EARTH SCIENCE
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
MINERAL
is a naturally occurring inorganic solid that possesses a definite chemical structure
ROCKS
is an aggregate or combination of one or more minerals
SOIL
is made up of tiny bits of rocks and organic materials from plants and animals
OCEANIC CRUST
mainly basalt with limestone, serpentine, and clay
CONTINENTAL CRUST
consists of mostly granite and some quartz
UPPER MANTLE
is thought to contain rocks such as olivine, peridotite, and garnet
OUTER CORE
The _______ is liquid iron, flowing plastically
INNER CORE
The _______, however is solid because of such extreme pressure.
LITHOSPHERE
consists of the crust and the upper mantle. As we read before, crust can be divided into two different types, continental and oceanic crust. Both types “float” on the denser mantle.
CONTINENTAL CRUST
is about 25-90 km (15-55 mi) thick and divided into tectonic plates. These plates move slowly (just a few centimeters) each year over the more fluid mantle
OCEANIC CRUST
which is much thinner than continental crust at only 6-11km (3-6 mi) thick, is where new crust is formed. This can happen by two plates moving apart and magma from the asthenosphere coming up and cooling to form new seafloor.
ASTHENOSPHERE
The Asthenosphere is more fluid than the rigid Lithosphere above it, with a plastic-like texture.
CONVERGE
Mountains are formed when two plates _______, or flow towards each other, and possibly even cause asthenospheric material to flow up through causing a volcano.
DIVERGE
Asthenosphereic material can also escape to the surface when plates move away from each other, or diverge.
MOHO
We move from the Asthenosphere into the Upper Mantle through the Mohorovicic discontinuity, or _____. It is characterized by a drastic increase in seismic rate
CONVECTIONS
Since the mantle is molten, flowing freely, it has ____ similar to those that occur when boiling water on a stove
OUTER CORE
is liquid iron alloy, at extremely high temperatures flowing molten
INNER CORE
is thought to be solid iron, and has been thought to be pure iron for many years until recently
PANGAEA
The theory of a landmass that existed when all the continents were joined from about 300 to 200 million years ago.
SEISMIC ACTIVITY
Shock wave of force or pressure that travels through the Earth.
SHIELD VOLCANO
This is a broad, shallow volcanic cone, which arises because the running lava, which is fluid and hot, cools slowly.
DOME VOLCANO
This one has a steep, convex slope from thick, fast-cooling lava
ASH-CINDER VOLCANO
Throws out - besides lava - much ash into the air. Through this the volcanic cone is built up from alternate layers of ash and cinder.
COMPOSITE VOLCANO
These are also built up from alternate layers of lava and ash but, besides its main crater, it has many little craters on its slope.
CALDERA VOLCANO
An older volcano with a large crater which can be 62 miles(100km) wide. In this crater many little new craters are formed.
IGNEOUS ROCKS
formed when magma or lava solidified. (granite, basalt, rhyolite)
EXTRUSIVE ROCKS
obsidian, pumice, basalt, felsites
INTRUSIVE ROCKS
granite, gabbros
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
limestone, conglomerate, dolomite, shale
METAMORPHIC ROCKS
rocks that have undergone changes due to heat and pressure
e.g. marble (from limestone), slate(from shale)
EROSION
the process by which rock fragments and sediments are carried along by such agents
DEPOSITION
the process by which rock fragments and sediments carried by agents of erosion are dropped or deposited in other places
COMPACTING
the process by which rock fragments and other materials that accumulated (usually at the bottom of a thick column of water), get cemented together and harden into rock
SEISMOGRAPH
an instrument that records earthquake waves
PRIMARY (P) WAVES
“push-pull waves”; can travel through solids, liquids and gases; temporarily changes the volume of the intervening material
SECONDARY (S) WAVES
shake the particle at their right angle to their direction of travel; cannot travel through fluids; temporarily change the shape of the material that transmits them
