CHAPTER 9 joints
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
articulations
place where a bone meets another…
bone, cartilage, or teeth
vary in stability and mobility
more mobility = less stability
classification by structures
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
classification by function
synarthrosis
amphiarthrosis
diarthrosis
synarthrosis
immobile joint
amphiarthrosis
slightly mobile joint
diarthrosis
freely moveable joint
fibrous joint
bones held together by dense regular CT
3 types:
gomphosis
sutures
syndesmoses
gomphoses
joints between teeth
synarthroses
sutures
joints between skull bones
synarthroses
syndesmoses
joints between parallel bones
in the forearm (radius, ulna)
in the leg (tibia, fibula)
amphiarthroses
cartilaginous joints
bones joined by cartilage
2 types:
synchondroses
symphyses
synchondroses
bones joined by hyaline cartilage
synarthroses
example:
costal cartilage
symphyses
bones joined by fibrocartilage
amphiarthroses
examples:
pubic symphysis
intervertebral disc
synovial joints
bones separated by fluid-filled joint cavity
freely mobile diarthroses
general anatomy of synovial joints
articular capsule
articular cartilage
joint cavity
ligaments
sensory nerves
blood vessels
accessory structures
articular capsule
2 layers
outer fibrous layer
made of dense regular CT
strengthens joint
inner synovial membrane
secretes synovial fluid
articular cartilage
articular surfaces in synovial joints covered by hyaline cartilage
reduces friction and acts as shock absorber
joint cavity
spaces between articulating bones
contains small amount of synovial fluid
synovial fluid
lubricates and nourishes articular cartilages
nourishes chondrocytes of articular cartilage
absorbs shock during compression of joint
ligaments
connect bone to bone
dense regular CT
strengthen and reinforce capsule
sensory nerves
detect pain and amount of stretch in a joint
blood vessels
nourishes tissues in the joint
accessory structures surrounding synovial joint
bursae
tendon sheath
fat pads
bursae
fluid filled sac where ligaments, muscles, tendons, and/or bones rub
contain synovial fluid
tendon sheath
elongated bursae around tendons where tendon rub each other
fat pads
packing material
also provide some protection
first class lever
has fulcrum in the middle: RFE
example:
seesaw
atlanto-occipital joint
second class lever
has resistance in the middle: ERF
example:
lifting handle of wheelbarrow
bouncing knee, hip joint is fulcrum
