Semester 2 Final Exam Vocab Review Set 1: DNA and Protein Synthesis Mrs. K
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
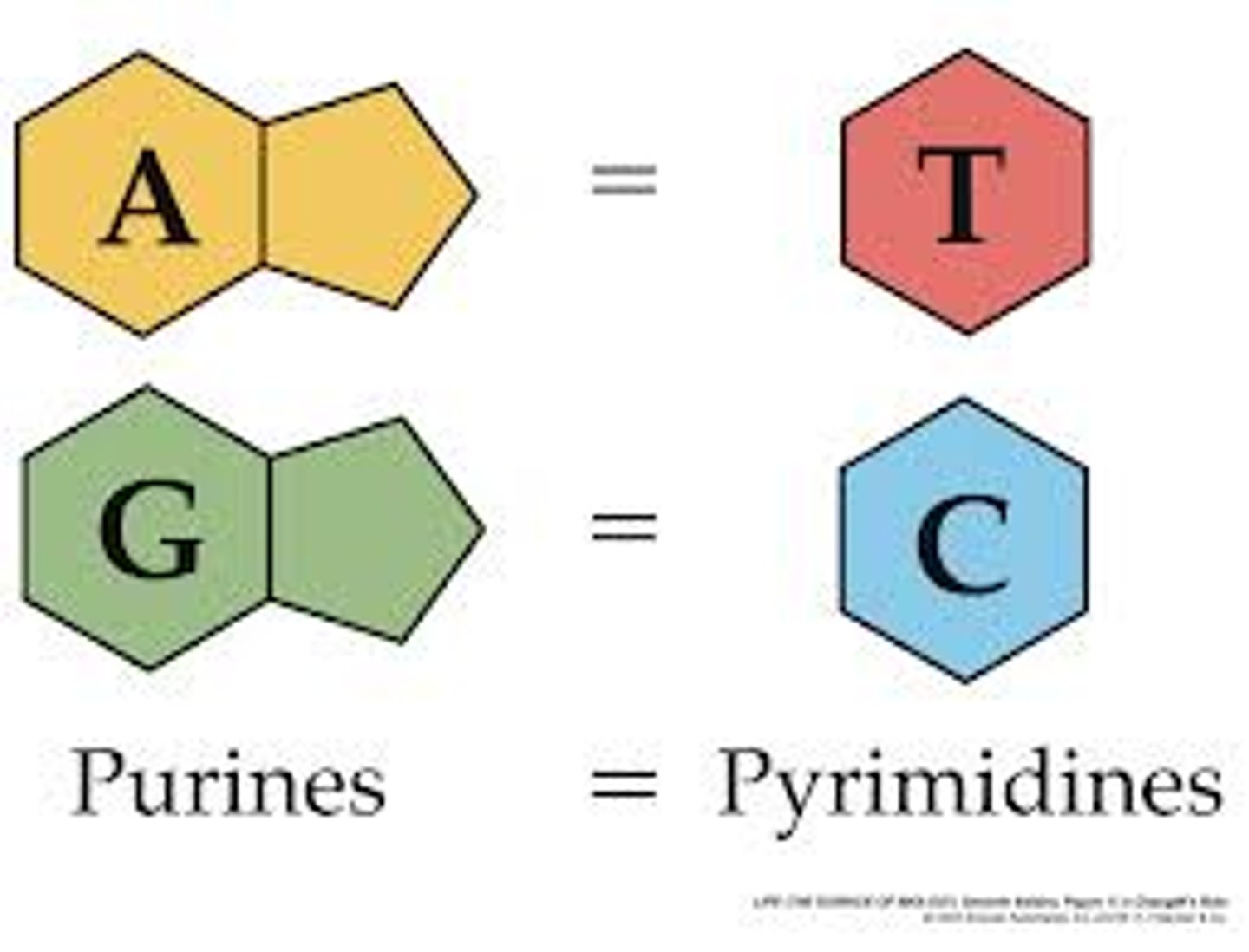
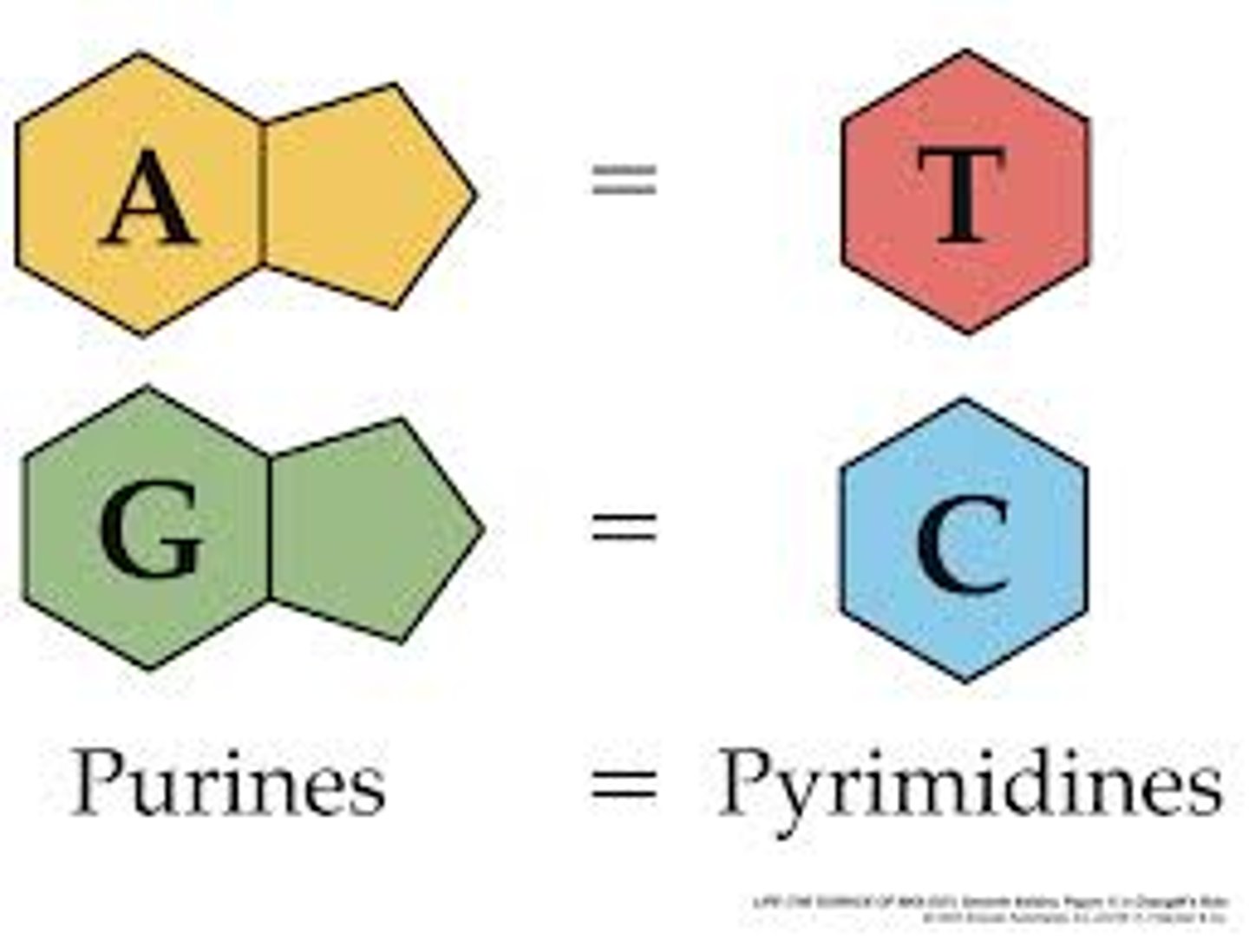
nitrogen base
The chemicals that make up the RUNGS of the DNA ladder. A-T and C-G match.
guanine
The base that pairs with Cytosine in DNA
cytosine
The base that pairs with Guanine with DNA
