POM II - CNS Neoplasms - Exam 2
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Primary Tumor Lesions - Statistics
-about 25,400 malignant tumors of brain or spinal cord were dx in 2023
-about 18,760 people estimated to die from brain and spinal cord tumors
-lifetime risk of developing malignant tumor of brain or spinal cord <1%
Primary Intracranial Tumors
-due to uncontrolled division of cells in the brain (astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, Schwann Cells)
-1/3 are meningiomas
-1/4 are gliomas
-Remainder: pituitary adenomas, neurofibromas, and other tumors
Microglia
-resident macrophages of the brain and spinal cord
-immunologically active
Oligodendrocytes
-source of myelin in the CNS
-support of neurons
Astrocytes
-physical support to neurons
-phagocytosis
-play a role in nourishment of the neuron
posterior fossa/infratentorial
what is the most common location of primary NS tumors in children?
anterior 2/3 of cerebral hemisphere/supratentorial
what is the most common location of primary NS tumors in adults?
M/C Childhood Primary Brain Tumors
-Medulloblastoma (malignant, 20%) Mini Medulloblastoma
-pilocytic Astrocytoma (grade I non-malignant)
-ependymoma (5% childhood tumors)
MC Adult Primary Brain Tumors
-glioblastoma (malignant)
-meningioma (most non-malignant, approx 35%)
Primary Brain Tumor - S/S
-headache, n/v, seizures, weakness, etc
-sx of increased IOP
-cranial nerve palsies
Frontal Lobe Lesions - S/S
-progressive intellectual decline
-slowing of mental activity
-personality changes
Temporal lobe Lesions - S/S
-seizures
-motor phenomena
-hallucinations
-depersonalization
Parietal Lobe Lesions - S/S
-contralateral disturbances of sensation
-seizures
-sensory loss or inattention
Occipital Lobe Lesions - S/S
-contralateral homonymous hemianopia OR a partial field defect
-loss of color perception
-prosopagnosia (inability to identify a familiar face)
Brainstem lesions - s/s
-cranial nerve palsies
-ataxia
-incoordination
-nystagmus
-pyramidal and sensory deficits
Cerebellar Lesions - s/s
-ataxia
-incoordination
-hypotonia of limbs
Primary Brain Lesions - Dx
-disturbance of cerebral function
-neuroradiologic evidence of space-occupying lesion - MRI
-biopsy
Primary Brain Lesion - Tx
-corticosteroids
-whole brain radiation therapy for tx of more than one tumor in the brain
-surgery - for solitary brain metastasis
-stereotactic radiosurgery - cyber knife
-chemo
-anti-seizure meds are given only if patient develops seizures
Primary Intracranial Tumor Types
-meningiomas
-gliomas
-pituitary adenomas
-neurofibromas
-other
Meningiomas
-common primary tumor in the CNS
-originates from dura mater or arachnoid (the meninges)
-usually, benign
-S/S: sx vary with tumor site
Meningiomas - Dx
-CT scan
-MRI: strong, homogenous enhancement with "dural tail"
Meningiomas - Tx
-Surgical: tumor may recur if removal is incomplete
-radiotherapy
Gliomas
-Benign or malignant
-about 35-50% of all gliomas in adults are glioblastomas (malignant)
-derived into: astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, ependymomas
Astrocytoma
-infiltrative tumor
-developed from astrocytes
-4 prognostic grades: Grade I, II, III, IV
-prognosis variable
Grade I Pilocytic Astrocytoma
-most common benign tumor in children
