forces on electrons
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
As we go across a period, from element to element (e.g. Li→Be→B→C→...),the nuclear charge...
increases by 1
As we go down a group from element to element (e.g. Li→Na→K→Rb...), the nuclear charge...
increases by more than 1
Nuclear charge is the...
the collective charge of all the protons in a nucleus
As an electron’s distance from the nucleus increases, the force it experiences...
decreases
The third shell can contain a maximum of how many electrons?
18
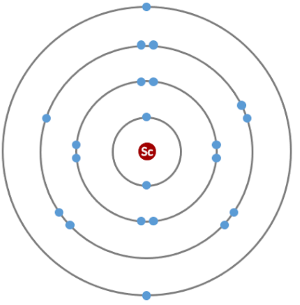
How do we represent the electrons in a scandium atom?
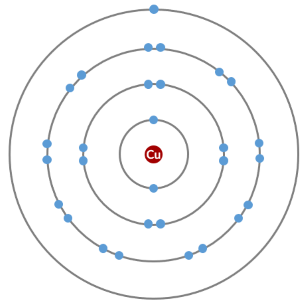
How do we represent the electrons in a copper atom?
The higher an atom’s nuclear charge...
the closer each shell is to the nucleus
Across a period, the distance between the nucleus and outer electrons...
decreases And that’s because…
nuclear charge increases across a period
Select the two main factors which affect the distance between the nucleus and outer electrons
nuclear charge
which shell the outer electrons are in
Down a group, the distance between the nucleus and outer electrons...
increases
And that’s because…electrons occupy a new shell that’s further from the nucleus
Instead of calculating all the individual repulsions between electrons in an atom, we assume that each electron...
shields some nuclear charge from other electrons
An electron in a shell closer to the nucleus...
shields the charge of one proton
An electron in the same shell...
shields a small amount of charge
Electron A will shield…
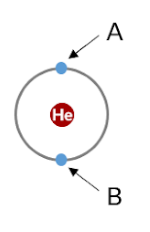
Some charge (much less than the charge of 1 proton) from electron B
Electron A will shield…
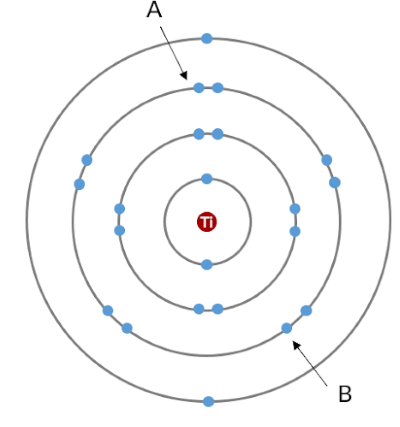
Some charge (much less than the charge of 1 proton) from electron B
As we move down a group, from beryllium to calcium what happens to inner and outer electrons?…
the number of inner electrons increases
the number of outer electrons stays the same
Across a period the amount of shielding on outer electrons...
stays roughly the same.
Down a group the amount of shielding on outer electrons…
increases significantly.
Which electron experiences more shielding?
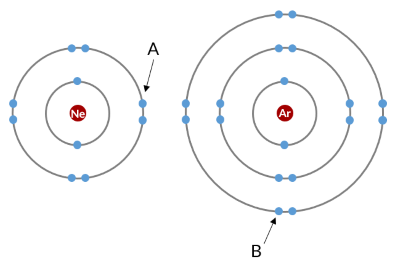
Electron B
Which electron experiences more shielding?
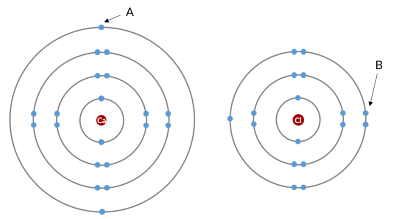
Electron A
elect the 3 key factors which affect an electron’s attraction to the nucleus.
shielding
nuclear charge
distance from nucleus
Across a period an outer electron’s attraction to the nucleus...
increases
what happens to nuclear charge down the group?
increases
Down a group the attraction of an outer electron to the nucleus...
decreases
In which atom do the outer electrons experience a stronger attraction to the nucleus?
An atom of helium
In which atom do the outer electron(s) experience a stronger attraction to the nucleus?
An atom of krypton