beh psy self control
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
traditional explanation
self control=strong willpower
lack of self control= no willpower
Behavioral analytic view
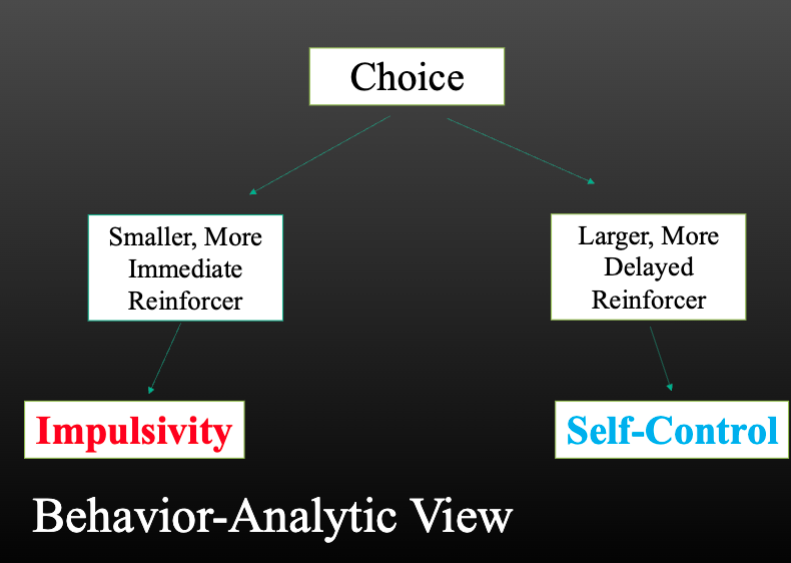
Choice
is behavior
Concurrent behavior
two or more behavior options are available simultaneously
this or that
Concurrent behavior chosen
based on past history and current situation
past history- reinforcers/punishers experiences on both options
current stimulus situation- SD/MO in effect for both options
Problems of behavioral excesses
doing too much of something
immediate reinforcer vs delayed punisher
The child receives immediate reinforcement through attention from peers when they yell, finding this attention rewarding. However, the teacher has implemented a delayed punisher, which is a loss of privilege (like recess time) that occurs later in the day if the yelling continues.
immediate reinforcer vs cumulative significant punishers
The immediate reinforcement comes in the form of social enjoyment and fun with friends during the night. However, the parents implement cumulative punishers, such as losing driving privileges for a week every time their curfew is violated.
the immediate joy of staying out late competes with the significant long-term consequence of losing a privilege, illustrating the challenge of managing behaviors when immediate rewards seem more appealing than the delayed consequences.
immediate reinforcers for problem beh vs delayed reinforcer for alternative beh
smoking
A person attempting to quit smoking might find that choosing to engage in exercise instead of smoking provides a delayed reinforcer: improved health and physical fitness over time, along with feelings of accomplishment and increased energy levels. While the immediate reinforcer for smoking is the nicotine high, their commitment to regular exercise will yield health benefits that manifest gradually, encouraging them to replace smoking with healthier habits.
problems of behavior deficits
too little of something
immediate small punisher vs cumulative significant reinforcer
wearing seatbelt is uncomfortable
overtime saves life during accident
immediate small punisher vs immediate but improbable major punisher if behavior does not occur
saving money now, unable to buy something
not saving money now can cause you to maybe miss out on vacation later
immediate small punisher vs delayed major punisher if beh does not occur
flossing hurts
cavities if continue to not floss later
behavioral model for self control
deal with causes of self control problem
occurs when an individual behaves in a way that arranges environment to manage their subsequent behavior
emitting a controlling behavior to affect a change in a controlled beh
steps in self control
1 specify problem/set goals
define behavior
write goal
2 make a commitment to change
statements/actions that indicate importance, benefits, commitment
publicly post/display announcement
use private verbal cues
well ahead of choice point (plan)
3 take data/analyze causes
record instances of beh
common antecedents/consequences for behavior excess/deficit
4 design/implement treatment plan
consider antecedent, behavior, consequences
Antecedent manipulations
Alter SD
Add SD for appropriate beh
Show three marshmallow
restrict /remove SD for inappropriate behavior
Look away/put away
Alter MOs
Add EO for appropriate beh
Add AO for inappropriate beh
Abolishing operation, demotivated
Make value less value —>Eat before grocery shopping
Alter response effort- things you do not want to do make difficult
Decrease- make appropriate beh easier to emit
Increase- make inappropriate beh more difficulties to emit
Snack- put it up high, lots of effort to get —>Make it difficult to go on tiktok
Demotivated self by telling friend to change algorithm