Section B:the living world
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
ecosystem
is all the biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) parts of an area
how can the organisms in an ecosystem can be classified as
-producer
-consumer
-decomposer
producer
uses sunlight energy to produce food
consumer
gets its energy by eating other organisms
decomposerr
gets energy by breaking dowd dead material
the nutrient cycle
shows how these organisms are linked via transfer of nutrients
what do food chains and food webs show
how each part of the ecosystem depends on other parts. if one part changes it affects all the other parts that depends on it (interdependence)
7 major types of ecosystems
tundra
taiga (boreal forests)
tropical rainforests
hot deserts
grassland
temperature deciduous forests
polar
tundra
-found at high latitudes in northern europe, canada and alaska
-winters are very cold, summers are very brief and there is little rainfall
-hardly any trees, but there is moss, grass and low shrubs. there is also permafrost on the ground all year
taiga
-found at mid-high latitudes
-winters are cold and dry, summers are mild and mosit
-trees are coniferous and have needles to conserve energy
tropical rainforest
-found at the equator between the tropics
-it is hot and wet all year round
-this is an area of lush forest with dense canopies of vegetation forming distinct layers
hot deserts
-found between 15 and 35 degrees north and south of the equator
-little rainfall and extreme temperatures( 45 degrees during day and 0 at night)
- hardly any vegetation, some needle like trees
temperate grasslands
-found at higher latitudes
-more variation in temp and less rainfall compared to savannah grasslands
-no trees-just grass
savannah grassland
-found between tropics
-there are dry and wet seasons although rainfall is still relatively low
-mostly grasses with scattered trees
temperate decidous forest
-found mainly at mid-latitudes where there are four dinstinct seasons
-summers are warm and winters are relatively mild and theres rainfall all year round
-decidous trees lose their leaves in the winter to cope with the winter
polar
-found around north and south poles
very cold and icy dry
-not much growth at all, they remain dark for several months each year so the growing season is very short-only 2 months
introduction to Epping Forest ecosystem UK
