MagBio Unit 5 Vocabulary: Evolution and Classification F23
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
evolution
the frequency of alleles in a population's gene pool changes over time; population experiences at least ONE of the following: mutation, genetic drift, gene flow, sexual selection, and natural selection
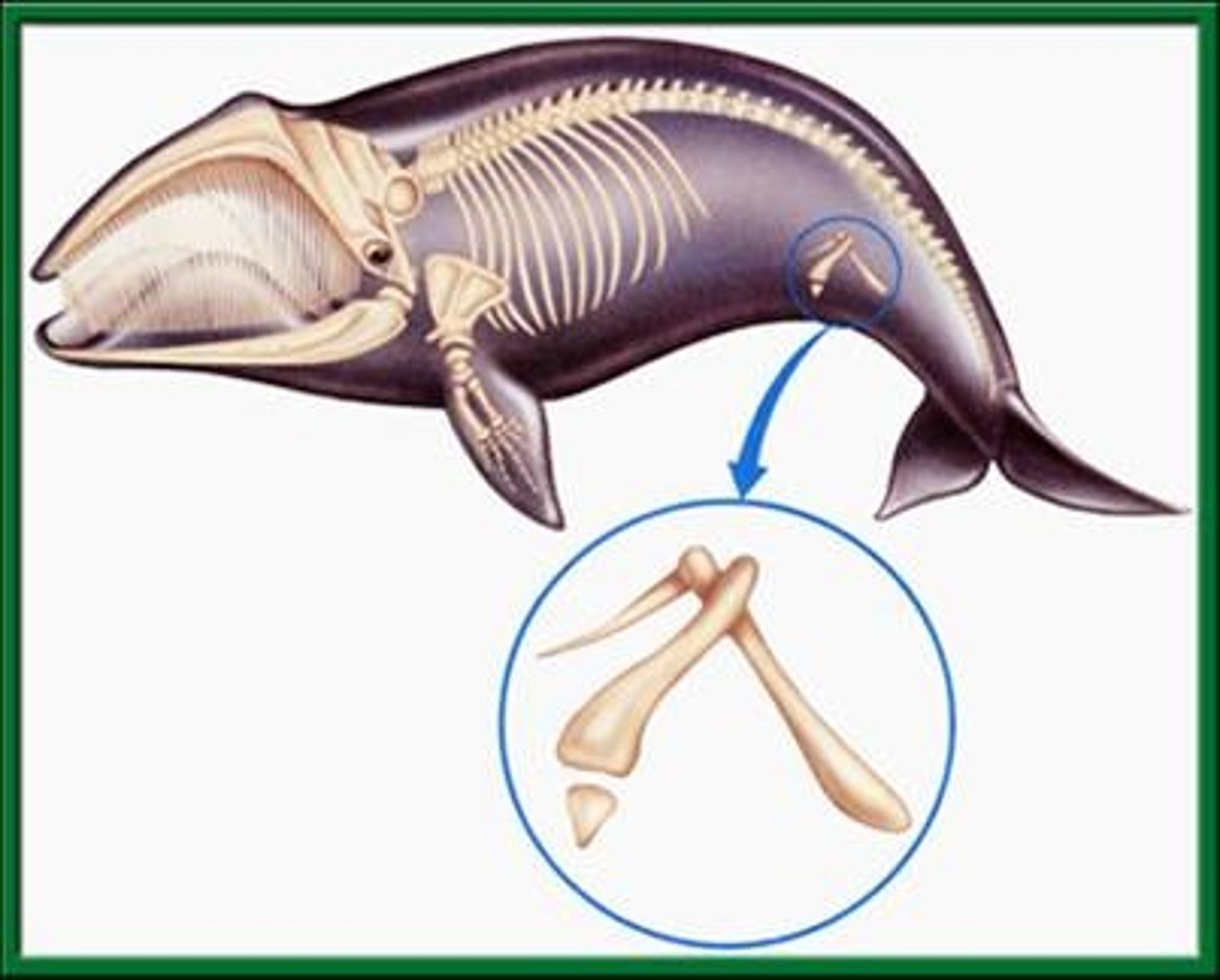
vestigial structures
body parts that have a reduced outward appearance because they have lost their function, but have retained an internal structure because they were inherited from a common ancestor
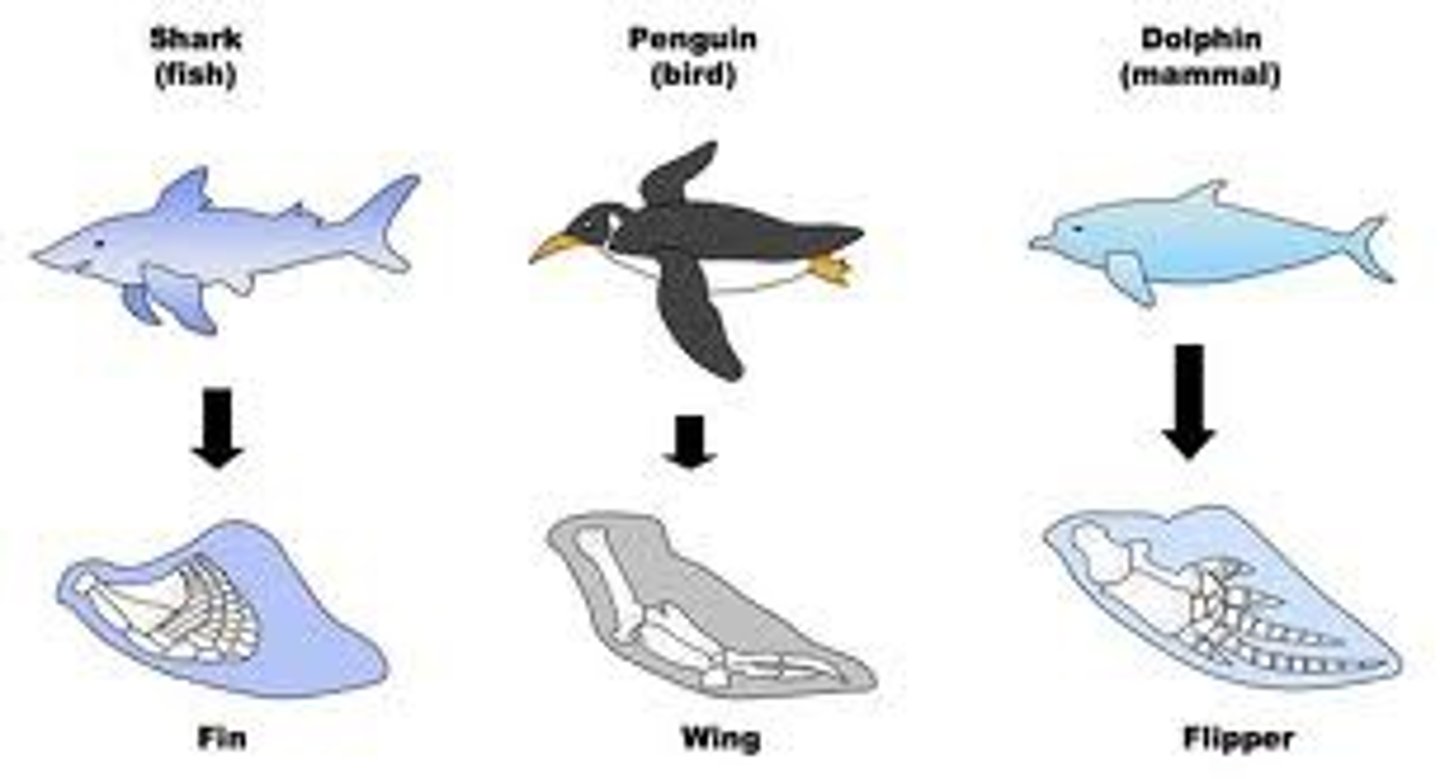
analogous structures
body parts that have a similar outward appearance because they have the same function, but have a different internal structure because they were not inherited from a common ancestor
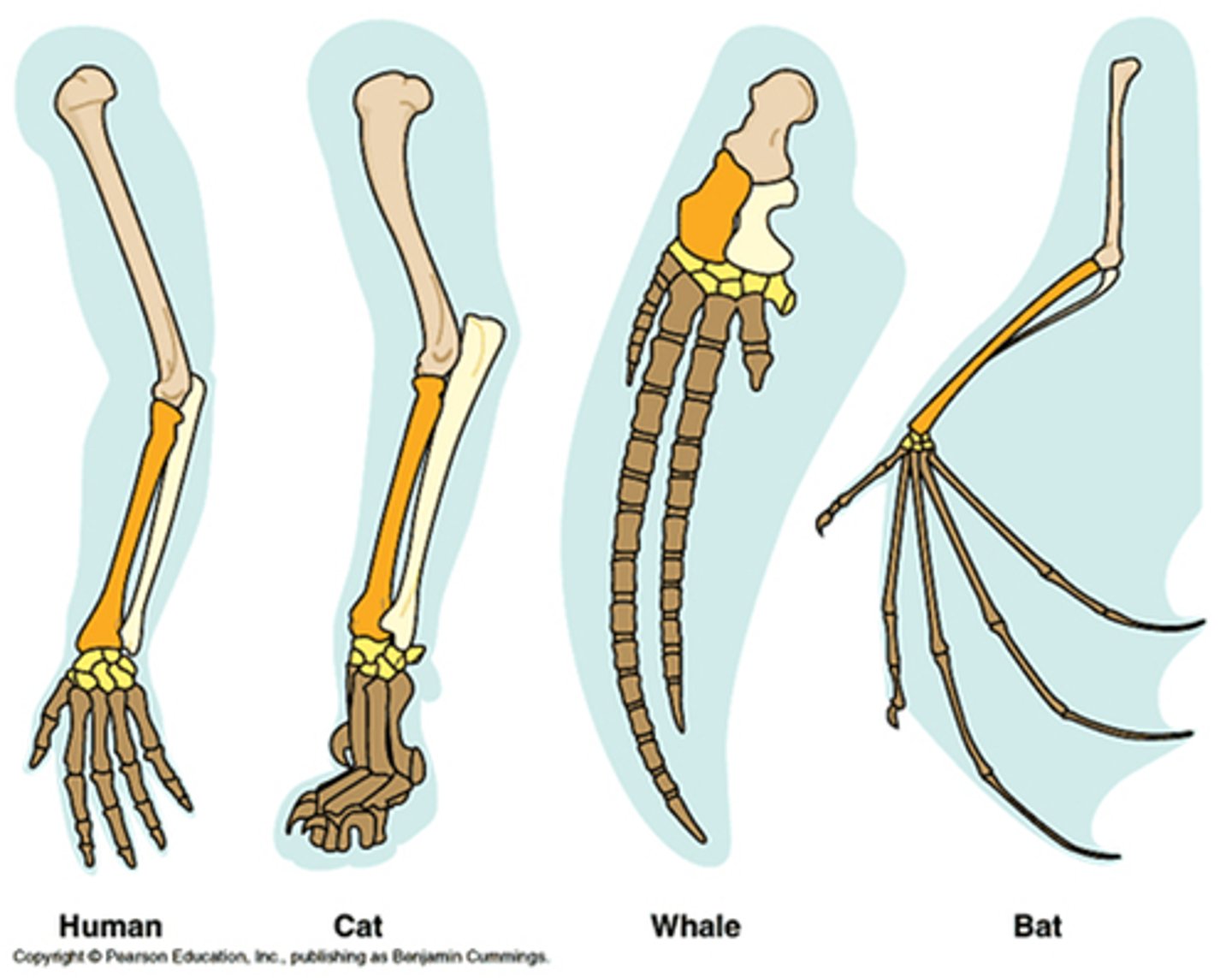
homologous structures
body parts that have a different outward appearance because they have different functions, but have a similar internal structure because they were inherited from a common ancestor
natural variation
phenotypic differences among individuals in a population
artificial selection
the offspring of individuals with traits that are more desired by humans increase over time
natural selection
the offspring of individuals with traits that are better suited to the environment increase over time
biological adaptation
a genetic trait that increases an individual organism's relative ability to survive and reproduce
biological species
a group of organisms capable of exchanging genetic information (interbreeding) and producing fertile offspring
mutation
a change in DNA, primary source of natural variation
camouflage
when an individual looks similar to the environment
mimicry
when an individual looks similar to an individual of another species
fossil
preserved evidence of an organism's existence; the primary evidence for evolution
adaptive radiation
the emergence of many different species from a single common ancestor
convergent evolution
when two unrelated species evolve in similar environments becoming more similar over time; results in analogous structures
divergent evolution
when two related species evolve in different environments becoming more different over time; results in homologous and/or vestigial structures
gene pool
all the alleles in a population; the combined genetic information of all members of a particular population
embryo
developing stage of a multicellular organism
fitness
a measure of how well an organism can survive and reproduce in its environment
gradualism
pattern of evolution in which small changes occur steadily over long periods of time
punctuated equilibrium
pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by short periods of rapid change
coevolution
when two species evolve in response to changes in each other; species closely interact
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
the frequency of alleles in a population's gene pool remains constant over time; population experiences ALL of the following: no mutation, no genetic drift, no gene flow, no sexual selection, and no natural selection.
p + q = 1
the Hardy-Weinberg equation that models the relative allele frequencies of population that is not evolving
bottleneck effect
a random event causes a small group of individuals to survive while a significantly larger population dies off but their survival is not related to their fitness
founder effect
a random event causes a small group of individuals to become separated from a significantly larger population but their separation in not related to their relative fitness
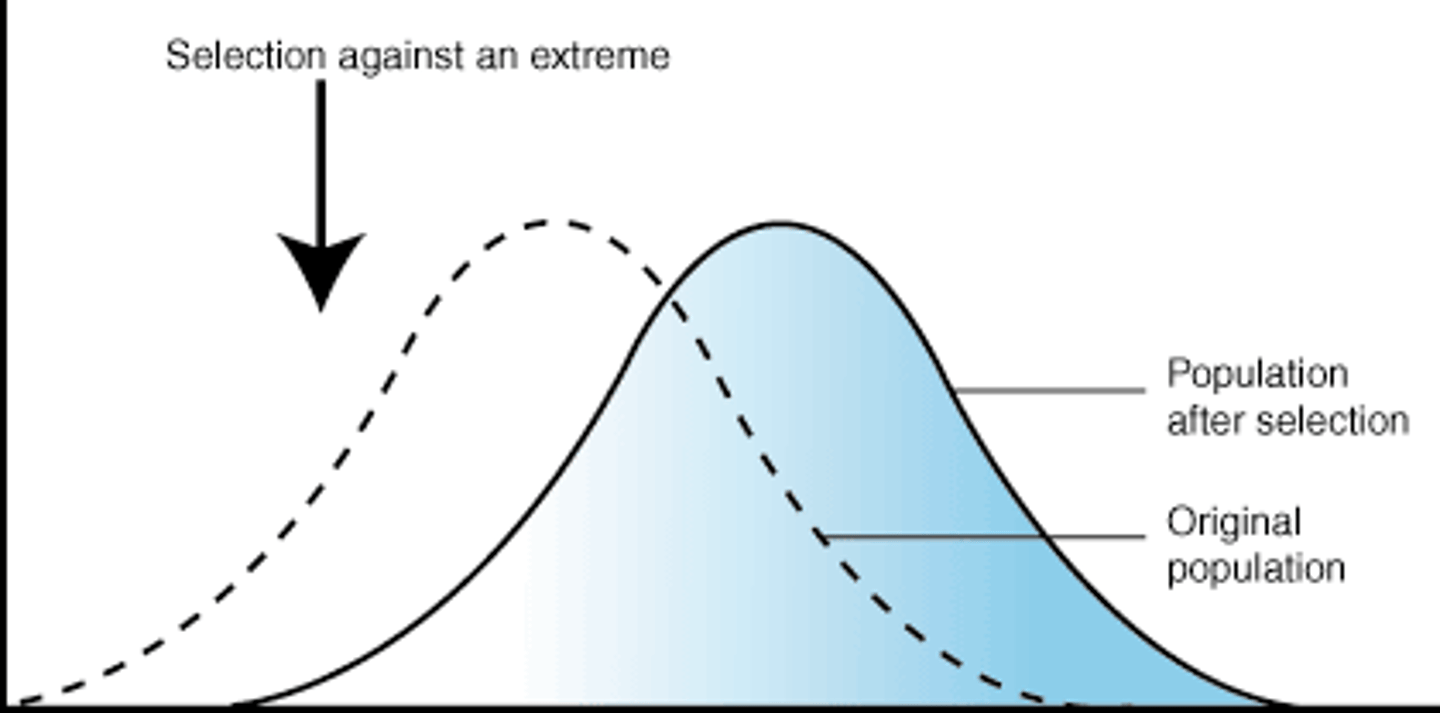
directional selection
occurs when the environment selects against one end of the phenotypic spectrum
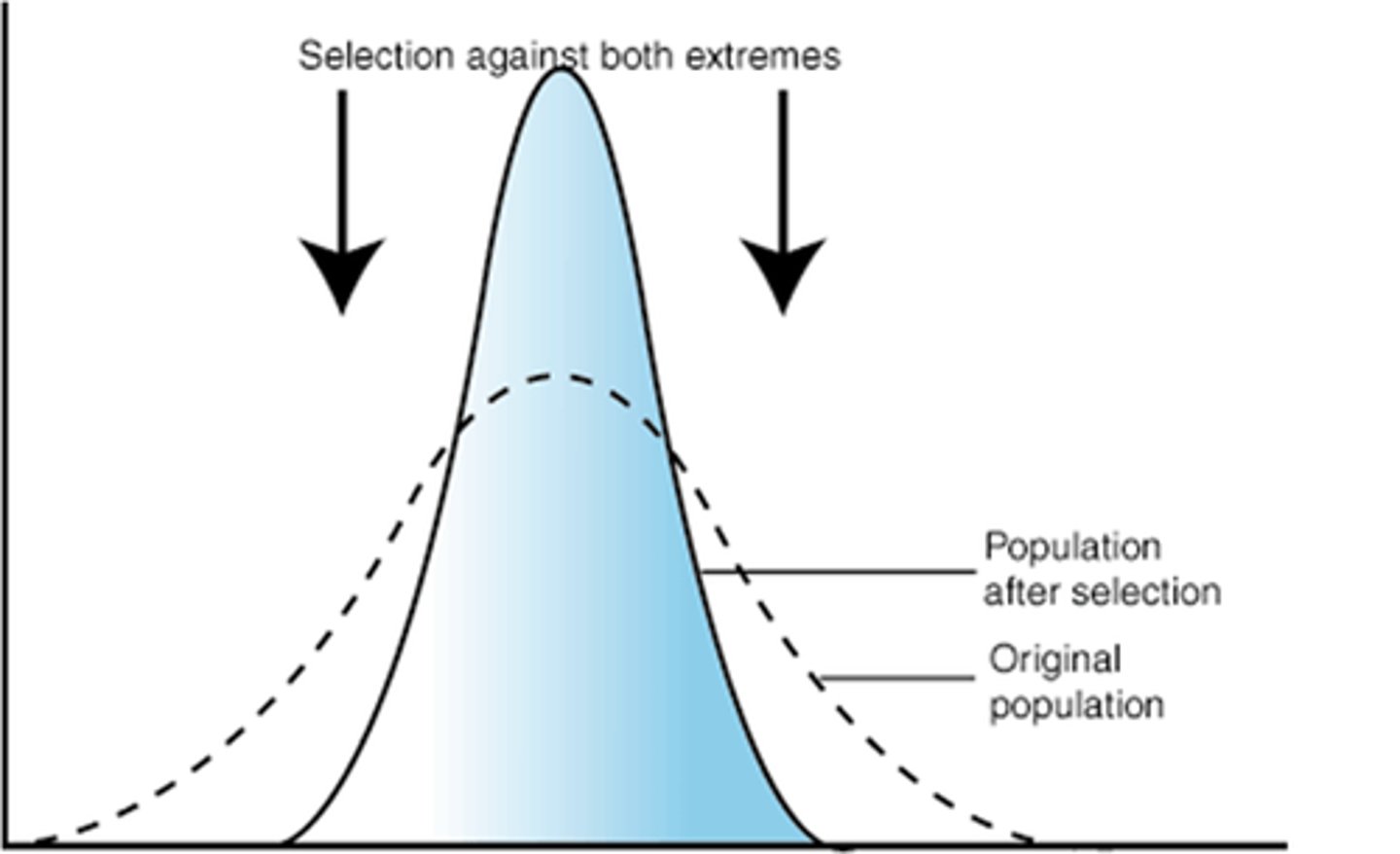
stabilizing selection
occurs when the environment selects against both extremes of the phenotypic spectrum
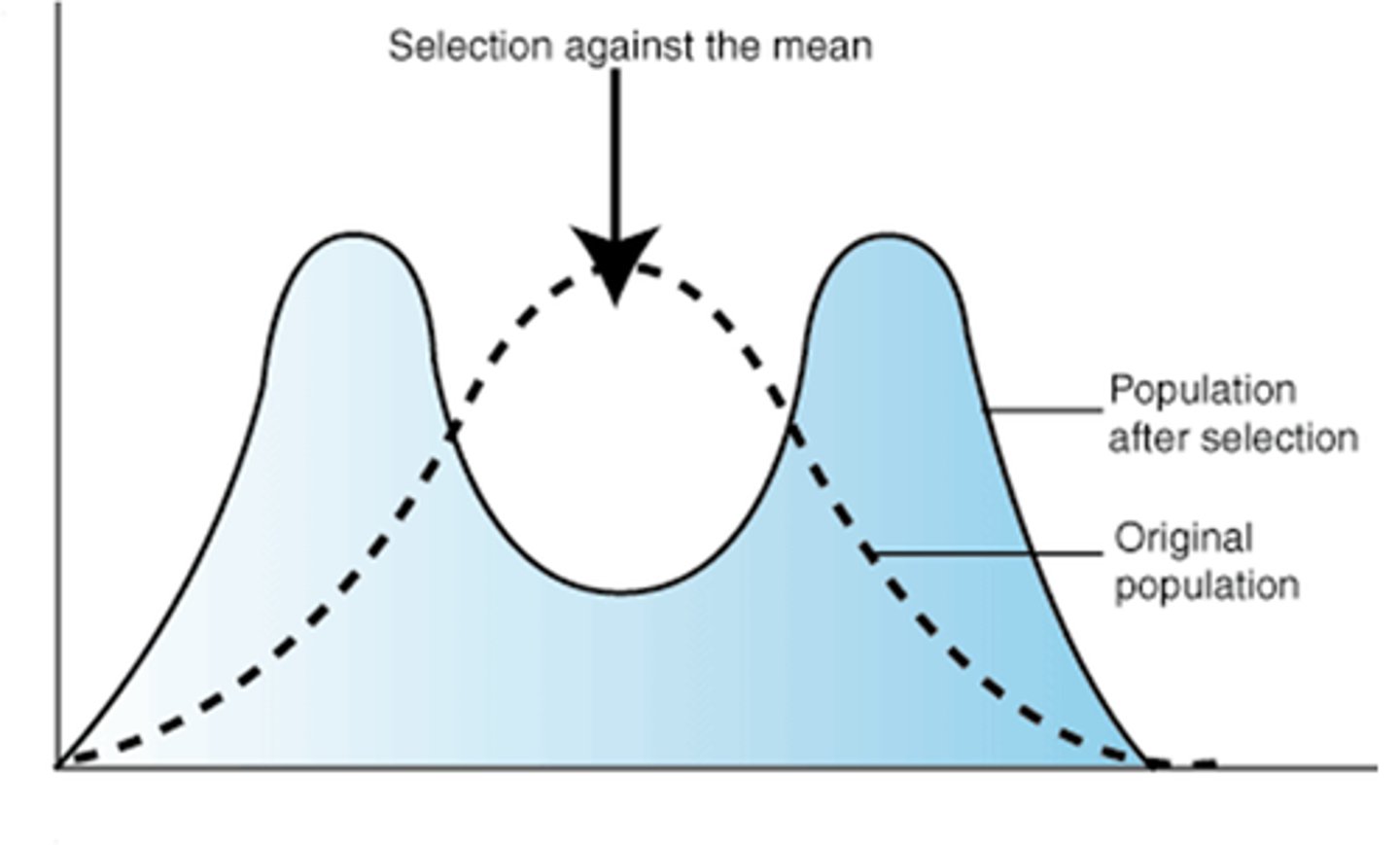
disruptive selection
occurs when the environment selects against the mean of a phenotypic spectrum
hybrid sterility
a post-zygotic barrier where offspring cannot produce functional gametes, as in mules
temporal isolation
a pre-zygotic barrier formed when a group of individuals breed at a different time of year than another group of individuals in a population
behavioral isolation
a pre-zygotic barrier formed when a group of individuals are not attracted by the mating rituals of another group of individuals in a population
geographical isolation
a pre-zygotic barrier formed when a group of individuals are physically separated from another group of individuals in a population
gene flow
genes entering or leaving a population due to migration
allopatric speciation
the divergence of a new species from two populations living in separate geographical areas
sympatric speciation
the divergence of a new species from one population living in the same geographical area
genetic drift
a random change in the gene pool of a population; not due to selection
pre-zygotic isolation
when some individuals are unable to mate with other individuals in a population of a sexually reproducing species
post-zygotic isolation
when some individuals are sterile in a population of a sexually reproducing species
phenotypic spectrum
a broad range of phenotypes that overlap to create a continuous series where each individual blends into the next in a continuous way
chitin
polysaccharide that forms fungal cell walls
cellulose
polysaccharide that forms plant cell walls
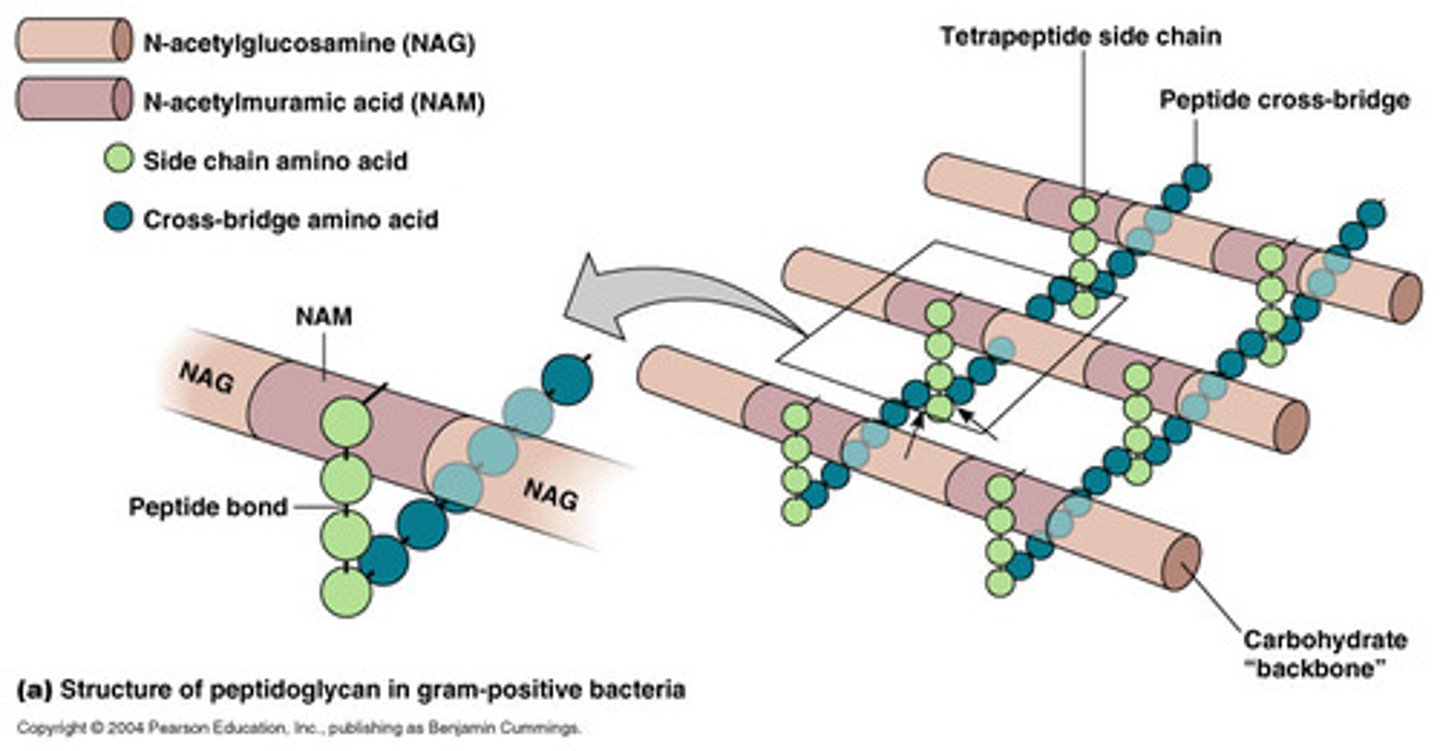
peptidoglycan
protein-carbohydrate that forms bacterial cell walls
plant
an organism that is: eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic, and has a cell wall made of cellulose
animal
an organism that is: eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, and does not have a cell wall
fungus
