Unit 3 Integumentary System
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
The integumentary system
Contains the skin, hair, nails and sweat and oil glands
It is the largest system in the body
Integument means covering
Glands
A group of cells that produces and secretes a substance
Produce and secrete sweat and oil
Integumentary system functions
Protects the body from injury, intrusion of harmful microorganisms, and ultraviolet rays of the sun
Helps to maintain the proper internal temperature of the body
Serves as a site for excretion of waste through perspiration
Serves as a important sensory organ
Layers of the skin
Epidermis
Dermis
Subcutaneous
Epidermis
Outer layer
Responsibly for protection and secretion
Does not contain blood vessels
Special pigment cells that produce melanin
Nerve endings reach into this outer layer that receive information about:
Heat
Cold
Pain
Pressure
Temperature regulation
Melanin
Melanin is essential in screening UV radiation
Variety of skin colour is caused mainly by melanin expression
Melanin is produced in special cells called melanocytes
Darker skin has more melanin
Albinism is a condition where skin does not produce melanie
Dermis
Second layer
Contains connective tissue that holds capillaries, lymph cells, nerve endings, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and hair follicles
Top layer (papillary layer) fits into ridges on the stratum germinativum to form lines
On fingers = fingerprints
Subcutaneous layer
Between the dermis and the inner organs
Consists of fatty tissue and some layers of fibrous tissue
Contains blood vessels and nerves
Goose Bumps
Are caused by the contraction of an arrector pilli muscle connected to each hair follicle
The contraction also causes the hair to stand on end
Hair
The entire body except the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet is covered with hair
Hair in the nose, eye and ear regions protect against dust, insects and foreign objects
Hair on the head helps retain heat
The shape of the hair follicle (from which hair grows) determines the shape of the hair – curly, straight, wavy.
Hair colour is determined by the presence of melanin
Gray hair occurs when we stop producing melanin
Nails
Generally pink
Blue could indicate poor oxygenation
Whitish half-moon at the base of most nails is the lunula
Narrow band of epidermis surrounds the nail of three sides is called the cuticle
What are nails made of
Hard keratin that cover the dorsal surface of the distal bone of the fingers and toes
Nail functions
Protect fingertips and toes
Helps us to grasp and scratch
Health and nutritional status can be reflected in the nails
Sweat and body odour
Sweat itself is odorless
Body odour is caused by the action of the skin’s normal bacteria on the sweat
Sweating = diaphoresis
Sweat consists of…
Water, salt and a small amount of wastes
Why do we sweat
To cool off during exercise and in hot environments
During stressful situations
During hormonal changes
With strong emotions
Sebaceous Gland
Secrete an oily substance called sebum into the space near the hair shaft
Sebum (oil) helps to keep the hair and skin soft and shiny and also inhibits the growth of bacteria on the surface of the skin.
Blue skin can indicate..
Poorly oxygenated blood
A condition called cyanosis
Common during heart failure and severe breathing disorders
Red skin can indicate..
Fever
Inflammation
Allergy
White (Pallor) skin can indicate..
Low blood pressure
Impaired blood flow into an area
Emotional stress (fear, anger, and others)
Yellow (Jaundice) skin can indicate..
Liver disorder in which excess bile pigments are absorbed into the blood, circulated throughout the body and deposited in body tissues
Can be seen in the eyes as well
Blue/Black skin can indicate..
Sites where blood has escaped from circulation and has clotted in the tissue spaces (=hematomas)
What is cancer
When cells multiply uncontrollably because the normal regulation of their division has been damaged
Malignant tumours
A mass of abnormal cells that divide excessively and do not carry out normal functions
These cells are often irregular in size and shape
Can spread into neighboring tissues and distant sites
Metastasis
The spread of cancerous cells to distant locations
The initial tumor is called the primary tumor and those that develop in remote sites are called secondary tumors
Benign tumors
Caused by cells that multiply abnormally and do not carry out their usual functions
These tumors are contained and do not spread
Causes of cancer
Carcinogens
Heredity
Carcinogens
Cancer-causing agents
Smoking, viruses, UV radiation, etc.
