Biomedical Unit 1 Study Guide
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Link Method
No set pattern
Not geometric
Investigators make up hinges as they go
Zone method
Used in houses - areas with a border
Splits areas into multiple spaces, do 1 at a time
Spiral method
Big open spaces, usually water
Starts in a specific areas
Two types - outwards→starts in the center, moves outwards and inwards →starts from an outside point and moves inwards
Line (strip) method
Used for large outdoors areas
Starts from a wall, goes out in 1 direction
Wheel or Ray method
Used on small, circular scenes
Starts from a critical point and moves outwards
Grid method
Used on large outdoor scenes
Starts in one point and goes in straight line usually formed a grid pattern
What are the 4 physiological responses during a polygraph test?
Heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate, skin conductivity
Trace evidence
Tiny fragments of physical evidence
Anagen
The hair grows
Cartagen
The follicle shrinks
Telegen
The hair sheds

Arch print
Arches slope upwards and then down
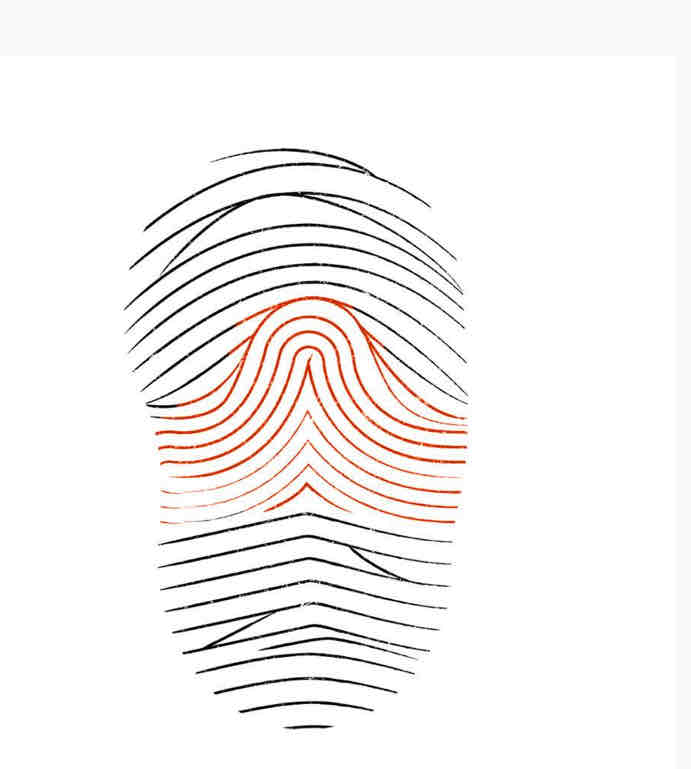

Tented arch print
Is similar to plain arch except the ridges in the center thrust upwards
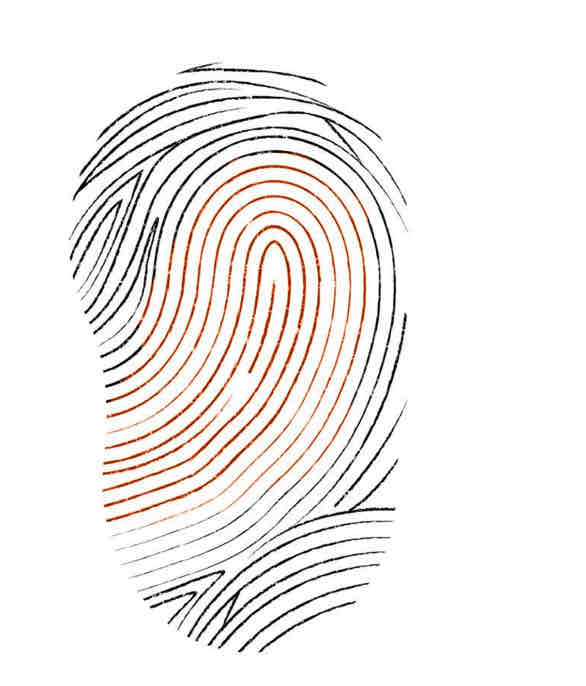

