6. Evolution & Behavioral Ecology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Behavioral Ecology def.
the study of ecological & evolutionary basis of animal behavior
Evolution def.
process of change through time in the genetically determined characteristics of organisms being passed on to successive generations
change in allele frequencies in a population over successive generations, ultimately involves changes in the frequency of heritable traits
Natural selection def.
Nonrandom process by which individuals with certain genotypes-phenotypes are favored to survive & reproduce over other phenotypes in a particular environment
Variation in the populations def.
Individuals are not exactly alike (different genotypes and phenotypes)
different allele combinations can represent advantages or disadvantages in a given environment
The environment def.
Conditions and resources show variation, some become limiting factors
Differences in survival and reproductive success
only individuals with advantageous characteristics survive and then reproduce
Heredity def.
parents able to pass on some of their distinctive characteristics
Fitness def.
a measure of the genetic information contributed by an organism’s descendants to future generations
Behaviors influence fitness therefore….
Behavioral traits are often shaped by natural selection
Two main causes of behaviors
Proximate and ultimate
Proximate def.
An immediate underlying cause based on the operation of internal mechanisms possessed by an individual
ex. an increase in testosterone secretion in the male will cause vigorous displays toward females
Ultimate def.
The evolutionary, historical reason why something is the way it is
ex. females prefer males who vigorously display, leading to selection of those males and their traits
Adaptations def.
A hereditary trait that has spread or is spreading by natural selection and has replaced or is replacing any alternative traits in the species
Foraging behavior
Animals make behavioral choices that enhance their energy gain and reduce their risk of becoming prey
Optimal foraging theory def.
Animals will maximize the amount of energy gained per unit of feeding time, and minimize the risks involved
Foraging Behavior
Profitability (P) of a food item depends on how much energy (E) the animal gets from the food relative to amount of time (t) it depends obtaining the food:
P = E / t
Infanticide in lions
Male lions killing male cubs to increase chance of mating with females and decrease number of males
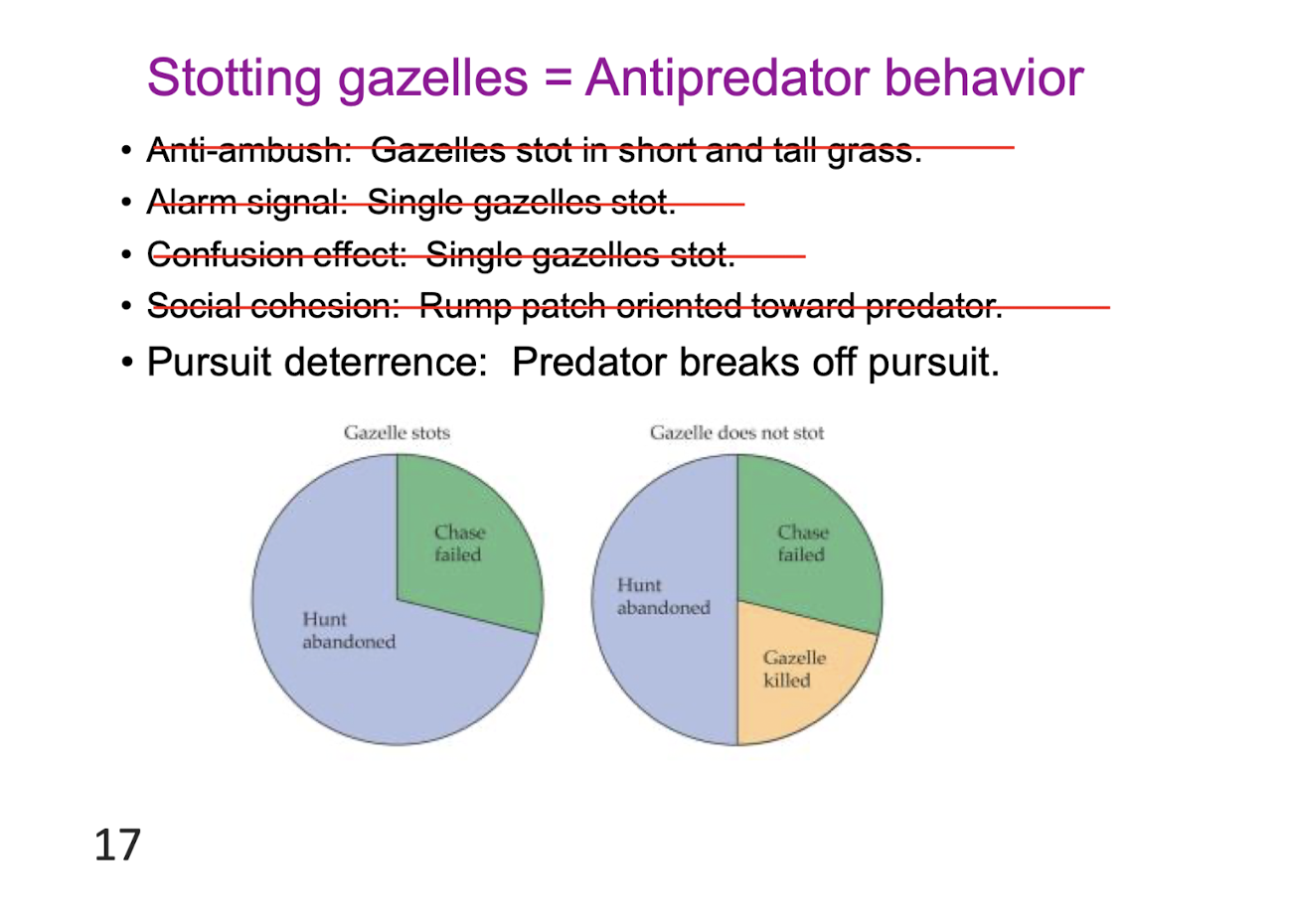
Stotting behavior
