Biological Psychology
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Monism
Theory that the mind and the body (or brain) are not distinct entities, but rather a single, physical substance
Dualism
theory that the mind (consciousness, thoughts) and the body (brain, physical matter) are two separate, distinct, and independent substances that interact with each other
Epigenetics
studies how environment and behavior (like stress, diet, or nurturing) change how genes work without altering the DNA sequence itself
Stress-diathesis model
suggests that mental disorders results from a combination of a pre-existing vulnerability (diathesis) and stressful life events
Reductionism
take a complex phenomenon and reduce it to its most basic component
Generalization
“if this, then that”
Explains how phenomenon works
Glial cells
Helper cells (assistants)
Neurons
Brain cells
building blocks of the bran and, therefore, consciousness
What makes the cell?
the cell wall
Rene Descartes
Hydraulic model: proposed the body functions like a hydraulic system (fluids, pistons)
Best known for his philosophy
philosophy x biology = psychology
J. Muller
Doctrine of specific nerve energies
Different systems, different types of electricity
L. Galvani
Experiments with animals (especially frogs)
Body works using electricity
P. Broca
Clinical method: track the health of the client throughout their life (medical records)
Broca’s area: the part of the brain that controls speech
Localization of function: specific parts of the brain serve specific functions
Fritsch and Hitzig
Research with animals (dogs)
Would open the skull to expose the brain to stimulate certain parts of the brain while the dog was awake
Discovered motor cortex: further proved localization
W. Wundt
Started a lab to discover what it means to be “us”
when was the beginning of psychology?
1879
S. R. Cajal
Artist/scientist
took brain slices, slid them under a microscope after putting ink on them, and saw individual cells
Discovered the neuron
Drew beautiful pictures of what he saw
C. Sherrington
SYNAPSES
Realizes cells don’t physically touch (small gap between; discovered synapses_
J. Eccles
CHEMICAL
Realizes neurons communicate with chemicals not electricity
discovered neurotransmitters
society for neuroscience
individuals get together and share research
The decade of the brain 1990-2000
Put aside taxpayer money for research on the brain
the BRAIN initiative
President Obama signed BRAIN initiative
Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Technologies
Glial cells (CNS & PNS)
Metabolic support
protection
insulation
structural support (hold neurons in place)
remove waste
modulate neurotransmission
Astrocytes
(play goalie: keep certain things from crossing over from the blood to the brain; barrier)
BBB: Blood Brain Barrier
Structural support: “infrastructure”
Phagocytosis (some)
Control level of chemicals/ions outside the neuron
Aid in the exchange of nutrients and waste
Microglia
Very small
phagocytosis
Immune system functions
Phagocytosis
phagocytes engulf large particles by extending their plasma membrane around the target forming an internal vesicle, then digesting it
Schwann Cells
only supports 1 axon
form myelin
only exist in the PNS
help neuronal growth following damage
guide axons to target neurons
wraps itself around the neuron
Oligodendrocytes
Supports numerous axons
support neurons
form myelin sheath
Only exist in the CNS
multiple sclerosis
Immune system attacks glial cells
Neurons die as glial cells no longer protect them
Neurogenesis
creation of new neurons
lipid = …..
fat.
