unit 4 - skeletal system
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
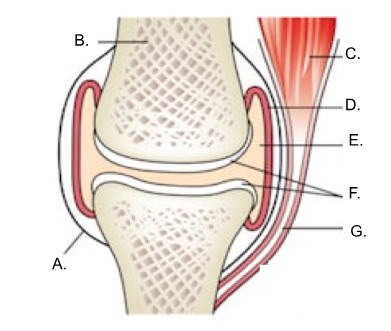
what is A?
ligament
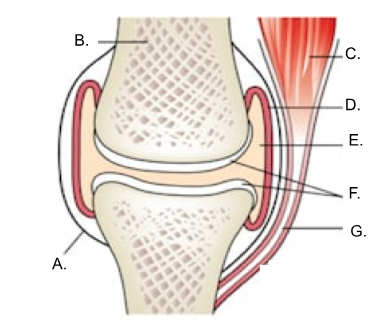
what is B?
bone
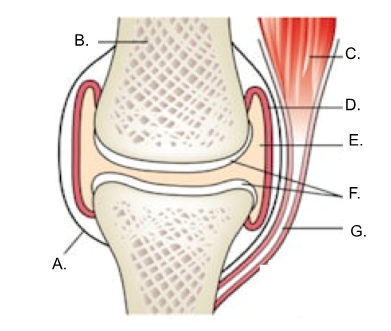
what is C?
muscle
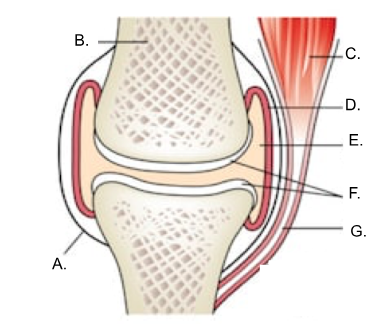
what is D?
synovial membrane
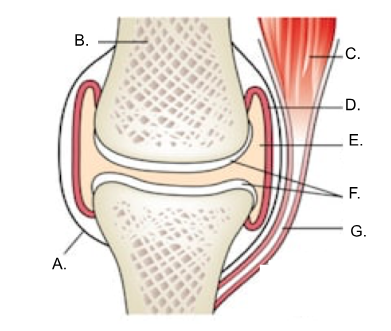
what is E?
joint cavity containing synovial fluid
synovial fluid
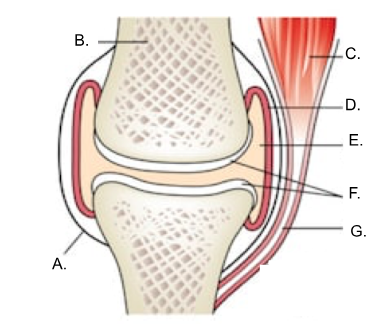
what is F?
articular cartilage
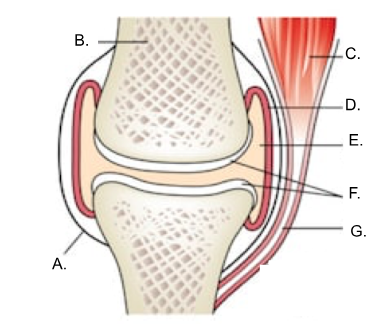
what is G?
tendon
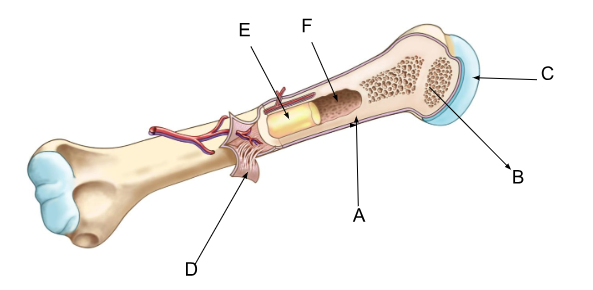
what is A?
compact bone
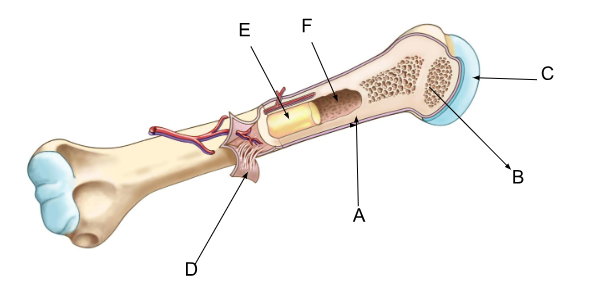
what is B?