Jumping high in gazelles, deers to avoid being prey, looking out for survival, traveling, survival
anti ambush hypothesis
alarm signal hypothesis
social cohesion hypothesis
confusion effect hypothesis
Purist deterrence hypothesis
stotting gazaelles = antipredator behavior
pursuit deterrence: predator breaks off pursuit
Elaborate traits exhibited by male birds
These traits are costly, detertimenetal to survival?
energy
time
visibility
developmental tradeoffs
Sexual Selection
Darwin proposed that extravagant features of some males resulted from sexual selection
Long-tailed widowbird
the longer the tale of the male the more nests it had

Mating behavior
In some species, male provide females with a direct benefit for mating; gifts of food, help in rearing young, access to a territory with good nesting sites, food, etc
in others, males provide nothing, instead females may receive indirect genetic benefits
The handicap hypothesis:
a male that can support a costly ornament is likely to be a vigorous individual and whose overall genetic quality is high
The sexy son hypothesis
the female receives indirect genetic benefits through her sons, who will themselves be attractive to females and produce many offspring
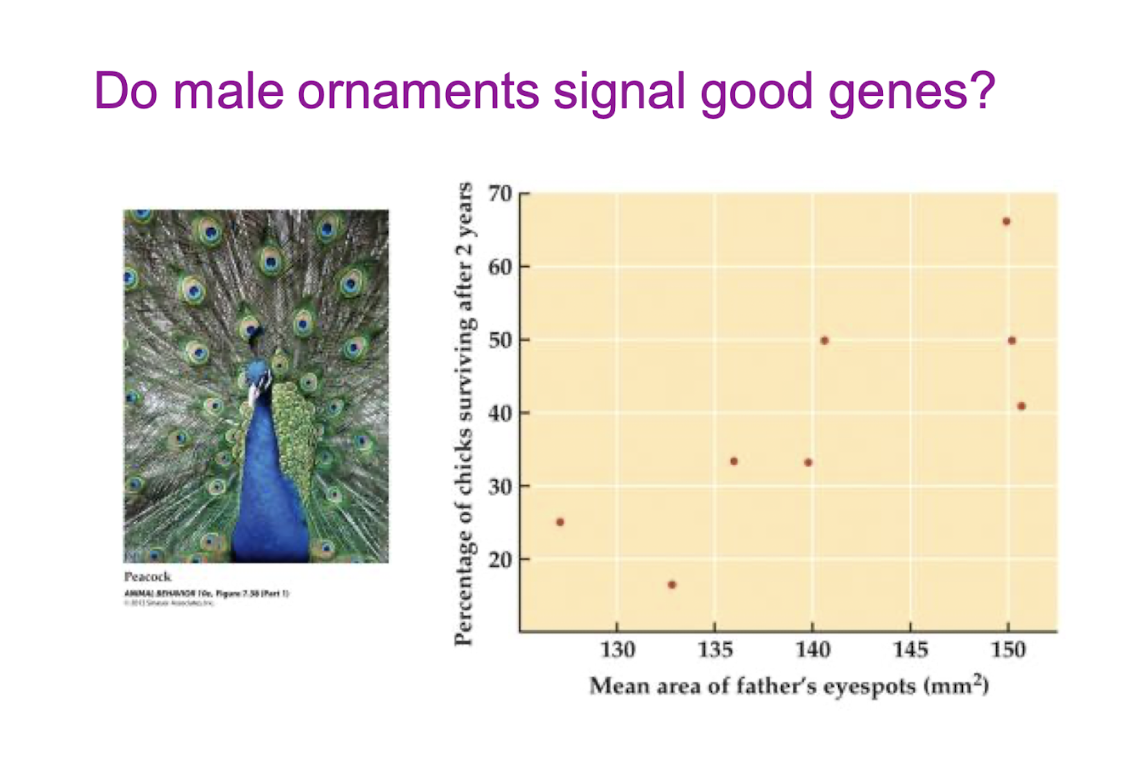
Male ornaments signal…
good genes
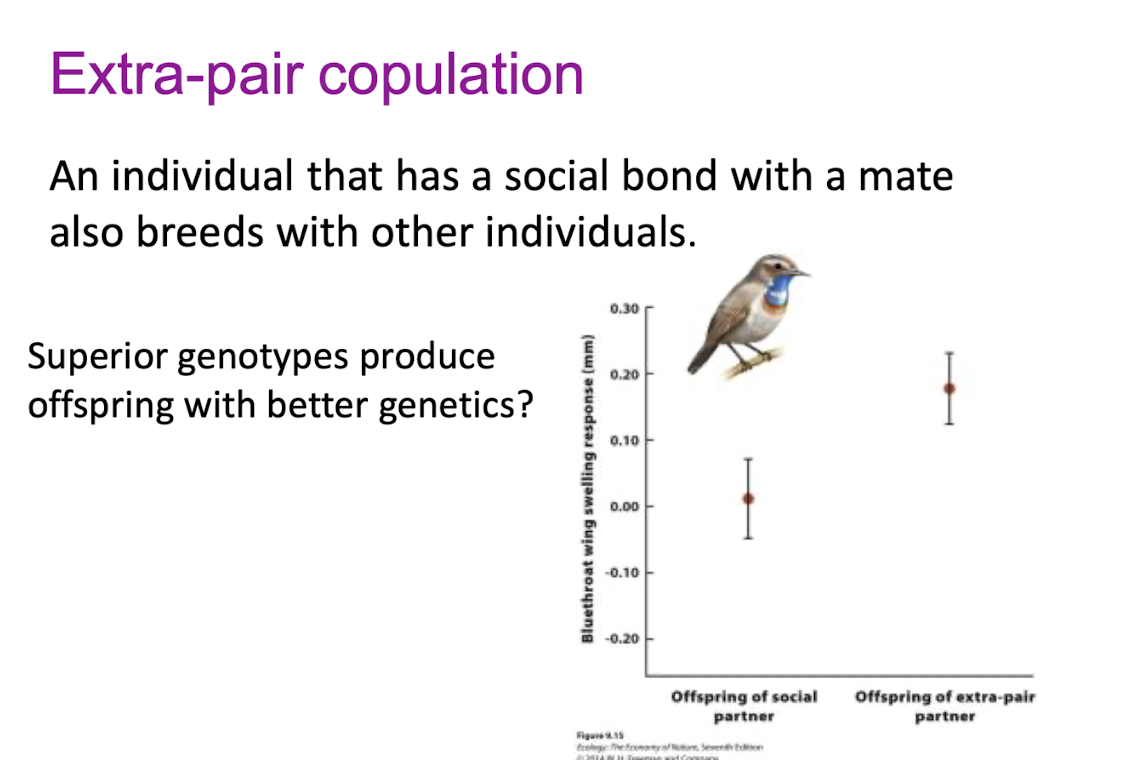
Extra-pair copulation def.