adenine
The base that pairs with Thymine inDNA
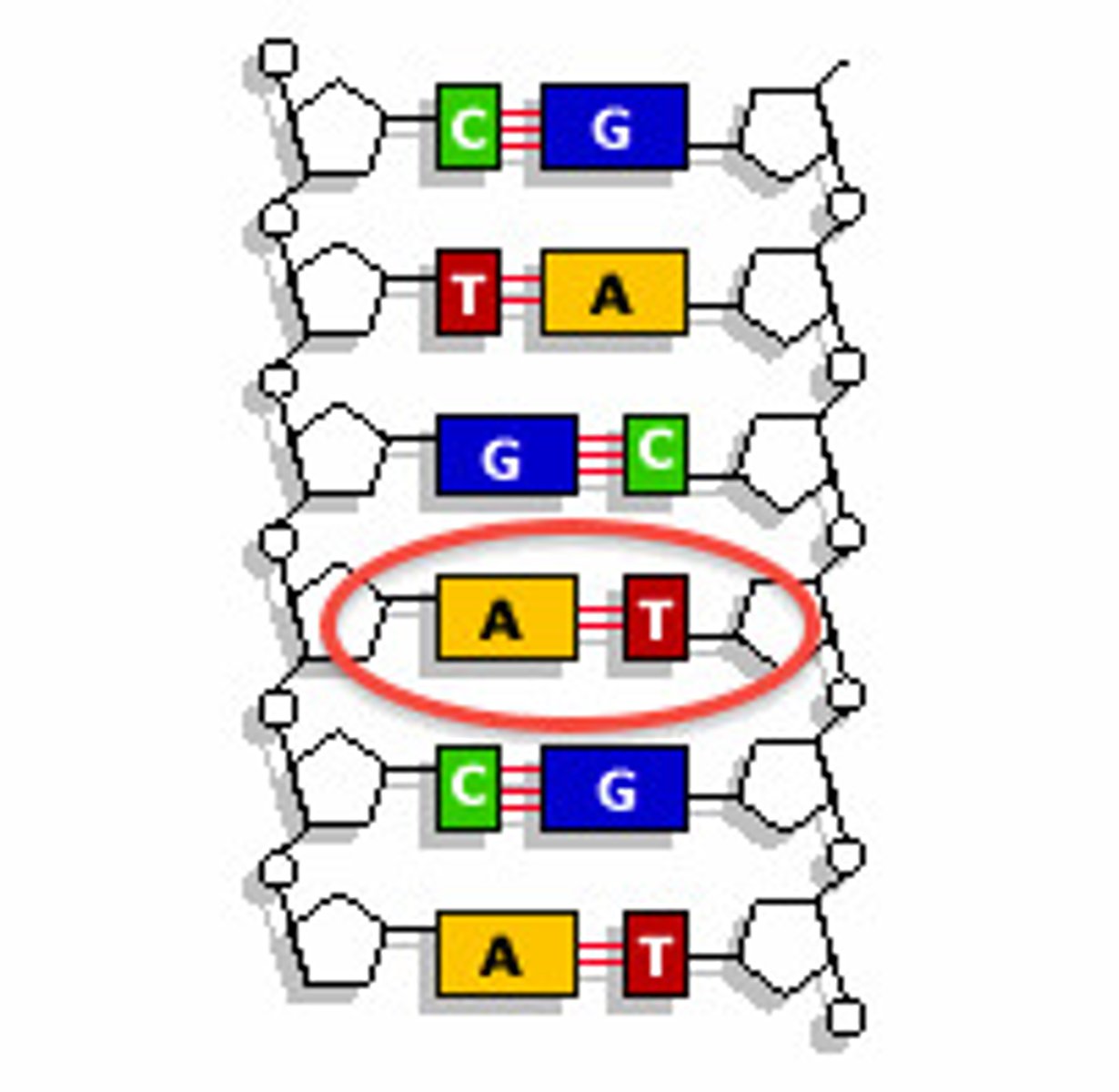
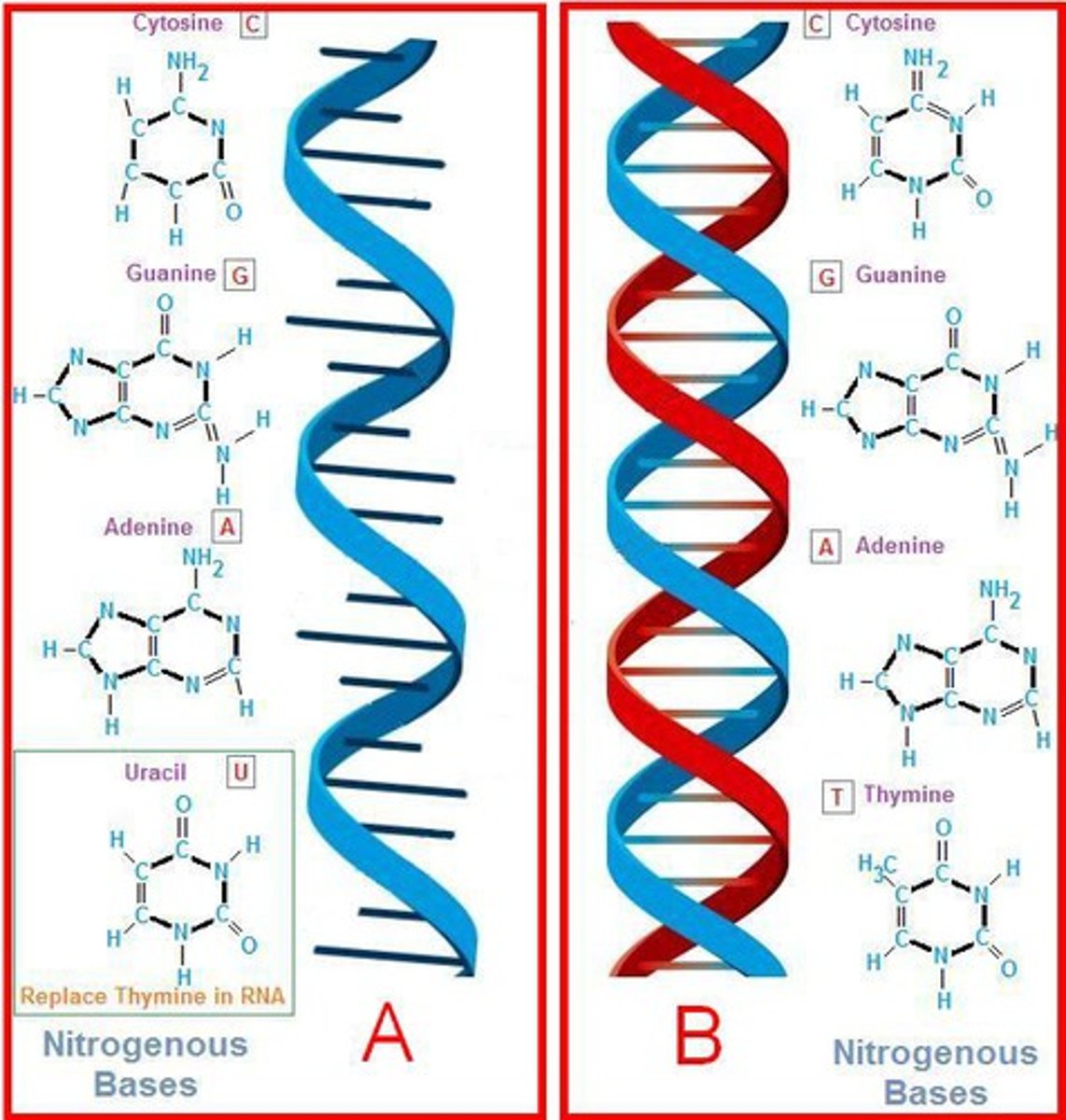
thymine
nitrogen base found ONLY in DNA that pairs with adenine
uracil
a nitrogen-containing base found in RNA (but not in DNA); pairs with adenine
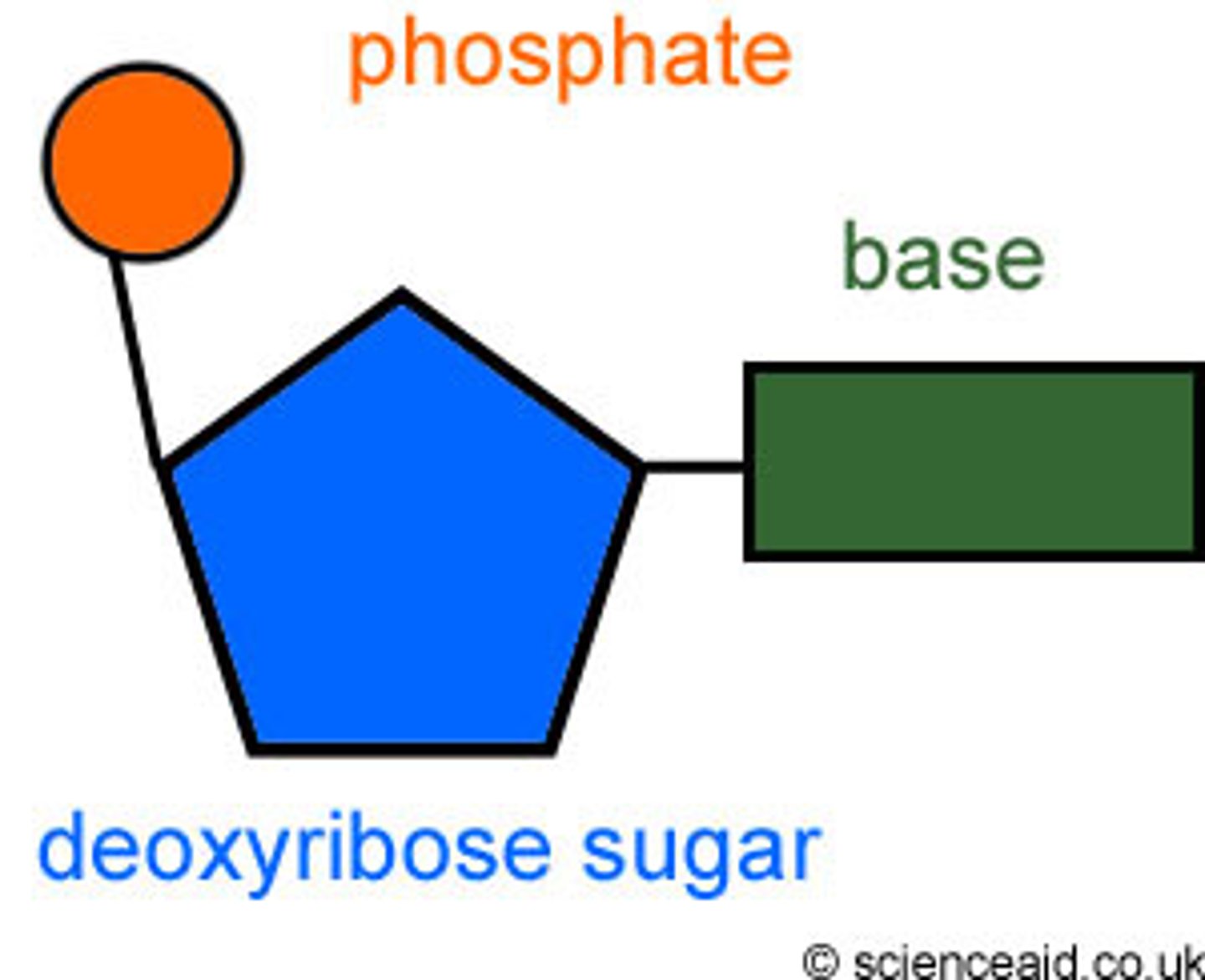
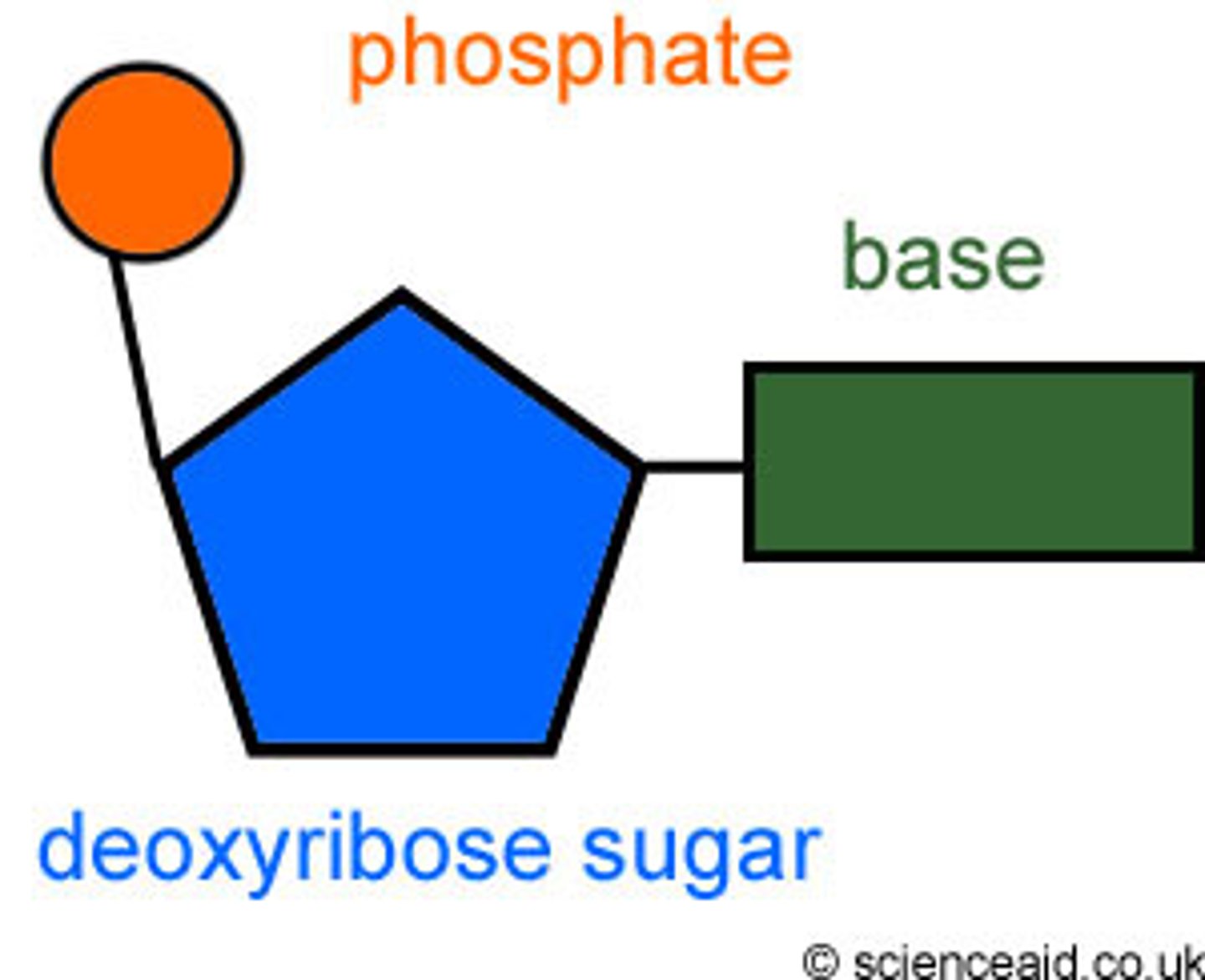