Damage specific genes (sections of DNA) called oncogenes that regulate cell division, growth, repair of damaged cells and the ability of a faulty cell to self-destruct
How does cancer start
Damage from carcinogens
Carcinogens continually bombard cells and eventually affect genes (oncogenes) on chromosomes
Permanent Damage
With time or higher-than-normal exposure to carcinogens, some of the genes suffer permanent damage
Cells Become Cancerous
Eventually a number of oncogenes are permanently altered
The cell functions abnormally and may become cancerous
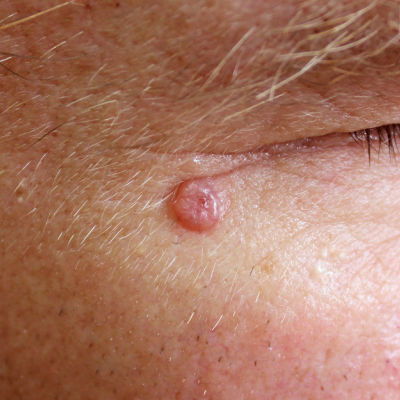
Basal cell carcinoma
Most common form of skin cancer
Usually appears as a small, pink bump or patch on the head or neck, and may occur on any part of the body
If untreated, the area will begin to open, bleed, or crust repeatedly and can cause extensive damage to the area involved
Grows slowly but rarely spread to other parts of the body
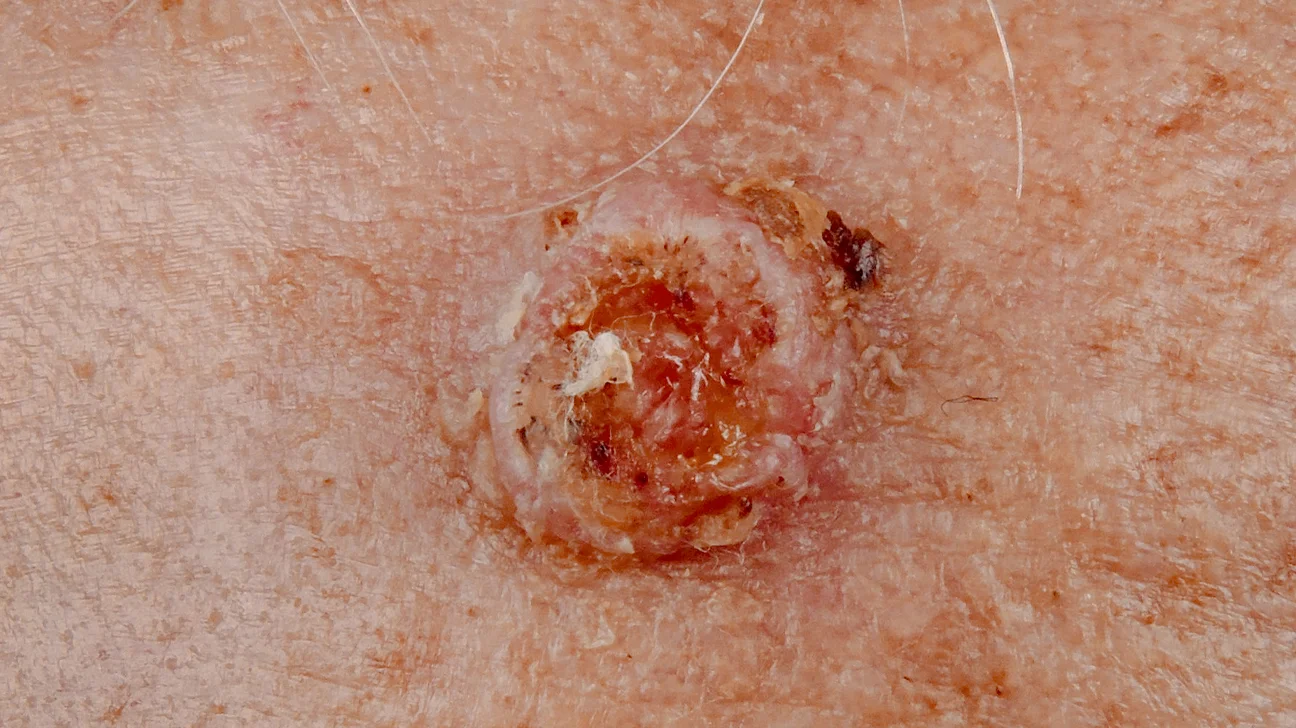
Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Can look similar to basal cell carcinomas, but are usually more scaly and stick out further from the skin’s surface
Often occur on the head and neck, and have a special tendency to grow on the ears, lips, and the backs of hands and arms
If treated early, is curable
If the tumor invades deeply, it can spread to the lymph nodes, which then must be removed
If treatment is unsuccessful, squamous cell carcinoma spreads internally and results in death
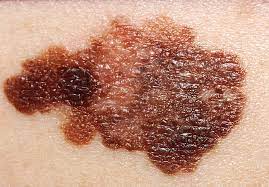
Malignant Melanoma
A cancer in melanocytes, or pigment-producing cells, in the skin
Usually appears as an irregular brown spot or changing mole
Can spread to other areas of the body, or metastasize
Can arise from normal skin or from a mole, which has turned bad
If caught early, is usually curable
If it spreads to other parts of the body, it can result in death
