Lab 3 - Introduction to Microbial Eukaryotes
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
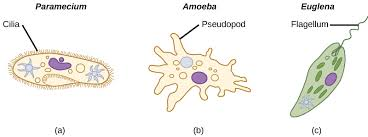
3 major body forms
Ciliate (Paramecium): have many short cilia on their surface which allow them to move rapidly and feed
Amoeboid (Amoeba): are irregular shaped and move slowly by cytoplasmic streaming via their pseudopodia
Flagellate (Euglena): have whip-like flagella(um) to move quickly
functions of the cytoskeleton
structure
adhesion to surfaces
movement
composition of the cytoskeleton
microtubules: part of cilium or flagellum
intermediate filaments: ropes of keratin proteins, not used for movement
microfilaments: used in amoeboid movement
motor proteins
amoeboid movement
use pseudopodia: temporary extensions of the cytoplasm formed by actin subunits that assemble into microfilaments
flagellate movement
flagellum: a whip-like flexible rod with a central core of microtubules made up of two tubulin subunits
use motor proteins dynein and kinesin
eukaryotes typically have 1-12
ciliate movement
like a shorter version of a flagellum
cell may have may have 100’s-1000’s of cilia on its surface
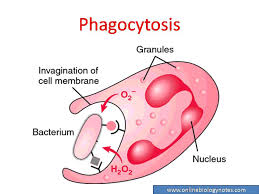
phagocytosis
allows for solid food to be taken directly into the cell
food is taken into a membrane-bound vacuole which contains digestive enzymes
nutrients released into cytoplasm
endosymbiotic theory
eukaryotic organelles could be the products of a symbiosis between bacteria and eukaryotes
mitochondria and chloroplasts arose only once in eukaryotes (primary endosymbiosis) but have been repeatedly lost, modified, and transferred between lineages
what evidence supports the endosymbiotic theory?
mitochondria and chloroplasts are haploid, have circular DNA, and reproduce via binary fission
mitochondria are closely related to proteobacteria and chloroplasts are closely related to cyanobacteria
the mitochondria and chloroplast genome are more similar to bacterial genomes than eukaryotic genomes
LECA
Last Eukaryotic Common Ancestor
secondary endosymbiosis
when a eukaryote gains its chloroplasts by engulfing a plant
tertiary endosymbiosis
eukaryote gains its chloroplasts by engulfing another microbial eukaryote
life cycle
events from birth until death including growth, changes in body form, sexual maturation, and reproduction
asexual reproduction in microbial eukaryotes
genotype is copied, creating an offspring that is genetically identical (but not necessarily morphologically identical)
what is phase contrast microscopy used for?
to view transparent parts of a live specimen without using stains to enhance visibility (stains usually kill it)
body forms of Naegleria gruberi
can switch between amoeboid and flagellate
slime molds (plasmodial vs cellular)
resemble fungi, but are distantly related
cool, moist, microenvironments
highly mobile, amoeboid body form
consume food via endocytosis
distance matrix
a way to summarize the percent difference in nucleotide sequence between taxa
can be used to draw unrooted trees that show relative relationships
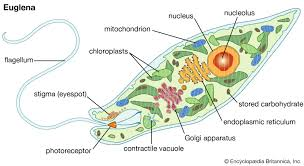
Euglena
green
very abundant in lab samples
flagellate
Amoeba
often surrounded by small microbial eukaryotes Chilomonas (food source)
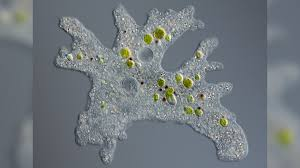
Blepharisma
large, pink, slipper shaped ciliates
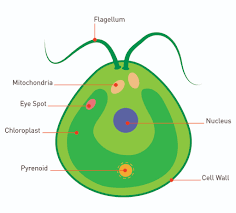
Chlamydomonas
circular, small, unicellular green alga
photosynthetic
flageallae
movement: jittery motion
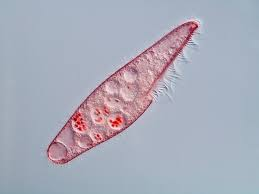
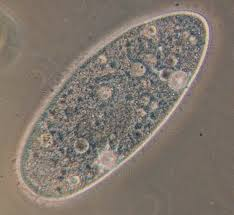
Paramecium
movement: quick, have cilia
unicellular
Stentor
green ciliates, irregular-trumpet shaped
size: large

setup of Naegleria experiment
grow Naegleria in the presence of food and without food to see if body form changes in response to removal of food source
count # of amoeboid vs non-amoeboid at 15 minute intervals
how to estimate organism size using microscope
compare organism size to the field diameter of 10X and 40X objective lenses
field diameter decreases as magnification increases
how to calibrate microscope
move objective lens to 10X
move filter wheel on condenser to Ph1
find phase centering telescope
remove right eyepiece
replace right eyepiece with phase contrast telescope
use phase contrast alignment knobs to center phase contrast rings so that they superimpose each other exactly
How did the mitochondria of eukaryotes evolve?
primary endosymbiosis: eukaryote engulfs a proteobacteria, which becomes the mitchondria
results in two membranes
evolved only once
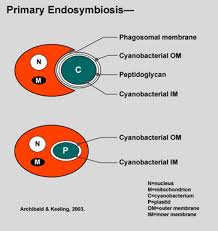
evidence for primary endosymbiosis of mitochondria
double membrane
mitochondria have circular DNA, like proteobacteria
how did chloroplasts evolve in eukaryotes?
initially evolved in plantae via primary endosymbiosis: eukaryote engulfed a cyanobacterium —> became chloroplast with 2 membranes
evolved once, but were transferred to other lineages via secondary endosymbiosis: eukaryote (w/o chloroplast) engulfs a plantae (that already has chloroplast) —> results in chloroplast with 3-4 membranes
monophyletic
protists
eukaryotes that are not plants, animals, or fungi
non-monophyletic
mostly microscopic and unicellular, but can be multicellular or form colonies
are eukaryotes monophyletic or non-monophyletic?
monophyletic
unicellular vs colonial vs multicellular
unicellular: one cell does everything
colonial: many cells are attached, but there is no division of labor/responsibilities
multicellular: many cells are attached and they have different functions
eukaryotic synapomorphies
linaer DNA
membrane bound organelles: nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast
cytoskeleton
mitosis
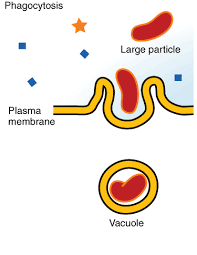
phagocytosis
organism takes in large particles
may/may not digest them
if they don’t digest them, they may form a membrane around them to form a symbiont