BIOL 145 - Week 4 - Simpson college
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Anabolism
Forming chemical bonds to build molecules
Catabolism
Breaking chemical bonds
Cellular respiration reactions
Release energy held in chemical bonds by breaking down carbohydrates, producing carbon dioxide and water
Photosynthesis-respiration cycle involves?
Transfer of energy via oxidation-reduction reactions
Oxidation
Loss of electron
Reduction
Gain of electrons
Essence of photosynthesis
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) gives cellular activity. Plants make it by using light as energy.
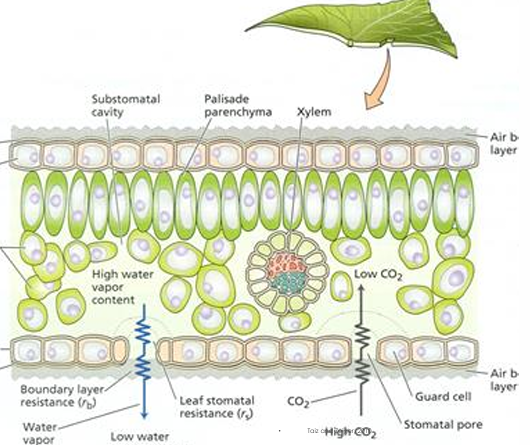
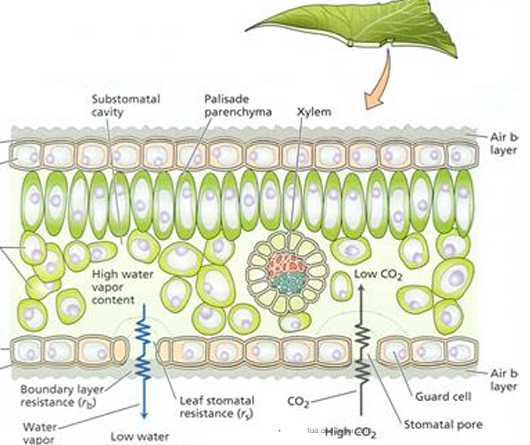
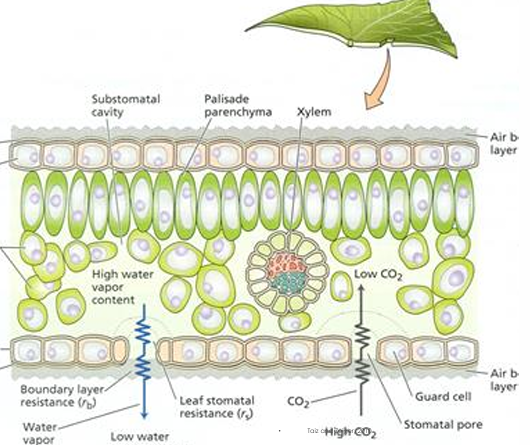
Carbon dioxide reaches chloroplast in mesophyll cells by
Diffusing through stomata into leaf interior
Three fates of light absorbed:
Photochemical, non-photochemical, and emission
Less than 1% of all water absorbed by plants is used in…
Photosynthesis
Most of water is used for?
Transpiration and other plant materials
PAR definition (for spectrum of colors)
Photosynthetic active radiation
Different colors =
Different wavelengths of light
Each pigment has its own distinctive pattern of light absorption =
Pigment absorption spectrum
If light and temp too high
Ratio of carbon dioxide to oxygen inside leaves may change
If light intensity is too high
