B3-Dermatology
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Derm definitions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Macule
small circumscribed area of change in skin color w/o elevation or depression
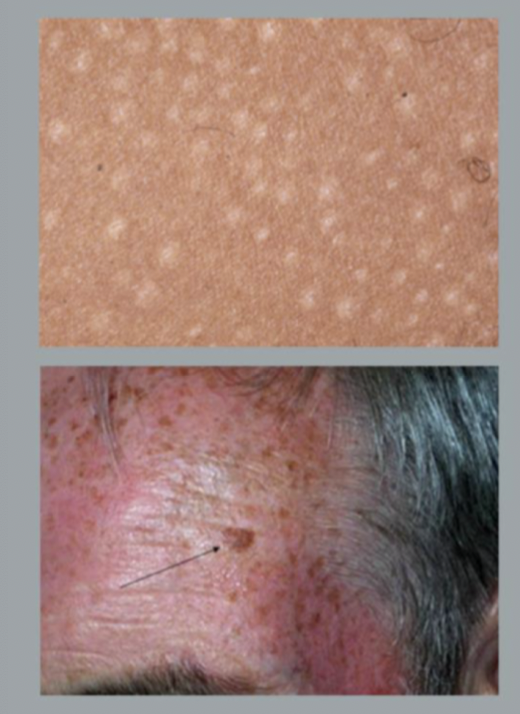
Papule
small solid, elevated lesion which projects above the plane of surrounding skin
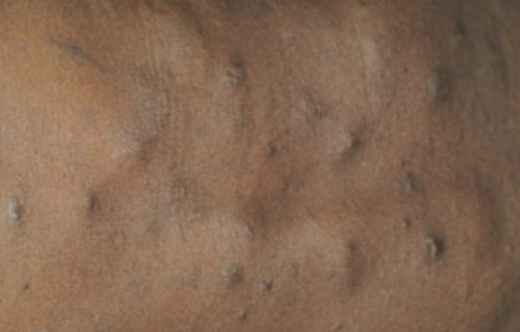
Nodule
large, solid elevated lesion
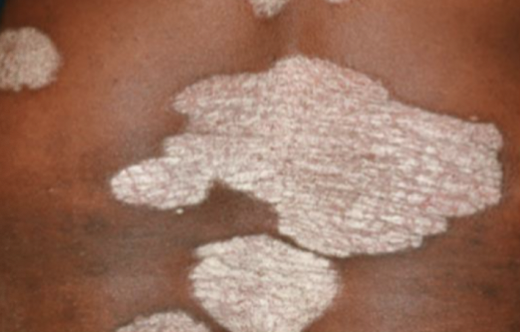
Patch
large, non-elevated area of skin with a different color than the surrounding area

Plaque
large plateau-like elevation above the skin
Vesicle
small circumscribed, elevated, superficial cavity of fluid
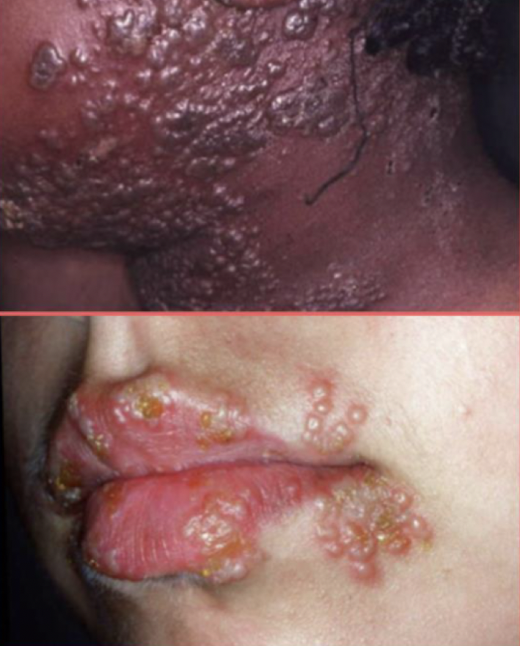
Bulla
large circumscribed, elevated, superficial cavity of fluid
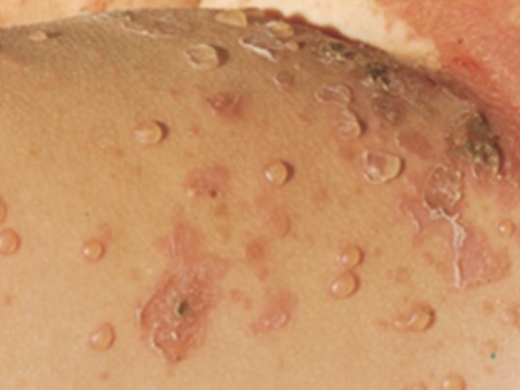
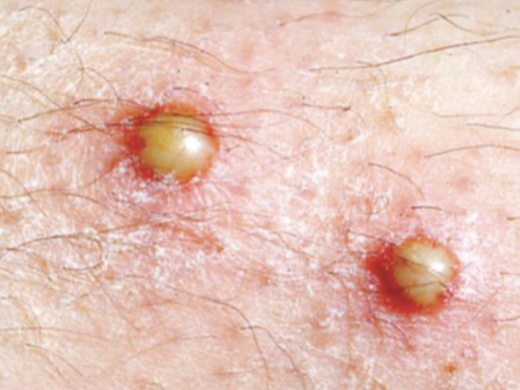
Pustule
circumscribed superficial cavity of skin that contains a purulent exudate which may be yellow
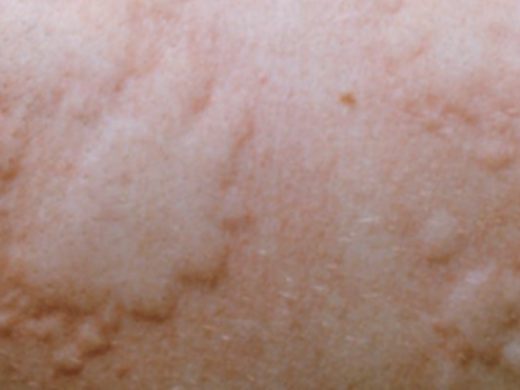
Wheal
a rounded or flat-topped pale papule/plaque that disappears in 48 hours; due to edema of the dermis
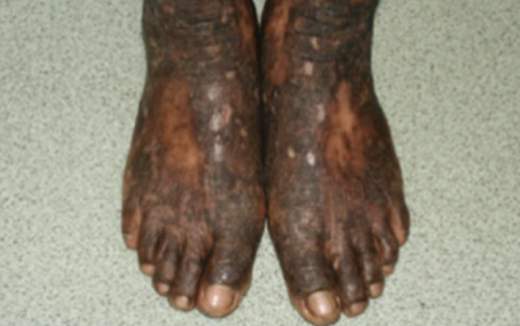
Scale
secondary skin change; flakes of the stratum corneum
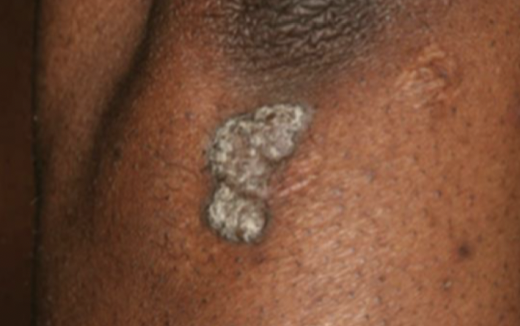
Lichenification
thickening of the epidermis with deepening of skin lines in parallel or rhomboidal pattern
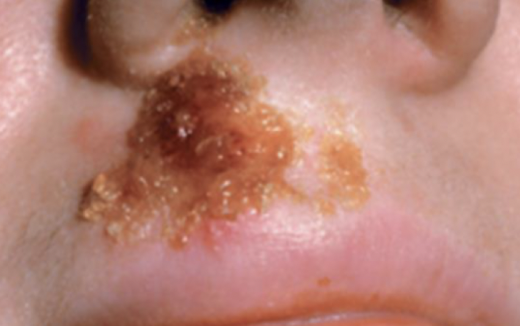
Crust
Develop when serum, blood, or pus dries on skin surface
Eczematous dermatitides
polymorphic inflammatory reaction pattern involving the epidermis and dermis that is red, itchy, and has surface change
Stratum spinosum
Hyperplasia of what skin layer occurs during eczematous dermatitides?