nucleotide
building block of DNA made up of deoxyribose, a phosphate , and a nitrogen base
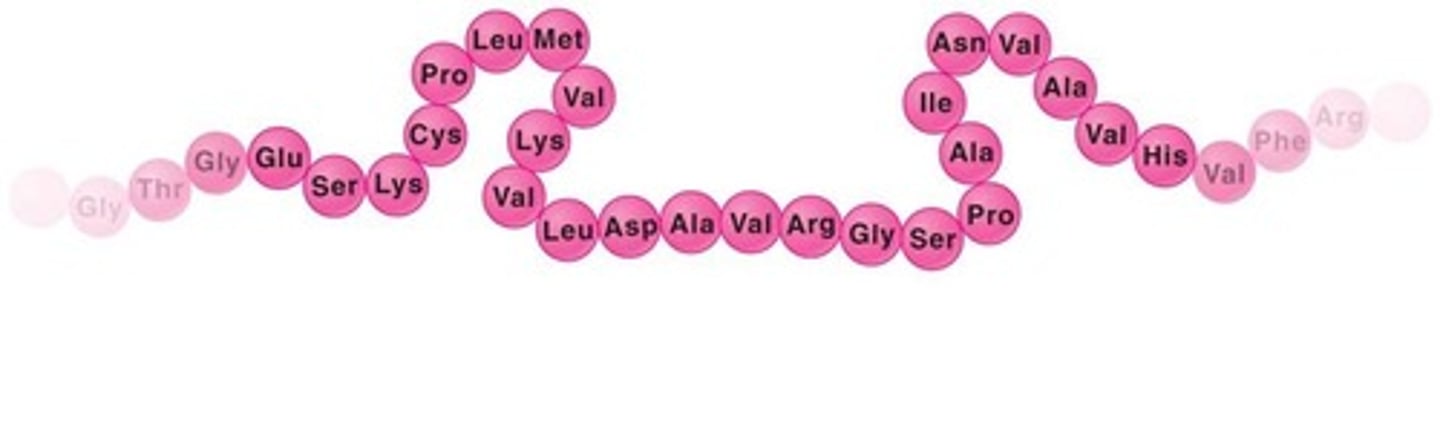
amino acid
building blocks of protein molecules
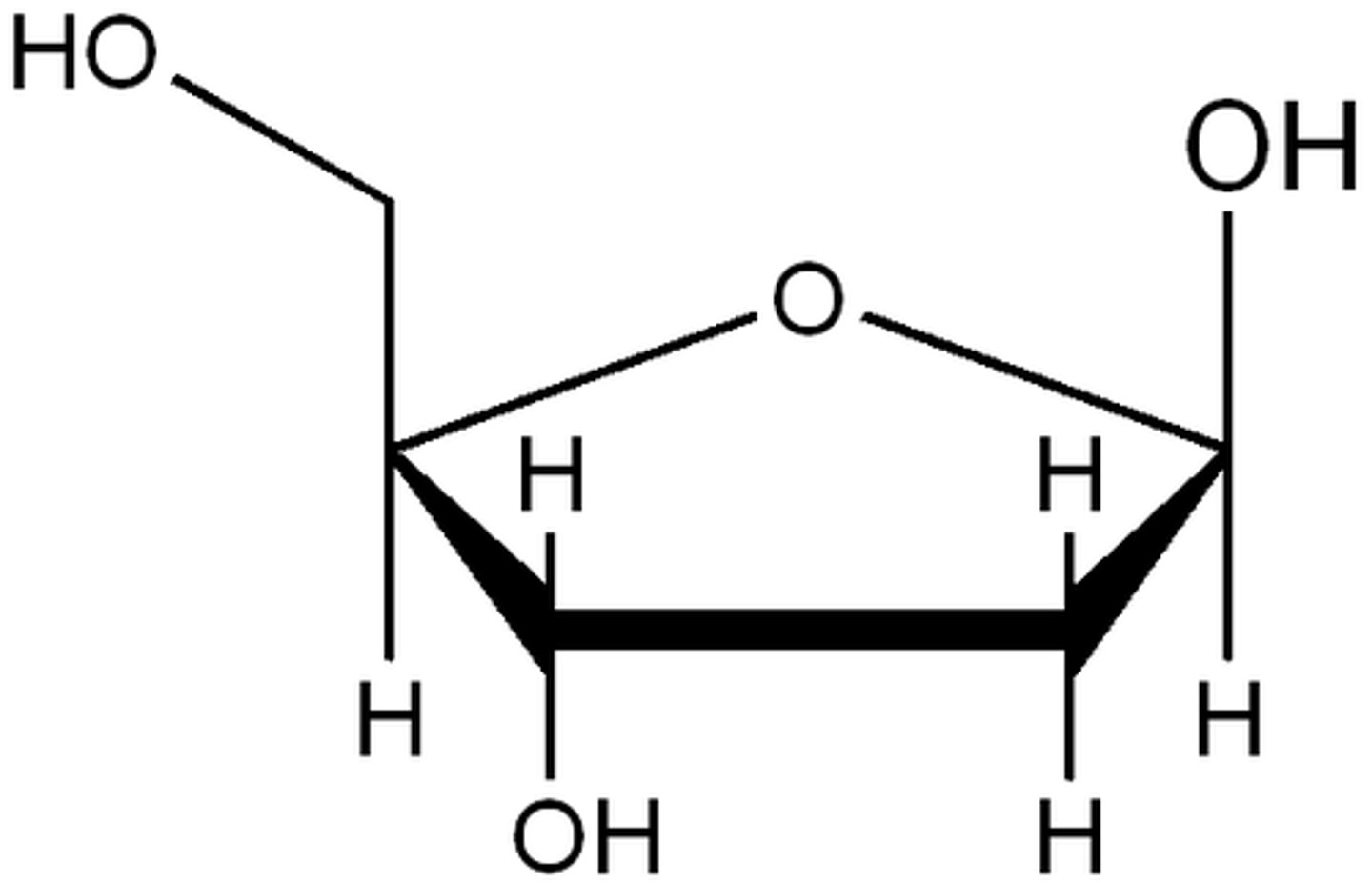
deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
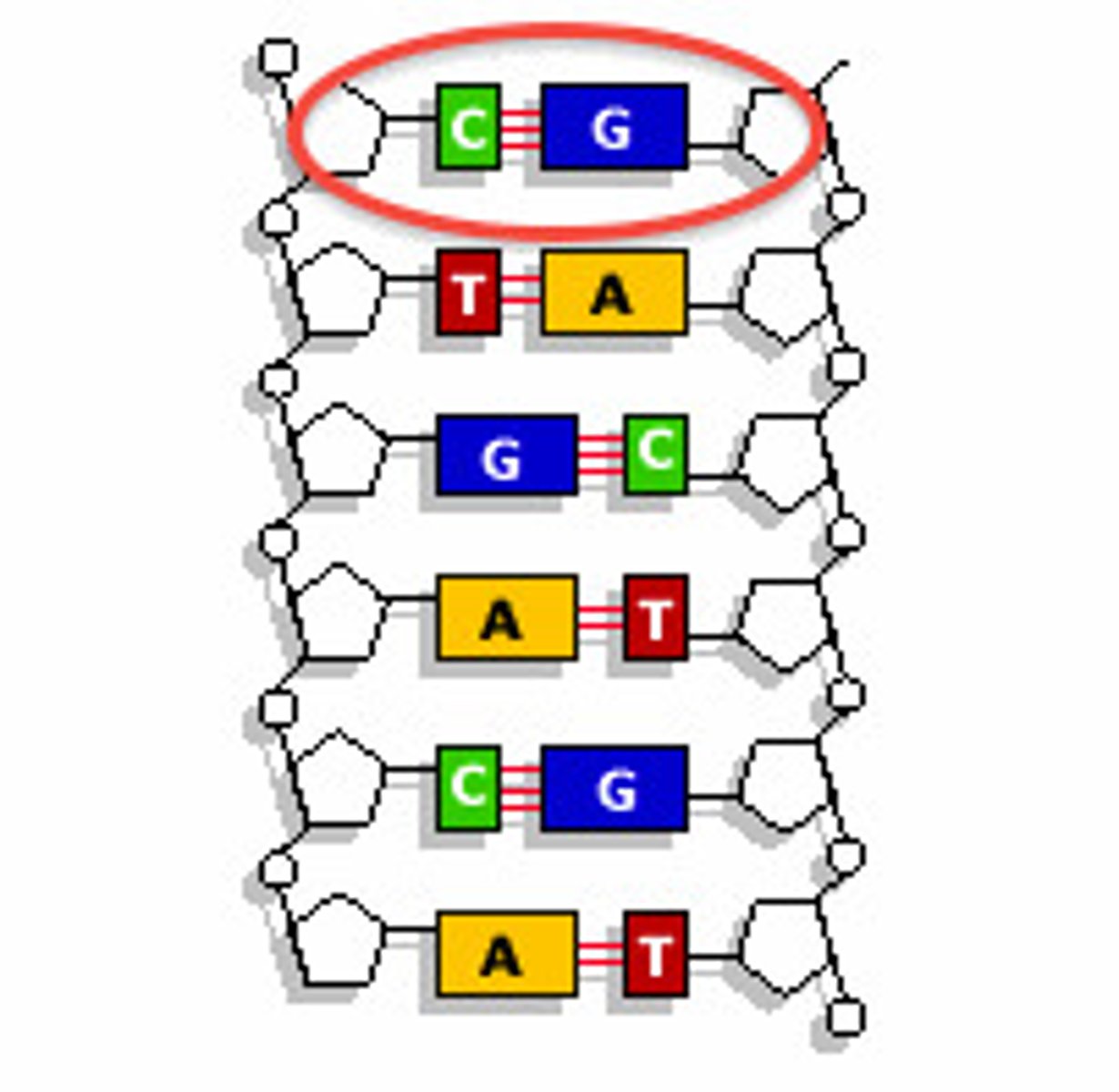
hydrogen bond
weak bond found between two nitrogen bases within a molecule of DNA