-rarely undergo malignant transformation
-well-demarcated
-Tx: surgery
Grade II Low Grade Astrocytoma
-infiltrative tumor
-usual presentation: seizures in young adults
-malignant transformation
-Tx: surgery, chemo and/or radiation depending upon recurrence or if unresectable
Grade III Anaplastic Astrocytoma
-median age 40-50 yrs
-Tx: surgery followed by combo radiation and chemo, or radiation then chemo
Grade IV Glioblastoma
-AKA glioblastoma multiforme
-most common malignant primary brain tumor in adults
-highly infiltrative
-median age 60-70 yrs
-tx: surgery, combo chemo + radiation
Glioblastoma Multiforme - Tx
-surgery
-radiation therapy and temozolomide
-poor prognosis
Oligodendroglioma
-arise from oligodendrocytes
-slow growing
-median age 40-50s
-Grade II (oligodendrogliomas), Grade III (anaplastic oligodendrogliomas)
-Grade II represents similar to Grade II Astrocytomas
Oligodendroglioma - Dx
-Co-deletion of 1p/19q and IDH mutation
-pathologic features: fried egg appearance
Oligodendroglioma - tx
-Surgical
-radiation and chemo (temozolomide or procarbazine)
Ependymoma
-arises from ependymal cells
-any age, most often children
-s/s: signs of increased ICP
-Tx: surgery, radiation
Neuronal and Mixed Neuronal Glial Tumors
-slow growing
-some benign, some malignant potential
-S/S: seizures, HA, dizziness and balance problems
-Tx: surgery
Brainstem Glioma
-less common
-s/s: CN palsies then long tract signs in limbs, increase ICP (late)
-Tx: inoperable, radiation and shunt for increased ICP
Medulloblastoma
-most common malignant brain tumor of childhood
-most likely dx in posterior fossa
-S/s: HA, N/V, papilledema
Medulloblastoma - Dx
-MRI of brain and whole spine
-CSF cytology
Medulloblastoma - Tx
surgery combined with radiation + chemo
Pineal Tumor
-s/s: increased ICP, sometimes associated with impaired upward gaze, hydrocephalus, lethargy
-Tx: shunting, surgery, irradiation
-prognosis: depending on histopathologic findings and extent of tumor
Pituitary Adenoma
-common cause of pituitary malfunction in adults
-types: nonfunctioning and functioning
Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenoma
-most common
-headache
-local mass effect
-bitemporal hemianopsia
-hypopituitarism
Functioning Pituitary Adenoma
-prolactinoma: 40-60%
-cortisol secreting: 15-25%
-GH secreting: 30%
Pituitary Adenoma - Dx
-MRI
-Prolactin level
-24 hr urine free cortisol
-OGTT
Pituitary Adenoma - Tx
-Bromocriptine or Cabergoline
-Surgical resection
-pituitary hormone replacement may be required
Vestibular Schwannoma
-rare, slow growing
-arise from Schwann cells on acoustic nerve
-S/S: ipsilateral/unilateral hearing loss, tinnitus, headache, vertigo, facial weakness, numbness
Vestibular Schwannoma - Dx
-MRI
-brainstem auditory evoked potential
surgery
what is the tx for vestibular schwannoma?
Primary Cerebral Lymphoma
-associated with AIDS/immunodeficient states
-S/S: focal deficits, disturbances of cognition/consciousness
-Tx: high dose MTX + corticosteroids, radiation
-prognosis: depends on CD4 count at dx
Cerebellar Hemangioblastoma
-slow growing
-abnormal vessel growth
-S/S: disequilibrium, ataxia of trunk or limbs, signs of increased ICP
-DX: MRI
-Tx: surgery, angiogenesis inhibitors
Neurofibroma
