Basic Principles of Genetics
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Hybrid
Offspring that are the result of mating between two genetically different parents. The opposite of a purebred
Genetics
The study of gene structure and the patterns of inheritance of traits form parents to offspring
Gregor Mendel
A European monk scientist who worked with pea plants. He discovered factors and that some were dominant and others were recessive. He also discovered that alleles for the same trait separate, and genes undergo independent assortment. Finally, he learned that two identical alleles are homozygous, and two different alleles are heterozygous
Blending Theory
A theory that inherited traits blend from generation to generation
Purebred
Offspring that are the results of mating between genetically similar kinds of parents. The opposite of hybrid
Genes
Units of inheritance usually occurring on a chromosome. The units are responsible for hereditary characteristics. Sequence of DNA
Alleles
Alternate forms of the same gene
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an individual
Homozygous Genotype
A genotype consisting of two identical alleles of a gene for a particular trait
Heterozygous Genotype
A genotype consisting of two different alleles of a gene for a particular trait
Phenotype
The observable or detectable characteristics of an individual organism
Dominant Allele
The general term for an allele that masks the presence of another allele in the phenotype
Recessive Allele
The general term for an allele that is masked in the phenotype by the presence of another allele
Principle of Segregation
Gregor Mendel's principle stating that the pair of genes from each parent separate and only one gene from each parent passes on to offspring
Principle Of Independent Assortment
Gregor Mendel's principle stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring independently so that new combinations of genes, present in neither parent are possible
Punnet Square
A method showing all of the potential combinations of offspring genotypes that can occur and their probability given the parent genotypes
Homozygous Dominant
The term for genotype in which there are two dominant alleles
Heterozygous
The term for a genotype in which there is a dominant allele and a recessive allele
Homozygous Recessive
The term for a genotype in which there are two recessive alleles
Mendelian Genetics
The general term for inheritance patterns which can be explained by simple rules of dominance and recessiveness of genes