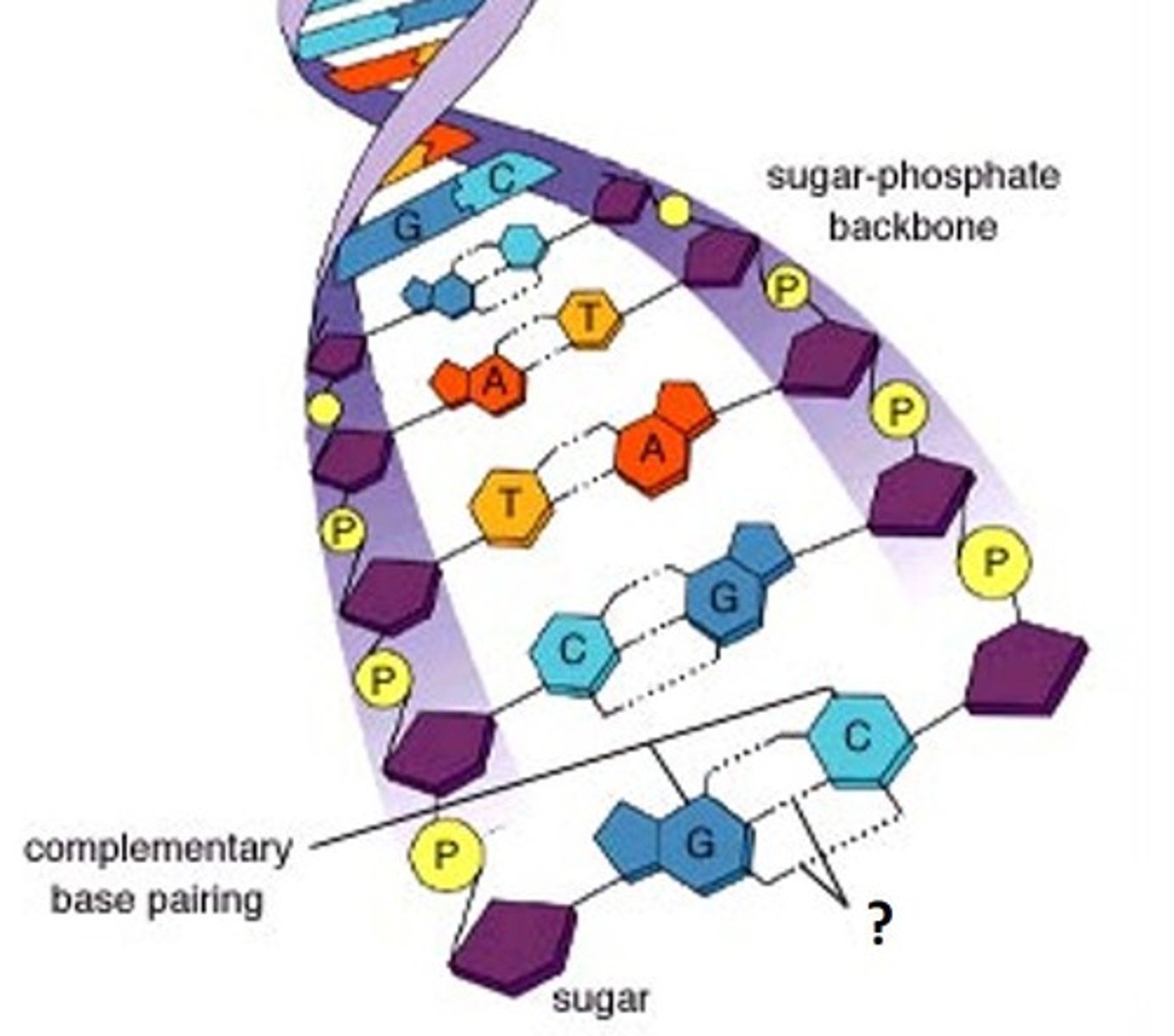
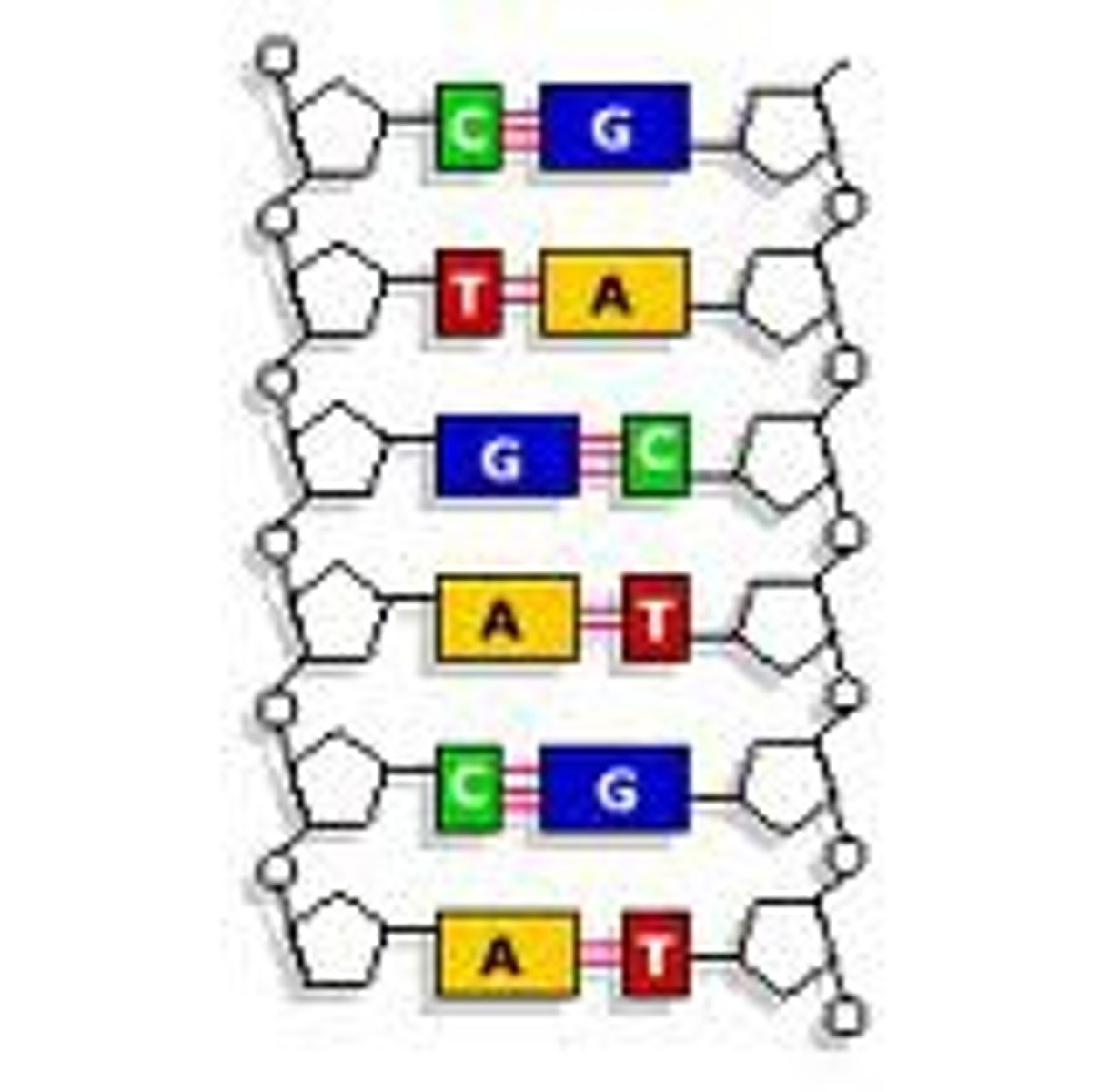
base pairing
bonds in DNA that form between adenine and thymine and between guanine and cytosine
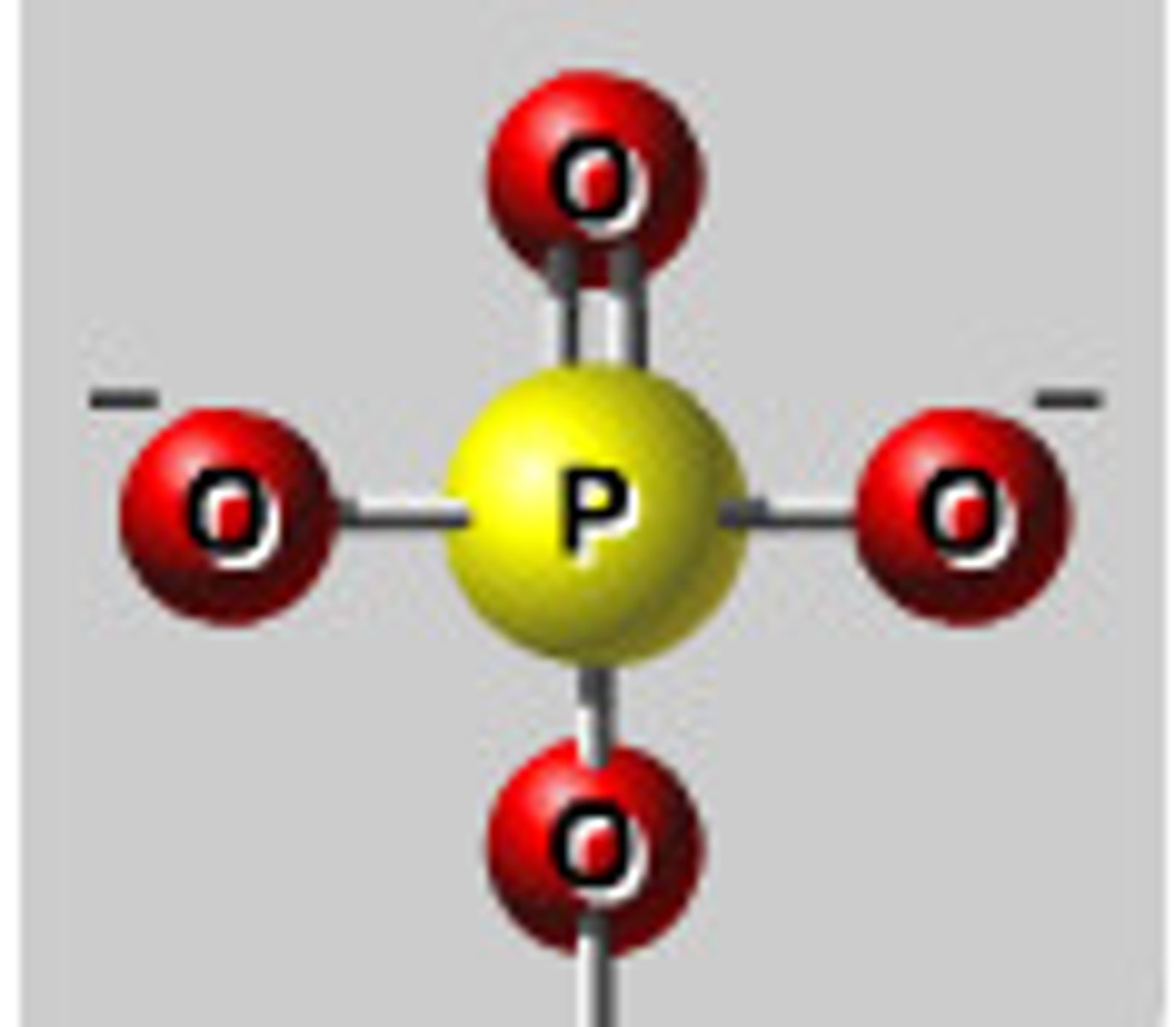
phosphate group
together with either deoxyribose (in DNA) or ribose (in RNA) make up the backbone of a DNA or RNA molecule
