helping patients change behaviour: models of behaviour change
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
block two week 3 socpop
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
health behaviours
Health behaviours are behaviours related to an individual’s health status.
categories of health behaviour
Good health behaviours
Sleeping 7–8 hours
Regular exercise
Healthy diet and eating breakfast
Health-protective behaviours
Wearing seatbelts
Attending screening and health checks
Health-impairing behaviours
Smoking
High-fat diet
Alcohol misuse
why all patients don’t change behaviour
Habit: Behaviour change requires effort and breaking habits.
Fear and lack of skills: Patients may feel unable to change.
Information alone is ineffective.
Short-term vs long-term benefits: Long-term gains may reduce motivation.
Being told what to do: Can cause frustration and disengagement.
Motivation: Skills and knowledge are insufficient without motivation.
social cognition theories
attempt to explain the relationship between social cognitions (beliefs, attitudes, goals) and behaviour
health belief model (rosenstock, 1966)
theory of plannes behaviour (ajzen, 1988)
transtheoretical model (prochaska and diclemente, 1983)
COM-B model
health belief model
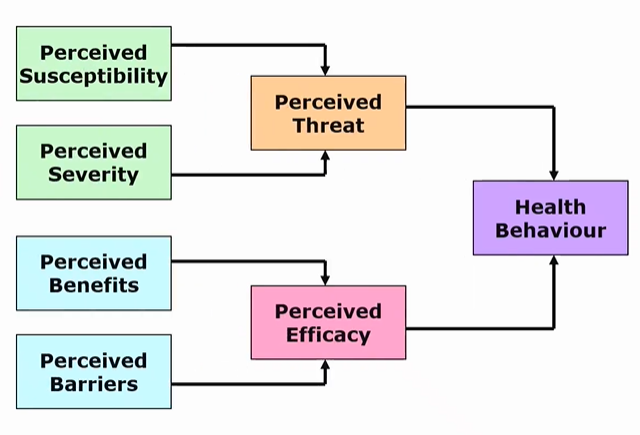
using HBM in the clinical practice
need to explore patient’s perceived susceptibility, severity, benefits and barriers
use education for perceptions of threat and goal setting/action planning and problem solving to help overcome barriers
e.g of HBM for smoking
how do you think smoking is affecting your health? (current susceptibility)
how might it affect your health in ten years time? (future susceptibility)
what would it be like if that happened to you/you got the illness (severity)
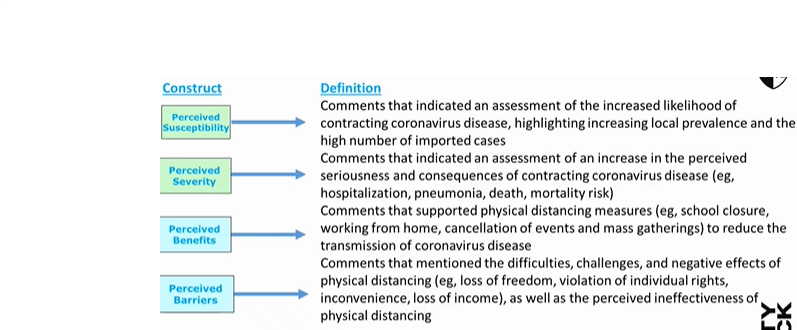
exploring perceived susceptibility and severity
educate pt about risks of smoking which can increase perceived susceptibility and severity
perceived benefits and barriers
what are the pros and cons of smoking for you
is there anything stopping you from giving up
work with the pt to problem solve and overcome barriers
HBM example for COVID
Health messaging targeted perceived susceptibility, severity, benefits, and barriers.
Highlighted importance of acknowledging barriers alongside benefits.
theory of planned behaviour
Behaviour determined by behavioural intention.
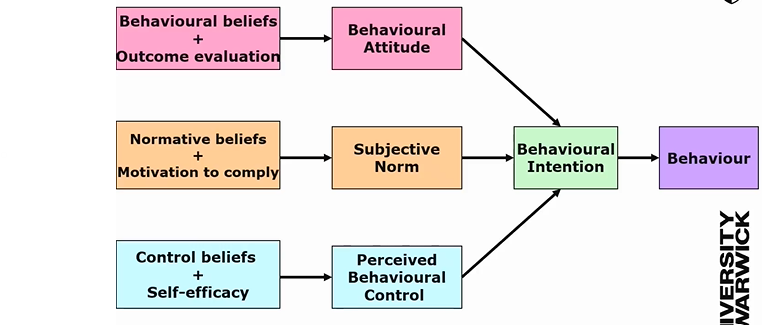
components of TPB
Attitude – beliefs and outcome evaluations
Subjective norms – influence of others and motivation to comply
Perceived behavioural control – skills, confidence, and external barriers
Perceived behavioural control is the strongest predictor.
Predicts 55–71% of health behaviour intentions.
clinical use:
Explore attitudes, norms, intentions, and control.