SEISMIC
______ waves travel at different speeds in materials of different densities.
MAGNITUDE
an index of the quakes energy at its source; Richter Scale
INTENSITY
measures the strength of shaking produced by an earthquake at a particular location; Mercalli Intensity Scale
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
the present seven continents originated from a big landmass called Pangea
PROOF FOR CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
fit of south america and africa
fossil evidences
rock structures
ancient climate
PLATE TECTONIC THEORY
lithosphere consists of plates that are in motion relative to each other
COLDER
Older crust tends to be ________________, and therefore is denser than younger crust
DIVERGENT
Of the three known boundaries, the "East-Pacific" Ridge or Rise, is considered to be a _______________________ boundary.
PACIFIC PLATE UNDER PHILIPPINE PLATE
The Mariana Trench was most likely created by the convergence of the
ASTHENOSPHERE
Which part of Earth’s interior is inferred to have convection currents that cause tectonic plates to move?
THREE
To find the epicenter of an earthquake, at least _____ seismic stations are needed.
LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION
Lasers are sometimes used to detect movements along faults. LASER is an acronym for: ____________
AROUND PACIFIC PLATE
The Ring of Fire is located...
CONVERGENT PLATE
Between the 3 known types of plate boundaries, the ___________________ zone is most dangerous to human life.
COMPRESSION
The type of stress that can form a trench is _______.
DECREASES
What happens to the amount of kinetic energy carried by the wave as the wave moves away from the focus?
STREAK
the _____ of the mineral is always the same
HARDNESS
Moh’s scale is used to determine the ________ of a mineral.
TROPOSPHERE
The lowest layer where the weather happens. It contains over 75 percent of all the atmosphere's gases and vast quantities of water and dust.
TROPOSPHERE
Air pressure drops, and temperatures get colder, as you climb higher in the _______
STRATOSPHERE
The infamous ozone layer is found within the _______ . Ozone molecules in this layer absorb high-energy ultraviolet (UV) light from the Sun, converting the UV energy into heat.
WARMER
The higher you get in the stratosphere, the _______ the air gets.
MESOSPHERE
Most meteors burn up in the _____ . Unlike the stratosphere, temperatures grow _______ as you rise up through the this layer
MESOSPHERE
The coldest temperatures in Earth's atmosphere, about -90° C (-130° F), are found near the top of this layer. The air in the ________ is far too thin to breathe
THERMOSPHERE
High-energy X-rays and UV radiation from the Sun are absorbed in the ________, raising its temperature to hundreds or at times thousands of degrees. However, the air in this layer is so thin that it would feel freezing cold to us
EXOSPHERE
others consider the _________ to be the actual "final frontier" of Earth's gaseous envelope. As you might imagine, the "air" in this layer is very, very, very thin, making this layer even more space-like than the thermosphere.
IONOSPHERE
is part of the thermosphere. It is made of electrically charged gas particles (ionised). The particles get this electric charge by ultraviolet rays of the sun. It is the reason why places all over the world can be reached via radio.
WEATHER
describes the condition of the atmosphere in a particular time (cool and dry, humid, windy, rainy, or stormy)
CLIMATE
average weather in a region over a number of years or usually decades (tropical)
CLOUDS
little drops of water or ice hanging in the atmosphere. A ceilometer measures the height of this
CYCLONES
low pressure areas in the tropics
FOSSILS
______ are the preserved remains of plants and animals whose bodies were buried in sediments, such as sand and mud, under ancient seas, lakes and rivers. Fossils also include any preserved trace of life that is typically more than 10 000 years old.
UNEARTHED
The word fossil is derived from the Latin fossilis meaning ‘_________’.
BODY FOSSILS
Preserved evidence of the body parts of ancient animals, plants and other life forms are called ‘________’.
TRACE FOSSILS
‘____ ______’ are the evidence left by organisms in sediment, such as footprints, burrows and plant roots.