-located east of London, Epping Forest is all that remains of a larger forest that colonised. England at the end of the last Ice Age
-bogs and ponds in the forest have their unique species including 20 kinds of dragonfly
-fro 1000 years, Epping Forest has been managed in a variety of ways:as hunting grounds for royalty, a timber resource and recreation
biodiversity of Epping Forest
-a large number of native tree species
-a lower shrub layer of holly and hazel at 5 metres, overlying a field layer of grasses, brambles bracken fern and flowering plants
-38 bird species
-700 types of fungi, which are important decomposers
how is the ecosystem interdependent
-the forests producers, consumers and decomposers are all interdependent which is shown through the annual life cycle of the tree
-most trees are deciduous meaning they lose leaves during winter
-by mid-autumn the forest floor is covered with a thick layer of leaves. by spring the lea litter has all but disappeared-the decomposers and detritivores work is now complete. nutrients stored in the leaves are converted to humus in the soil to support the new seasons plant growth including fruits and berries
how are people interdependent on the ecosystem
-coppicing was common (cutting back trees to encourage the new growth of wood)
-visitors pick berries and flowers and in turn this helps spread the seeds which stick to their clothing
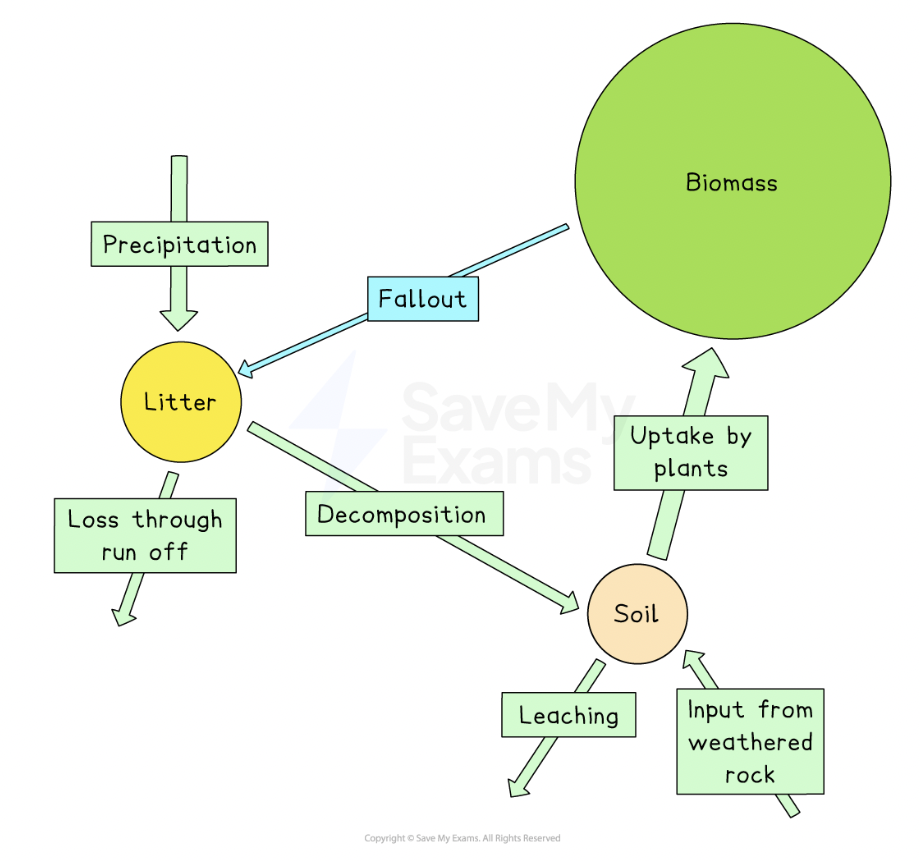
what explains the characteristics of epping forest’s nutrient cycle
-the biomass store is large because of the great height of trees and the dense undergrowth beneath them. the soil store is large too because there is always plenty of humus.
-the high flow rates between litter, soil and biomass stores reflect the vigorous cycle of new growth that takes place each year. the forest also loses a lot of nutrients each year, via leaching during episodes of heavy rainfall
ecosystem balance
A stable ecosystem is one where all the biotic and abiotic components are in balance so that the populations remain constant
natural events that disrupt the ecosystem balance
Wildfires caused by lightning
Climate change (though it can be argued this is human-induced)
Spread of invasive species
Disease
Extreme weather events: Flood or drought
human activities that disrupt the ecosystem balance
Deforestation
Hunting of animals/birds
Introduction of invasive species such as grey squirrels which outcompete red squirrels for food and space. They also carry a disease called squirrel pox which kills red squirrels but not grey squirrels