Melanoma risk factors
A mole that is changing
Having a mole that is >15mm in diameter and has been present since birth
White race
A prior skin cancer
A close family member with melanoma
Using a tanning bed ten times a year or more before age 30
More than 50 moles on your body
Suppression of the immune system
The tendency to burn and freckle instead of tan
Skin cancer prevention
Avoid sun exposure. Severe sunburn is a major risk factor
Apply generous amounts of sunscreen
Avoid the peak hours of sun intensity (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.)
Ask your doctor if your medications increase your sensitivity to the sun, because many medications make your skin more vulnerable to sun damage
Avoid tanning salons
Burns
Caused when body tissue is in contact with extreme heat, corrosive chemicals, radiation, or high voltages
Skin damage occurs when skin touches anything over 44°C
A burn victim is at risk for infection, shock, pain, loss of body heat and fluids, swelling of breathing passages and death
First-degree burns
Superficial burns
Involves only the epidermis
Characterized by pain, redness and swelling
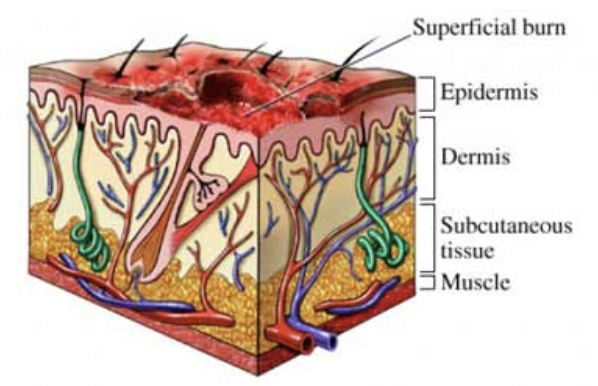
Second-degree burns
Involves the epidermis and dermis
Pain, redness, swelling and blistering
Should treat any 2nd degree burn that affects 1% or more of the body surface
Shock is likely to develop if injuries affect more 9% of body surface
Can be life-threatening
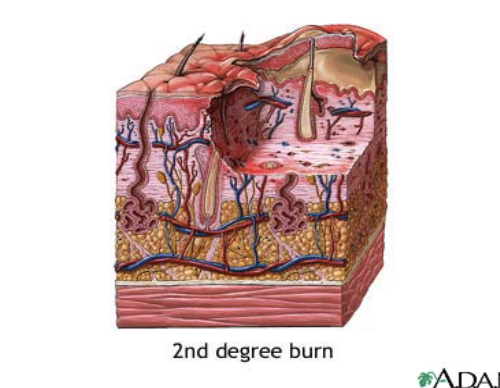
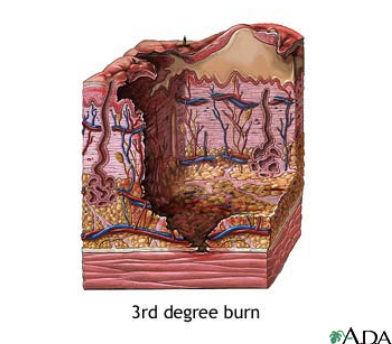
Third-degree burns
Involve all layers of skin and often underlying muscles and bones
Skin often looks charred and black
Always requires medical attention
Guidelines for Treating Burns
Anything sticking to the burn should not be removed
Butter, lotions or ointments should NOT be applied to the burn unless prescribed.
