Forensics Exam 2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Where do most forensic anthropologists work?
Universities and museums.
How do anthropologists become certified to testify in court?
Through the American Board of Forensic Anthropology.
What methods are used to locate human remains?
Cadaver dogs and remote sensing instruments.
What tasks can an anthropologist perform at a crime scene?
Find small bones, recover clothing and trace materials, prevent bone damage, map bone locations, and maintain chain of custody.
How do anthropologists identify if a bone is human or non-human?
Most bones can be identified by sight; use a reference collection for difficult cases.
What traits are listed in a biological profile?
Age, sex, stature, and ancestry.
What individual characteristics might anthropologists record?
Surgical procedures and broken bones.
What are the limitations of determining time or cause of death?
Time of death can be estimated if soft tissue remains; cause of death can involve sharp force, blunt force, and antemortem vs postmortem breaks.
What is a coroner?
An elected official with no required medical training.
What is a medical examiner?
A physician with a medical degree who investigates deaths.
What is a forensic pathologist?
A doctor who studies disease and determines cause of death, performing autopsies.
What education is needed to be a medical examiner?
Undergraduate degree (4 years), Medical degree (4 years), Anatomic pathology training (4 years), and Forensic pathology fellowship (1 year).
How is a body examined by a medical examiner?
Chest opened, organs dissected, brain removed, tissues fixed in formaldehyde.
What samples are collected for toxicology and DNA?
Blood, urine, bile, and diseased tissues preserved.
What is the difference between cause, mechanism, and manner of death?
Cause: Disease or injury initiating death. Mechanism: Physical abnormality incompatible with life. Manner: Natural, accidental, homicidal, suicidal, or undetermined.
How do blunt force wounds and sharp force wounds differ?
Blunt force = lacerations with rough edges; Sharp force = incised wounds with sharp edges.
What are features of gunshot wounds at different ranges?
Contact = skin tearing and burning; Intermediate = stippling; Distance = clean hole with abraded rim.
Why is the entrance wound smaller than the exit wound?
Body supports skin at entrance; exit wound bursts outward unless shored.
How does a gunshot cause tissue damage?
Bullet pushes tissue aside creating cavity; tissue tears on rebound.
What questions does a forensic entomologist answer?
Insect infestation, body movement, wounds, drug use, time of death.
What are the two important arthropod orders?
Diptera (flies) and Coleoptera (beetles).
What are two important types of flies?
Blowflies (shiny) and flesh flies (gray, large).
Why are phorid flies useful?
They access bodies behind barriers.
Which insects undergo complete metamorphosis?
Flies and beetles.
How much of the immature insect sample is preserved?
50%.
Why are some maggots kept alive?
To raise to adults for species identification.
How are immature insects preserved?
In ethanol or Kahle's solution.
What is postmortem interval (PMI)?
Time between death and discovery.
Why is species identification important for PMI?
Different species grow at different rates.
How are insect species identified?
Morphology and mitochondrial DNA (cytochrome oxidase I).
How does maggot growth rate change with temperature?
Hotter = faster growth.
What 3 things are needed to estimate maggot age?
Species, instar stage, ambient temperature.
What are the raised and lowered areas of a fingerprint?
Ridges are raised; furrows are lowered.
What part of the finger makes contact with surfaces?
The fingertip.
Do identical twins have identical fingerprints?
No.
What are the 3 fingerprint patterns?
Arch, loop, and whorl.
What are the four types of fingerprint minutiae?
Bifurcation, ridge ending, island, and dot.
How does computer software compare fingerprints?
By comparing the location of minutiae.
What was the Bertillon system?
Using body measurements to identify individuals.
What is the Henry system for fingerprint classification?
Classifying fingerprints based on all 10 prints.
What is the US fingerprint database called?
AFIS (Automated Fingerprint Identification System).
What are the three types of fingerprints?
Visible, impression, latent.
What are five methods for developing fingerprints?
Dusting, iodine fuming, silver nitrate, ninhydrin, super glue fuming.
Which fingerprint development method works best for each surface?
Dusting (non-porous), iodine (lipids, porous/non-porous), silver nitrate (porous), ninhydrin (porous), super glue (non-porous).
How can fingerprints be documented?
Photograph, scan, lift with tape.
What are the ethical obligations of forensic scientists?
Tell the truth, no distortion, no omissions.
Why is a Sherlock Holmes witness bad?
Draws conclusions without considering other explanations.
What is the Frye Test for admissibility?
Checks if theory and method are generally accepted.
What is the Daubert Test for admissibility?
Checks testing, peer review, error rates, general acceptance.
What is Revised Rule 702?
Expert testimony must be based on sufficient facts and reliable methods.
Is forensic evidence circumstantial?
Yes.
How are forensic psychologists certified?
Through the American Board of Forensic Psychology.
What is the difference between psychology and psychiatry?