The cell wall
semipermeable membrane: some things can get through it
phospholipid bilayer
contains numerous specialized proteins
phospholipid bilayer
phospho heads: hydrophilic (love water, always want to face the water)
lipid tails: hydrophobic (repel water)
outside the cell
extracellular fluid
inside the cell
cytoplasm
membrane proteins and functions
receptors (sites of action for neurotransmitters)
gated ion channels (allow for ions to move back and forth)
pumps/transporters (move ions and molecules across biological membranes)
structural, recognition, others
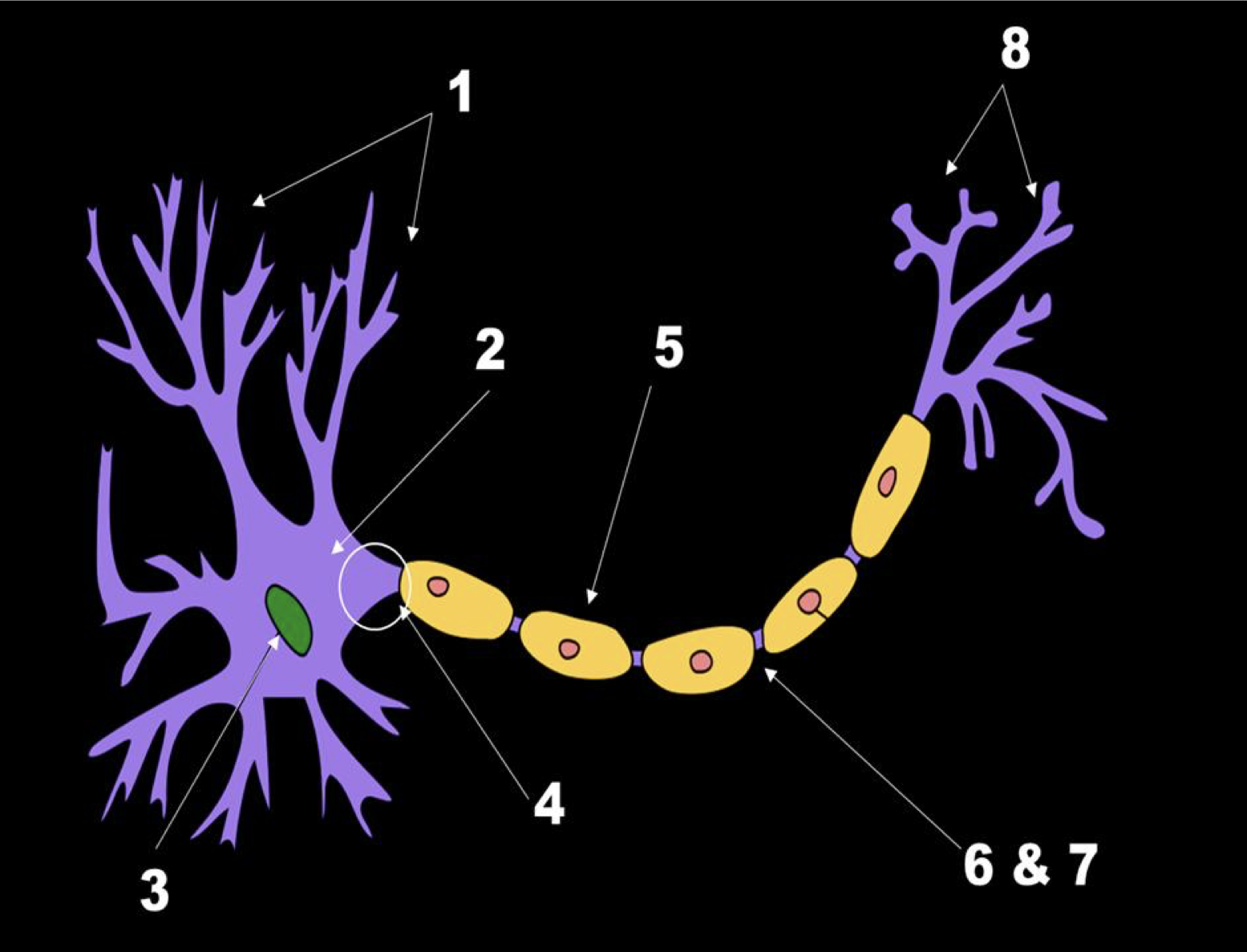
identify the parts of the neuron
Dendrites
soma
cell nucleus
axon hillock
myelin
axon
node of ranvier
axon terminals
dendrites
receive signals from other neurons
dendritic spines
ligand-gated receptors: specialized proteins activated by chemicals
soma (or cell body)
contains nucleus, other organelles
protein synthesis for cellular growth and survival
- receptors, enzymes, cell membrane
cell nucleus (inside soma)
chromosomes: long strands of DNA