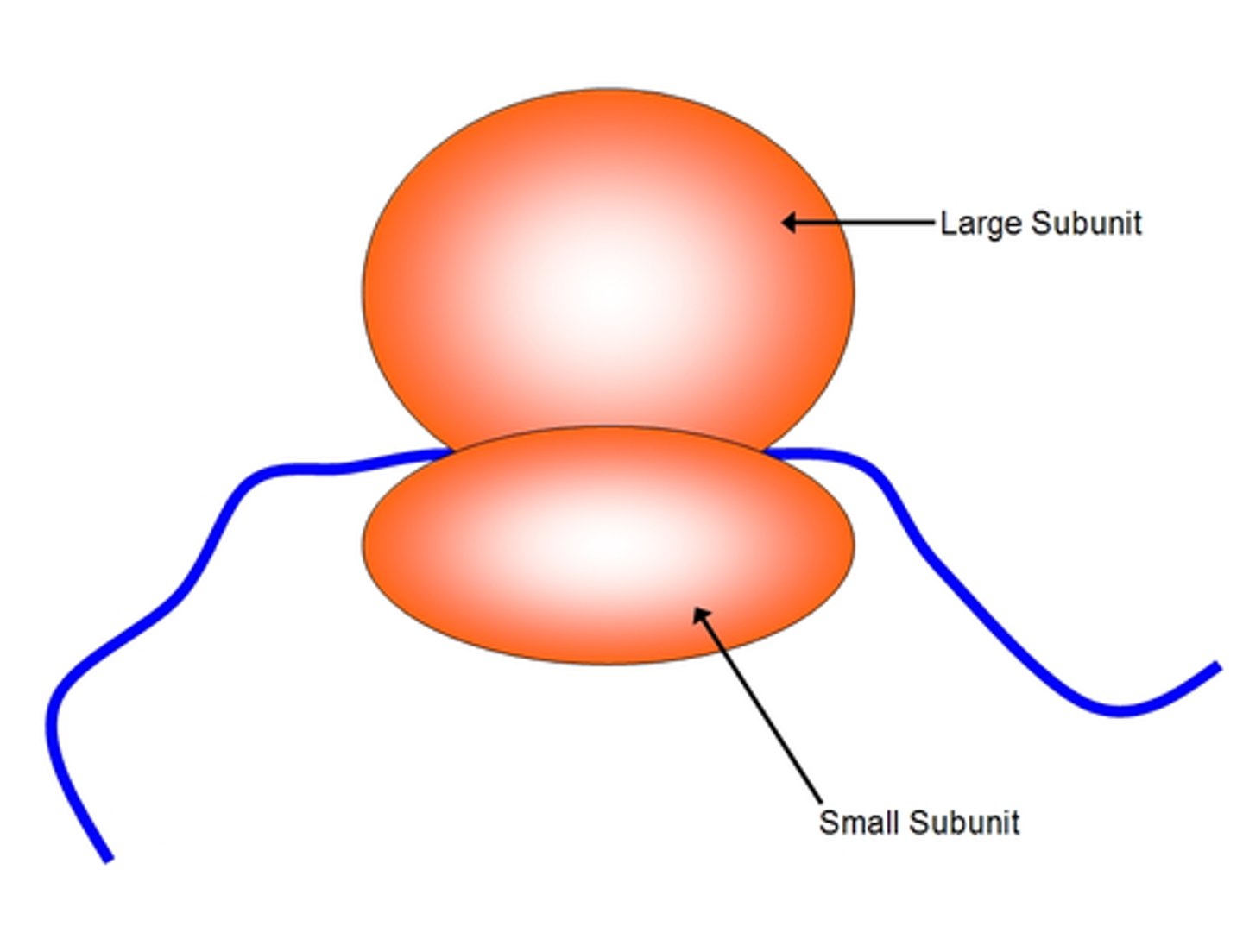
ribosome
a cell organelle composed of RNA and protein; the site of protein synthesis
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
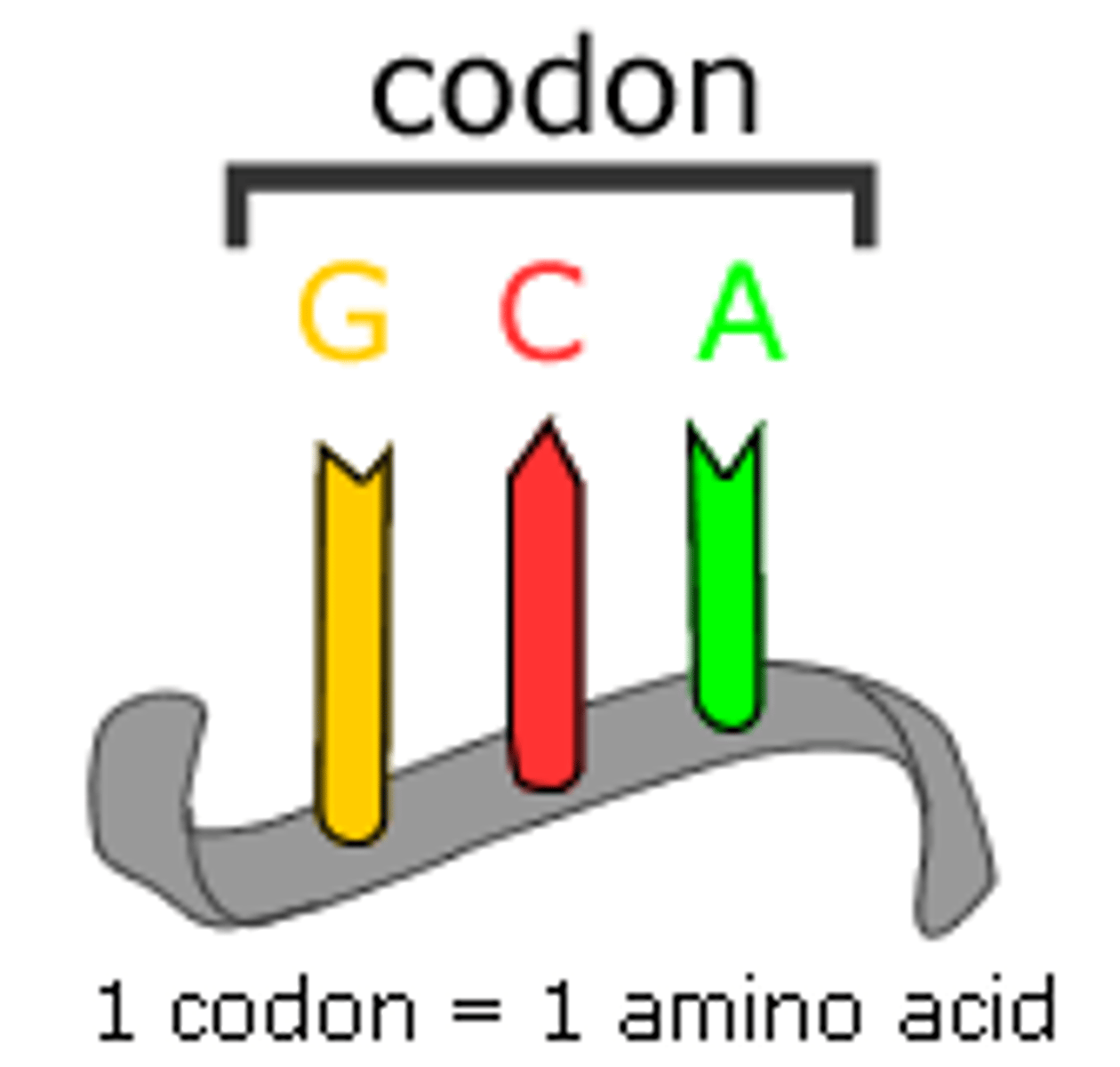
codon
three-nucleotide sequence on mRNA that codes for a single amino acid
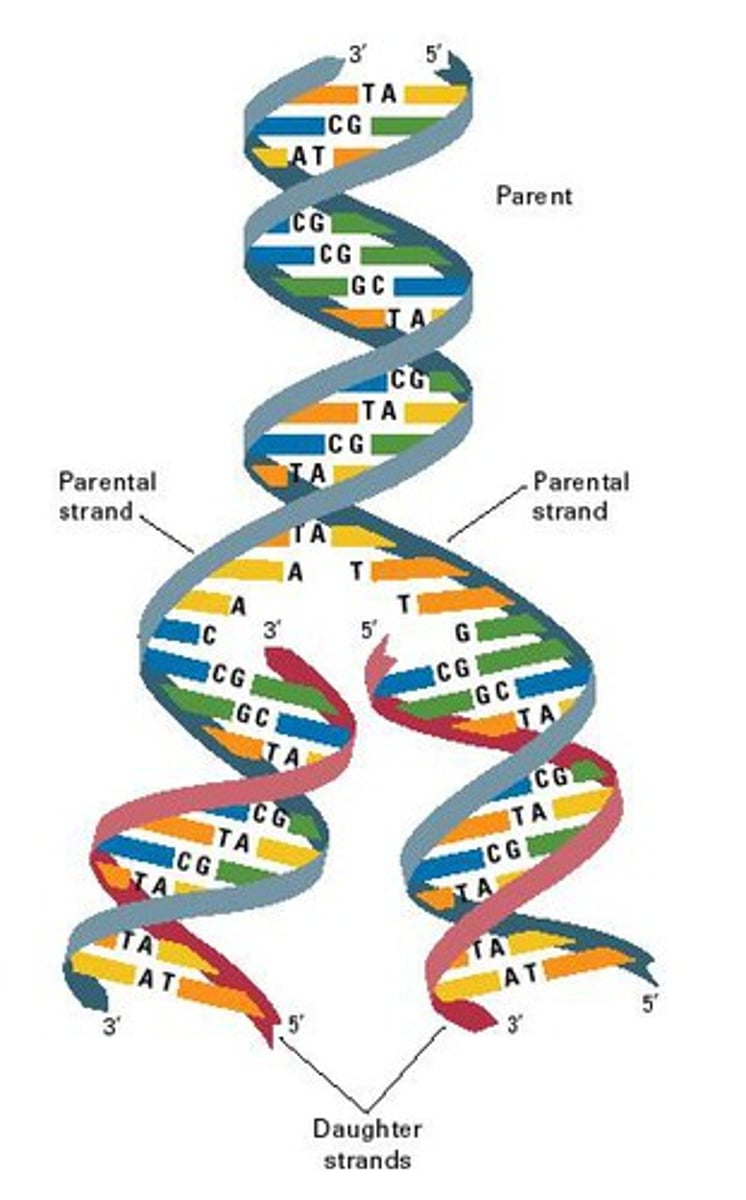
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself.
protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
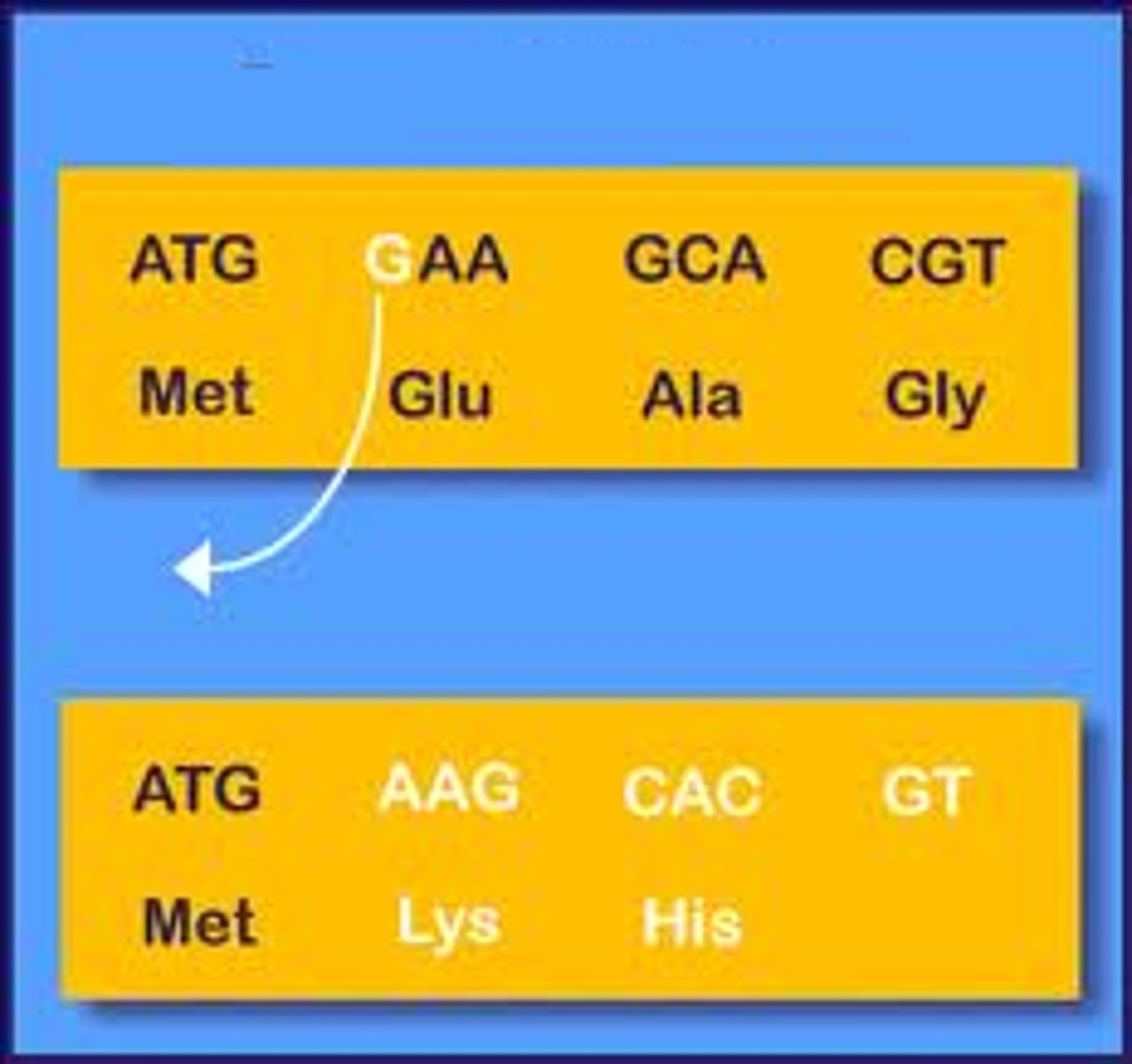
frameshift mutation
mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in the DNA sequence
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
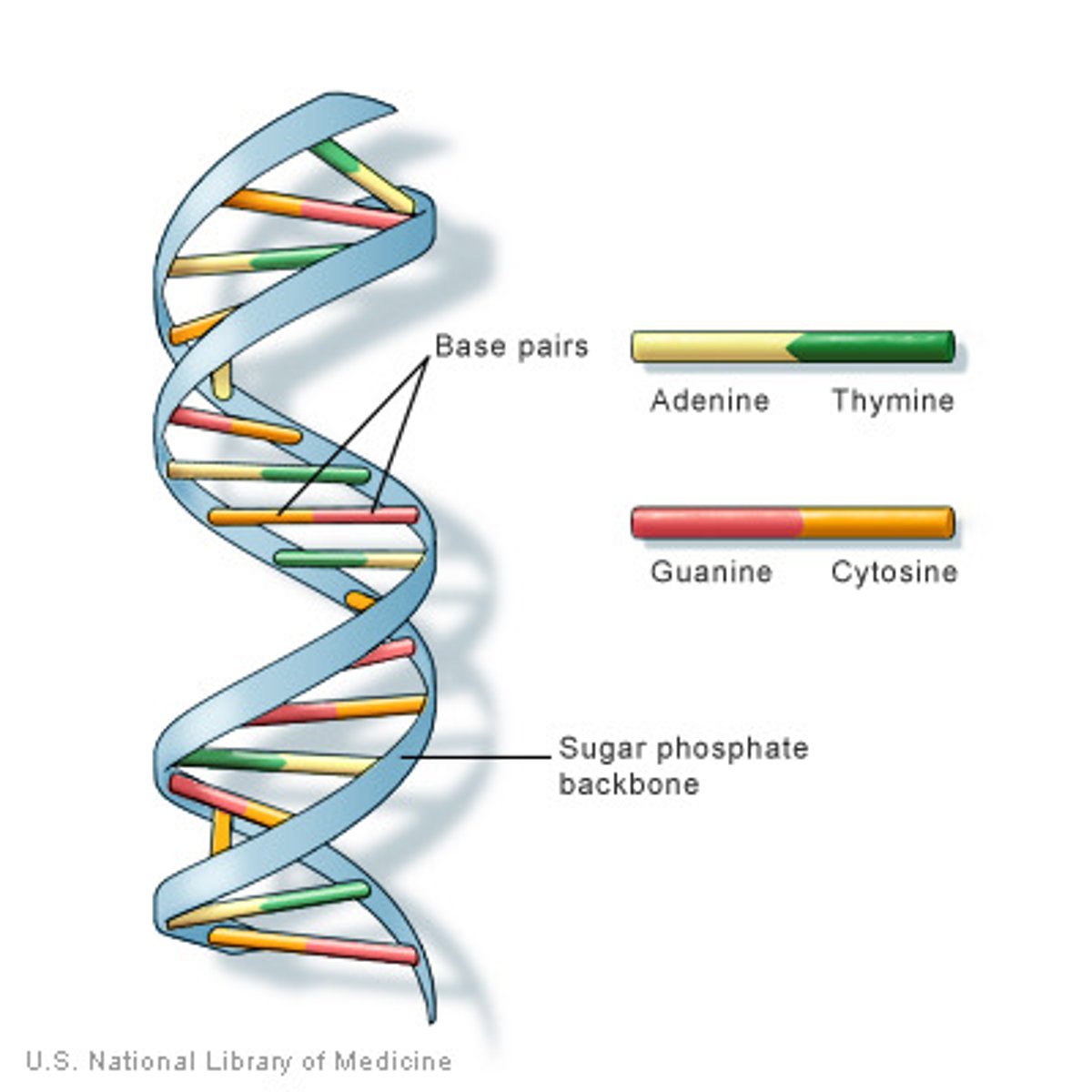
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
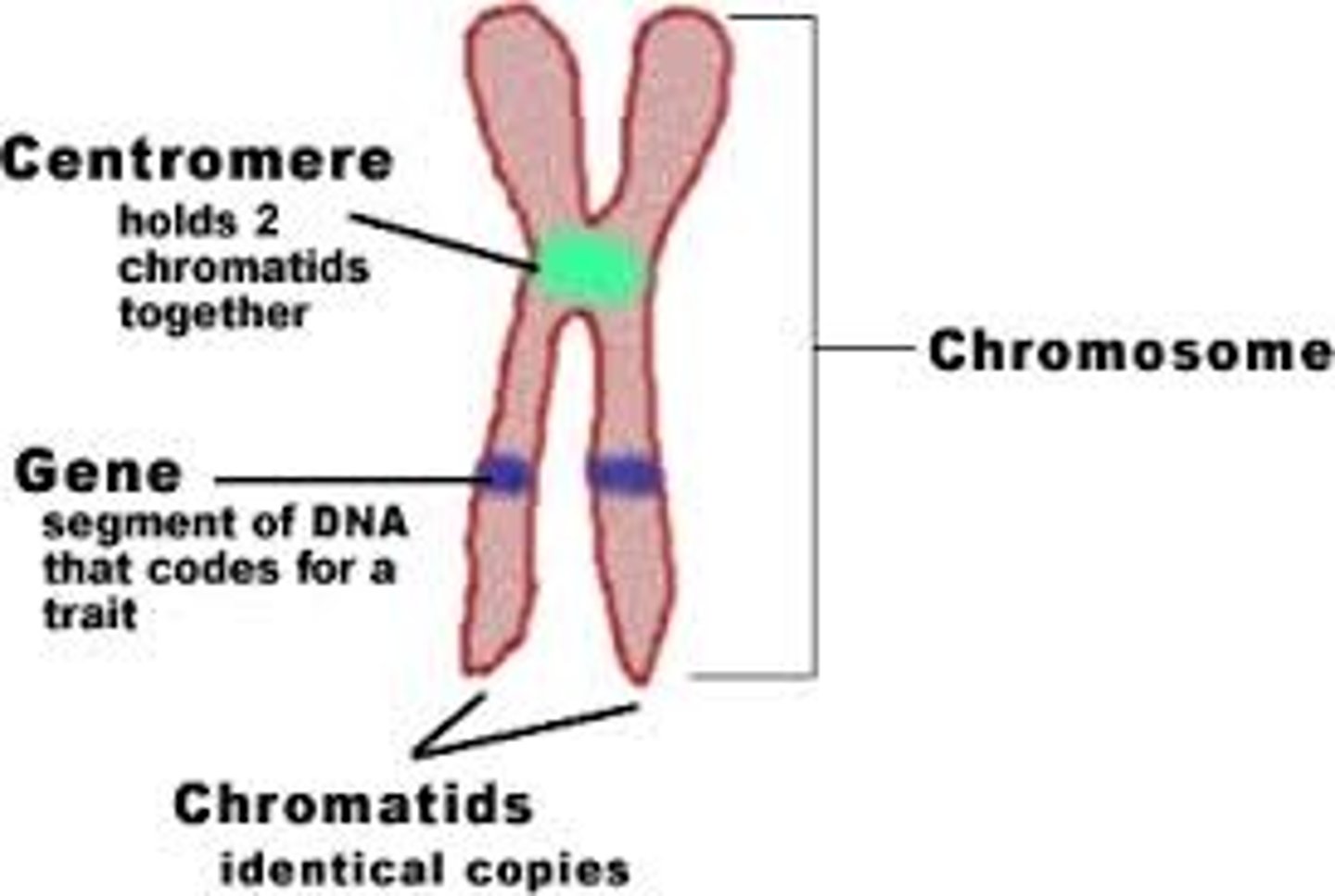
