becomes less elastic, and need corrective lenses
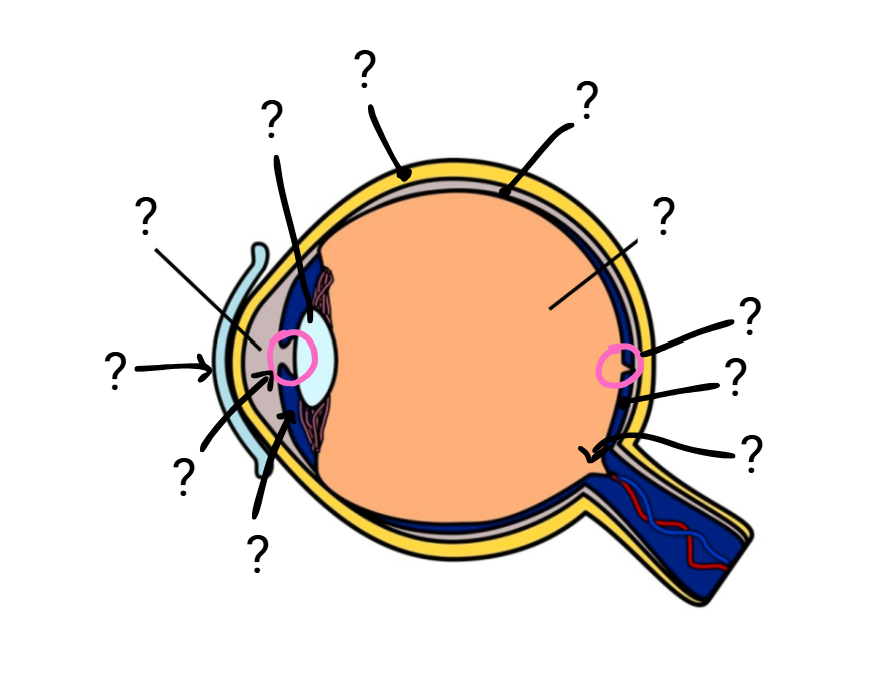
Eye anatomy
sclera
choroid
retina
vitreous humor (thick, gel-like substance btwn lens and retina)
aqueous humor
cornea
iris
pupil
lens
fovea centralis
optic nerve
Types of photoreceptors in the RPE
Rods
all over retina
very sensitive
for low light vision
Cones
center of retina
less sensitive
color/detail
Fovea centralis
only has cones, point w/ the sharpest image
center focal point of the retina
Blind spot
no photoreceptors where the optic nerve meets the eye
*brain ‘fills in’ the missing images
Section of the retina
RPE (retinal pigment epithelium)
rods
cones
bipolar cells
ganglion cells
What causes near-sightedness and far-sightedness?
eye too long → myopia (short-sightedness) (focuses in front of the retina in the vitreous humor)
eye too short → hyperopia (far-sightedness) (focuses behind the retina)
Corrective lenses help refract light so it accurately converges on the retina
Structure of the Brain
Scalp
Skull
dura mater
arachnoid
pia mater
subarachnoid space (think arachnoid layer) (btwn arachnoid layer and pia mater)
subdural space (think dura mater) (btwn dura mater and arachnoid layer)
choroid plexus
Lateral ventricle
Foramen of Monro
Third ventricle
Fourth ventricle
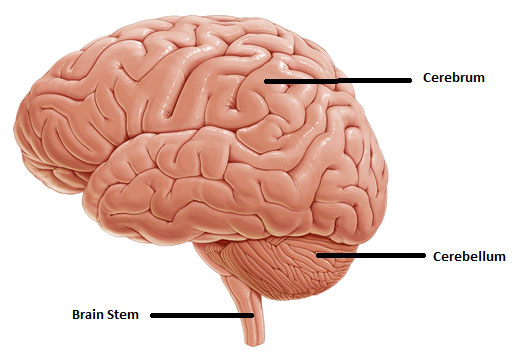
!!! Where cerebellum/brainstem is
!!!