genes: small portions of chromosomes, code for the production of specific proteins
axon hillock
summation of all incoming signals: takes all the synaptic signals + summates them
Once summated, signal is generated here and sent down the axon
myelin
protective layer formed by glial cells (Schwann)
axon
carries signal to axon terminal
also carries nutrient and waste
Node of ranvier
gaps where there is no myelin
axon contains voltage-gated (change in electricity on the axon) ion channels
axon terminals (terminal buttons)
release neurotransmitters
inside the axon: axoplasmic transport
microtubules run down the axon
newly made proteins carried down the microtubules to axon terminal (anterograde transport, motor protein: kinesin)
at terminals, new proteins are released
waste carried back to the soma (retrograde transport, motor protein dynein)
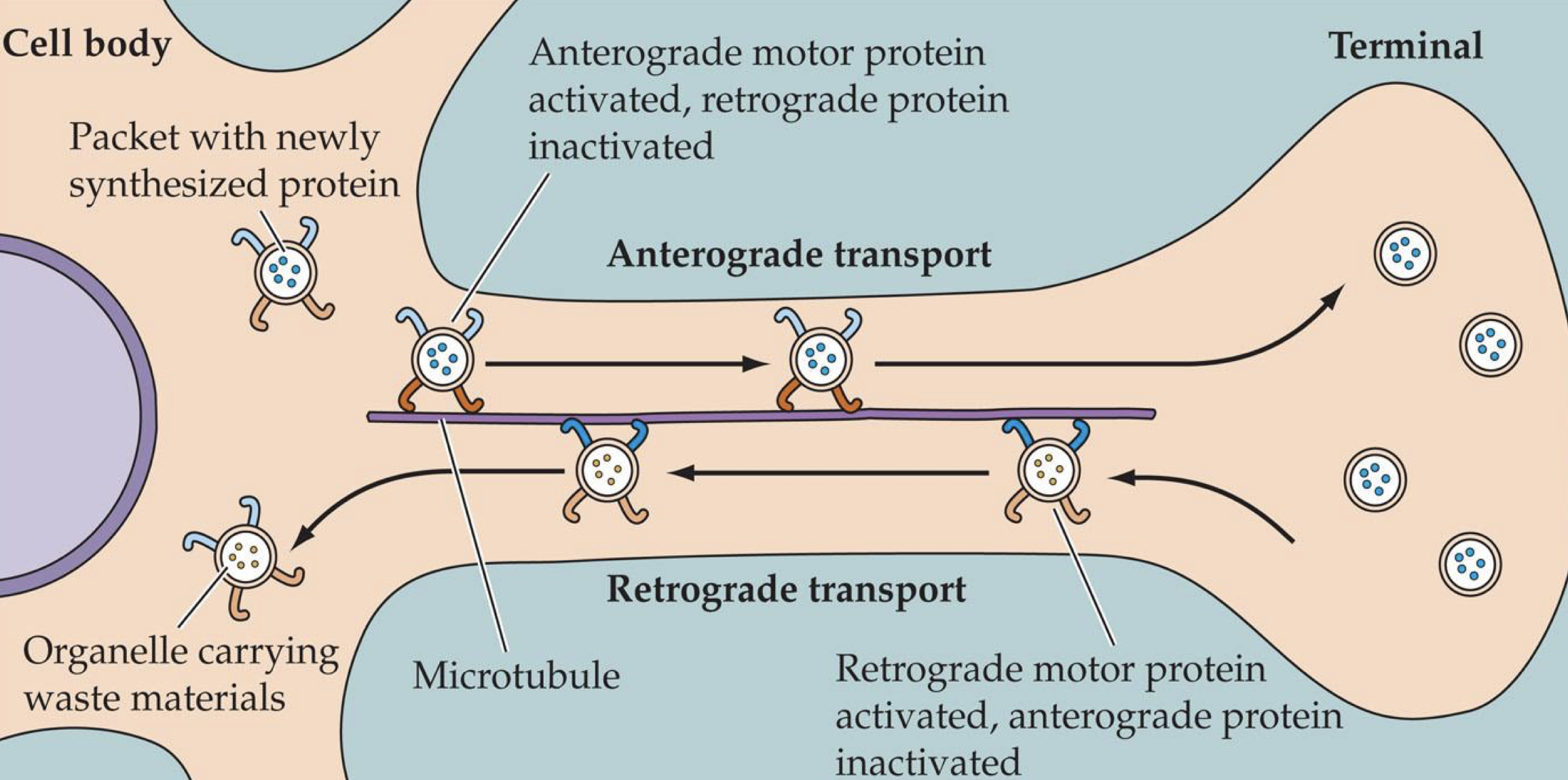
anterograde transport
biological process of moving materials—such as proteins, neurotransmitters, and cellular structures—outward from the center of a nerve cell (the
cell bodyor soma) toward the tip of the cell (theaxon terminal).
