Audition + Vestibular
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
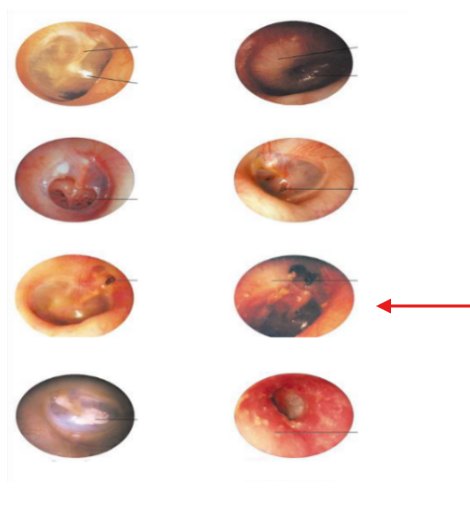
Normal TM
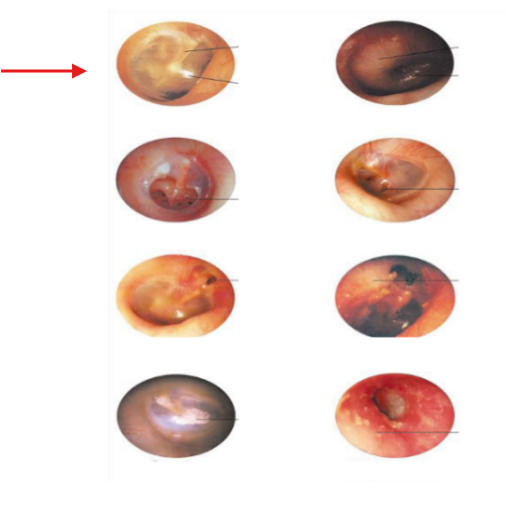
Perforation
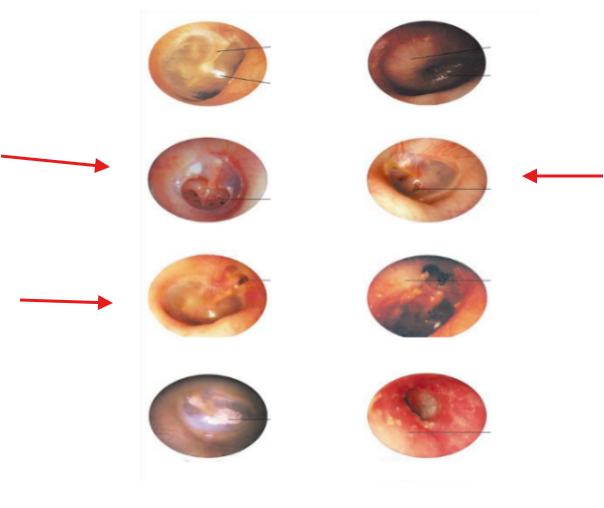
Otitis Media
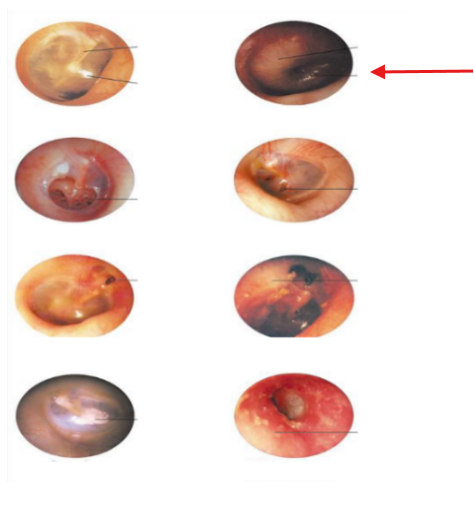
Otitis Externa
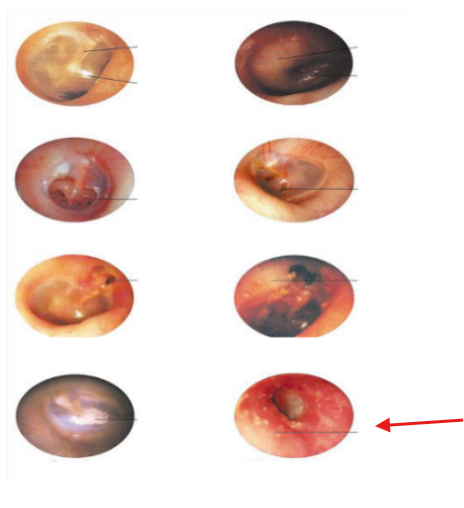
Scarring of TM
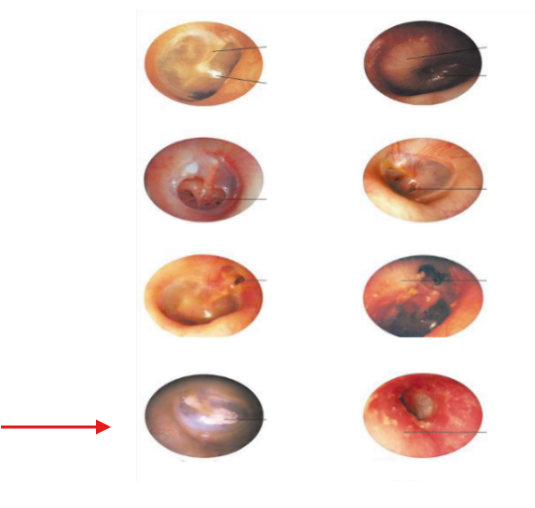
Attic cholesteatoma
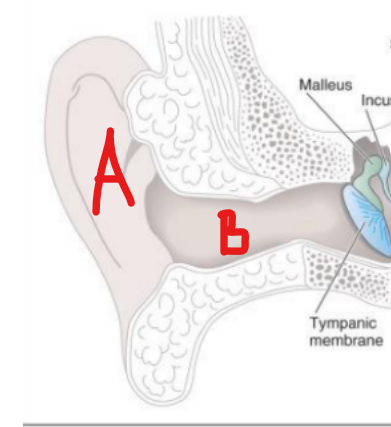
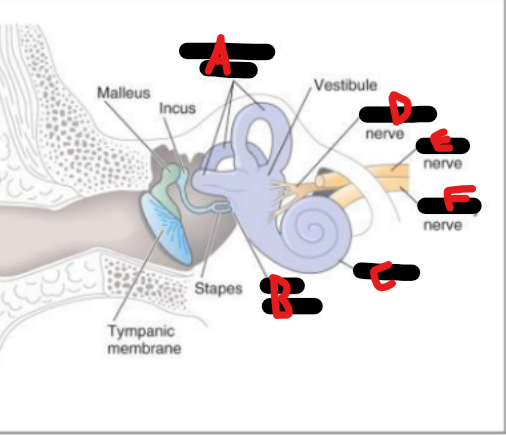
Pinna, external auditory canal
Tympanic membrane, malleus, incus, stapes, oval window
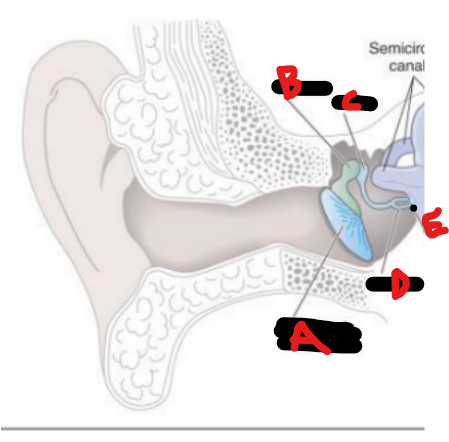
Semicircular canals, oval window, cochlea, vestibular n, facial n, auditory n
Structures + nerves of inner ear
External Ear
Funnel sound waves to tympanic membrane via pinna and external auditory canal
Otitis Externa
Inflammation of external ear and tympanic membrane “swimmer’s ear”
Middle ear
Normally filled with air, Tympanic M vibrates and small muscles modulate vibrations
(general ear landmark)
Malleus, incus, stapes, oval window
Order of Middle Ear Bones
__
__
__
__ __
Eustachian tube
Middle ear structure connects to nasal pharynx
Pressure, equilibration
Changes to outside __ directly impact eustachian tube __
(i.e. airplane ascending)
Otitis Media
Inflammation of middle ear
Acute otitis media sx
Bulging ear drum, dull/absent light reflex
Inner Ear
For sensing movement/body position/sound perception
(general ear landmark)
Bony labyrinth, VIII, 3
Inner Ear
Filled with fluid, encased in “__ __”
Innervated by CN _
Composed of vestibular organ and cochlea
Cochlear with _ chambers separated by membranes
Vestibular Organ
Sensing movement and body position from inner ear
Cochlea
Perception of sound to electrical signals from inner ear via the…
Organ of corti, stiff base, flexible apex
The __ __ __ is an Inner ear structure responsible for sensing sound
high frequencies stimulate the __, narrow __ of the cochlea (near the oval window)
low frequencies resonate with the __, wide __ (the tip of the spiral)
Basilar Membrane
Contains hair cells and relatively flexible
Frequency, amplitude, timbre, frequency
Basilar membrane
Vibrates according to sound __, __, and __