Spongeosis
intracellular edema in the epidermis
Atopic Dermatitis
elevated serum IgE (type 1 HS), activated T cells in the dermis cause red, patchy, itchy skin
Allergic contact dermatitis
cell mediated HS (type IV) that requires prior sensitization to a chemical
Primary Irritant Dermatitis
direct irritation that is non-immunologic
Drug related eczematous dermatitis
caused by drugs that effect the skin barrier or lead to immunologic response (statins, immune modulating drugs)
Seborrheic dermatitis
common, seen in areas with the most sebaceous glands, may present with dandruff or cardle cap
Parkinsons & HIV/AIDs
What population has an increased incidence of seborrheic dermatitis?
Psoriasis
chronic disorder with a polygenic predisposition that affects 1.5-2% of population
Koebner phenomenon
appearance of new skin lesions on areas of cutaneous injury
Auspitz sign
Pinpoint bleeding spots from exposure of dermal papillae
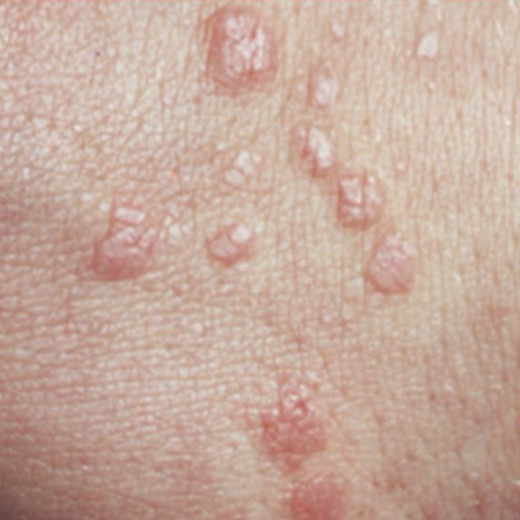
Lichen planus
papule, purple, polygonal, pruritic; arms and legs as well as while papules in the mouth
Saw tooth ridges
Wickham’s striae
Fine white lines on surface of papules of plaques in lichen planus
Acne rosacea
inflammation of pilosebaceous units, cause redness and pustules but no comedones
Mastocytosis
increased mast cells in the skin
Darier sign
lesions become red and raised when stroked due to mast cell degranulation
dermatographism
stroking normal skin with a pointed instrument causes degranulation and hives resembling shape drawn
mycosis fungoides
lymphoma of CD4+ T helper cells
develops from flat to plaque to nodule
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Intraepidermal/suprabasal bullous disease
Bullous pemphigoid
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Subepidermal bullous disease
Desmosomes
cell to cell attachments between the epithelial cells of the epidermis
Hemidesmosomes
attach basal cells to the basement membrane (epidermis to basement membrane)
Anchoring fibrils
type 7 collagen that anchors the hemidesmosomes/basement membrane to the dermis
Pemphigus Vulgaris
autoantibodies against desmogleins (3 or 3/1) which disrupt the attachments and result in acantolysis
would expect to find a blister ABOVE the basal cell layer
IgG deposition along cell membranes (light green immunofluorescence) showing loss in cell to cell adhesion
*Nikolsky Sign
Tx: corticosteroids
Nikolsky Sign
slight rubbing/pressure produces exfoliation of the outermost layer of skin
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
IgA transglutaminase autoantibodies bind reticulin (anchoring fibril) so that the epidermal basement membrane is no longer anchored to the dermis
Granular IgA deposits in dermal papillae causing inflammation
Almost everyone with dermatitis herpetiformis also has CROHNS DISEASE
strikingly bilateral lesions
tx: dapsone and gluten free diet
Bullous pemphigoid
TENSE bullae w/ epidermis that remains intact
antibodies against BPAGs which are components of hemidesmosomes (*BPAG2/BP180)
subepidermal, nonacantholytic blisters w/ entire epidermis in the root
eosinophils
linear IgG deposition along dermoepidermal junction *involves complement activation