Support problem-solving or planning depending on perceived control.
using TPB in clinical practice
TPB can predict between 55-71% of intentions for these health related behaviours: smoking, testicular cancer, self examination, exercise, diet and oral hygiene
explore attitude: what do you think about smoking? is smoking good/bad for you and in what way?
explore perceived norms: what do your family think about smoking
whose opinion is most important to you: motivation to comply
would you like to give up smoking for :
using TPB in clinical practice continued
explore intentions:
have you ever thought about giving up smoking
do you intend to give up smoking in the next few months
explore perceived behavioural control
do you think you can give up smoking
if control is low, you can explore further by asking why
if perceived control is high, ready to attempt behaviour change and then work with patient to plan next steps
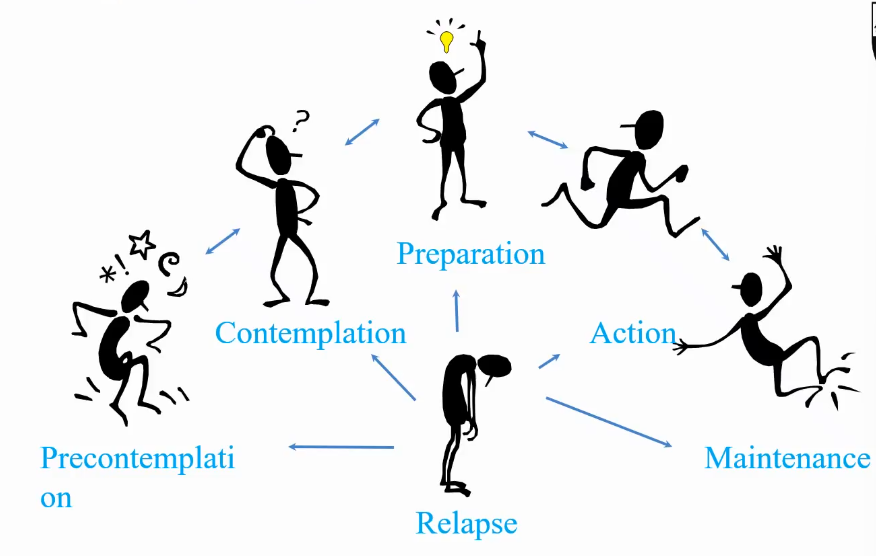
transtheoretical model (stages of change)
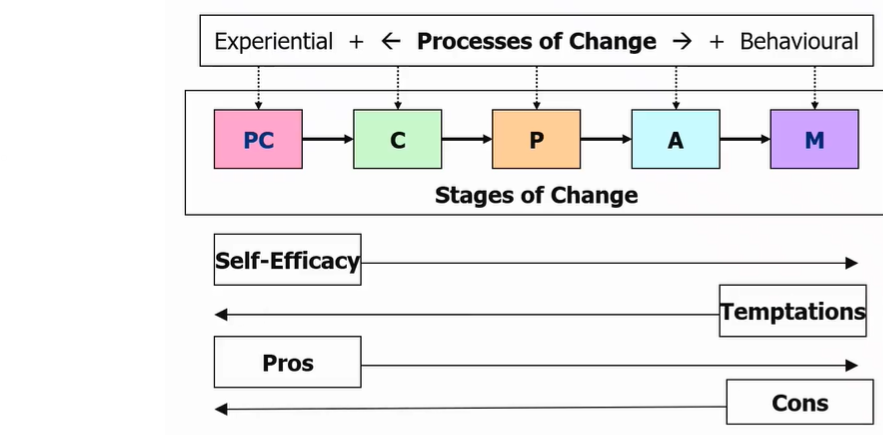
stages of change
the behaviour change wheel
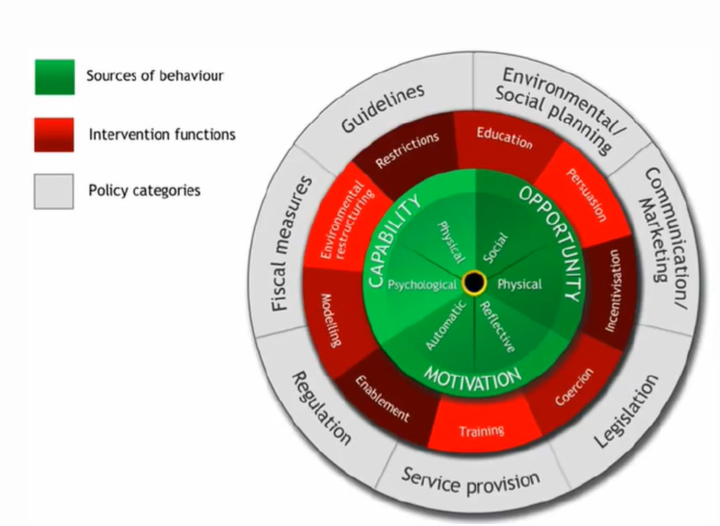
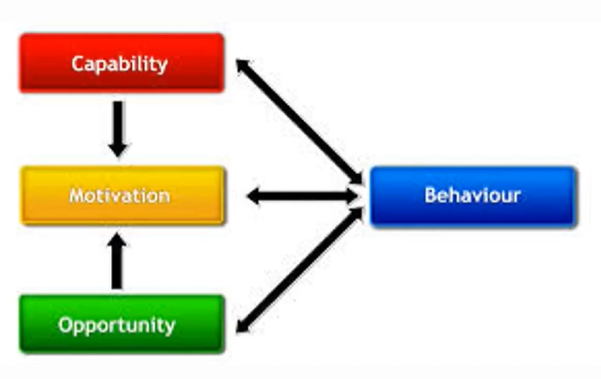
the COM-B model
Capability: physical and psychological skills
Opportunity: physical and social environment
Motivation: reflective (planning, intentions) and automatic (habits, emotions)
All three interact to influence behaviour.