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait/protein
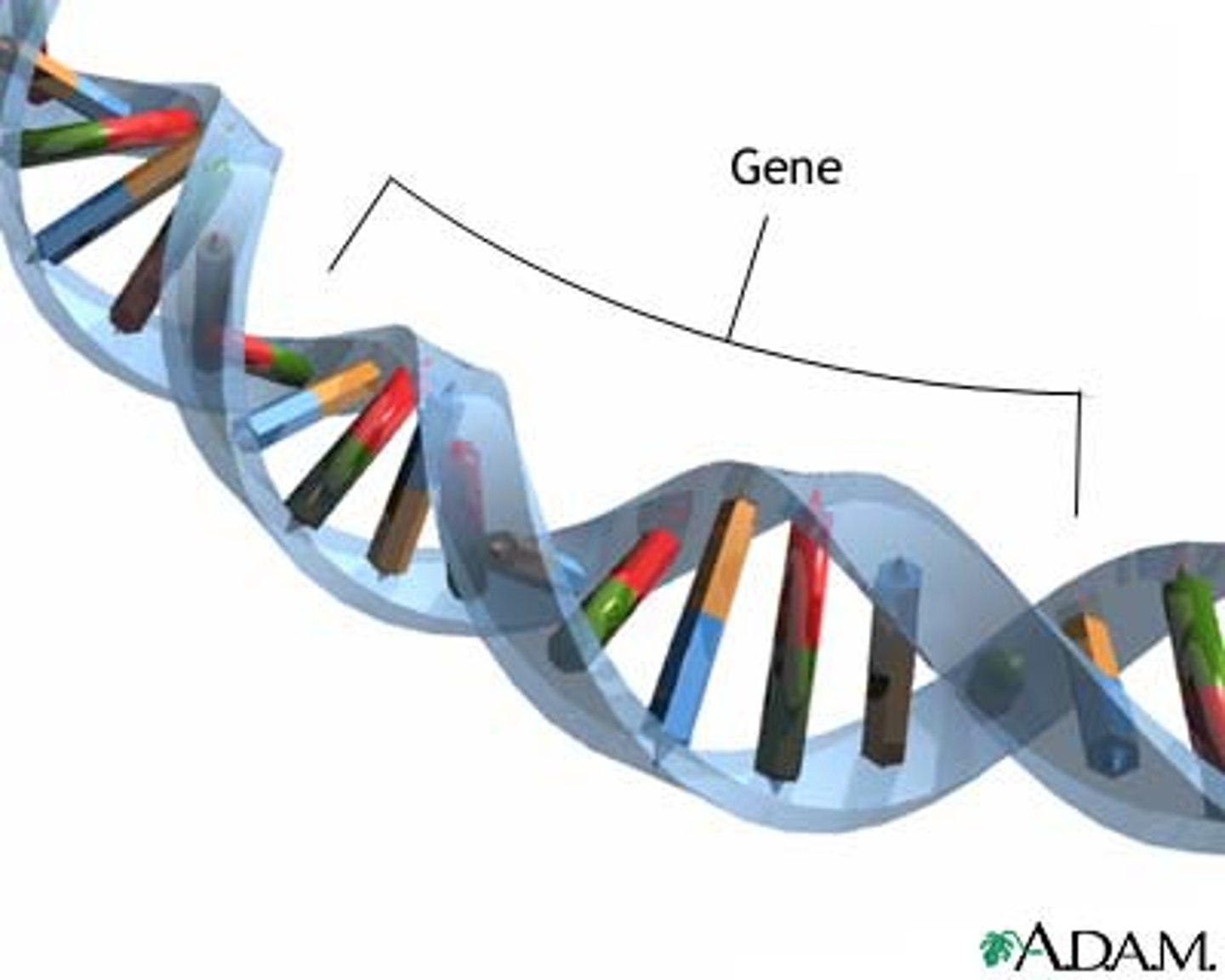
double helix
Shape of DNA
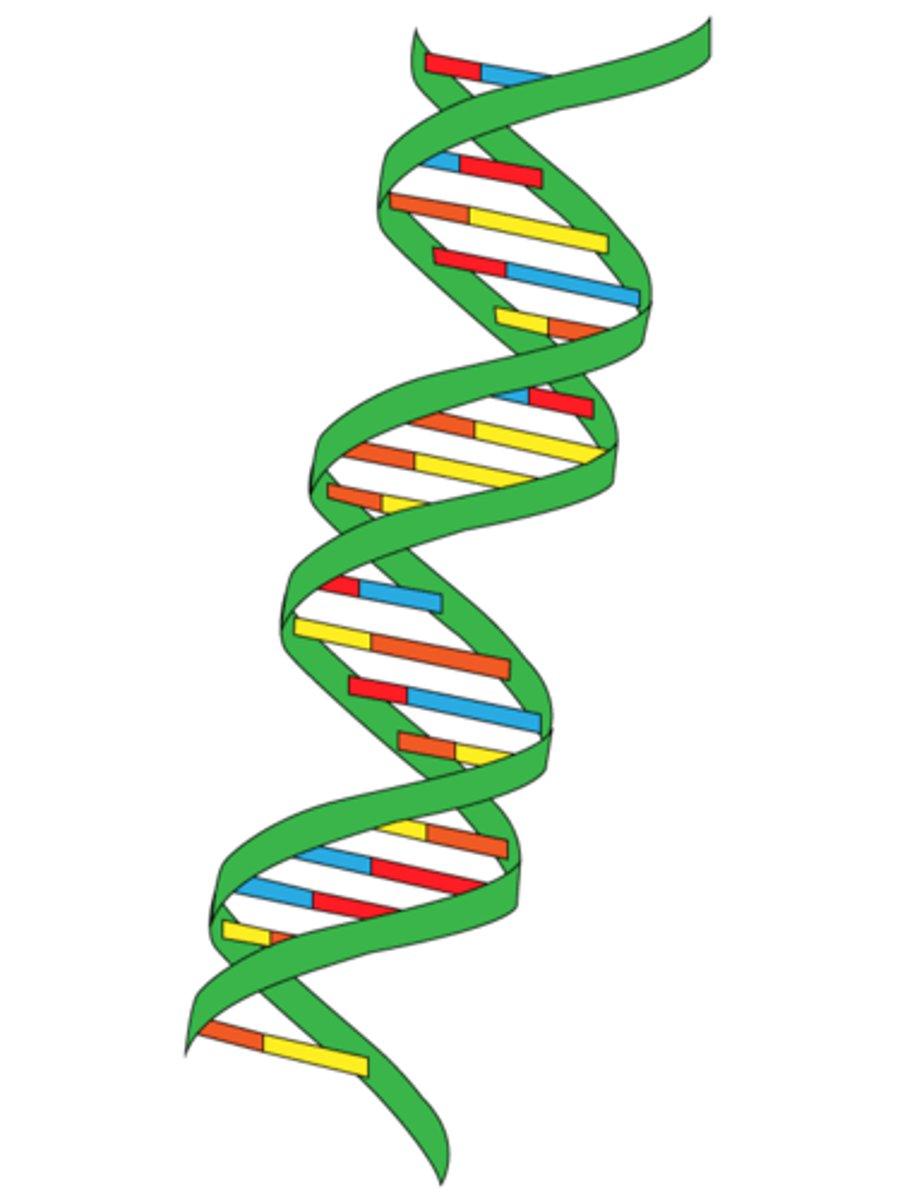
DNA replication
the process of making a copy of DNA that produces two new identical double helixes.
steps of protein synthesis
1. Transcription
2. Translation
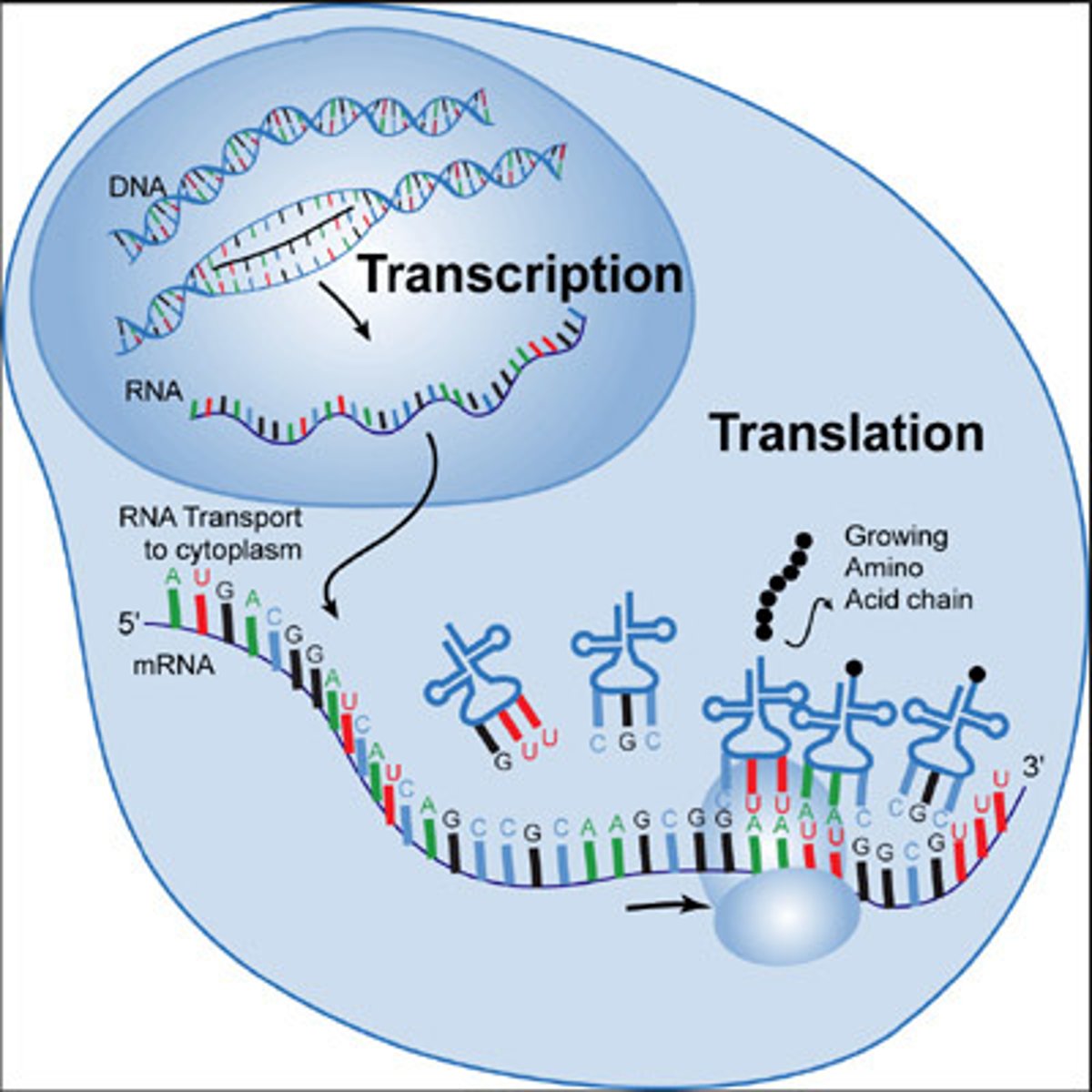
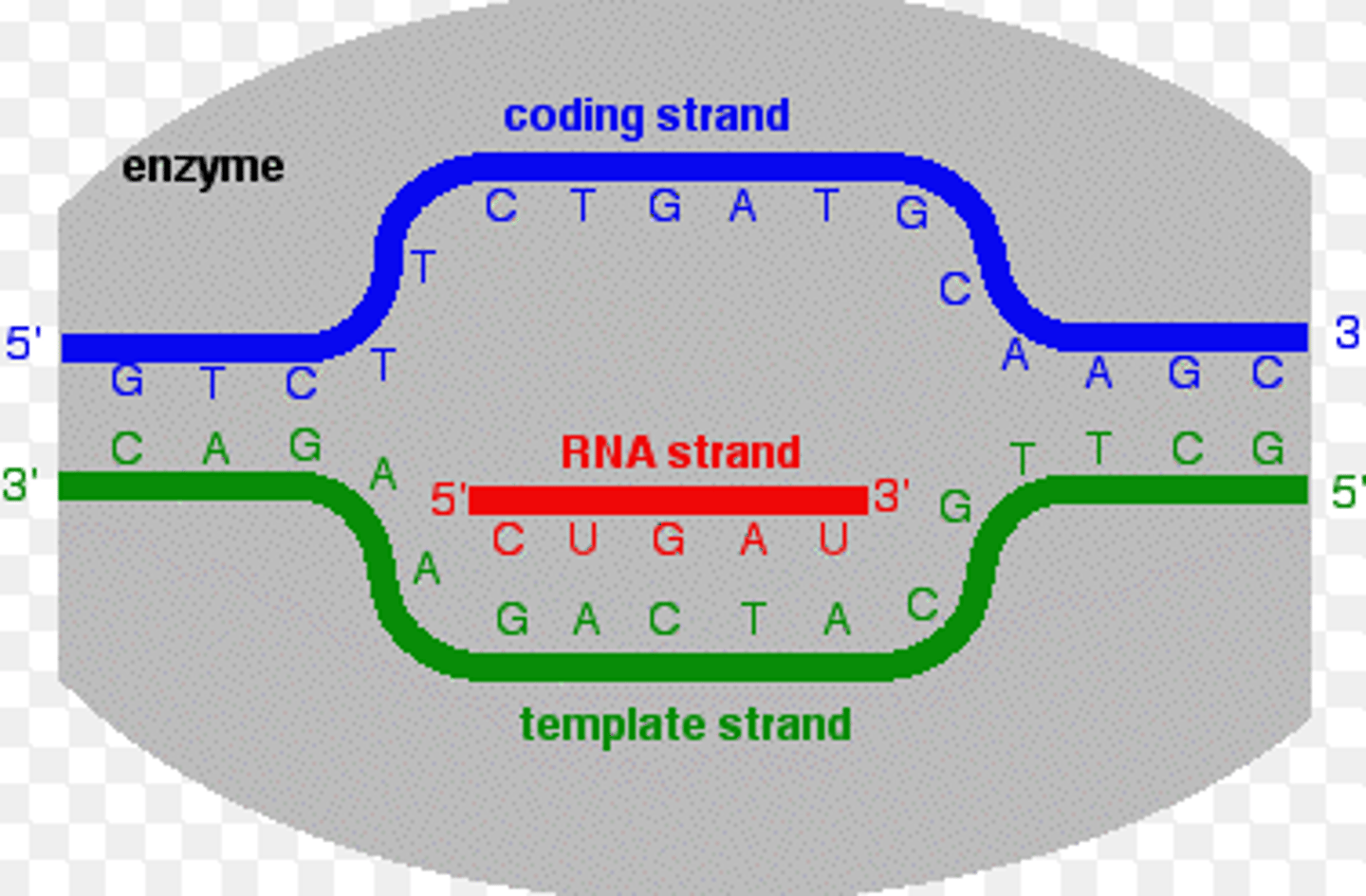
