Ch.16 - Conjugated Pi Systems and Pericyclic Reactions
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Dienes
2 double bonds
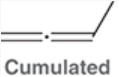
Cumulated Dienes
pi bonds are adjacent to each other; p orbitals are perpendicular to each other (no conjugation).
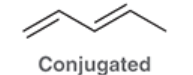
Conjugated Diene
pi bonds separated by a single bond; continuous system of overlapping p orbitals
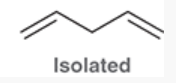
Isolated Diene
pi bonds separated by more than one single bond; p orbitals are separated (no conjugation).
Conjugated dienes can be prepared from:
allylic halides via elimination and a sterically hindered base (i.e. t-BuOk).
Conjugated diene can also be prepared from:
dihalides via two elimination reactions (+ sterically hindered base).
Single bonds of a conjugated pi system are:
shorter than typical single bonds
Why are single bonds of a conjugated pi system shorter than typical single bonds?
in part, due to the overlap of sp2 orbitals in the diene vs. sp3 orbitals in the single bond molecule.
the more s character the shorter the orbital and the shorter sigma bonds will be.
Heats of hydrogenation show that conjugated double bonds are…
more stable than isolated double bonds (alkenes) by 15kJ.
Highest energy conformer is not…
conjugated and is 15kJ less stable than the diene.
The more substituted a double bond…
the more stable the bond
p orbitals only conjugated into…rotamers.
2; s-cis and s-trans
Compared to s-cis, s-trans is…
lower in energy due to less steric hindrance.
pi bonds are constructed by…
two overlapping p orbitals which produces 2 molecular orbitals (bonding and anti-bonding).
Bonding MO
happy + more stable (lower energy)
Anti-bonding MO
less happy + less stable (higher energy)
HOMO
highest occupied molecular orbital
LUMO
lowest unoccupied molecular orbital
No p orbital overlap =
no double bond character
Light can be used to excite an electron from…
HOMO to LUMO (the smallest energy gap).
Electrophilic Addition/ Markovnikov
addition of H-X to a C=C double bond
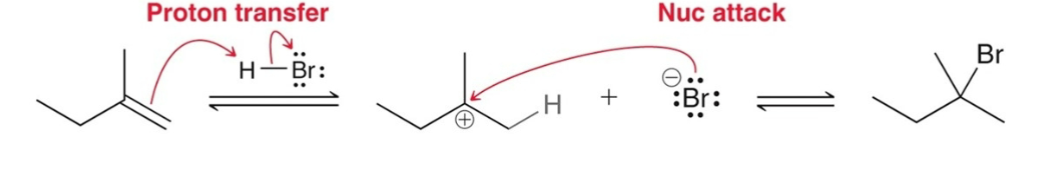
Electrophilic Addition of a conjugated diene results in two products:
1,2-addition and 1,4-addition
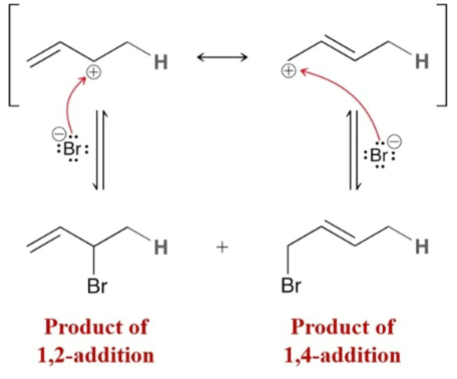
(Electrophilic Addition) Protonation results in…and a primary carbonation…
the most stable carbocation; will not form
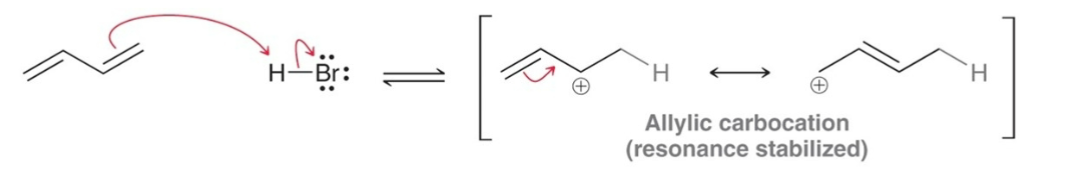
Addition of bromine to a conjugated diene also…
results in two products
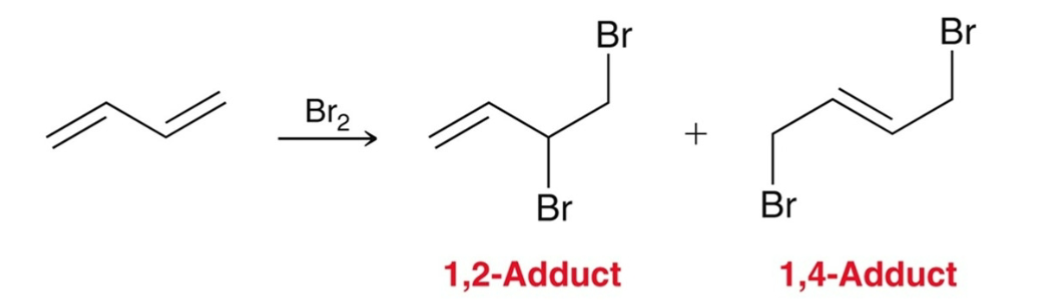
Formation of 1,2-adduct occurs faster so it is…
kinetically favored
1,4-adduct is more stable (more substituted double bond) so it is...