-seen in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1
-S/S: typically mild; soft, fleshy, sessile or pedunculated flesh-colored growths found along peripheral nerves under the skin or deeper inside body
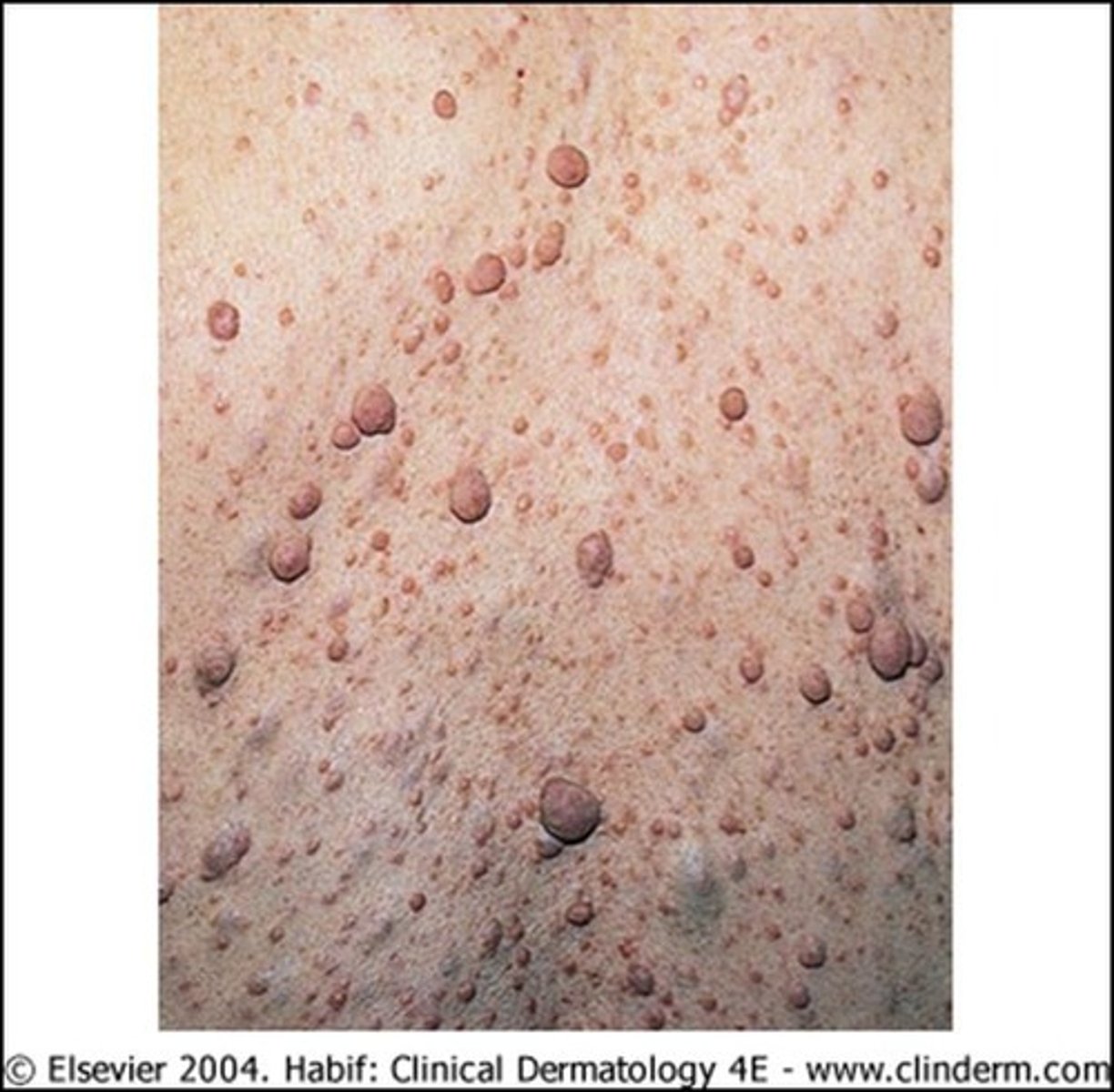
Neurofibroma - Dx
-Medical hx
-PX
-imaging
Neurofibroma - Tx
-observation
-surgery
Spinal Tumors
-1/6th as common as brain tumors
-60% are benign
-classify by histology and by location
Spinal Tumor S/S
-develop gradually
-pain: characteristically aggravated by cough/straining, radicular, localized to back or diffuse in extremity
-motor deficits
-paresthesias or numbness, commonly legs
-bladder, bowel, and/or sexual dysfunction
Spinal Tumor - PX
-localized spinal tenderness
-LMN deficit
-Dermatomal sensory changes
-UMN deficit
-sensory disturbances
Spinal Tumor - Dx
-Imaging: MRI, CT myelography
-Other studies: CSF Cytology
Spinal Tumor - CSF
-xanthochromic
-increased protein
-normal cell count
-normal glucose
Spinal Tumor - Tx
-intramedullary --> decompression, dexamethasone, surgery
-surgical excision
-radiation
Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumor
-ependymoma most common
-remainder are gliomas
Extramedullary Spinal Cord Tumor
-can be extradural or intradural in location
-neurofibromas
-meningiomas
Extradural Spinal Tumors (outside of the spinal cord)
-metastatic tumors, usually arise in vertebral body
-hallmarks: bony destruction
-symptoms: local back pain
-ex: schwannoma, meningioma
Intradural - extramedullary spinal tumor
-sx: radiculopathy, unilateral, segmentally distributed pain
-ex: schwannoma, meningioma, mets
Intradural - intramedullary spinal tumor
-hallmark: (spinal) cord expansion
-sx: diffuse pain, myelopathy, or radiculopathy
-ex: glioma-ependymoma, astrocytoma
Brain Mets - MC sites
-lung: 42.3%
-kidney: 9.8%
-skin - melanoma: 7.4%
-breast: 5%
-GI: 1.2%
Brain Mets - S/S
-headache
-n/v
-focal weakness, speech difficulty, etc
-confusion, agitation, lethargy
-focal signs: focal neuro deficit, optic papilledema
Brain Mets - Dx
-Imaging: CT, MRI
-Other studies: visual fields, endocrine workup, audiology, arteriogram
Brain Mets - Tx
-Medical tx: steroids, anticonvulsants only if seizures
-Surgery: biopsy, craniotomy
-Radiation: brain radiation, stereotactic radiosurgery
-Chemo: systemic, intrathecal
Paraneoplastic Syndromes
-rare
-triggered by altered immune system response to neoplasm
-60% of pts may present with sx before tumor known
Paraneoplastic Syndromes - Pathophys
-antibodies or T cells directed against the tumor may mistakenly attack normal nerve cells and destroy them
-physiologically active substances released by the tumor
-cancers produce proteins that are physiologically expressed in utero by embryonic and fetal cells but not expressed by normal adult cells
-paraneoplastic anti-neural antibody detection
Paraneoplastic Syndromes - Sx
-endocrine
-neuromuscular or MSK
-CV
-cutaneous
-hematologic
-GI
-renal
Paraneoplastic Disorders
-misc - fever, anorexia, cachexia
-rheum - polymyalgia, rheumatic polyarthritis, scleroderma, SLE
-renal - SCLC
-GI - watery diarrhea, electrolyte imbalances (thyroid CA)
-Heme - anemia, thrombocytosis
-Cutaneous - itching, herpes zoster
-endocrine - Cushing's (SCLC)
-neuro/neuromuscular