Specific hair cells along organ of corti signal electrical single that correlates to specific __
tectorial membrane, fluid
Organ of corti
Hair cell cilia either lodged in rigid __ __ OR free in the __
Sound Waves
Literal definition of changes in air compression
Frequency
Number of oscillations per second; pitch
Pitch, Hertz
Frequency
correlated with __
Units are in __
Volume, decibels, 100
Amplitude
correlated with __
Units are in __
Over __ lead to damage
Amplitude
Height of sound wave; volume
Timbre
Quality of sound determined by specific harmonic vibrations, vibrato
Air, waves, pinna, vibrates, malleus, attenuate, oval window, electrical
Auditory transduction
1. __ is compressed
2. __ captured by the __ of ear and funneled into external auditory meatus
3. Tympanic membrane __ back and forth
4. __ (attached to tympanic M) vibrates and transmits those vibrations through incus and stapes
5. Small muscles tense and relax to __ the vibrations
6. Stapes vibrates __ __ of cochlea, causing vibrations in organ of corti
7. Organ of corti then processes vibration to become __ signals
Hair cells, cilia, first
Why do people lose their high-frequency/pitch hearing first?
High amplitudes damage __ __ and __ (more fragile high-frequency cells)
Organ of corti topographically experience high frequencies __ (order)
Mechanoreceptors, Ca2+, K+, cochlear, vestibulocochlear, bilaterally
Hair cells to brain
Bending of cilia open __ that depolarize the cell (__- 2 ions)
Signal conducted through __ nerve to __ nerve
First order neurons synapse in brainstem and send info to temporal lobe(s) __ (uni/bilaterally)
Conductive Hearing Loss
External sound block, fluid in middle ear, fixation of middle ear bones (hearing loss)
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Damage to inner ear, cochlea, auditory nerve going to brain (hearing loss)
Conductive, sensorineural
In __ hearing loss, sound is adequately transmitted through bones of skull
In __ hearing loss, sound is not adequately transmitted through bones of skull
Weber and Rinne Tests
Tests for conductive vs sensorineural hearing loss AFTER already determining the good and bad ears
AC > BC
Normal Rinne
BC > AC
Abnormal Rinne