Transciption
1st step of protein synthesis where part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA (a gene) is copied into a complementary sequence in mRNA
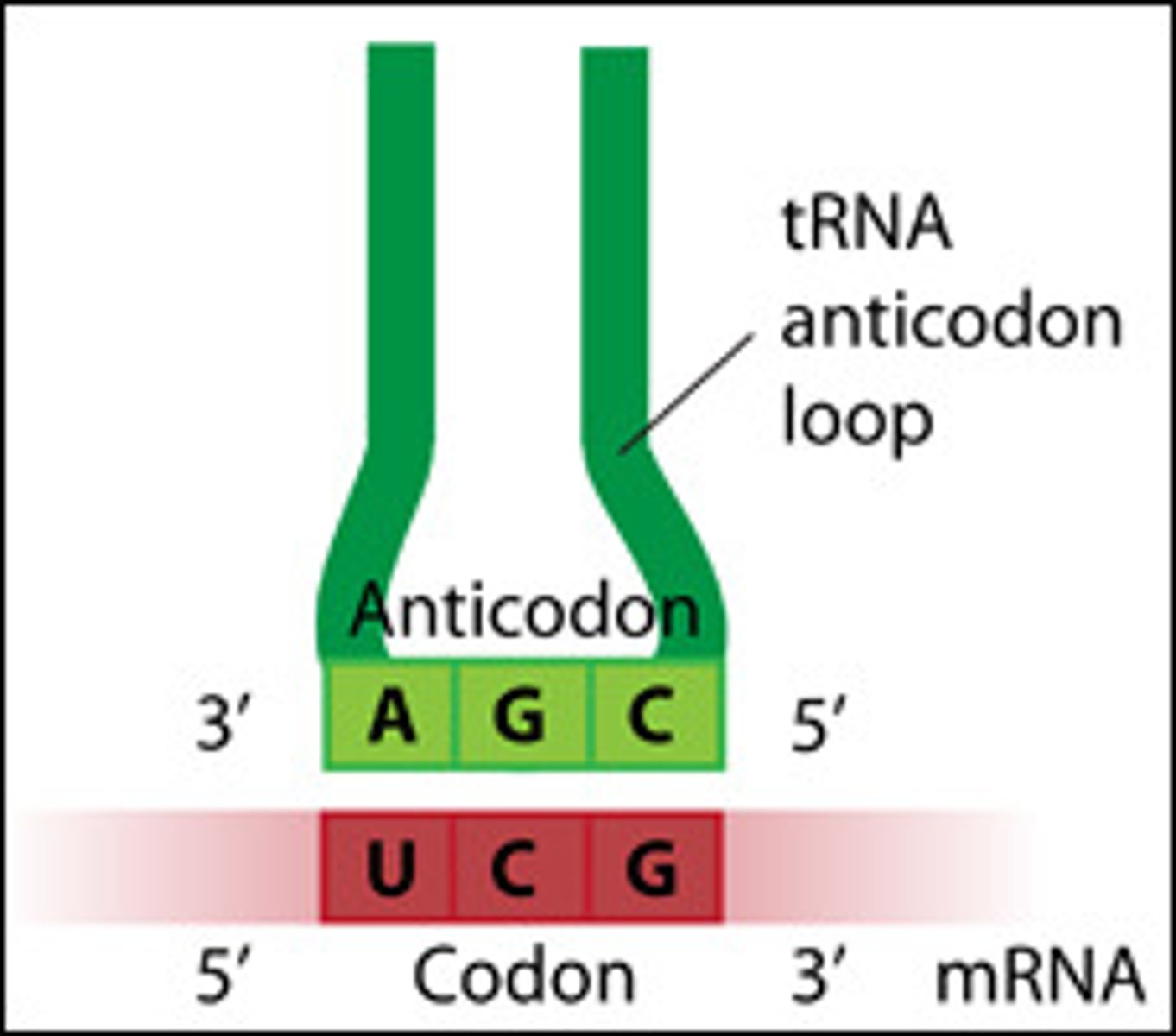
Anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
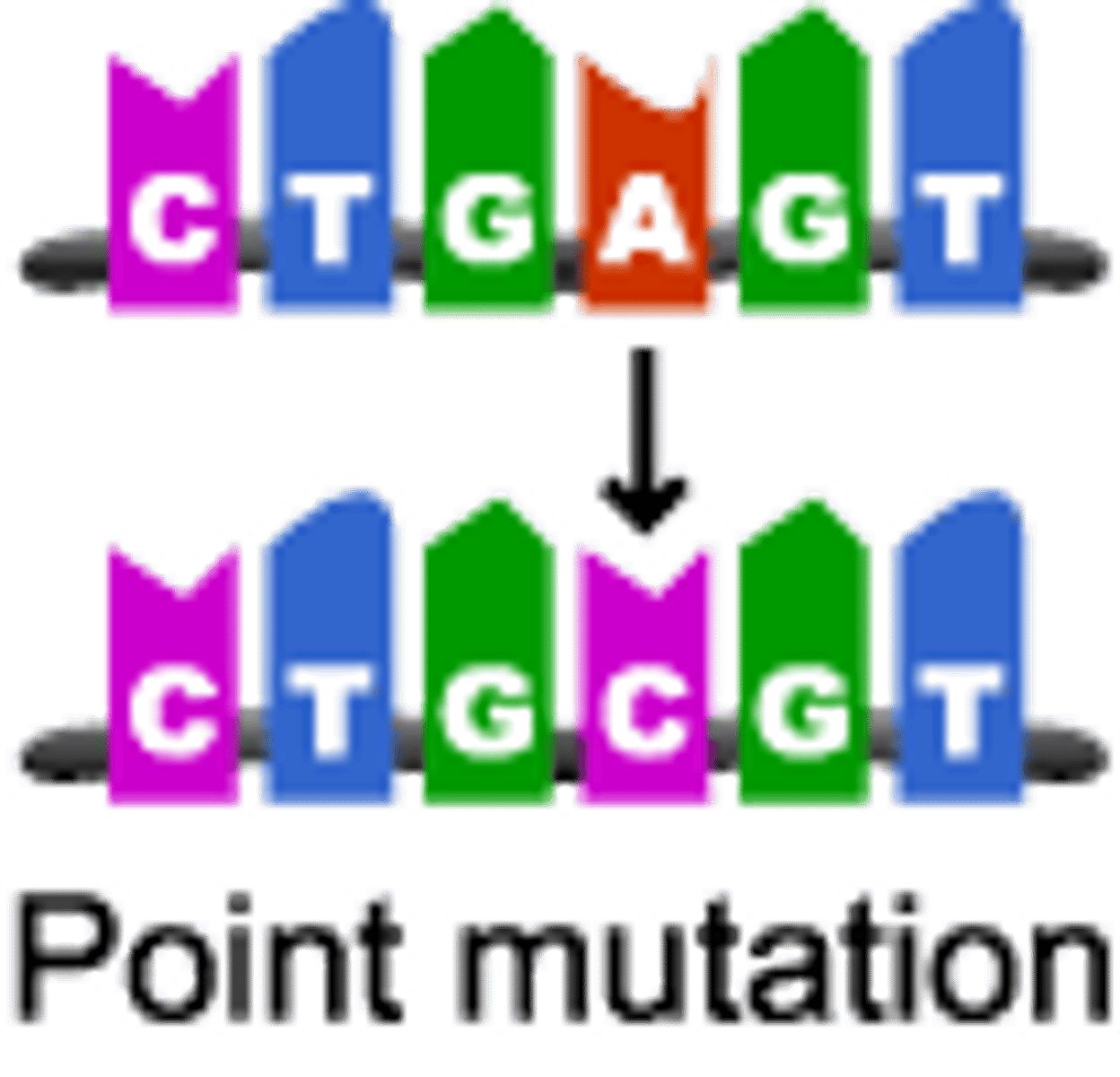
point mutation
gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed