science final review guide
1/318
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
319 Terms
primary function of carbohydrates
short term energy
monomers of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
polymers of carbohydrates
polysaccharides
primary function of lipids
long term energy
primary function of proteins
all cellular functions
monomers of protein
amino acids
polymers of proteins
proteins
primary function of nucleic acid
storing and passing genetic information
monomers of nucleic acid
nucleotides
polymers for nucleic acid
nucleic acid
metabolism
Obtain and use materials and energy
stimulis
Respond to the environment
homeostasis
Maintain a stable internal environment
Evolution
change in population over time
covalent bonds
bonds between two atoms that share energy
hydrogen bond
weaker covalent bond between a hydrogen atom and a negatively charged atom
ionic bond
electrosn are transferred from one atom to another
adhesion
when water molecules cling on to other surfaces
cohesion
when water molecules cling on to each other
solutions
when a solid can dissolve in a liquid when partial charges interact
suspensions
when a solid can’t dissolve in a liquid
PH level below 7 with alot of H+
acidic solution
PH level above 7 with little H+
basic solution
PH level at 7 and H+ and OH are equal
nuetral solution
catalyst
alter the requirements for chemical reactions (heat)
enzymes
biological catalyst made from proteins
role of enzymes
lower the amount of activation energy required for chemical reactions
anabolism
when catalyst build up big molecules
catabolism
when catalyst break down big molecules into smaller ones
chemical reactions
when molecules hit at a specific angle with a certain amount of energy to create new molecules
activation energy
enegry requiered for chemical reactions
The effect of tempature
When temperature increases, enzyme activity increases to a point known as optimal temperature
the effect of PH
When pH increases or decreases, the H+ and OH charges will change. has optimal PH level
the effect of substrate concentration
When substate concentration increases, enzyme activity increases
organism
a single living thing
population
group of individuals from the same species that live in the same area
community
many populations of different species living in the same area
ecosystem
all the organisms (biotic factors) in one place, along with the nonliving (abiotic) factors in that area.
biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and similar types of organisms