Hedgerow removal
Changes to water supply/drainage patterns or temperature
Addition of chemicals: Fertilisers/herbicides/pesticides
Fires used to clear land
physical characteristic of a tropical rainforest
-contains the highest biodiversity in the world
-contains many indigenous people who have adapted to live in the rainforests and make a living by hunting, farming and fishing
-most of the trees are evergreen to help them take advantage of the continual growing season
-many trees are very tall and the vegetation cover is dense-very little light reaches the forest floor
-lots of epiphytes (plants that grow on other living plants and take the nutrients from the air)
-the soil is not very fertile as heavy rain washes away the nutrients but there is surface nutrients due to decayed leaf fall
-the climate is the same all year round-generally beteen 20-28 degrees celsius (because the suns energy is more intense near equatpr as it is overhead all year round)
-rainfall is very high, around 2000mm per year (it rains every day)
describe interdependence in tropical rainforest
litter(dead organic material such as fallen leaves or tree trunks or dead animals) - nutrients become part of the soil when dead matter decomposes - soil(developed by the mxing of dead organic material with weathered bedrock)- plants take up nutrients which are dissolved in soil- biomass(all living things in the ecosystem both plants and animals) - nutrients fall to the ground when plants and animals die-litter
humans can get fruits from the trees
structure of tropical rainforest
Ground layer (0m)
Shrub layer (3-4m)
Under canopy (15m)
Canopy (30m)
Emergents (45-55m)
Plant adaptations
Waxy leaves with drip tips: These ensure that rainwater runs off the leaf and does not remain which would encourage mould growth or break the leaf
Buttress roots: These large roots above the ground which help to support the very tall trees because the roots below the surface are shallow
Lianas: Vines which use the tall trees as support to reach the sunlight
Epiphytes: These are plants which grow on trunks and branches of trees getting nutrients from air, rain or debris accumulating around the plant
Straight, smooth trunks: To reduce the number of epiphytes using the tree
Animal adaptations
Sloth: Algae grow in the fur of the sloth helping to camouflage it