spongy bone
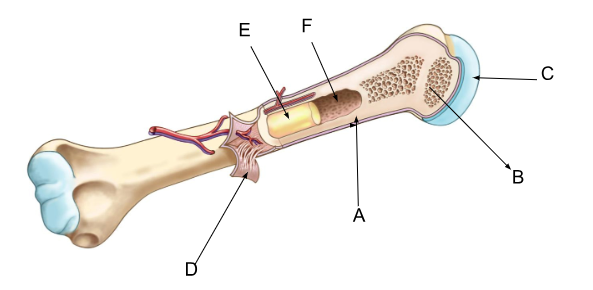
what is C?
cartilage
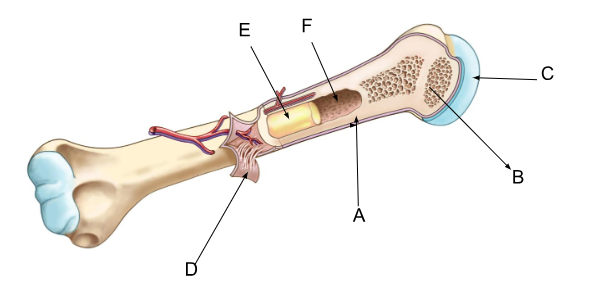
what is D?
periosteum
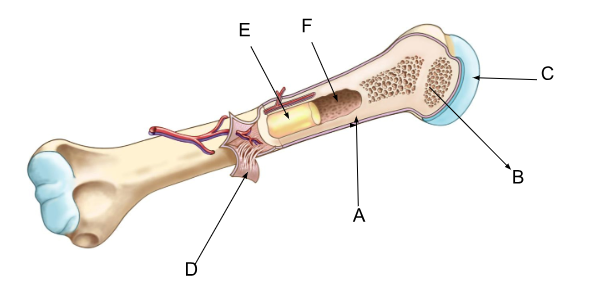
what is E?
yellow bone marrow
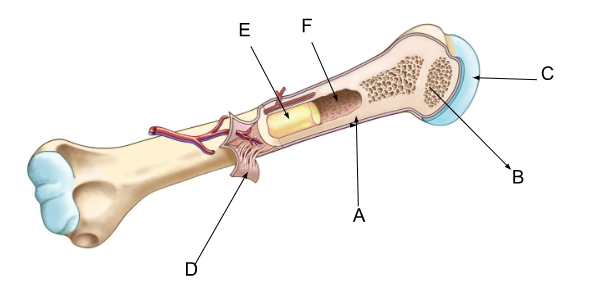
what is F?
marrow cavity
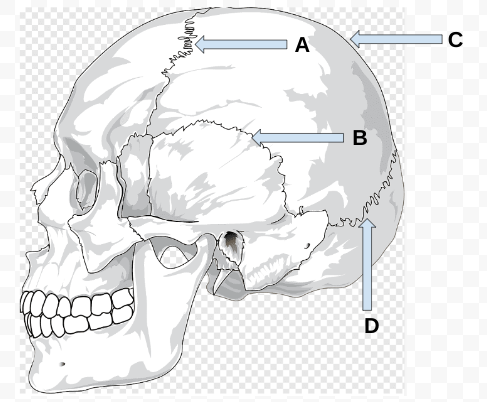
what is A?
coronal suture
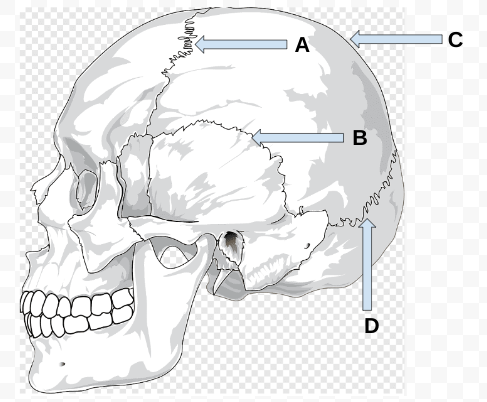
what is B?
squamous suture
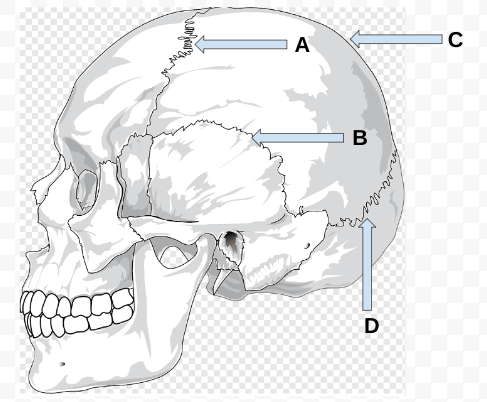
what is C?