third class lever
has effort in the middle: REF
example:
paddling canoe
forearm when flexing elbow
uniaxial
joint moves in 1 plane or axis
biaxial
joint moves in 2 plane or axis
multiaxial
joint moves in 3 plane or axis
movements of synovial joints
4 types of motion
gliding motion
angular motion
rotational motion
special movement
gliding motion
articular surfaces sliding
back and forth
side to side
occurs mainly in plane joints
example:
between carpals
angular motion
increases or decreases the angle between bones
flexion vs extension
abduction vs adduction
hyperextension
lateral flexion
circumduction
rotational motion
a bone turning on its longitudinal axis
lateral rotation vs medial rotation
pronation vs supination
examples:
atlantoaxial joint turning back and forth in the “no” gesture
limbs turning to and from median plan
special movements
occur only at specific joints
depression vs elevation
dorsiflexion vs plantar flexion
inversion vs eversion
protraction vs retraction
opposition
temporomandibular joint
between mandibular condyle and temporal bone
hinge joint
articular disc
ligaments
sphenomandibular ligament
stylomandibular ligament
temporomandibular (lateral) ligament
intervertebral articulations
amphiarthroses between vertebral bodies
diarthroses between articular processes
vertebral bodies separated by intervertebral disc
ligaments:
anterior longitudinal ligament
posterior longitudinal ligament
joints of pectoral girdle and upper limbs
selected joints include:
sternoclavicular joint
acromioclavicular joint
glenohumeral (shoulder) joint
elbow joint
radiocarpal (wrist) joint
sternoclavicular joint
between manubrium of sternum and sternal end of clavicle
saddle joint
ligaments
anterior and posterior sternoclavicular ligament
costoclavicular ligament
interclavicular ligament
acromioclavicular joint
between acromial end of clavicle and acromion of scapula
ligaments
acromioclavicular joint
coracoclavicular joint
glenohumeral joint
between head of humerus and glenoid cavity of scapula
ball and socket joint
features
fibrocartilaginous glenoid labrum
ligament
coracoacromial ligament
corahumeral ligament
glenohumeral ligament
transverse humeral ligament
rotator cuff muscles
bursae
subacromial bursae
subcoracoid bursae
subdeltoid bursae
subscapular bursae
elbow joint
composed of humeroulnar and humeroradial joints
hinge joint and pivot joint
ligaments
radial (lateral) collateral ligament
ulnar (medial) collateral ligament
