Topic 2: Genes and Health
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
What are the properties of gas exchange surfaces?
1. large surface area to volume ratio
2. Thin diffusion surface to decrease the diffusion distance
3. Maintaining a steep concentration gradient
2. Thin diffusion surface to decrease the diffusion distance
3. Maintaining a steep concentration gradient
2
New cards
How does the mammalian lung achieve this?
1. MANY alveoli and Many capillaries that provide a large surface area
2. Alveoli and capillaries are also one cell thick for short diffusion distance
3. Ventilation and Large blood supplied from the extensive capillary network replenish oxygen and carbon dioxide maintaining a steep concentration gradient
2. Alveoli and capillaries are also one cell thick for short diffusion distance
3. Ventilation and Large blood supplied from the extensive capillary network replenish oxygen and carbon dioxide maintaining a steep concentration gradient
3
New cards
How do you work out the surface area of a sphere?
4πr ²
4
New cards
How do you work out the volume of a sphere?
4/3πr ³
5
New cards
State Fick's Law
1. The rate of Diffusion is directly proportional to the concentration gradient
2. The rate of Diffusion is directly proportional to the surface area
3. The rate of Diffusion is inversely proportional to the thickness/diffusion distance
2. The rate of Diffusion is directly proportional to the surface area
3. The rate of Diffusion is inversely proportional to the thickness/diffusion distance

6
New cards
What are the function of goblet cells?
Goblet cells produce mucus that trap bacteria and dust
7
New cards
What are the function of cilia?
Cilia waft mucus up to the back of your throat to be swallowed and it's pathogens killed by stomach hydrochloric acid.
8
New cards
How does cystic fibrosis lead to shortness of breath?
Cystic Fibrosis causes an overproduction of mucus, the mucus increases the diffusion distance slowing down the rate of diffusion limiting oxygen and leading to shortness of breath.
9
New cards
What are the functions of a cell surface membrane?
1. to control the **exchange of substances** from one side of a membrane to the other
2. an **interface for communication**
3. separating the internal cell environment from the external environment
10
New cards
What are the functions of an intracellular surface membrane?
**intracellular membranes** form compartments within the cell such as the **nucleus**, **mitochondria,** and **endoplasmic reticulum**
11
New cards
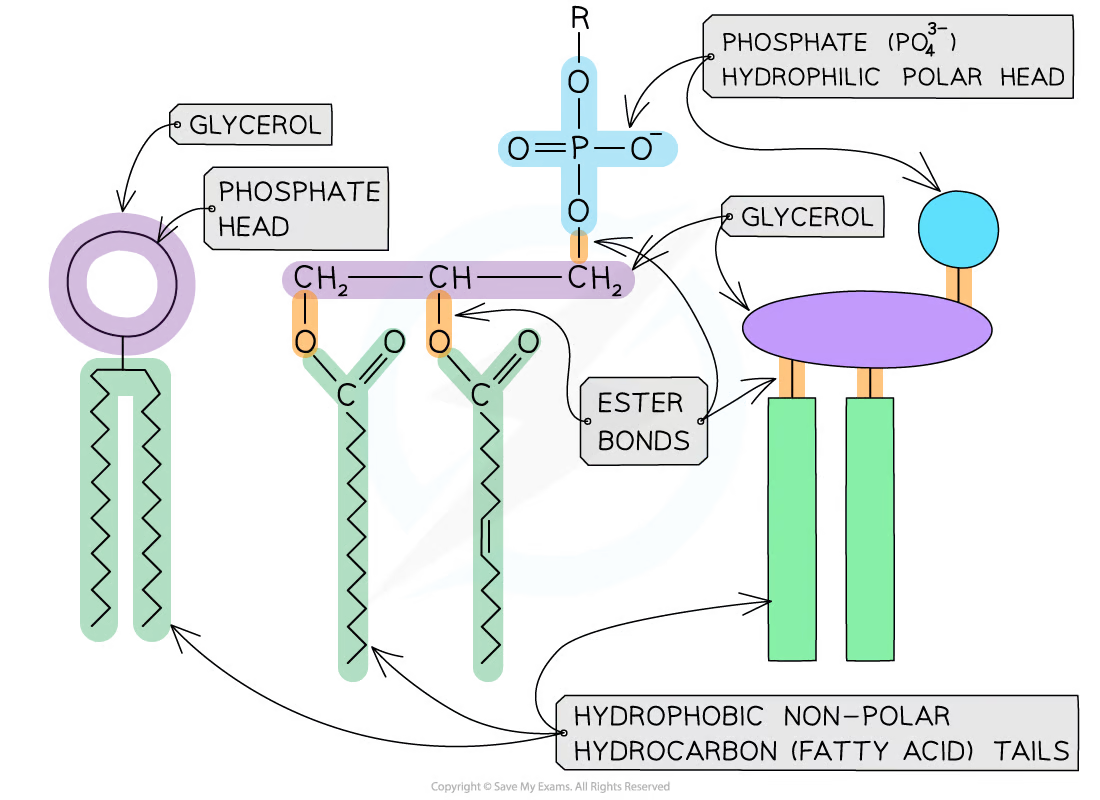
What do phospholipids consist of?
* A molecule of **glycerol**
* A **phosphate group**, which forms the **phosphate head**
* **Two fatty acid tails**, making up the **lipid tail**
* A **phosphate group**, which forms the **phosphate head**
* **Two fatty acid tails**, making up the **lipid tail**
12
New cards
Describe the properties of a **phosphate head**
the **phosphate head** of a phospholipid is **polar,** meaning that it can interact with polar water molecules; the head is therefore described as being **hydrophilic**
13
New cards
Describe the properties of a **phosphate head**
The lipid tail is **non-polar,** meaning that it cannot interact with polar molecules; the tail is therefore described as **hydrophobic**
14
New cards
What factors affect the permeability of cell membranes?
* **Temperature**
* **pH**
* **pH**
15
New cards
How can the amount of pigment in a sample be measured?
It can be measured using a piece of equipment known as a **colourimeter**
16
New cards
Explain calibration of a colorimeter
The colorimeter must be **zeroed** before each colorimeter is used; this can be done using **distilled water** in a small container called a cuvette
17
New cards
**Apparatus for investigating the effect of temperature on membrane permeability**
* Scalpel
* Cork borer
* Cutting board
* Ruler
* Digital balance
* Test tubes
* Measuring cylinder
* Water baths
* Digital stopwatch
* Pipettes
* Colorimeter and cuvettes
* Cork borer
* Cutting board
* Ruler
* Digital balance
* Test tubes
* Measuring cylinder
* Water baths
* Digital stopwatch
* Pipettes
* Colorimeter and cuvettes
18
New cards
Method for **investigating the rate**