AGE CORRELATION
For geologists, fossils are one of the most important tools for ________
MARINE, MOUNTAINTOPS
Fossils are more likely to be preserved in ______ environments for example, where rapid burial by sediments is possible. Less favourable environments include rocky _______ where carcasses decay quickly or few sediments are being deposited to bury them.
PRESERVATION
The rarest form of fossilization is the ______ of original skeletal material and even soft tissue. For example, insects have been preserved perfectly in amber, which is ancient tree sap.
PERMINERALIZATION/PETRIFICATION
The most common method of fossilization is ________. After a bone, wood fragment, or shell is buried in sediment, it may be exposed to mineral-rich water that moves through the sediment. (Ex. Fossil dinosaur bones, petrified wood, and many marine fossils)
MOLDS AND CASTS
In some cases, the original bone or shell dissolves away, leaving behind an empty space in the shape of the shell or bone. This depression is called a _______. Later the space may be filled with other sediments to form a matching ______ in the shape of the original organism. (Ex. mollusks (clams, snails, octopi and squid))
REPLACEMENT
In some cases, the original shell or bone dissolves away and is replaced by a different mineral. For example, shells that were originally calcite may be replaced by dolomite, quartz, or pyrite.
COMPRESSION
Some fossils form when their remains are compressed by high pressure. This can leave behind a dark imprint of the fossil. _______ is most common for fossils of leaves and ferns, but can occur with other organisms, as well
LESS SIMILAR
Fossils in relatively young rocks tend to resemble animals and plants that are living today. In older rocks, fossils are ________ to modern organisms.
INDEX FOSSILS
Some fossils proved particularly useful in matching up rock layers from different regions. These fossils, called _________, are widespread but only existed for a relatively brief period of time.
MICROFOSSILS
Ammonites, trilobites, and graptolites are often used as index fossils, as are various ________, or fossils of microscopic organisms.
LIVING FOSSILS
In contrast to index fossils, _______ are organisms that have existed for a tremendously long period of time without changing very much at all. For example, the Lingulata brachiopods have existed from the Cambrian period to the present, a time span of over 500 million years
MARINE, TERRESTRIAL
The first clue that fossils can give is whether an environment was ______ (underwater) or ________ (on land)
CLIMATE
Fossils can also reveal clues about past _______. For example, fossils of plants and coal beds have been found in Antarctica. Although Antarctica is frozen today, in the past it must have been much warmer.
MASS EXTINCTIONS
One of the most fascinating patterns revealed by the fossil record is a number of _________, times when many species died off.
PRESERVATION
________ as a fossil is a relatively rare process. The chances of becoming a fossil are enhanced by quick burial and the presence of preservable hard parts, such as bones or shells.
FOSSILS
_______ give clues about the history of life on Earth, environments, climate, movement of plates, and other events.
LAW OF SUPERSITION
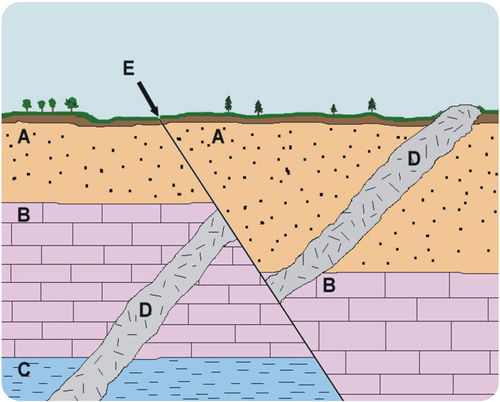
A = ???