annular ligament
radiocarpal joint
between…
distal articular surface of radius
and three proximal carpal bones (scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum)
condylar joint
diarthrotic
joints of the pelvic girdle and lower limbs
selected joint include
hip (coxal) joint
knee joint
talocrural (ankle) joint
joints of the foot
coxal joint
between head of femur and acetabulum of os coxae
ball and socket joint
articular capsule with retinacular fibers
ligaments:
iliofemoral ligament
ishiofemoral ligament
pubofemoral ligament
ligaments of head and femur
knee joint
between femur, tibia, and patella
hinge joint
largest and most complex joint in body with
medial and lateral menisci
ligaments
patellar ligament
fibular (lateral) collateral ligament
tibial (medial) collateral ligament
anterior and posterior crucial ligaments (ACL and PCL)
talocrural joint
composed of two articulations
between distal end of tibia and talus
between distal end of fibula and lateral aspect of talus
hinge joint
ligaments
deltoid ligament
lateral ligament
anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligament
joints of foot
4 types of diarthroses
intertarsal joint
tarsometatarsal joint
metatarsophalangeal (MP) joint
interphalangeal (IP) joint
intertarsal joint
plane joint between tarsals
tarsometatarsal joint
plane joint between distal tarsal bone and metatarsals
metatarsophalangeal joint
between metatarsal and proximal phalanges
condylar joint
interphalangeal joint
hinge joint between phalanges
arthritis
broad term for inflammation of joints
bursitis
inflammation of bursa
usually due to overuse of a joint
dislocation
displacement of bone from normal position at a joint
most common at fingers, thumbs, shoulder, knee
gout
uric acid crystals accumulate in joints and irritate articular cartilage and synovial membrane
swelling and pain
tissue degeneration
sometimes fusion of joint
most commonly affect great toe
rheumatism
broad term for any pain including bones, ligaments, tendons, muscles
sprain
torn ligaments
sometimes with damage to a meniscus or other cartilage
strain
painful overstretching of a tendon or muscle without serious tissue damage
often results from inadequate warm-up before exercise
synorvitis
inflammation of a joint capsule
often as a complication of a sprain
tendinitis
a form of bursitis in which a tendon sheath is inflamed
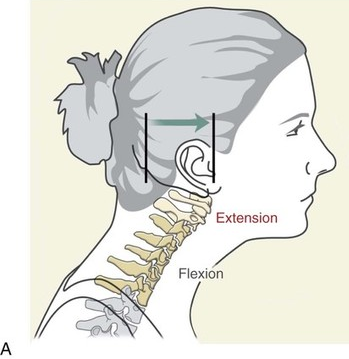
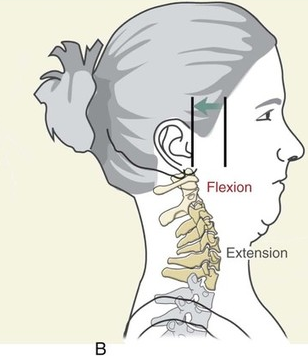
flexion
decreases angle of joint