Psychology studies behavior; psychiatry treats mental disorders.
How might offenders use deception?
Proclaim innocence or use psychological defenses.
What is malingering?
Faking mental illness.
What is dissimulation?
Minimizing mental disorder symptoms.
What is the McNaughten Rule?
Defines not guilty by reason of insanity.
What is guilty but mentally ill?
Defendant was mentally ill but is still criminally responsible.
What is modus operandi?
A criminal's method of operation.
What is a criminal signature?
Unusual act or item left at a crime.
Which agencies offer profiling assistance?
FBI Behavioral Science Unit and NCAVC.
What is Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)?
A method to separate ink dyes using a solvent.
What are stationary and mobile phases in TLC?
Stationary phase is solid (silica/alumina); mobile phase is solvent.
What is Video Spectral Comparison?
Analyzes documents with UV, infrared, visible light.
How can ink appear under alternate light?
Glow, disappear, change color, or stay the same.
What are common class characteristics of paper?
Staple holes, additives, size, thickness, opacity, watermarks.
How can altered multipage documents be identified?
Microdots with hidden time and date info.
How do machines leave individual markings?
From natural mechanical variations.
How does handwriting change over time?
Changes in coordination and perception.
What is a requested vs. non-requested handwriting sample?
Requested: controlled but may be disguised; Non-requested: normal writing habits.
What are class characteristics of handwriting?
Slant, spacing, height ratio, beginning/ending strokes, size.
What is toxicology?
Study of poisons.
What is forensic toxicology?
Study of toxicity with legal implications.
What are three categories of forensic toxicology?
Postmortem drug testing, workplace drug testing, criminal drug testing.
What is the difference between toxicology and drug chemistry?
Toxicology tests biological samples; drug chemistry analyzes drugs.
What are advantages of blood, urine, hair, and breath samples?
Blood: current drugs; Urine: past drugs; Hair: long-term use; Breath: quick alcohol detection.
What drugs are included in a standard NIDA drug test?
Amphetamines, opiates, PCP, cocaine, cannabinoids.
What is immunoassay?
Rapid screening test using antibodies.
How are biological samples prepared for confirmation?
Extraction into solvent, then GC/MS analysis.
What is GC/MS?
Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry for drug identification. (drugs of abuse)
What are the three types of shoeprints found at crime scenes?
Visible 2D, visible 3D, latent 2D.
Why should all shoeprints be documented?
Due to numerous unique nuances.
How is a barely visible shoeprint located?
Dark room, bright low-angle light.
How is a 2D shoeprint collected?
Dusted, photographed, lifted with adhesive/gelatin.
What is electrostatic lifting?
Using a charge to lift dry materials onto film.
How is a 3D shoeprint collected?
Dental stone casting.
What are class and individual characteristics of shoes?
Class: Pattern, size. Individual: Cuts, rocks, wear marks.
How do individual shoe characteristics change over time?
Shoes wear down and get damaged.
Why are replacement tires easier to identify than OE tires?
They differ from the original tires.
What is a tread wear indicator?
Marks that appear after tire wears down.
What are wheelbase, track width, and turning diameter?
Wheelbase: front-to-back; Track width: side-to-side; Turning diameter: full wheel turn circle size.
How are tire impressions documented and collected?
Photographed with overlap and ruler, and cast with dental stone.
What are tire impression class and individual characteristics?
Class: Size, tread design. Individual: Cuts, rocks, wear patterns.
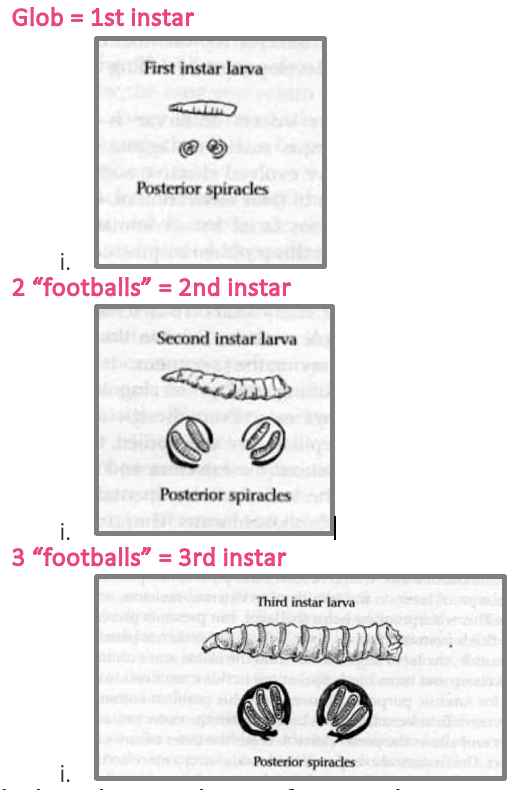
Maggot Instar Stages