Photooxidation occurs, which results destruction of chlorophyll
Several types of chlorophyll molecules
Magnesium end captures light. Lipid tail anchors into thylakoid membrane. Contain chlorophyll a (blue-green) and chlorophyll b (yello-green)
Chlorophyll b transfers
Energy from light to chlorophyll
Other photosynthetic pigments include
Carotenoids, phycobilin’s, and several types of chlorophyll
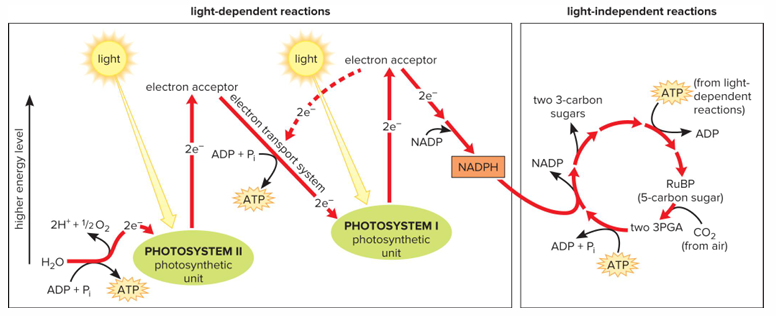
Two phases of photosynthesis
Light-dependent reaction and light-independent reactions
Light-dependent reactions
In thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. Water molecules split apart, releasing electrons and hydrogen ions; oxygen gas released. Electrons pass along electron transport system. ATP produced. NADP is reduced, forming NADPH (used in light-independent reactions)
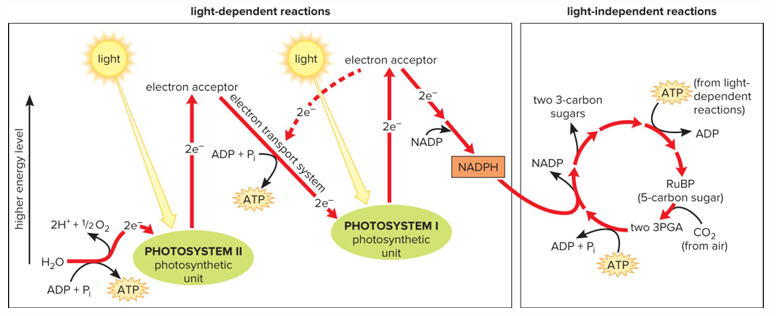
Light-independent reactions
In stroma of chloroplasts. Utilize ATP and NADPH to form sugars. Calvin cycle
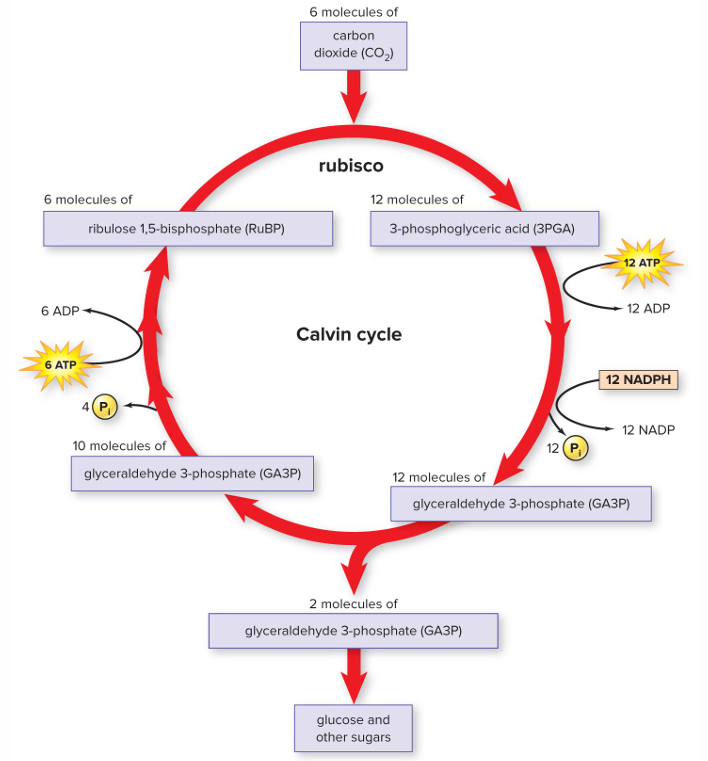
Calvin cycle
Carbon dioxide combine RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate) and then combined molecules are converted to sugars (glucose). Energy furnished from ATP and NADPH produced during light-dependent reactions
Chlorophyll fluorescence II
When electrons are not able to be processed, energy must be dissipated. Heat or fluorescence.