an individual that has a social bond with a mate also breeds with other individuals
superior genotypes produce offspring with better genetics?
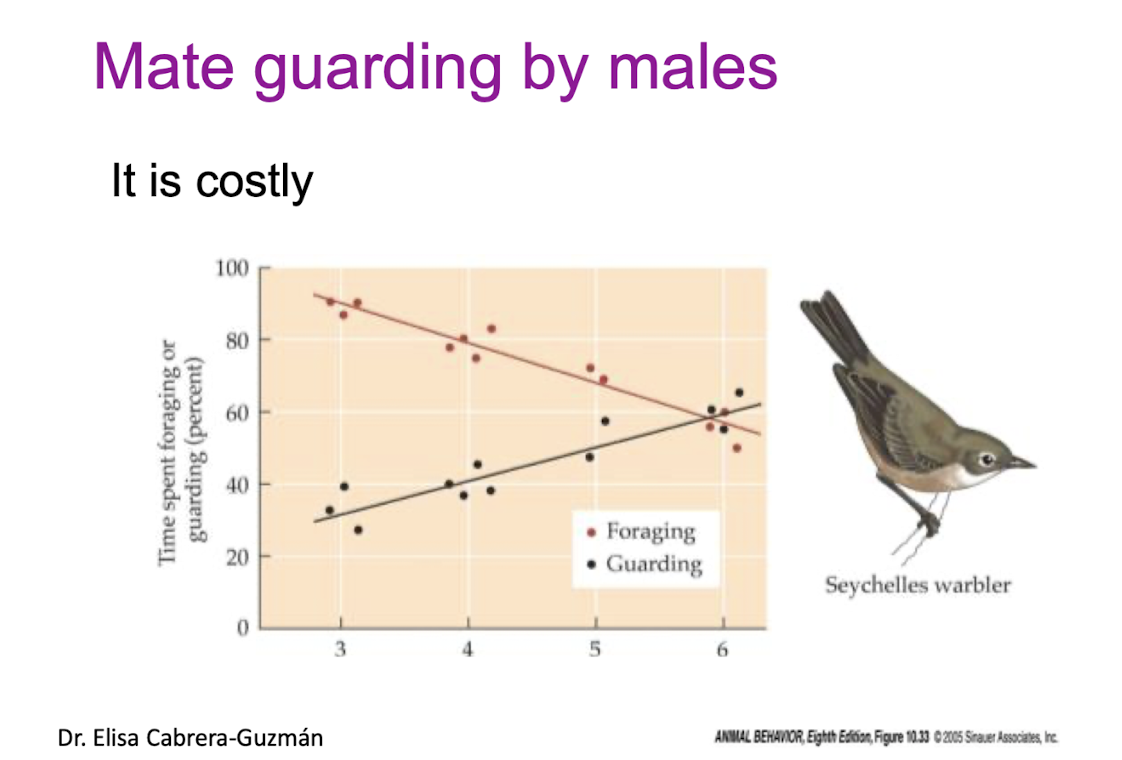
Mate guarding by males
is costly