Toucan: They have a large bill to reach and cut fruit from the branches of trees. They are also strong allowing them to crack nuts open
Primates: They have prehensile tails to help them climb trees
Geckos: They have large, flattened toe pads with sticky scales which allow them to grip the smooth tree trunks
Stick Insects: Their stick and leave shapes help them to be camouflaged
Biodiversity issues
Tropical rainforests have some of the highest levels of biodiversity of any ecosystem
The wet and warm climate means there is year round growth
Wide variety of plants provides a range of habitats and food
Rapid nutrient cycling increases plant growth
Lack of human activity has in the past meant that plants and animals are undisturbed
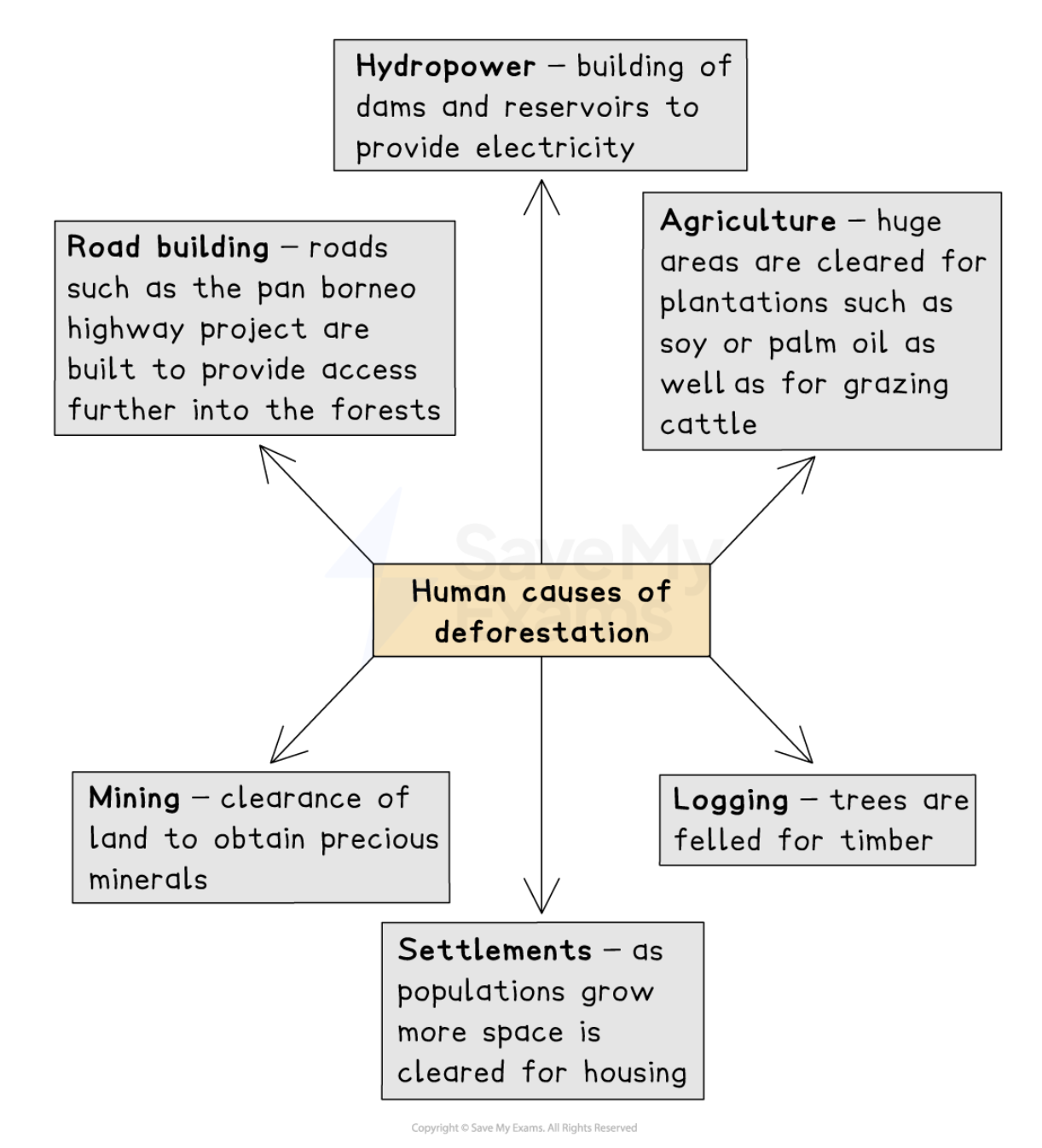
Threats to the rainforest biodiversity are increasing mainly due to human activity and include:
Agriculture, particularly large scale slash and burn
Mining
Hydroelectric power
Logging
Road building and settlements
Wildfires (although natural, increasing frequency and severity is linked to climate change)
The interdependence of the rainforest components means that when one element is affected it then impacts all the other components
A decline in one species (especially if it is a keystone species) can lead to a decline in other species
The Zam tree produces seed which are food for agouti and who disperse the seeds
The agouti is hunted for meat reducing their populations this means fewer seeds are dispersed
Fewer new Zam trees will germinate and so there is less food for leaf cutter ants which in turn means less food for the tree frogs which eat the ants and the snakes which prey on the frogs
The Zam tree is pollinated by a particular species of butterfly. Without the flowers the numbers of the butterfly species will decline - this also affects the beetles which lay their eggs in the butterfly faeces
Plant and animal species may become extinct - this may happen to some before they are even discovered
Important medicinal plants may become extinct
Indigenous communities may be forced to abandon their traditional lifestyle due to the lack of food to hunt and gather
Changing rates of deforestation
Deforestation is the felling and clearance of trees
Brazil, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Bolivia and Indonesia are experiencing the highest levels of deforestation in the world
Rates of deforestation steadily increased from 2001 to 2016
Since 2016 there has been a slight decrease in deforestation of tropical forests