sagittal suture
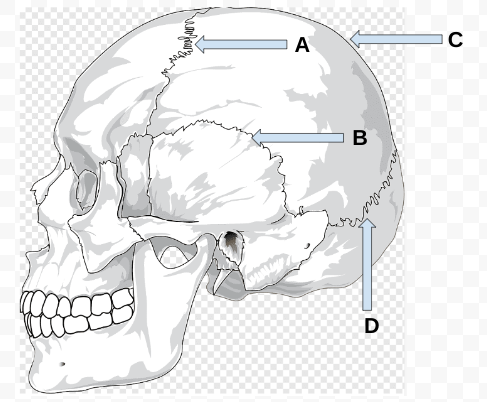
what is D?
lambdoid suture
cranium
axial
mandible
axial
magnum foramen
axial
vertebral column
axial
sternum
axial
ribs
axial
costal cartilage
axial
sacrum
axial
coccyx
axial
scapula
appendicular
clavicle
appendicular
humerus
appendicular
radius
appendicular
ulna
appendicular
hands & fingers
appendicular
pelvis
appendicular
femur
appendicular
tibia
appendicular
fibula
appendicular
foot & toes
appendicular
compound fracture
ends of bones protruding through skin
simple fracture
bone splinters/fragments between two main fragments, due to compression
greenstick fracture
partial fracture, one side breaks & other bends
occurs in children (bones are fully ossified)
spiral fracture
bone breaks in half by a twisting force or impact
transverse fracture
breaks straight across bone
stress fracture
thin crack, also “hairline fracture”
fibrous joints
immovable
found in sutures of cranium
cartilaginous joint
semi-movable
found in vertebral disc
synovial joint
fully moveable
found in knee & elbow
SYNOVIAL - hinge
angular, open-closing motion
found in: elbow & knee
SYNOVIAL - pivot
“peg in hole”, rotation on central axis
found in: atlantoaxial joint (allows head to move side to side)
SYNOVIAL - planar
2 surfaces glide against each other; side to side and back and fourth
found in: carpals & tarsals
SYNOVIAL - ball & socket
ball-like surface of one bone fits into the cup like depression of another bone
found in: shoulder & hip
JOINT INJURY - sprain
twisting/wrenching of joint
may damage blood vessels, muscles, tendons, nerves
swelling, pain, bruising
JOINT INJURY- dislocation
displacement of bone from joint
JOINT INJURY - avulsion
skin layers torn off to reveal muscles & tendons
JOINT INJURY - subluxation
partial dislocation
BONE MARROW - yellow
found in: shaft of long bone
purpose: produce cartilage, fat, bone
BONE MARROW - red
found in: flat bones
purpose: contains cells that create red, white blood cells and platelets
male spread of pelvis
more vertical & less flared
female spread of pelvis
more flared & oval
male shape or obturator foramen
larger & rounder
female shape of obturator foramen
smaller & triangular
male angle across pubic symphysis
less than 90 degrees & acute angle
female angle across pubic symphysis
greater than 90 degrees & obtuse angle
male inner diameter of pelvic inlet
smaller
female inner diameter of pelvic inlet
larger (room for baby head)
long bones
greater in length/width
long shaft
short bones
somewhat cubed shape
equal in length and width
ex: tarsal & carpals
flat bones
thin
provide protection
ex: ribes, cranial
irregular bones
complex shape
ex: vertebrae, some facial bones
sesamoid bones
protect tendons from wear and tear
ex: patella
diaphysis
long cylindrical
main portion of bone
adds to length
epiphysis
distal and proximal ends of bone
help to form joint
contains spongy bone
metaphysis
where epiphysis meets diaphysis
epiphyseal plate
layer of cartilage being replaced by bone
cartilage
reduces friction
absorbs shock
spongey bone
contains red marrow
ex: hip bones, ribs, breast bones
compact bone
solid, dense bone
external layer of all bones of body
bulk of body of long bones
provides protection
marrow cavity
space within diaphysis which contains yellow marrow (fat)
periosteum
tough sheath of dense irregular connective tissue
surrounds bone surface
protects bone
helps with repair
point of attachment
endosteum
lines surface of marrow cavity
containing bone forming cells (growth in width of bone)