The burn should be cooled with large amounts of cold water and covered with a sterile sheet or plastic bag
Burns to the face however should not be covered
Emergency medical personnel should be contacted for serious burns
In burns to the mouth and throat, the airways should be checked to see if there is any swelling
Burns to the head are always more serious than burns to other body parts
Wounds
A break in the skin or mucous membrane that becomes a portal of entry for microbes
When injury does occur, infection is a major threat, so wound care is important for preventing infection and further injury to the wound and nearby tissues
Abrasion
A partial-thickness wound caused by the scraping away or rubbing of the skin
Contusion
A closed wound caused by a blow to the body
Incision
A open wound with clean, straight edges (usually intentionally created)
Laceration
An open wound with torn tissues and jagged edges
Penetrating wound
An open wound in which the skin and underlying tissues are pierced
Punctured wound
An open wound made by a sharp object; entry of the skin and underlying tissues may be intentional or unintentional
What is a skin tear?
An acute traumatic wound resulting from external friction and/or shearing forces that separate the epidermis from the dermis
Usually present on hands and upper extremities
What are the risk factors for skin tears
Occurs in individuals with fragile skin
Older adults at high risk
Previous skin tears
Compromised nutrition
Cognitive impairment
Impaired mobility
Dry skin/Dehydration
Presence of pressure or shear
Impaired sensory perception
Prevention and treatment of skin tears
LIFT do not drag patients
Avoid tape or adhesives
Exercise caution during bathing, dressing, and transferring