Causes of deforestation
Wildfires are a natural cause of deforestation:
The frequency and severity of wildfires have increased this is linked to human induced climate change
Impacts of deforestation
Areas that have been deforested are planted with monoculture which reduces biodiversity
Interception and infiltration decrease which reduces evapotranspiration and as a result precipitation decreases
This also increases overland flow which leads to soil erosion and sedimentation of the rivers
Sediment builds up on riverbeds reducing their capacity and increasing the flood risk
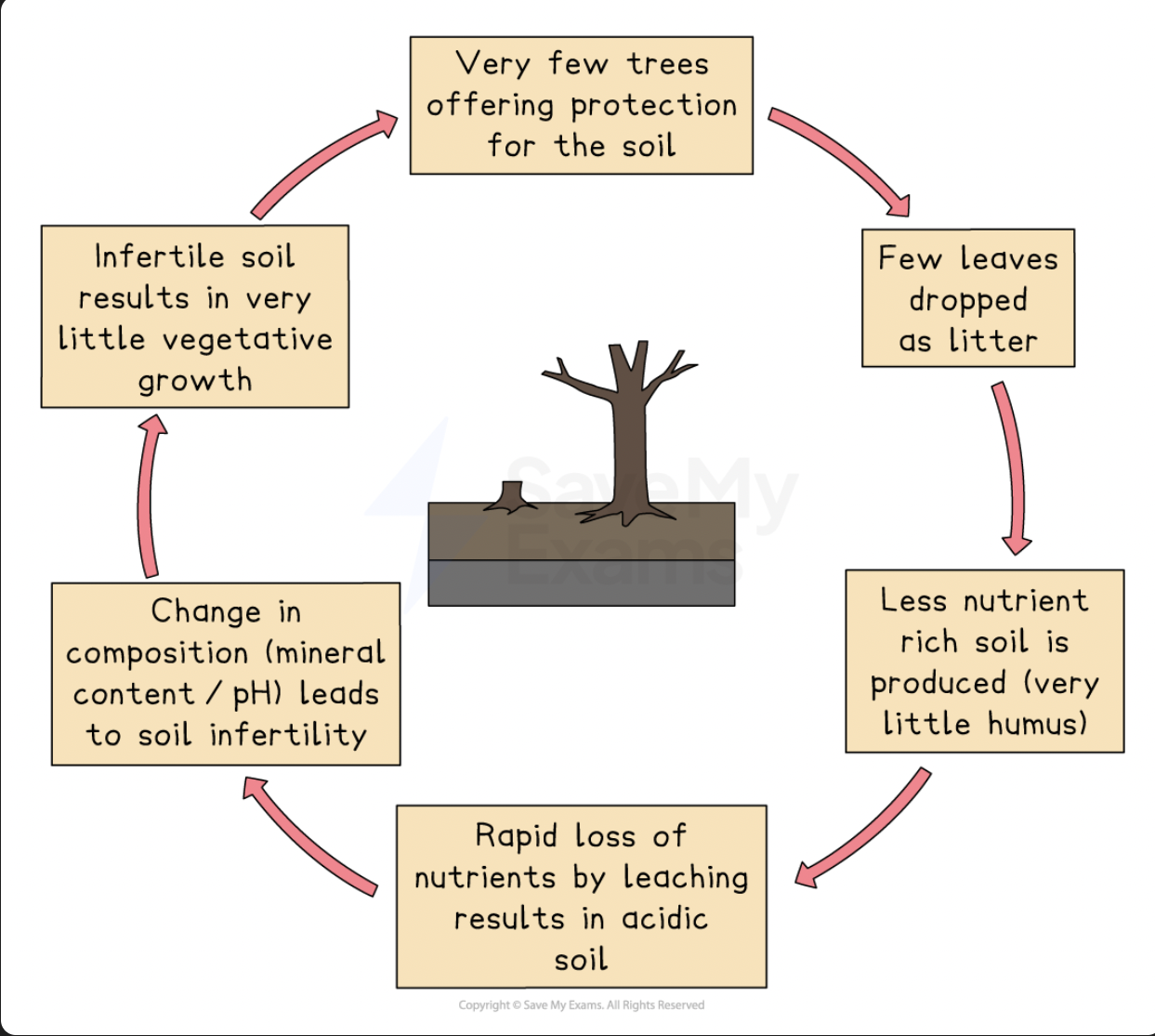
Lack of interception increases the leaching of nutrients
Fewer trees increase the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere adding to the enhanced greenhouse effect
Soils become less fertile and drier
They may turn reddish brown due to increased iron oxide
Impact on the nutrient cycle
Social impacts of deforestation
Indigenous communities have less land to sustain their traditional way of life this means:
Land does not get the opportunity to recover
Less food available
Improved quality of life for some people due to increased income and jobs
Indigenous communities may give up their way of life leading to a loss of culture and traditions
Increased risk of landslides which can destroy homes and block roads
Loss of potential medicines
Increased risk of flooding settlements
Economic impacts of deforestation
More jobs available in mining, forestry, agriculture and HEP
Increased income for the country through the export of goods from the forest - minerals, timber, crops
Almost a quarter of Brazil's GDP comes from activities in the deforested areas of the Amazon
deforestation in Brazil
Brazilian rainforest occupies the huge lowland basin drained by the Amazon and its tributaries.
-most of clearance has been south of Amazon- this part most accessible from Brazil’s main cities such Brasilia
for centuries the rainforest has been lived in and used by indigenous tribes for
-harvested fruits and nuts
-cut wood for fuel
-used timber for build dwellings
-discovered cures for various illnesses
-cleared small areas by a technique known as slash and butn
logging
Timber companies will get trees such as mahogany and teak and sell them to other countries to make furniture. smaaller trees are often used as wood for fuel or made into pulp or charcoal
mineral extractionn