Conductive, bad, sensorineural, good
Weber Test
In __ loss - BC > AC for bad ear; lateralizes to the __ ear
In __ loss - AC > BC for both ears; lateralizes to the __ ear
Speech, behavioral, dementia, social
Manifestations of Hearing Loss
Children - Present with delayed __, __ problems, inattentive, ignoring
Elderly - Present like __, __ withdrawal
Vestibular Organ
Senses equilibrium and balance via movement of head
Cerebellum, brainstem, extraocular
Vestibular organ
Coordinates with the __ and __ (brain regions) medial motor tracts for balance
Coordinates with the __ muscles to maintain a stable visual field
Angular, linear
The Semicircular Canals are for __ acceleration
Whereas the Otolith Organs are for __ acceleration
Rotation, tilt, delayed, fixed, normal, rotation, lags, opposite, fall, electrical
Angular Acceleration
1. Sense head __ and __ (front to back and side to side)
2. As head is turned, fluid in canal is slightly __ and pushes against __ hair cells
3. Eventually fluid starts to move as well “catches us” → Results in hair cells to return to __ position even though __ may still happen
4. When rotation stops, fluid __ behind and bends hairs in __ direction
Makes us perceive spinning in opposite direction and sometimes __
5. Info is then converted from __ info about movement
Utricle, saccule, linear
Otolith organs
__ and __ contain gelatinous layer embedded with otoliths (crystals)
Movement (particularly __ acceleration) moves otolith mass and bends the hairs
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
Calcium carbonate debris within semicircular canals leads to inappropriate bending of hair cells with movement, signaling spinning
Angular, semicircular canal, posterior
Vertigo with spinning relates to __ circulation
__ __ pathology
BPPV usually affects the __ canal
Dix-Hallpike Maneuver
Reproducible vertigo and nystagmus when head tilted toward dysfunction side to dx BPPV
Eply Maneuver
Therapeutic rotation of head in different planes to move crystals out back to correct site
posterior vertigo, antihistamines
Eply Maneuver
Only 2% of patients require more than 3 treatments for __ __ (vertigo type)
__ (i.e. meclizine, diphenhydramine) help with sx after this maneuver