Fluorescence as a measure of light stress:
Measure of fluorescence when reaction centers are all open (Fo) vs when all reaction centers are closed (Fm) The difference is Fm-Fo= Fv
Fv/Fm used as a measure of the efficiency of PSII and an indicator of the health of photosynthesis
Photosystem I =
Chlorophyll a, small amount of chlorophyll b, carotenoid pigment, and p700
( Photosystem I) P700 =
Reaction-center molecule - Only one that actually can use light energy
(Photosystem I) Remaining pigments =
antenna pigments
Photosystem II =
Chlorophyll a, B-carotene, small amounts of chlorophyll b, and reaction-center molecule: P680
(Photosystem II) Pheophytin (Pheo)
Primary electron acceptor
Light Dependent & Independent Reactions
Both work in tandem. Calvin cycle (aka Independent Reactions) do not necessarily need active light (photosynthesis) to continue metabolic processes
Photorespiration
Competes with carbon-fixing role of photosynthesis
Photorespiration forms
CO2, and PGA that can reenter Calvin cycle. No ATP formed
C4 plants can manage higher temps due to
Efficiency of photosynthesis because of higher internal CO2 levels
CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) photosynthesis
Often do not have well defined palisade mesophyll. Chloroplasts resemble the mesophyll cell chloroplasts of C3 plants. Organic acids accumulate at night (stomata open)
CAM Photosynthesis
Most water efficient
Factors Affecting the Rate of Respiration
Temperature, Water, and Oxygen
Factors Affecting the Rate of Respiration: Temperature
When air temperature rises from 20C to 30C, respiration rates double or triple
Factors Affecting the Rate of Respiration: Water
Low water levels decrease respiration. Water acts as a medium for enzymatic reactions
Factors Affecting the Rate of Respiration: Oxygen
Flooding can reduce the oxygen supply to roots
Growth
Irreversible increase in mass due to division and enlargement of cells
Determinate growth
Plant grows, stops growing and dies in one season
Indeterminate growth
Plant or parts of plant grow and continue to be active for several to many years
Differentiation
Cells develop different forms adapted to specific functions
Development
Coordination of growth and differentiation of a single cell into tissues and organs
Nutrients
Furnish elements and energy for plant growth and maintenance. Obtained from air and soil
Vitamins
Organic molecules that participate in catalyzed reactions, mostly by functioning as electron acceptors or donor. Synthesized in cell membranes and cytoplasm. Required in small amounts for normal growth and development
Plant hormones definition
Compounds which are synthesized in one part of the plant and translocated to another part where they influence growth or other processes
Plant Hormones movement is
Either upwards in the sap from the roots in the xylem tissue or moves with sugar and other solutes in the phloem
Plant Hormones five groups
auxins , gibberellins , cytokinins , abscisic acid , ethylene
Plant Hormones act by
Chemically binding to specific receptors. Triggers series of biochemical events, including turning genes on and off
Biochemical events =
Signal transduction
Plant Hormones: Auxins (to grow)
Formed in vegetative growing points, expanding leaves, and in growing seeds
Auxin production occurs mainly in
apical meristems, buds, young leaves and actively growing parts of plants
Effects of Auxins
Inhibit lateral branching. Promote cell enlargement and stem growth, cell division in the cambium, and initiation of roots, and differentiation of cell types
Gibberellins (GA)
Dramatically increases stem growth. Cell Division/Cell Elongation
Gibberellins (GA) site of action is
Before the pathway enters into the Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cytokinins
Speed up the transition to mitosis from the G2 phase, if auxin is present. Synthesized in root tips and germinating seeds
Abscisic Acid (ABA)
Has inhibitory effect on stimulatory effects of other hormones. Helps leaves respond to excessive water loss
Abscisic Acid (ABA) Interferes with
Transport or retention of potassium ions in guard cells, causing stomata to close
Ethylene
Produced by fruits, flowers, seeds, leaves and roots. Produced from amino acid methionine. Causes leaf abscission
Positive Phototropism
Toward light
Phototropism
Growth movement toward or away from light
Negative phototropism
Away from light
Gravitropism
Growth responses to stimulus of gravity
Primary roots
Positively gravitropic
Shoots
Negatively gravitropic
Thermotropism
Temperature
Turgor movements
Result from changes in internal water pressures and often initiated by contact with objects outside of plant
Solar tracking
Heliotropism-Leaves often twist on their petioles in response to illumination and become perpendicularly oriented to light source. Blades oriented at right angles to sun
Taxes (taxic movement)
Movement that involves entire plant or reproductive cells
Photoperiodism
Length of day (night) directly related to onset of flowering
Phytochromes
Pigments that control photoperiodism
Cryptochromes
Blue, light-sensitive pigments that play a role in circadian rhythms and interact with phytochromes to control reactions to light. Also important for maintaining stability of CO proteins involved in flower induction
Phytochromes two stable forms
Pr & Pfr
Pr
Absorbs red light
Pfr
Absorbs far-red light
Dormancy
Period of growth inactivity in seeds, buds, bulbs, and other plant organs even when temperature, water, or day length would typically cause growth
Quiescence
State in which seed cannot germinate unless environmental conditions normally required for growth are present
Stratification
Artificially breaking dormancy