“fast-delivery delivery service”
motor protein: kinesin
acts as a microscopic delivery truck inside cells, including neurons (nerve cells)
kinesin moves toward the microtubule plus end(outward from the cell center)
motor protein: dynein
acts as a microscopic transport worker inside cells, particularly in brain neurons.
moves toward the minus end (inward toward the cell center)
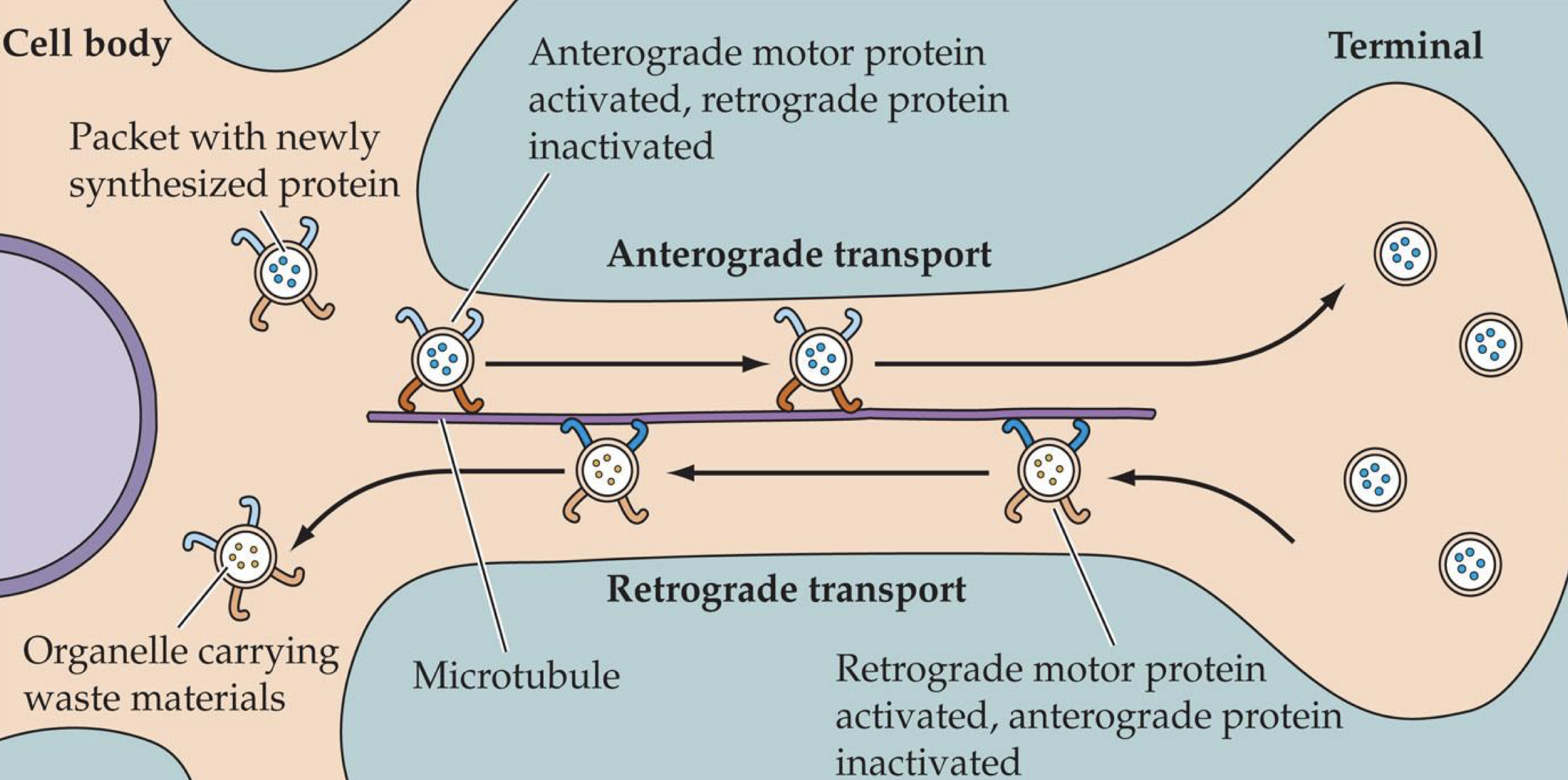
retrograde transport
It is the process where materials are moved backward from the axon terminals (the end of the nerve branch) to the cell body (soma), which is the center of the neuron.