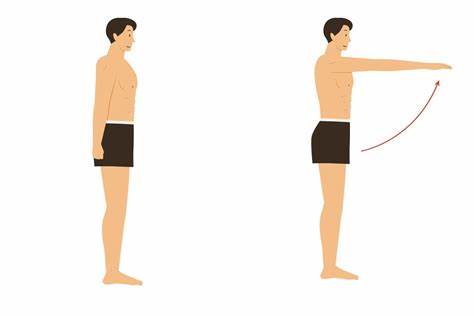
extension
increases angle of joint
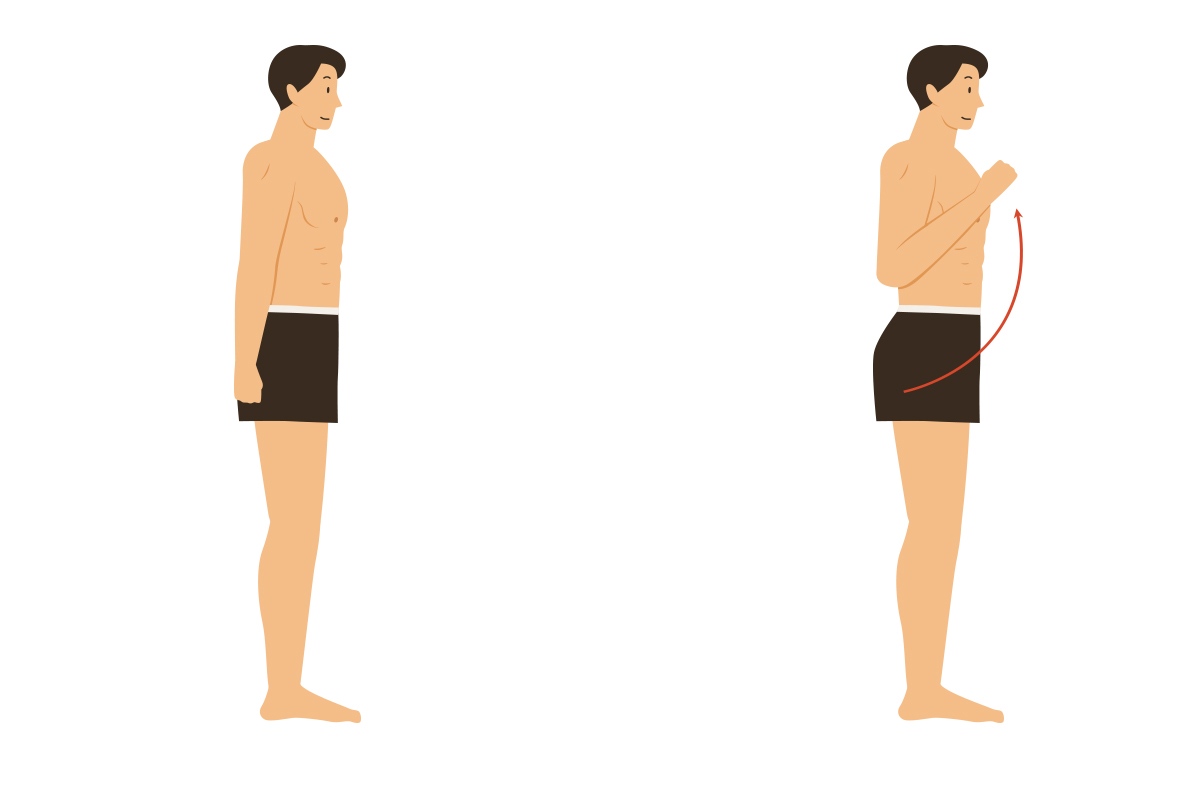
hyperextension
extends beyond anatomical position angle of joint and/or causes injury
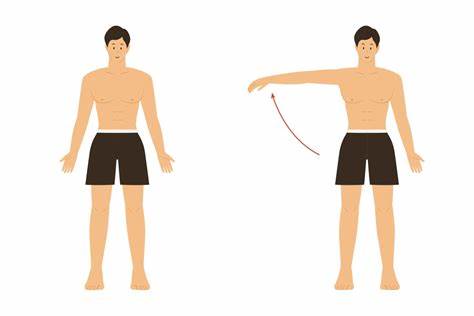
abduction
movement away from midline of body
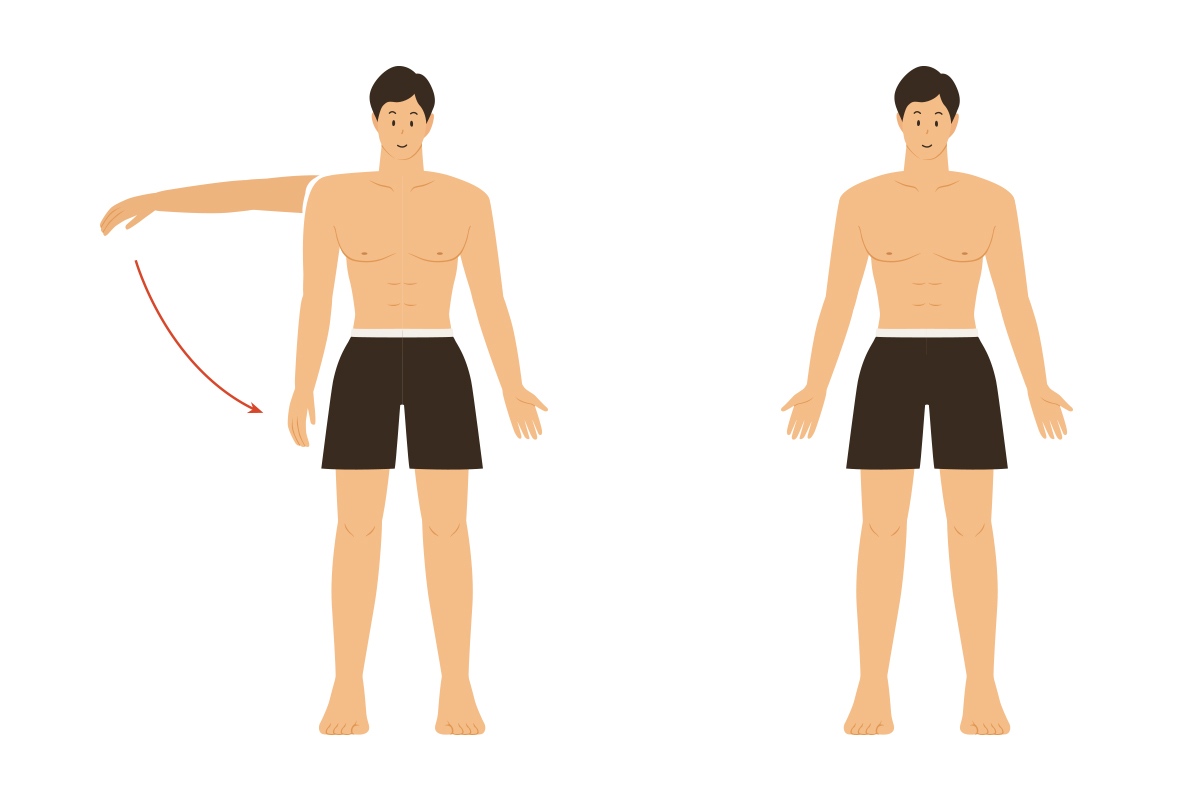
adduction
movement toward midline of body
elevation
raises body part vertically
depression
lowers body part
protraction
anterior movement of body part
retraction
posterior movement of body part
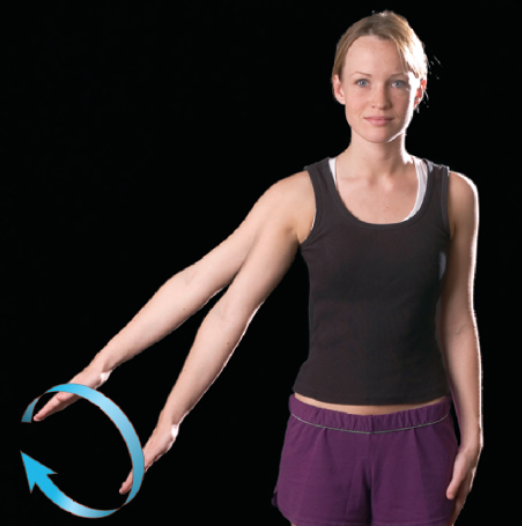
circumduction
distal end of limb or digit moves in a circle

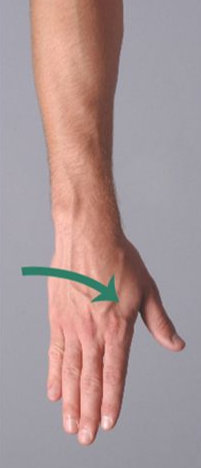
pronation
radius and ulna end up crossed; palms turned posteriorly
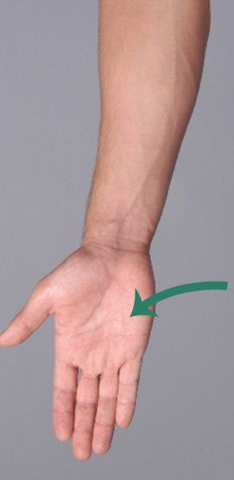
supination
radius and ulna end up parallel; palms turned anteriorly
opposition
thumb and finger meet together
dorsiflexion
dorsum of foot is brought towards to anterior surface of leg
plantar flexion
sole of foot is brought towards to posterior surface of leg
inversion
turns the sole medially or inward
eversion
turns the sole laterally or outward
ball and socket joint
round head of one bone rest within cup shape bone
movement in all directions
multiaxial
example:
glenohumeral joint
hip joint
plane joint
flattened face slide across one another
sliding movement
biaxial
example:
intercarpal joints
intertarsal joints
hinge joint
convex feature of one bone fits into concave of bone
movement in one direction like door
monaxial
examples:
elbow joint
knee joint
pivot joint
bone with round surface fits into ring form by ligament and/or another bone
rotation on single axis
monaxial
example:
atlantoaxial joint
atlas and axis vertebrae
radius and ulna
saddle joint
saddle shape surfaces
movement back and forth, side to side
biaxial
example:
thumb (carpometacarpal joint)
condylar joint
oval surfaces
movement in two planes with no rotation
biaxial
examples:
metacarpophalangeal
lateral rotation
limb or body move away from midline longitudinally
medial rotation
limb or body move toward midline longitudinally
lateral flexion
vertebral column bends in lateral direction
humeroulnar joint
between trochlea of humerus and trochlear notch of ulna
hinge joint
flexion and extension of forearm
humeroradial joint
between capitulum of humerus and head of radius
hinge joint
flexion and extension
radioulnar joint
between head of radius and radial notch of ulna
pivot joint
pronation and supination