CH. 13 | Nuclear Reactions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Nuclear radioactivity
Spontaneous emission of particles or energy from an unstable nucleus
3 Types of Radioactive decay
Alpha decay
Beta decay
Gamma decay
Nuclear equations
Atomic number = number of protons in nucleus
Isotopes: same atomic number; different number of neutrons
Nuclear reactions
Represented by balanced equations
Charge conserved
Mass number conserved
Nature of the Nucleus
Strong nuclear force
Binds protons and neutrons
Very short ranged, less than
Overcomes proton-proton Coulomb repulsion
Nuclear shell model
Nucleon quantum energy levels
Maximum stability for nucleon number = 2 , 8 , 20 , 28 , 50 , 82 , or 126
→ Filled + half-filled orbitals are more stable
Band of stability
Generalizations: Nuclear Stability

Types of Radioactive Decay
Alpha emission
Expulsion of helium nucleus
Least penetrating: stopped by paper
Beta emission
Beta emission
Expulsion of an electron
More penetrating: 1 cm of aluminum
Gamma decay
Emission of a high-energy photon
Most penetrating: 5 cm of lead

Cont…
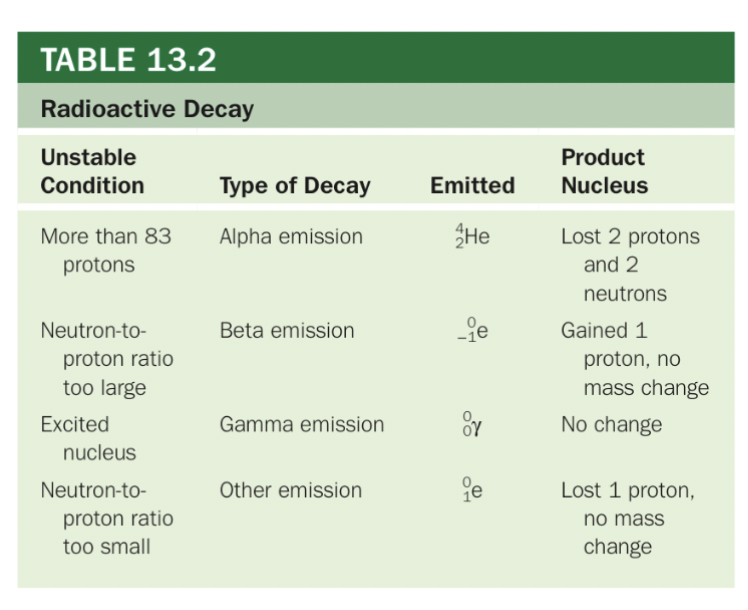
Half life
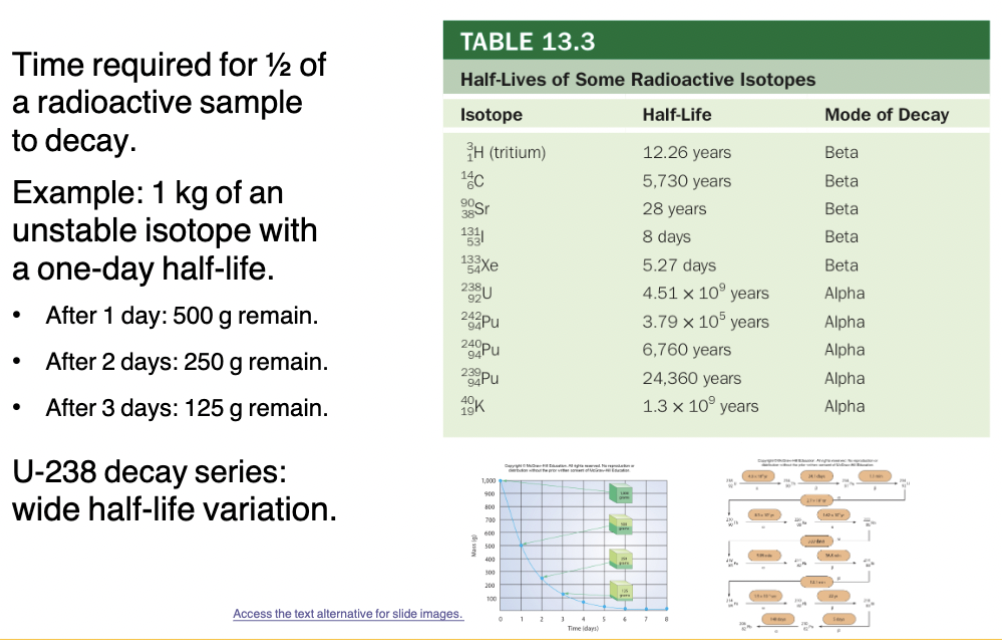
Measurement of Radiation
Ionization counters
Detect ions produced by radiation
i.e., Gelger counter
Scintillation counters
Rely on flashes of light produced as radiation strikes a phosphor
Zinc sulfide
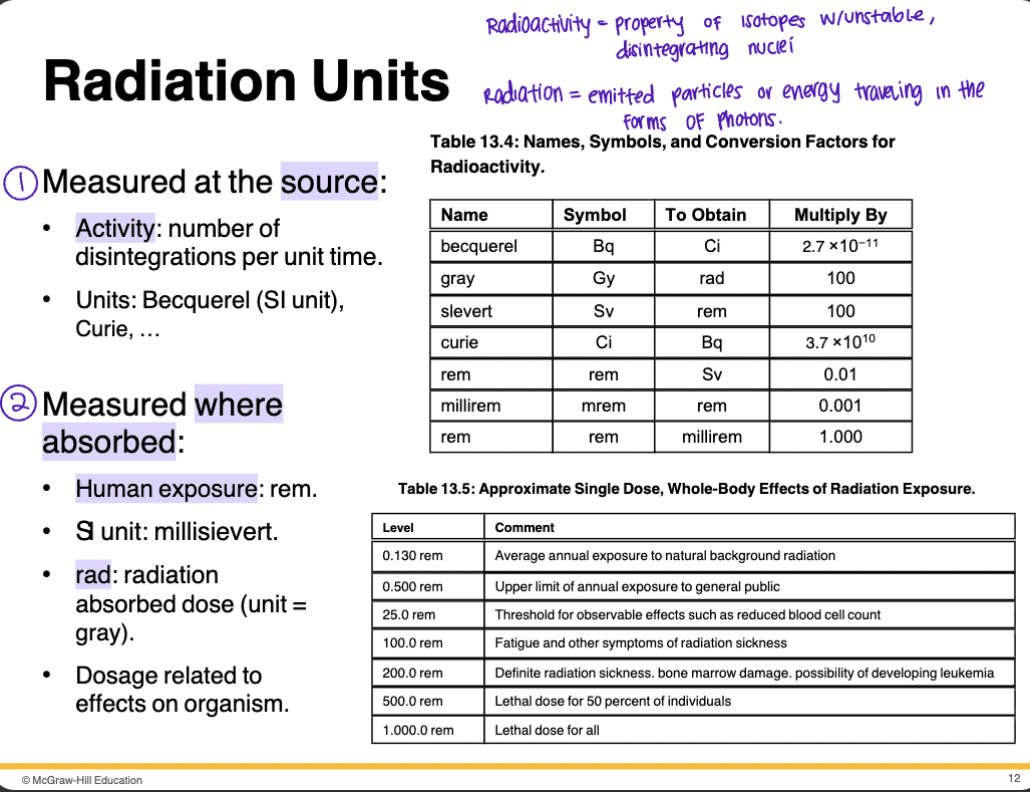
Radiation Units
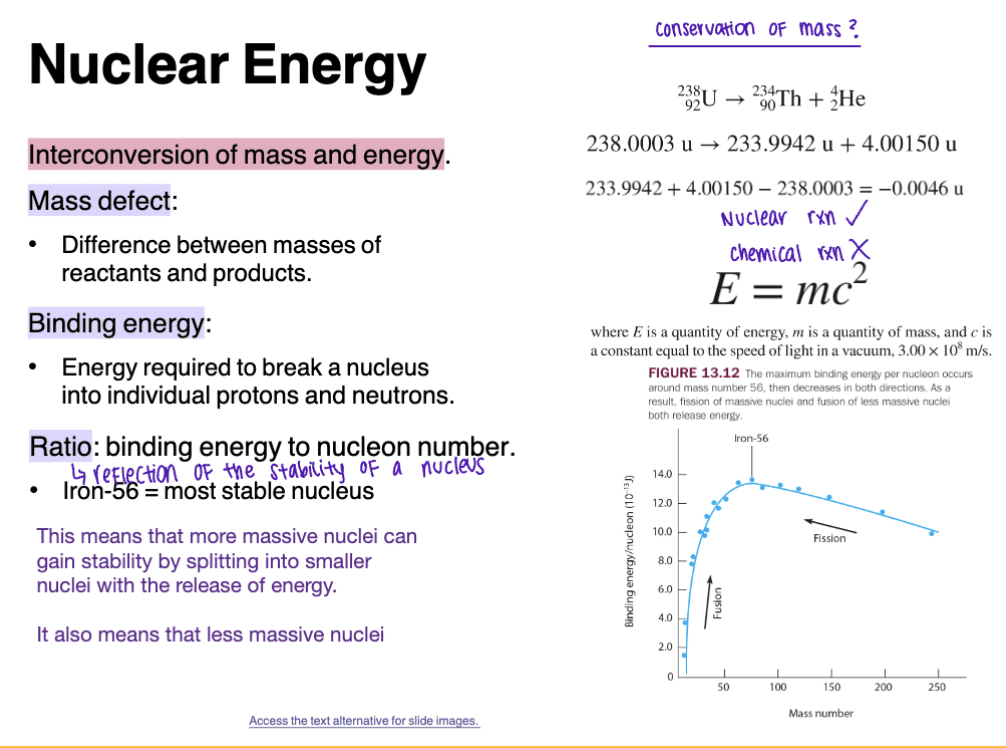
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear Fission

Nuclear Fusion