The “return shipping” service of a neuron
2 processes of neural communication
an electrical processes occurs inside the cell (the action potential)
a chemical process occurs between cells (ligands, neurotransmitters or hormones, or drugs)
resting membrane potential
compared to the outside of the cell the inside of the cell holds a charge of -70mv (millivolts)
specialized protein pump
uneven distribution of ions
resting neuron has 70mv fewer than outside the cell
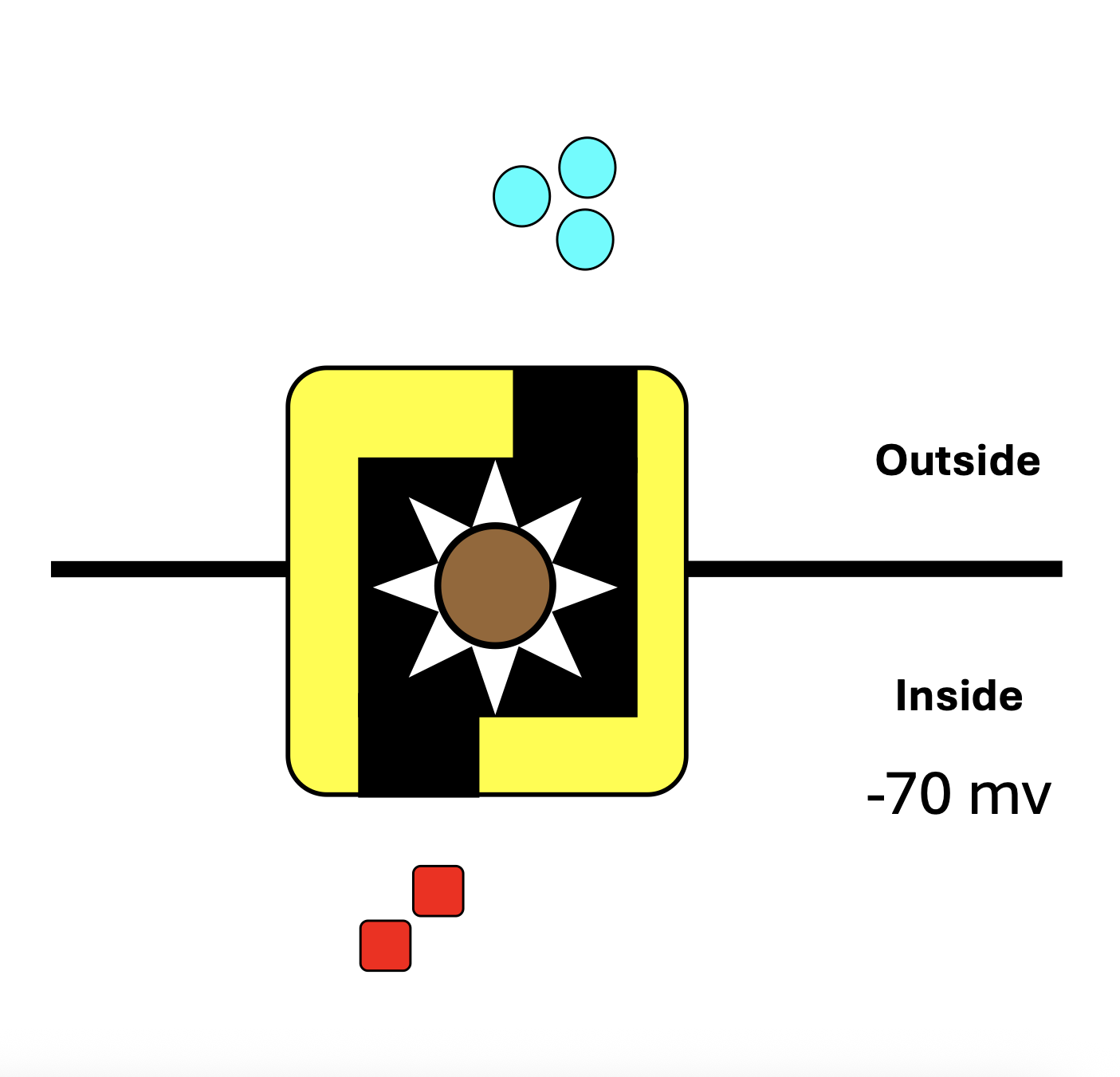
specialized protein: the Na+/K Pump
For every two K+ ions pumped into the cell…
three Na+ ions pumped out of the cell
Uneven movement of + ions helps maintain RMP of -70mv
concentration force
wants to balance amount of things
greater amount moved to where there is a lesser amount
is the natural tendency of molecules or ions to move from an area where they are highly crowded (high concentration) to an area where they are less crowded (low concentration).
electrostatic force
electrical charge
think of a magnet —> similar charges repel, opposites attract
opposite electrical charges attract each other, and like charges repel each other, driving the movement of ions (charged particles) in and out of nerve cells.
depolarization
the process where a neuron (nerve cell) becomes activated, shifting its internal electrical charge from negative to positive, which triggers a nerve impulse (action potential).
if it reaches -65mv, it reaches threshold of excitation, causing more action
hyperpolarization
a change in a neuron's membrane potential that makes the inside of the cell more negatively charged compared to its normal resting state
the action potential (AP)
ligand binds to post-synaptic receptor on dendrite
ligand-gated Na+ channels open; Na+ influx
internal charge moves from -70mv to -65 mv (threshold of excitation)
voltage gated Na+ channels open
at +55mv, Na+ channels close/V-gated K+ channels open