Polygenic Trait
A trait that is determined by the combined effect of more than one gene
Incomplete Dominance
Inheritance pattern in which a trait is expressed in the phenotype of heterozygous individuals as an apparent blend or an intermediate expression
Codominance
The inheritance pattern in which two different alleles for a trait are expressed unblended in the phenotype of heterozygous individuals
Multiple Allele Series
The inheritance pattern in which a gene has more than two alleles
Modifying Gene
Genes that can alter how certain other genes are expressed in the phenotype
Regulator Genes
Genes that can neither initiate or block the expression of other genes. They are responsible for changes that occurred in our bodies as we grow older
Incompletely Penetrant Genes
Genes whose effects does not normally occur unless certain environmental factors are present
Sex-Limited Genes
Genes that are inherited by both men and women that are normally only expressed the phenotypes of one of them
Sex-Controlled Genes
Genes that are expressed in both men and women but differently
Genome Imprinting
An inheritance pattern in which a gene will have a different effect depending on the gender of the parent from whom it is inherited
Pleiotropy
The inheritance pattern in which a single allele is responsible for a variety of traits
Stuttering Alleles Or Unstable Alleles
Defective alleles that have segments which are doubled in their transmission from generation to generation
Monozygotic Twins
Identical twins that are genetically the same
Human Genome Project
The international research effort design to discover all human genes and to determine their functions
Fertilization
When sex cells join
True Breeding
Producing offspring identical to itself
Trait
Specific characteristic
Gamete
Sex cell
Homologous
Corresponding chromosomes from each parent
Diploid
Contains two sets of homologous chromosomes
Haploid
Contains only one set of chromosomes
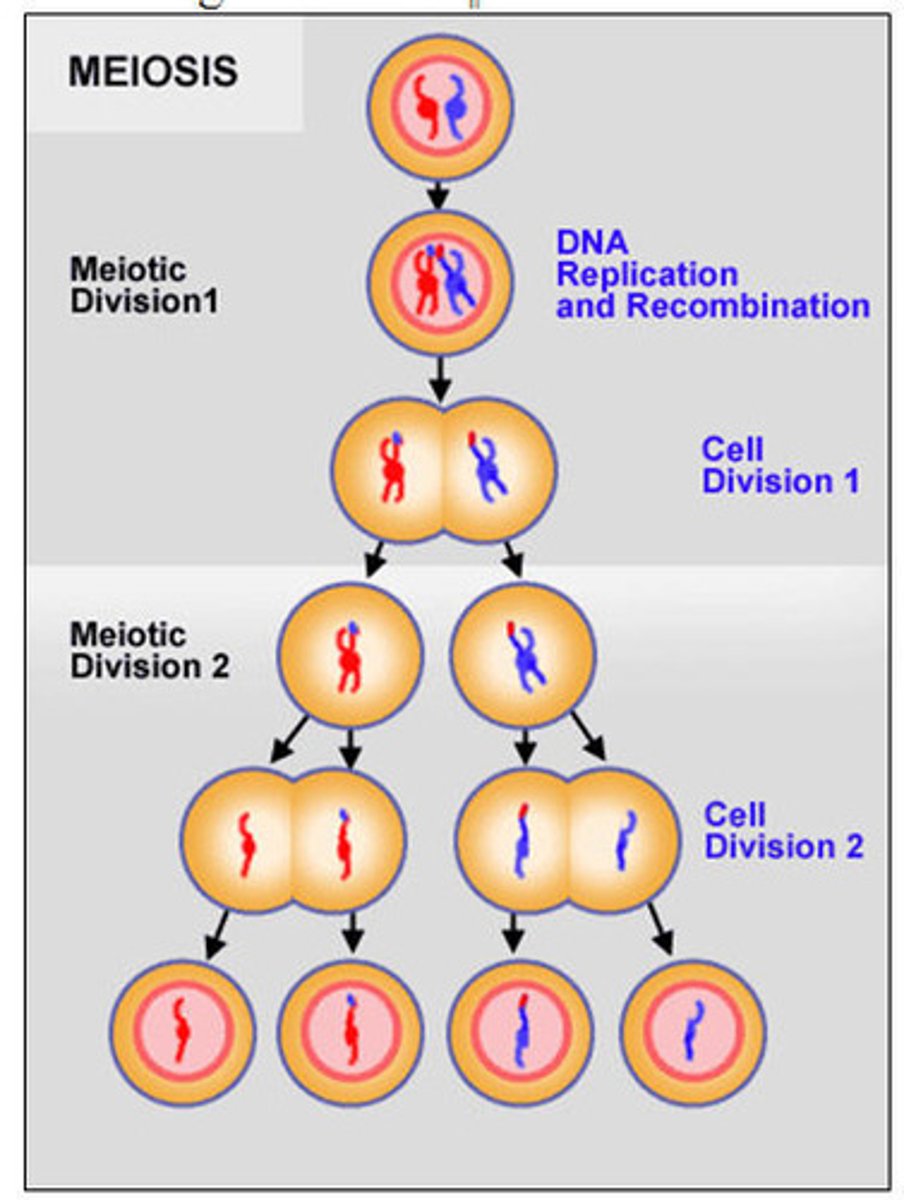
Meiosis
Sex cells, double division, reducing chromosomes to half
Heredity
The passing of traits from parents to their offspring
Segregation
The separation of paired alleles during meiosis so that members of each pair of alleles appear in different gametes
Test cross
First introduced by Gregor Mendel, involves the breeding of an individual with a phenotypically recessive individual, in order to determine the zygosity of the former by analyzing proportions of offspring phenotypes. Zygosity can either be heterozygous or homozygous.
Translation
The process in which ribosomes create proteins. Messenger RNA (mRNA)—produced by transcription from DNA—is decoded by a ribosome to produce a specific amino acid chain
Transcription
The process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). This takes place in the nucleus
Crossing-over
The exchange of genes between two chromosomes, resulting in non-identical chromatids that comprise the genetic material of gametes. This process occurs during Prophase I of Meiosis, just prior to chromosome alignment and splitting of the cell
Self-pollination
The pollination of a flower by pollen from the same flower or from another flower on the same plant
Cross-pollination
The transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organ of one plant to the female reproductive organ
Probability
The likelihood of an event to occur
Zygote
Egg and sperm combined
Applying Mendel's principles
Probability rules apply to genetics, and genetic problems are solved using Punnet Squares
Explain how DNA was discovered
In the early 1950s two scientists, Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins, studied DNA using x-rays. Franklin produced an x-ray photograph that allowed two other researchers, James Watson and Francis Crick to work out the 3D structure of DNA. The structure of DNA was found to be a double helix
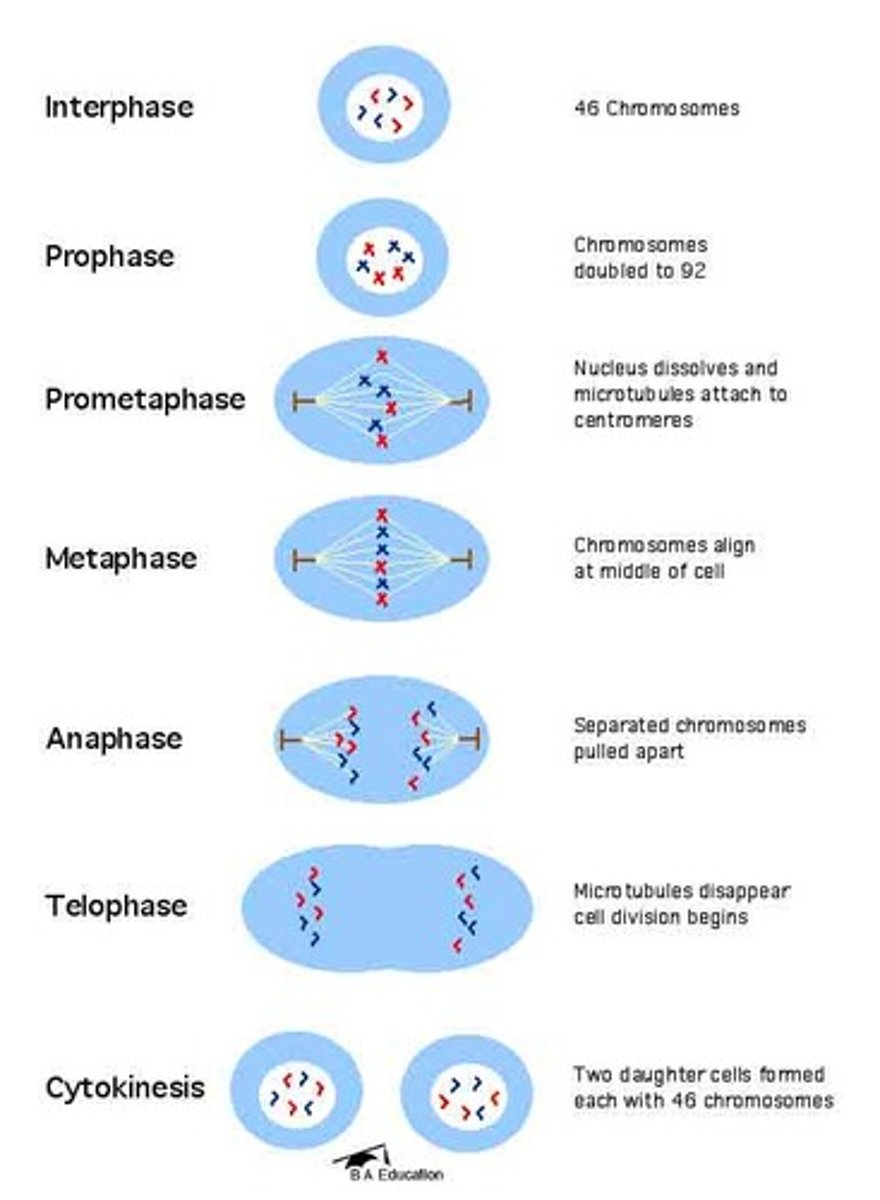
Draw and label mitosis
Draw and label meiosis