Pad bed rails, wheelchair arm and leg supports
Maximize nutrition and hydration
What are Pressure Ulcers?
An area of the skin that has broken down because of constant pressure or friction
The skin becomes injured because of lack of circulation, which destroys the tissue
Also called decubitus ulcers, bed sores or pressure sores
If untreated they become large and painful
The wound must be kept extremely clean, since it provides a portal of entry into a susceptible host
Standard precautions are used when treating a resident with a pressure ulcer
What increases the risk of pressure ulcers
Immobility and limited activity
Moisture, particularly when due to incontinence or poor hygiene
Poor nutrition or hydration
Friction and shearing forces
Loss of sensory perception (unable to feel)
Atrophic skin (as skin ages, it becomes thinner, fragile and less elastic)
Residents who are paralyzed, diabetic, unconscious, obese, or very thin
Where do pressure ulcers commonly occur
Over bony prominences
Shoulder blades
elbows
knees
heels
ankles
the back of the head
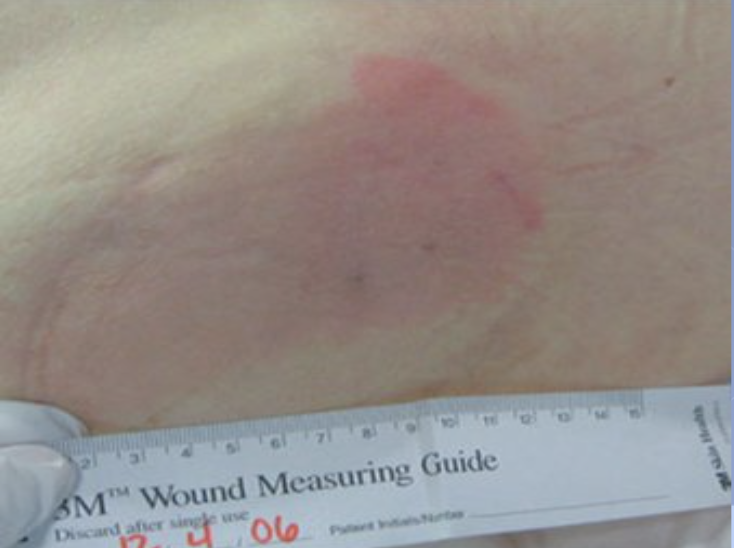
Stage 1 pressure ulcer
Skin remains intact, but there has been a colour change to either extreme whiteness or redness
Stage 2 pressure ulcer
Skin is broken or cracked through the epidermis, dermis or both
The sore is considered superficial and may look like a blister or a tear in the skin
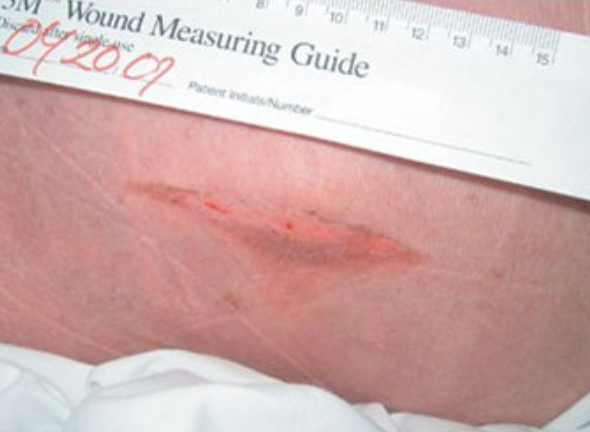
Stage 3 pressure ulcer
Full thickness tissue loss
Subcutaneous fat may be visible but bone, tendon or muscle are not exposed
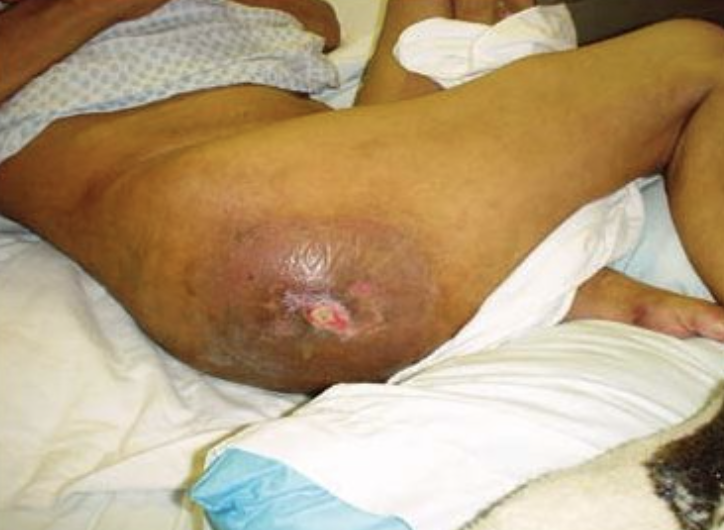
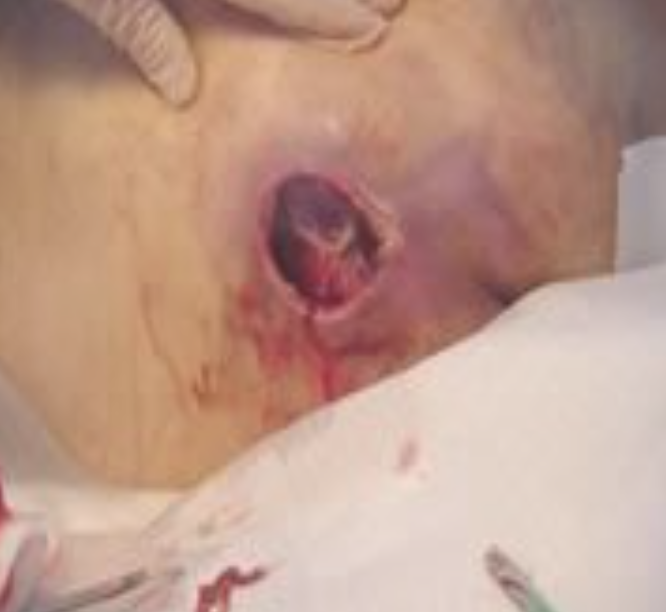
Stage 4 pressure ulcer
Involves the breakdown of the tissue, muscle, tendons, etc.