K+ efflux (flowing out of a particular substance or particle); internal charge to -90mv (hyperpolarization)
at -90mv K+ channels close
V-gated Cl- channels open, Cl- efflux
Return to RMP (resting membrane potential) of -70mv
Vesicle & NT Release
AP reaches terminal button
voltage-gated Ca++ channels open, Ca++ influx
Ca++ activates Calmodulin kinase KII
CamKII phosphorylates synapsin
Vesicles move toward terminal membrane (synapse)
SNAP proteins line up
Vesicle joins with membrane
Neurotransmitter released in synapse (exocytosis)
neurotransmission
the process where nerve cells (neurons) send chemical messages to each other to communicate, allowing the brain to control thoughts, feelings, and behavior
ionotropic receptors
4-5 protein subunits (they mesh together)
ion channel located in the protein receptor
NT binds to receptor (ion channel opens, ions move either in our out of the cell)
fast but rapid
metabotropic receptors
Think metabolism
single protein (but winds in and out of the cell wall, typically 7 times)
metabolic process
ion channel located distantly in cell wall (no ion channel here, close but far away)
slower transmission (takes longer because of process outside the cell)
slower but longer effects
kinases
responsible for opening distant ion channel
excitatory NT and receptor combination
causing depolarization and AP in post-synaptic cell
excitatory post-synaptic potential (aka EPSP)
excitatory post-synaptic potential (aka EPSP)
a temporary, positive change in a neuron's voltage that makes it more likely to fire an electrical impulse (action potential).
inhibitory NT and receptor combination
causing hyperpolarization and no AP in post-synaptic cell
inhibitory post-synaptic potential (aka IPSP)
inhibitory post-synaptic potential (aka IPSP)
a temporary reduction in a neuron's likelihood of firing an electrical signal (action potential).