Loop print
Forms when ridges curve back on themselves
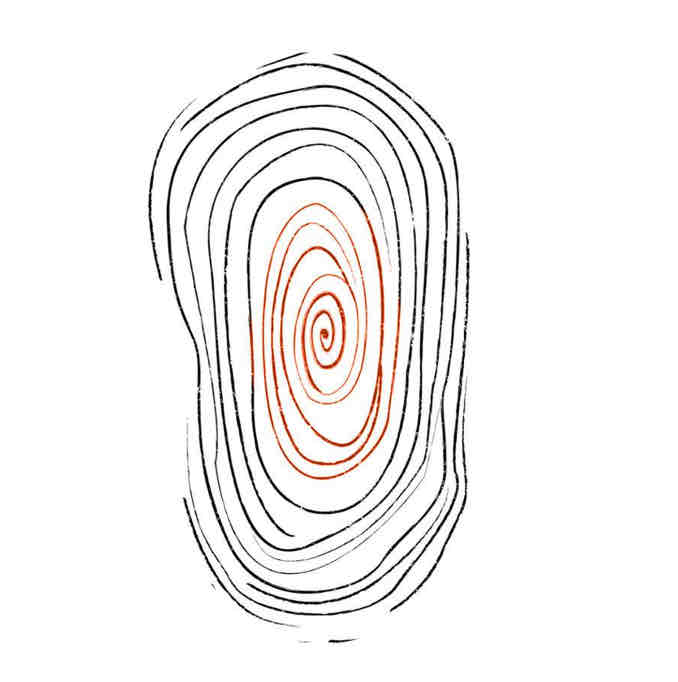

Whorl
Forms circular or spiral patterns
Ridge ending
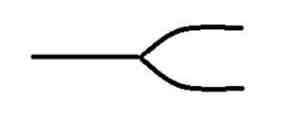
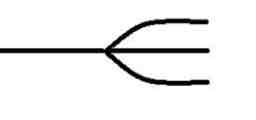
Fork
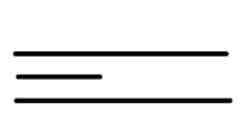
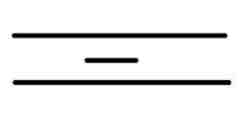
Short ridge
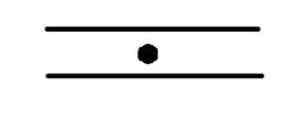
Dot
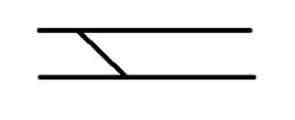
Bridge
Hook

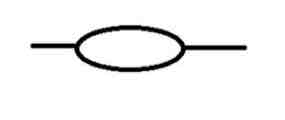
Eye
Double fork

Delta

Triple fork
Human blood is composed of what 3 main types of cells and or fragments?
Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
What do red blood cells do? (Erythrocytes)
Carry oxygen
What do white blood cells do? (Leukocytes)
Helps fights diseases and infections
What do platelets do? (Thrombocytes)
Stops bleeding and heals wounds
What does plasma do?
Takes nutrients and proteins to the parts of the body that need it
Presumptive testing
The initial testing that suggests a sample may be blood
Leucocrystal violet
Reacts with hemoglobin and turns a violet color
Used on porous surfaces
Not the best test for the lab
Why is it important to have base polygraph results? (Heart rate etc..)
So you can see the difference in heart and respiration rate
Why is it important to have blood/finger print samples?
So you can figure out more specifically how it matches up to the suspects.
Luminal
Glows a bright blue in the dark when it comes in contact with blood
Not the best to use in the laboratory
Kastle-Meyer
Figures out if blood is real or fake
Blood will turn pink if real
Used in the lab
What antigens are present in type A blood?
Type A antigens
What antigens are present in type B blood?
Type B antigens
What antigens are present in type AB blood?
Type A and B antigens
What antigens are present in type O blood?
No antigens
What antibodies are presented in type A blood?
Anti-B
what type of antibodies are present in type B blood?
Anti-A
What antibodies are present in type AB blood?
No antibodies
What antibodies are present in type O blood?
Both Anti-A and anti-B
What is an agglutination test?
Determines what blood type is the blood sample
What method is best for a single victim in the middle of a large, flat desert?
The grid method → large, empty area
Which search method would most likely be used in a house?
The zone method
Why are polygraph results not always permissible in court?
Because some people can control their polygraph results better than other people
Why is it important that baseline measurements are taken during a polygraph test?
In order to see the differences and changes in the different rates
Which search method would be best used to search for evidence/bodies in a boat wreck in open water?
The outwards spiral method
What is agglutination?
When the blood clumps up because the antibodies attack the antigens/carohydrates
If blood does not agglutinate in the anti-A well, but does in the anti-B well, which blood type is present in the tray?
Type B
What system is responsible for eliminating waste from the body and regulating eater balance of blood?
Urinary system
What is the location in the crime scene where from which you take all measurements?
The critical point
If our scale was 1 foot = 1 cm and a piece of evidence was 12 feet away, how far would we draw the sketch?
12 cm
What happens physiologically (inside the body) to result in death is?
The heart stops
What are sources of DNA that can be collected from a crime scene and used as potential means for identifying a person of interest in a crime?
Blood, hair, and fingerprints