aqueous humor (maintains eye pressure/shape)
vitreous humor (keeps eye shape, keeps lens/retina in place)
drugs addicting -> dopamine, glutamate (reward)
Bell's palsy caused by inflammation/swelling of facial nerve (7th)
^symptoms: weakness/paralysis of 1 side of face, droopy eye/mouth/brow, hard to smile, drool, headache (+loss of taste, more sensitive to sound)
diminished prefrontal cortex in adolescence
-pros: more creative/explore, more sensitive to rewards, social learning/connect, neuroplasticity ('use it or lose it')
-cons: poor impulse control/judgment/planning, difficulty regulating emotions, more risk-taking
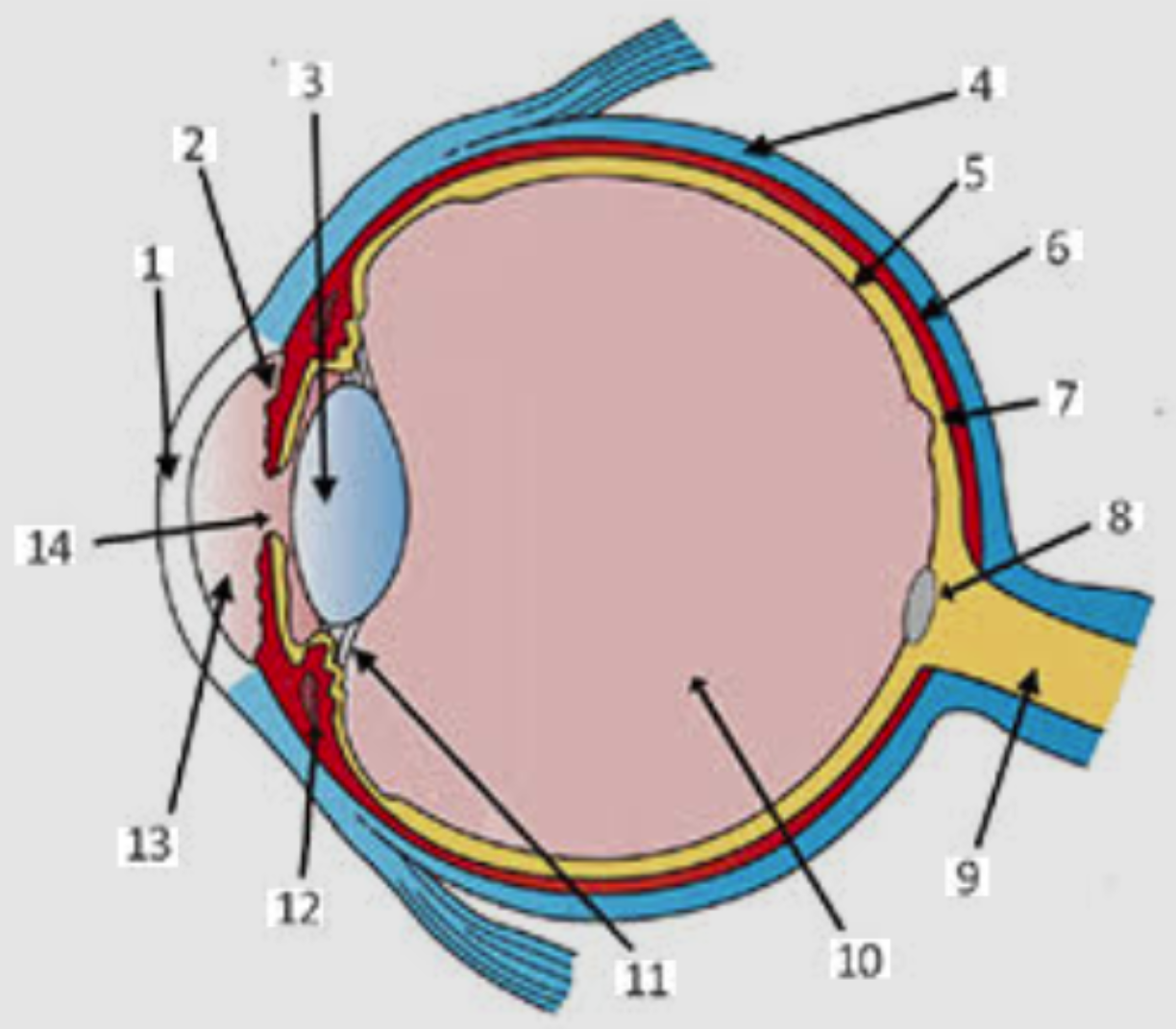
Label eye anatomy (pro)