an organism that is: eukaryotic, heterotrophic, and has a cell wall made of chitin
protist
an organism that is: eukaryotic and does not fit the description of plant, animal, or fungus
bacteria
an organism that is: prokaryotic, unicellular, and has a cell wall made of peptidoglycan
archaea
an organism that is: prokaryotic, unicellular, and is considered to be an extremophile
domain
a taxon that contains one or more related kingdoms
kingdom
a taxon that contains one or more related phyla
phylum
a taxon that contains one or more related classes
class
a taxon that contains one or more related orders
order
a taxon that contains one or more related families
family
a taxon that contains one or more related genera
genus
a taxon that contains one or more related species
species
a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring
binomial nomenclature
Genus species; Genus is capitalized, species is lowercase. Both words are underlined or italicized.
protist classification
animal-like: heterotrophic; plant-like: autotrophic; fungus-like: external absorption
molecular clocks
models that use mutation rates to measure evolutionary time
clade
evolutionary branch of a cladogram that includes a single common ancestor and all of its descendants
cladogram
a model of common ancestry that is based on patterns of ancestral and derived traits
phylogenetic tree
a model of common ancestry that shows the relationships between clades over a specified period of time
common ancestor
the shared ancestor of new, different species that arose from one population
node
a point on a cladogram or phylogenetic tree that represent the common ancestor of two related species; represents the moment of speciation
derived trait
a trait that is not shared by other members of a clade or their common ancestor
ancestral trait
a trait shared by all members of a clade through a common ancestor
speciation
the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.