biosphere
all the places on Earth where life exists
Biotic factors
Living parts of an environment
abiotic factors
Nonliving parts of an environment
weather
day-to-day conditions of Earth’s atmosphere
climate
long-term patterns of temperature and precipitation over many years
Greenhouse effect
gases that trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere, causing it to warm
tropical zone
where the sun's rays hit Earth the most directly
temperate zones
where the sun's rays hit the Earth less directy then the tropical zones, but more directly then the polar zones
polar zones
where the suns rays hit earth the least directly
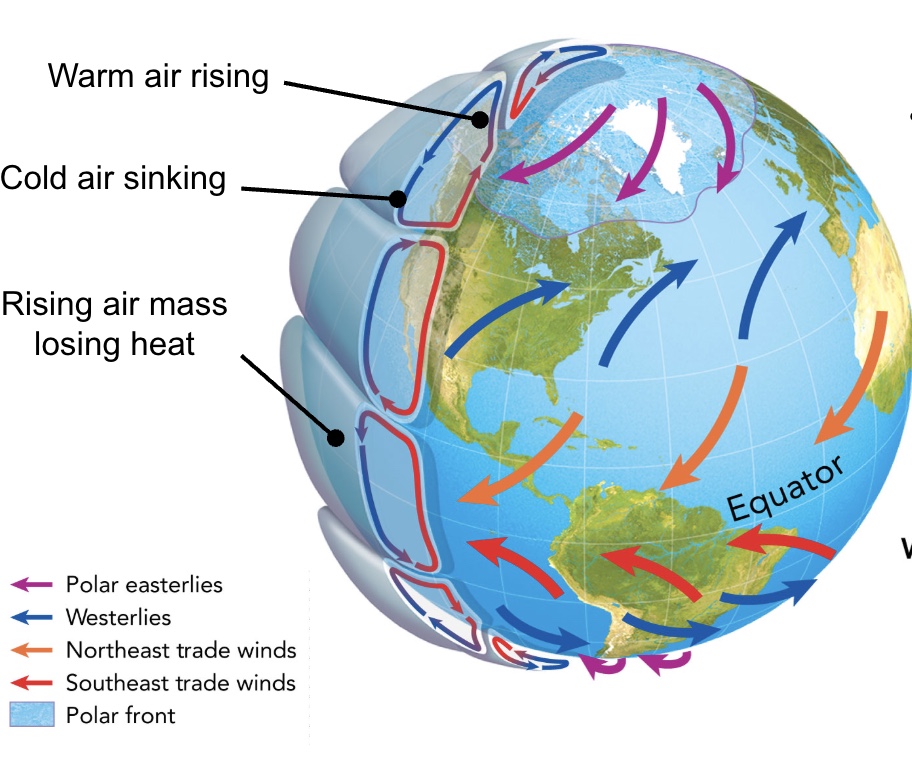
global winds
Wind current is caused by heat being unequally distributed across the atmosphere. Earth’s rotation causes winds to move east to west in the temperate zones and west to east in the tropical/polar zones
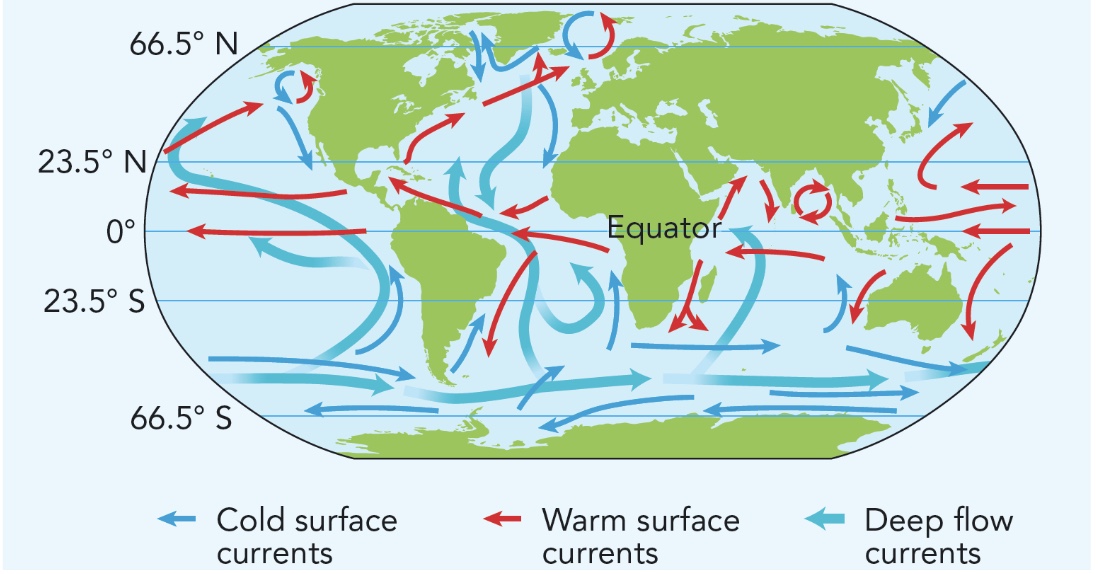
ocean currents
driven by warm/cool air and the placement of the continents
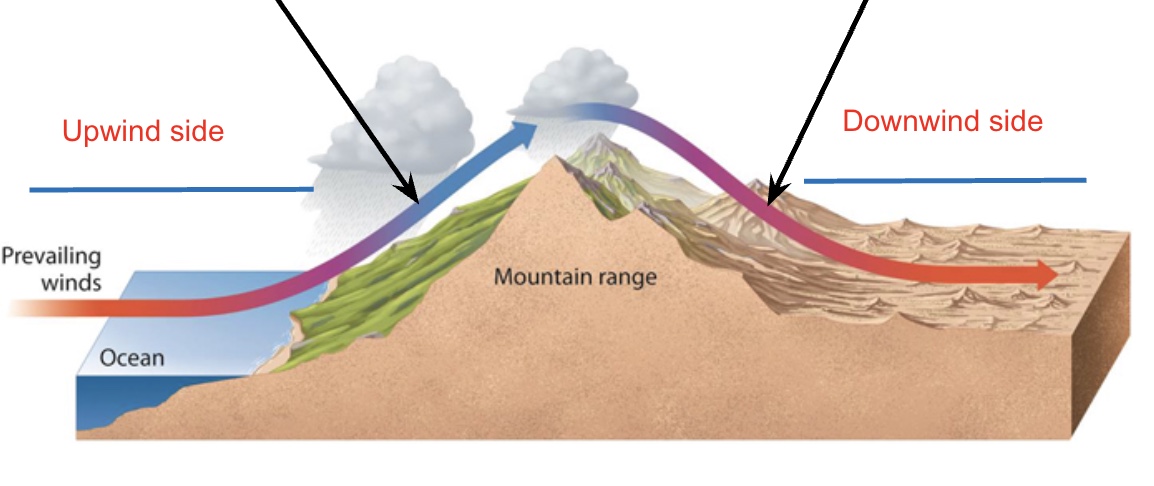
regional climate
Shaped by latitude, winds, ocean currents, mountains, and water
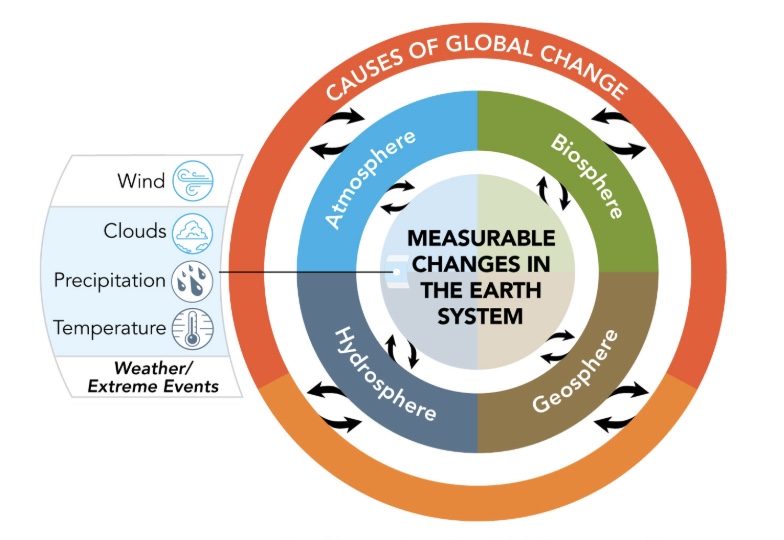
Changes in Climate