thermodynamically favored
1,2-abbuct forms faster because…
Halogens are usually closer to carbon 2 rather than carbon 4.
At low temps, reactions are under…. At high temps, reactions are under…
kinetic control; thermodynamic control
When under thermodynamic control, the reaction will produce…
the more stable, major product
Cycloadditon Reactions
A concerted combination of two pi-electron systems to form a ring of atoms having two new σ bonds and two fewer pi bonds
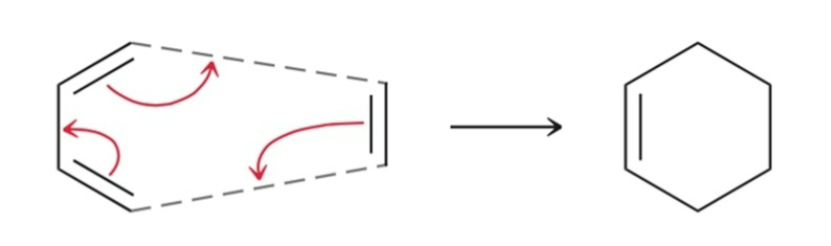
Electrocyclic Reactions
A reaction where a single bond is formed between the termini of a pi system; cyclic system formed.
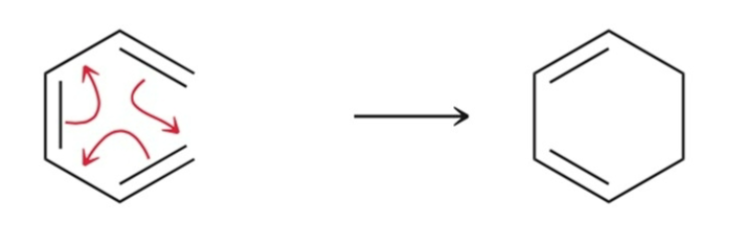
Sigmatropic Rearrangement
intramolecular reactions involving the migration of a sigma bond across a pi system.
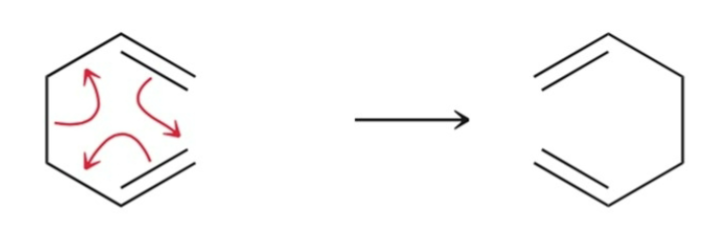
4 Characteristics of pericycle rxns:
Mechanism is concerted (one step, no intermediates).
Mechanism involves a ring of electrons moving around a closed loop.
Transition state is cyclic.
Polarity of the solvent generally has no effect on reaction rate.
Cycloaddition: Change in # of Sigma and Pi Bonds
+2 sigma bonds, -2 pi bonds
Electrocyclic: Change in # of Sigma and Pi Bonds
+1 sigma bond, -1 pi bond
Sigmatropic: Change in # of Sigma and Pi Bonds
no change in number of sigma or pi bonds.
