Readers' Response Criticism
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
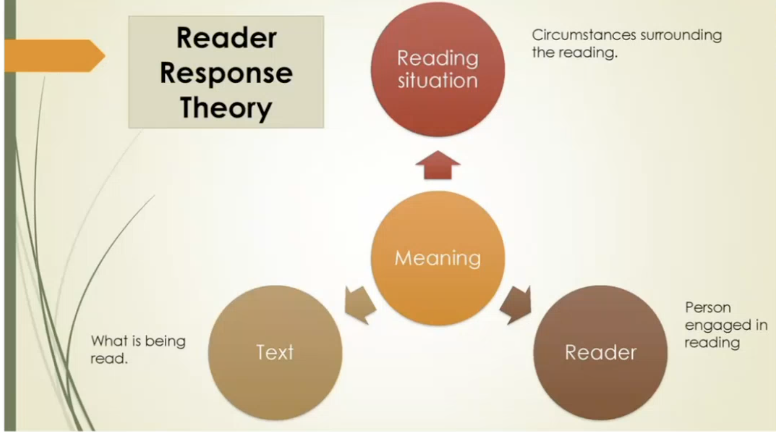
Reader-Response Criticism
it emphasizes how reader’s engagement shapes interpretation. It promotes the idea that a text has multiple meanings based on the person reading it
Key Tenets of Reader-Response Criticism
Subjectivity, Active Engagement, Text as a Catalyst
Subjectivity
the inherent subjectivity of interpretation, recognizing that readers bring their own experiences, beliefs, and values to the reading process.
Active Engagement
the idea that readers don’t just receive meaning from a text but they actively shape it.
eg. draws conclusions, engages with the author’s ideas, makes connections, and creates their own interpretation
Text as a Catalyst
The text acts as a guide for the meaning the readers’ ought to make.
The Reader as Co-Creator
Reading is an active process where readers connect ideas, make inferences, and engage with the author’s message to build meaning.
Types of Reader Response Criticism
Transactional Reader-Response, Affective Stylistics, & Social Reader-Response
Transactional Reader-Response
It focuses on how the reader and text interacts, therefore the meaning isn’t fixed but it changes based on reader’s interpretation
Affective Stylistics
how the reader’s emotions towards a text shapes their interpretation
Social Reader-Response
how the social and cultural backgrounds influence the way a reader can understand a text
Applications of Reader-Response Criticism
Literary Analysis, Teaching Literature, Communication Studies
Literary Analysis
Critics use this approach to study how readers interact with text and how different interpretations emerge
Teaching Literature
helps to create engaging lessons via critical thinking, where readers reflect on their experiences to interpret texts in different ways
Communication Studies
explores how audiences interpret meaning in different forms of communication.
eg. books, speeches, & media
Limitations of Reader-Response Criticism
Subjectivity
Readers may interpret texts too personally, therefore fully ignoring the text’s original meaning
Relativism
Allows multiple interpretation without clear criteria for evaluation
Lack of Context
It may overlook important factors like the history, society, and traditions set forth.
Reader-Response in Practice
Analyzing a Poem
focuses on emotions, personal connections, & experiences to shape the interpretation
Interpreting a Novel
Considers personal background, culture, beliefs, & values in regards to understanding the characters, plot, & themes
Engaging with a Play
Recognizes how expectations and biases influence the interpretation of the characters, themes, and the message
Reader Response Theory
Engaging with Reader Response
Makes Literary Analysis more personal and insightful
Deepens engagement with literature
Improves critical thinking & broadens our understanding of interpretation
helps us understand how readers shape the meaning of a text