Involves changes in temperature, clouds, winds, patterns and amounts of precipitation, and the frequency and severity of extreme weather events.
Photosynthesis
process that uses energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates and oxygen
Chemosynthesis
process that uses chemical energy to produce carbohydrates
Autotroph/primary producers
organisms that captures energy from nonliving sources and converts it to a form that cells can use
Consumers/Heterotrophs
Organisms that rely on other organisms for energy and nutrients
Carnivore
eats only other animals
Herbivore
only eats plants
Omnivore
eats both plants and animals
Detritivore
chew up detritus and digest it
scavenger
animals that consume other animals that are already dead
Decomposer (saprotroph)
chemically break down organic matter outside of the body
food chain
a series of organisms in which energy is transferred from one organism to another.
food web
a network of feeding interactions representing a community of organisms.
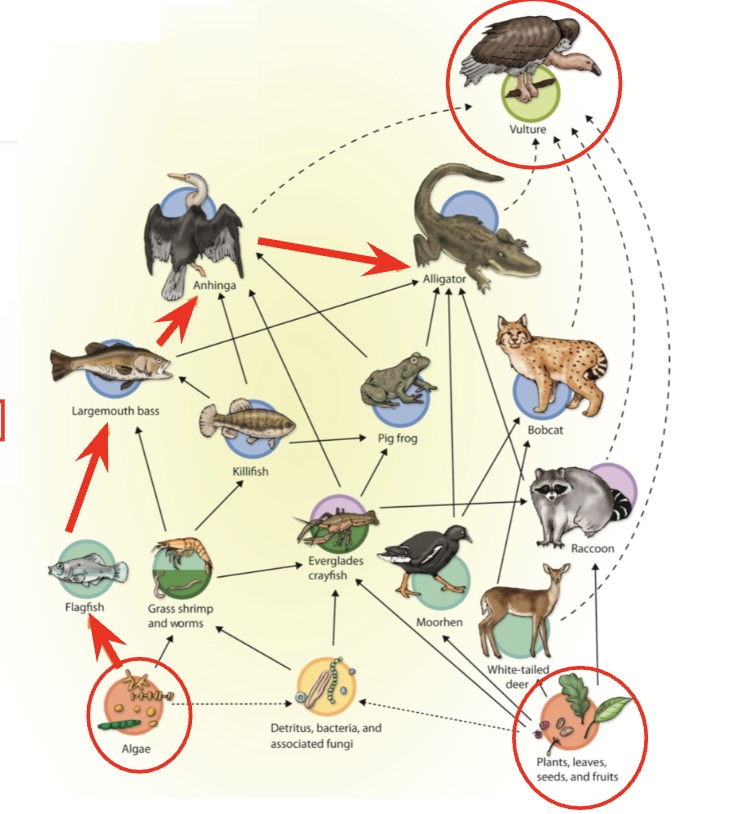
Pyramid of Energy
Show the amount of energy available at each level of the food chain
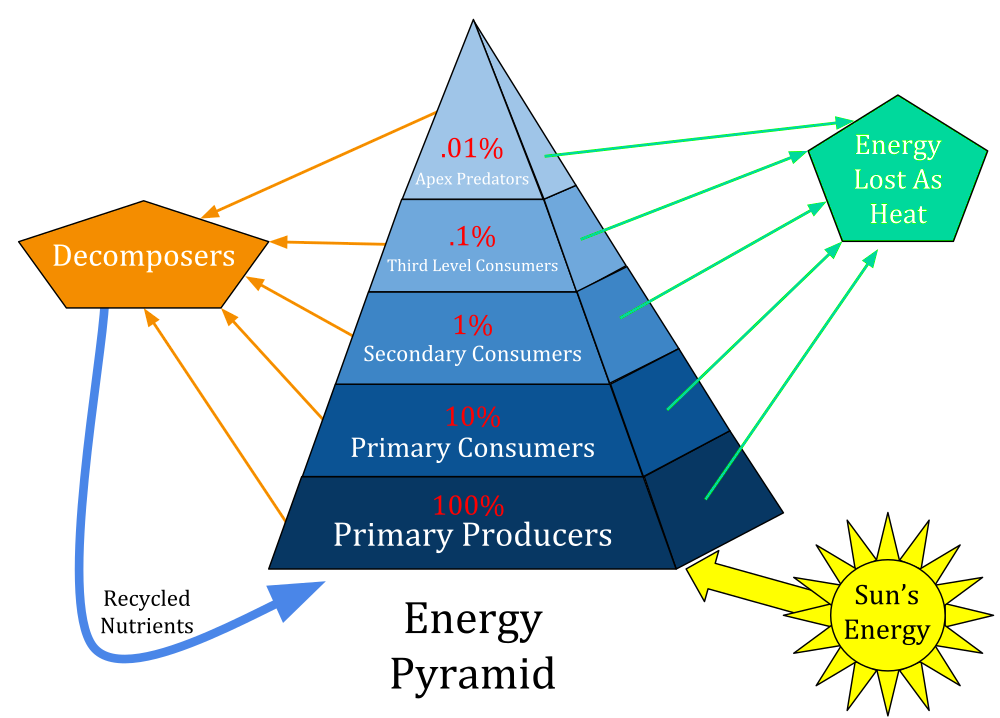
Biomass Pyramid
illustrates the relative amount of living organic matter in each trophic level