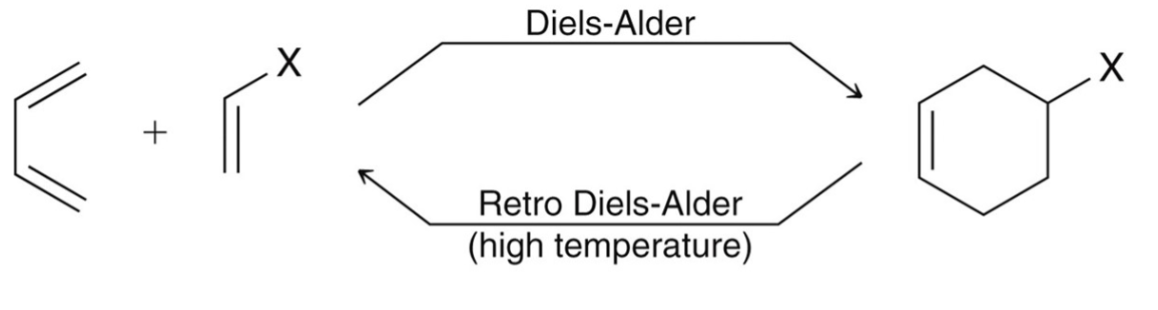
Diels-Alder Reactions
also known as [4+2] cycloaddition; takes place between two different pi systems, one of which is associated with four atoms while the other is associated with two atoms.
![<p>also known as <strong>[4+2] cycloaddition</strong>; <span>takes place between two different pi systems, one of which is associated with four atoms while the other is associated with two atoms.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7a175579-9368-4abd-b84f-2bb642610c66.png)
Most Diels-Alder Reactions are thermodynamically favored at…
low or moderate temperatures; product stability dominates.
At temperatures above 20oC, retro Diels-Alder…
can predominate; entropy the dominate factor.
pi bond to sigma bond conversion provides…
a negative change in enthalpy (-H)
S (change in entropy and part of entropy term) should be…
negative; two molecules combine to form a single product.
For Diels-Alder rxns, the enthalpy term must be…than the entropy term for the rxn to be favored.
larger
At very high temps, the entropy term…
opposes the formation of product (retro Diels-Alder).
Ideal temp for Diels-Alder Rxns:
between room temp and 200oC
Dienophile
a compound that reacts with a diene; must possess an electron withdrawing group which lowers the energy barrier.
If a dienophile does not possess an electron withdrawing group:
rxn will require high temps which does not favor product formation.
Alkynes can act as…
dienophiles
When an electron-withdrawing group is attached:
rxn occurs at lower temps
rxn is generally spontaneous
higher yield
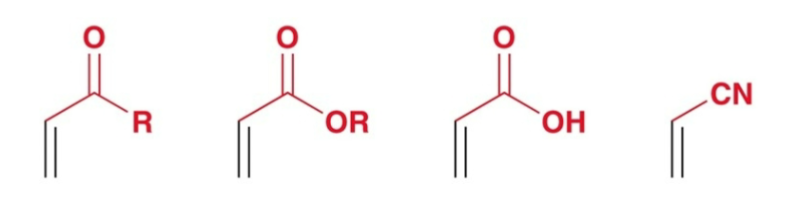
Electron-Withdrawing Group Examples
carbonyls (aldehydes, carboxylic acids, etc.)
CN
Diels-Alders rxns are stereospecific and depends on…
whether E or Z dienophile is used
Diels-Alder rxns can only occur when dienes are in…
s-cis conformation; when s-trans, carbon 1 and 4 are too far apart to undergo rxn.
Dienes locked into s-cis conformation undergo…
Diels-Alder readily (the quickest)
Cyclopentadiene is so reactive towards Diels-Alder reaction that it…
reacts with itself at room temperature to
form a dimer.
The electron-withdrawing groups attached to dieneophiles tend to occupy…
the ENDO position; often the endo product is the only observed product.
ENDO
cis to the larger bridge
EXO
trans to the larger bridge
Which is favorable: ENDO or EXO
ENDO; b/c EXO pi bonds are too far from the electron withdrawing group and ENDO is lower energy.
If the diene or dienophile are symmetrical…
there’s only one regiochemical outcome.
If both diene and dienophile are symmetrical…
two regiosomeric products are possible (one is major).
Major product of Diels-Alder can be predicted through…
charge distribution of the reactants
1,4-position on ring
Para
1,3-position on ring
meta
1,2-position on ring
ortho
For Diels-Alder, HOMO of one compound must interact with….
the LUMO of the other.
With an electron withdrawing group, the dienophile’s LUMO will accept…
electrons from the diene’s HOMO.
If phase of HOMO and LUMO match, then…
the rxn is symmetry-allowed.