Slough may be present on some parts of the wound
Often include tunneling
Good skin care
Clean and dry
Free of moisture from urine, stool, perspiration and wound drainage.
Change linens and clothing as needed
Apply moisturizers on dry areas
Protective devices for pressure ulcers
Bed cradle (Anderson frame)
Elbow protectors
Heel elevators
Floatation pads
Eggcrate-like mattress
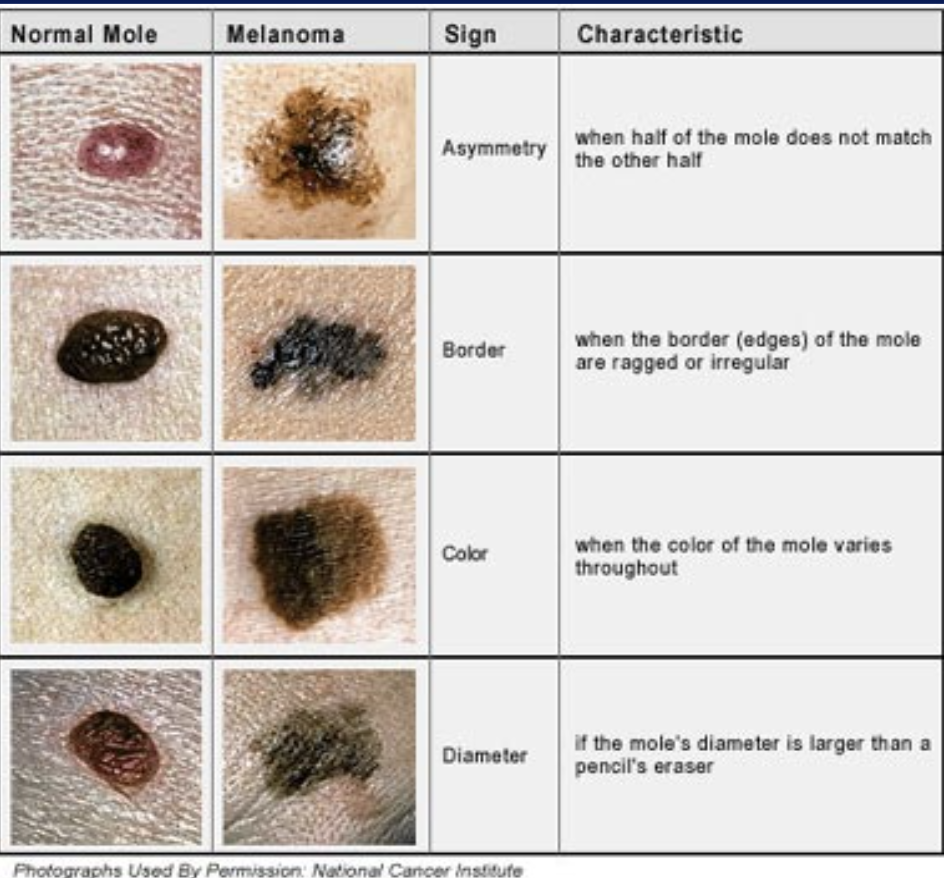
ABCD’s of moles
Characteristics of skin damage that doctors look for when diagnosing and classifying melanomas