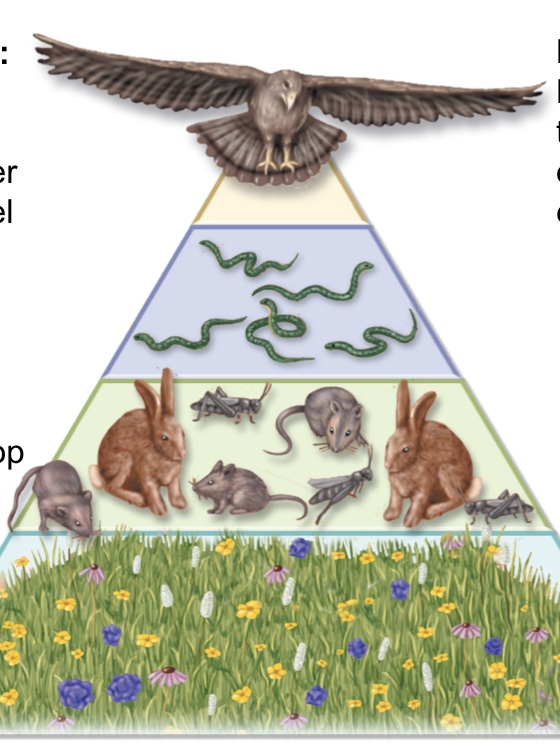
Pyramid of Numbers
illustrates the relative number of individuals in each trophic level
Water cycle
Evaporation, Precipitation, and runoff
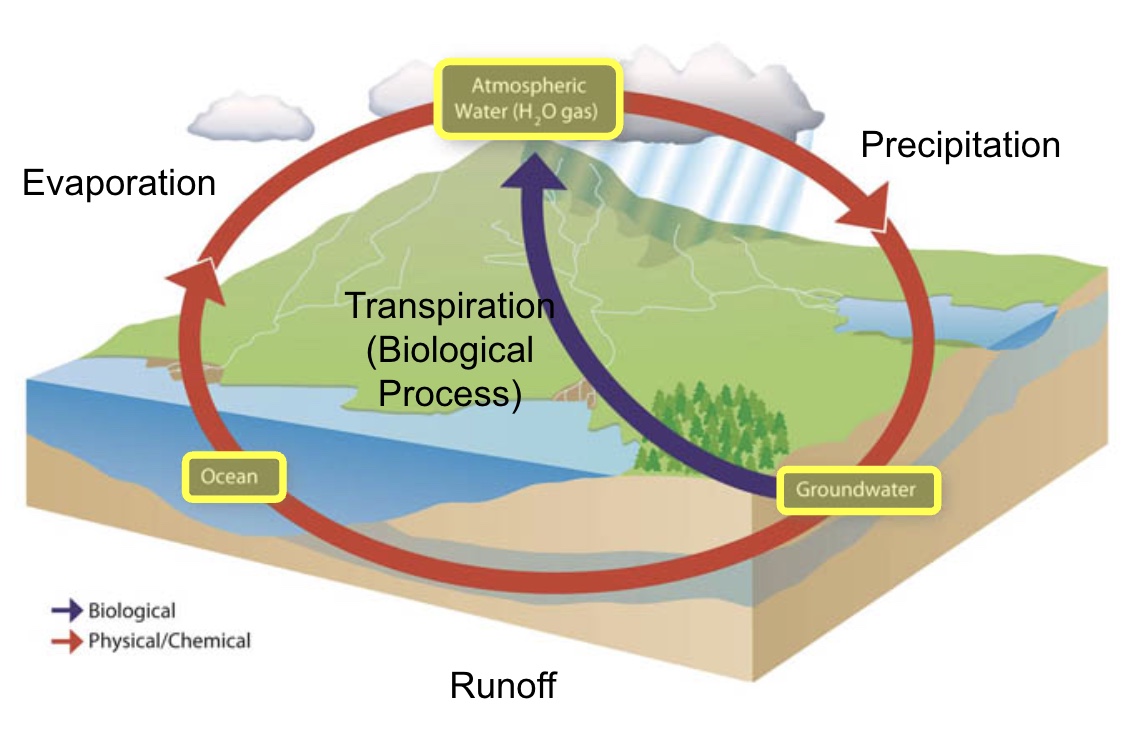
transpiration
biological evaporation
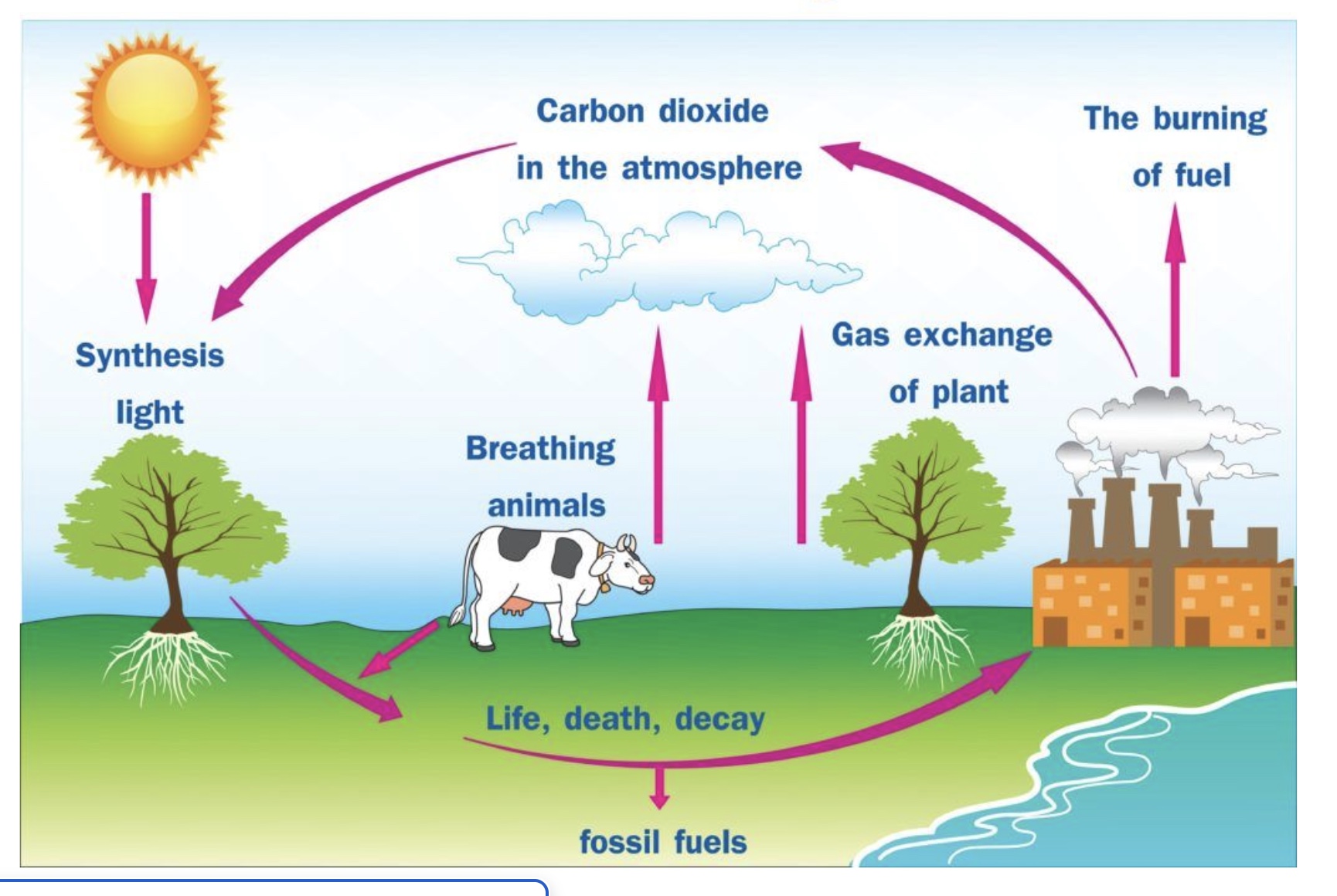
Carbon cycle
synthesized by light, breathed in by organisms, decays into the ground and becomes fossil fuels or goes back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide through cellular respiration
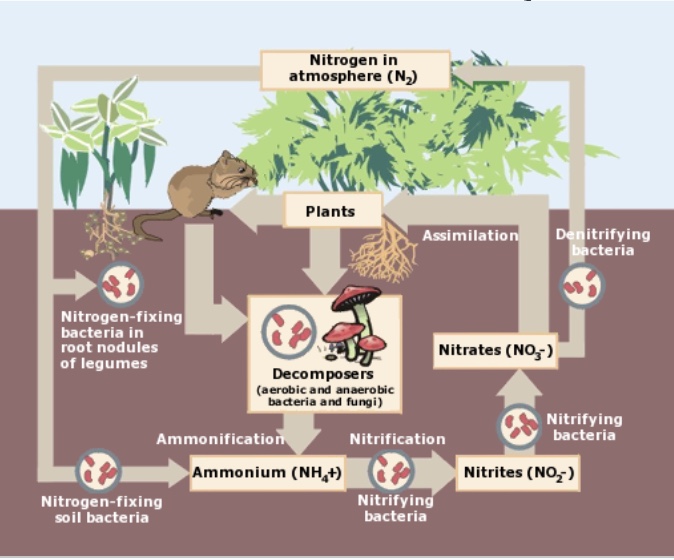
Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen is taken in by primary producers, nitrogen-fixing bacteria take the nitrogen into the soil, taken in by nitrifying bacteria, and then used for plants, or taken in by denitrifying bacteria and put back into the atmosphere
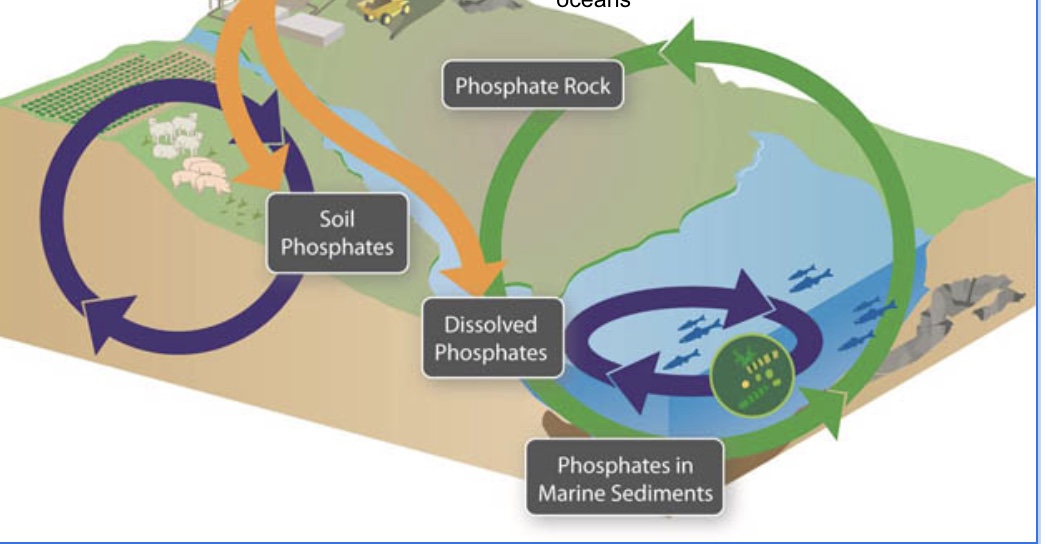
phosphorus cycle
Phosphorus is dissolved into water, taken up by primary producers, reused by consumers, and released via excretions. harvested by human for fertilizer
Geographic Range
The area inhabited by a population is called its geographic range.
Population Density
number of individuals that can be found per unit area.
Population Distribution
The way individuals are spaced out across the range.