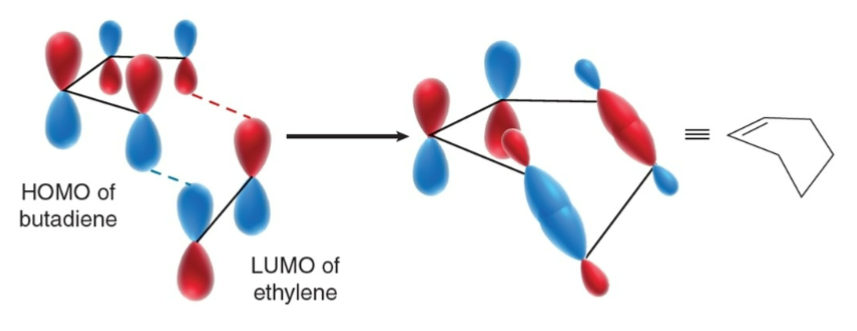
If phases of HOMO and LUMO do not line up, then…
the rxn is symmetry forbidden.
[2+2] cycloaddition possible when…
light is used to excite an electron.
Use of light vs. heat yields…
different stereoisomers
Stereochemistry of reactants and conditions (heat v. light) affect the…
stereochemistry of the product
Disrotatory Rotation
one rotates clockwise, the other counterclockwise;
Conrotatory Rotation
both rotate clockwise or counterclockwise
(Thermal v. Light): 4-pi electrons
Thermal: conrotatory; Light: disrotatory
(Thermal v. Light): 6-pi electrons
Thermal: disrotatory; Light: conrotatory
[1,5] sigmatropic rearrangement
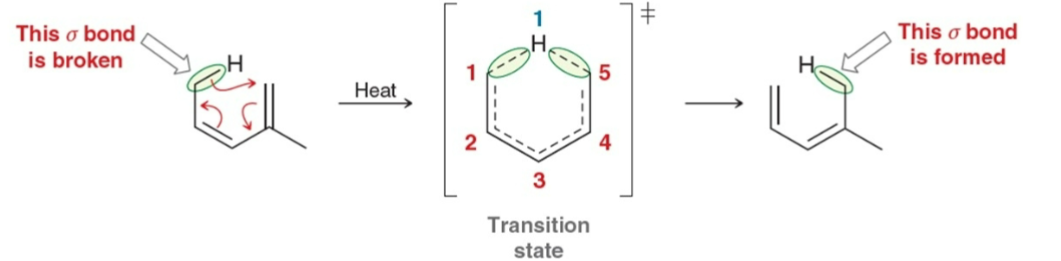
Cope rearrangement
[3,3] sigmatropic reaction; all 6 atoms are carbons
![<p>[3,3] sigmatropic reaction; all 6 atoms are carbons</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ed10018e-85e9-4d68-b72b-678575afb210.png)
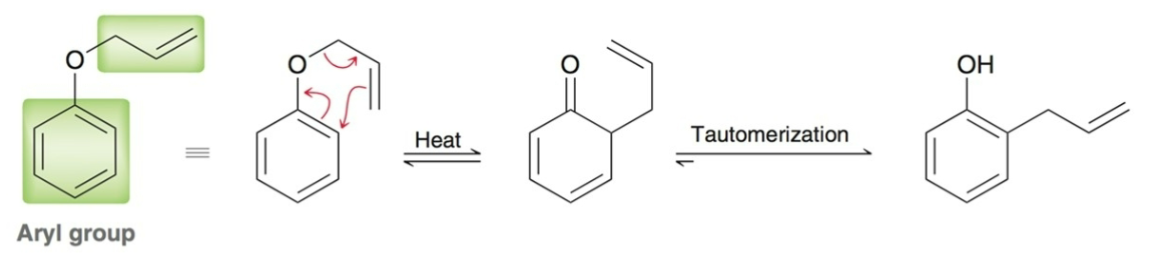
Claisen rearrangement
[3,3] sigmatropic reaction; oxygen analogue to cope rearrangement; occurs with allylic vinylic ethers.
![<p>[3,3] sigmatropic reaction; oxygen analogue to cope rearrangement; occurs with allylic vinylic ethers.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/94d6e1b6-a149-47ba-8f29-c04217c93ebd.png)
Claisen rearrangement also occurs in…
allylic aryl ethers
Compounds with conjugated pi systems absorb…
UV or visible light
UV-Vis Spectroscopy gives…
structural info of molecules; through absorbance (A).
More conjugation gives…
smaller energy gaps
Smaller energy gaps give…
greater λmax
Chromophore
the group of atoms responsible for absorbing UV-Vis light
4 pi-electrons + heat
Conrotatory
4 pi-electrons + light
Disrotatory
6 pi-electrons + heat
Disrotatory
6 pi-electrons + light
Conrotatory