LAW OF LATERAL CONTINUITY
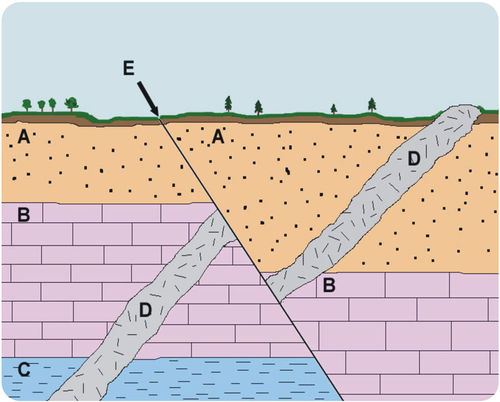
B = ???\
LAW OF ORIGINAL HORIZONTALITY
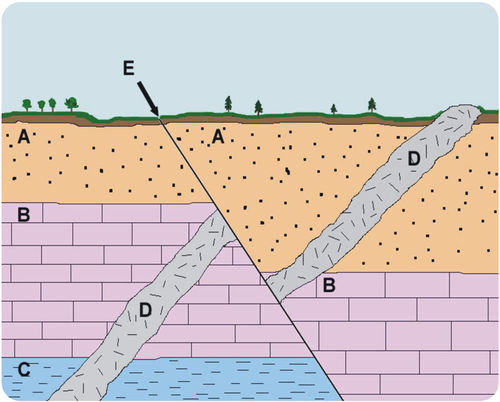
C = ???
LAW OF CROSS-CUTTING RELATIONSHIPS
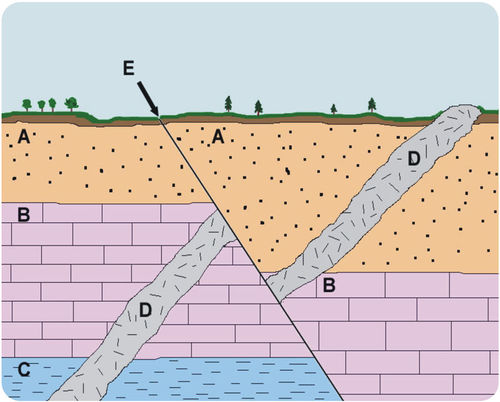
D = ???
STRATIGRAPHY
The study of rock strata
LAW OF SUPERSITION

New rock layers are always deposited on top of existing rock layers. Therefore, deeper layers must be older than layers closer to the surface. This is the ________.
LATERAL CONTINUITY

Rock layers extend laterally, or out to the sides. They may cover very broad areas, especially if they formed at the bottom of ancient seas. Erosion may have worn away some of the rock, but layers on either side of eroded areas will still “match up.”
ORIGINAL HORIZONTALITY
Sediments were deposited in ancient seas in horizontal, or flat, layers. If sedimentary rock layers are tilted, they must have moved after they were deposited.
CROSS-CUTTING RELATIONSHIPS
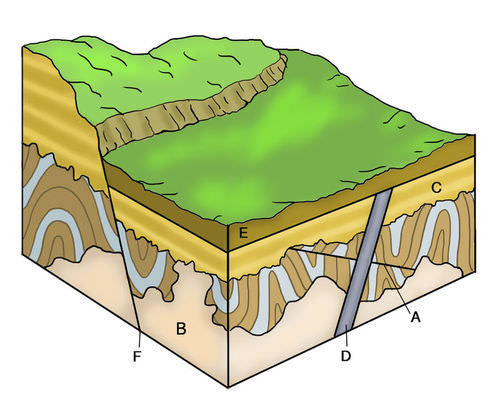
Rock layers may have another rock cutting across them, like the igneous rock in Figure. Which rock is older? To determine this, we use the law of _________. The cut rock layers are older than the rock that cuts across them.
UNCONFORMITIES

A gap in the sequence of rock layers is called an _______ .
CROSS-CUTTING RELATIONSHIPS
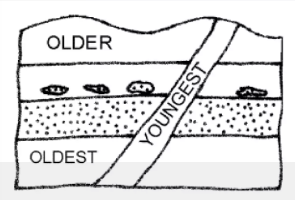
LAW OF LATERAL CONTINUITY