Age Structure
Distribution of age and sex across the population.
Exponential Growth
Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially, meaning the larger a population is, the faster it grows
Logistic Growth
When a population’s growth slows and then stops, following a period of exponential growth, it is called logistic growth (S curve).
Carrying Capacity
The maximum number of individuals of a particular species that a particular environment can support. Limited by biotic and abiotic factors
Limiting Factors
any factor that controls the growth of a population
Density-dependent limiting factors
operate strongly when population density reaches a certain level.
Competition
More individuals use up resources sooner
Parasitism and Disease
Parasites, disease, and Stress from overcrowding can lead to lower birth rates, higher death rates, and higher emigration rates.
Herbivore Effects
Populations of herbivores and plants cycle up and down like populations of predators and prey.
Density-Independent Factors
affect all populations regardless of population size and density.
Extinction
If carrying capacity falls low enough, populations can be wiped out, leading to population extinction.
Habitat
An area with a particular combination of physical and biological environmental factors that affect which organisms can live within it.
microhabitat
a tiny part of a much larger habitat. It has its own set of environmental conditions called its microclimate.
microbiome
a microbial community
Tolerance
The range of external conditions within which a species can survive and reproduce. A species best survives and reproduces within its optimal range.
Niche
A species’ range of physical and biological conditions in which it can survive and reproduce, as well as the way it obtains the resources it needs.
Keystone Species
a species that plays a vital and unique role in maintaining structure, stability, and diversity in an ecosystem
Intraspecific
competition by members of the same species
interspecific
competition by members of different species
Competitive Exclusion Principle
No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same habitat at exactly the same time.
Symbiosis
relationship between two species
Commensalism
A relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
Parasitism
A relationship in which one organism lives inside or on another organism and harms it.
Ecological Succession
A series of events that occur in a community over time.