MAN 3025 - Module 10 Notes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Motivation
the psychological processes that arouse and direct goal-directed behavior
Extrinsic Reward
rewards given by other (the payoff, such as money, recognition, or encouragement, etc.)
Intrinsic Reward
satisfaction, such as a feeling of accomplishment, a person receives from performing the particular task itself
Four Major Perspectives on Motivation
(1) Content - emphasizes needs as motivators
(2) Process - focuses on the thoughts and perceptions that motivate behavior
(3) Job Design - focuses on designing jobs that lead to employee satisfaction and performance
(4) Reinforcement - motivation is a function of behavioral consequences not unmet needsontC
Content Perspectives
theories that emphasize the needs that motivate people
Needs
physiological or psychological deficiencies that arouse behaviors
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
proposes that people are motivated by five levels of needs
physiological = need for food and clothing (most important)
safety = need for physical, emotional, and job security
love = need for friendship and affection
esteem = need for self-respect, status, etc.
self-actualization = need for self-fulfillment
Maslow’s work paved way for organization to think how they can improve their employee’s overall well-being
McClelland’s Acquired Needs Thoery
Two Important Assumptions:
Needs are learned
One need often dominates
There are three needs (achievement, affiliation, and power)
Achievement - desire to excel and do better or more efficiently
Affiliation - desire for friendly and warm relations with other people
Power - desire to be responsible for other people or influence their behavior
Deci and Ryan’s Self-Determination Theory
assumes that people are driven to try to grow and attain fulfillment
Focuses on intrinsic motivation and rewards
intrinsic is longer lasting and has a more positive impact on task performance
Competence - people want to feel qualified, knowledgeable, and capable of completing a goal or task
Managers can provide time for mentoring, coaching, etc.
Autonomy - people want to feel they have freedom and discretion
Managers should develop trust and delegate tasks
Relatedness - people need to feel a sense of belonging of attachment to others
Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory
proposed that work satisfaction and dissatisfaction arise from two different factors (work satisfaction from motivating factors and work dissatisfaction for hygiene factors)
Hygiene Factors (lower-level needs) - salary, working conditions, interpersonal relationships, and company policy
Motivating Factors (higher-level needs) - achievement, recognition, responsibility, and advancement
First, climate dissatisfaction (make pay levels, company policies, etc. reasonable)
Then, spurr motivation ( provide opportunities for achievement, recognition, responsibility, etc.)
Process Perspectives
concerned with the thought process by which people decide how to act
Equity Theory
a model of motivation that explains how people strive for fairness and justice in social exchanges
based on COGNITIVE DISSONANCE ( the psychological discomfort people experience between their cognitive attitudes and incompatible behaviors
- Theory suggests that people compare the ration of their outcomes against others
When people perceive “inequity”, they feel resentful and act to change the inequity
Perceived Inequity = reduce their inputs, leave the job, etc.
Distributive Justice
reflected the perceived fairness of the outcomes being distributed or allocated among employees
ex. when employees have fair share of rewards and resources
Procedural Justice
the perceived fairness of the process and procedures used to make allocation decisions
ex. when employees can voice their opinions
Interactional Justice
how organizational representatives treat employees in the process of implementing procedures and making decisions
ex. managers communicate truthfully and treat people with courtesy and respect
Voice
employees’ expression of work-related concerns, ideas, and/or constructive suggestions to managers
knowledge of equity and justice theories allows you to hear and better understand your employee concerns and coworkers
Justice Climate
shared sense of fairness felt by the entire workgroup
increased job satisfaction
more helping behaviors
Expectancy Theory
how much effort to exert in a specific task situation
Expectancy.- the belief that a particular level of effort will lead to a particular level of performance
High Expectancy = the more hours I spend studying, the better my grade will be
Low Expectancy = regardless of how much I practice, I will never…
Instrumentality - successful performance of the task will lead to the outcome desired
Valence - the importance a worker assigns to the possible outcome or reward
Managers should think, “what rewards will motivate my employees?”
Goal-Setting Theory
suggest that employees can be motivated by goals that are specific and challenging but achievable
Direct Attention toward goal-relevant tasks
Regulate Effort based on goal’s difficulty and time deadlines
Increase persistence - goal setting makes obstacles challenges to be overcome, not reasons to fail
Foster the use of strategies and action plans - makes it more more likely that you’ll realize success
Stretch Goals
goals beyond what they actually expect to achieve
ex. forcing people out of their comfort zones to achieve more, building employees’ confidence when they succeed, etc.
Cons: Sometimes can demotivate employees if goals seem unattainable, lead companies to take unnecessary risks, etc.
Goals Should Be:
Specific
Linked to Action Plans
Have the correct conditions (employees must have the ability to achieve the goal, be committed to the goals, and receive timely feedback)
Job Design
(1) the division of an organization’s work among its employees and (2) the application of motivational theories to jobs to increase satisfaction and performance
Scientific Management
the process of reducing the number of tasks a worker performs
Pros: worker can focus on one task
Cons: research says that simplified jobs lead to job dissatisfaction, poor mental health, and low sense of accomplishment and personal growth
2 Techniques to Make Work Compatible with the Worker for Higher Performance
Job Enlargement and Job Enrichment
Job Enlargement
increase the number of tasks in a job to increase variety and motivation
- horizontal loading (addition tasks of similar difficulty)
Jon Enrichment
building into a job such motivating factors as responsibility, achievement, recognition, stimulating work, and advancement
vertical loading (more responsibility)
Job Characteristics Model
the 5 core characteristics affect a worker’s motivation because it affects the 3 psychological states
- these psychological states fuel the outcomes Contingency Factors = a person wants personal and psychological development
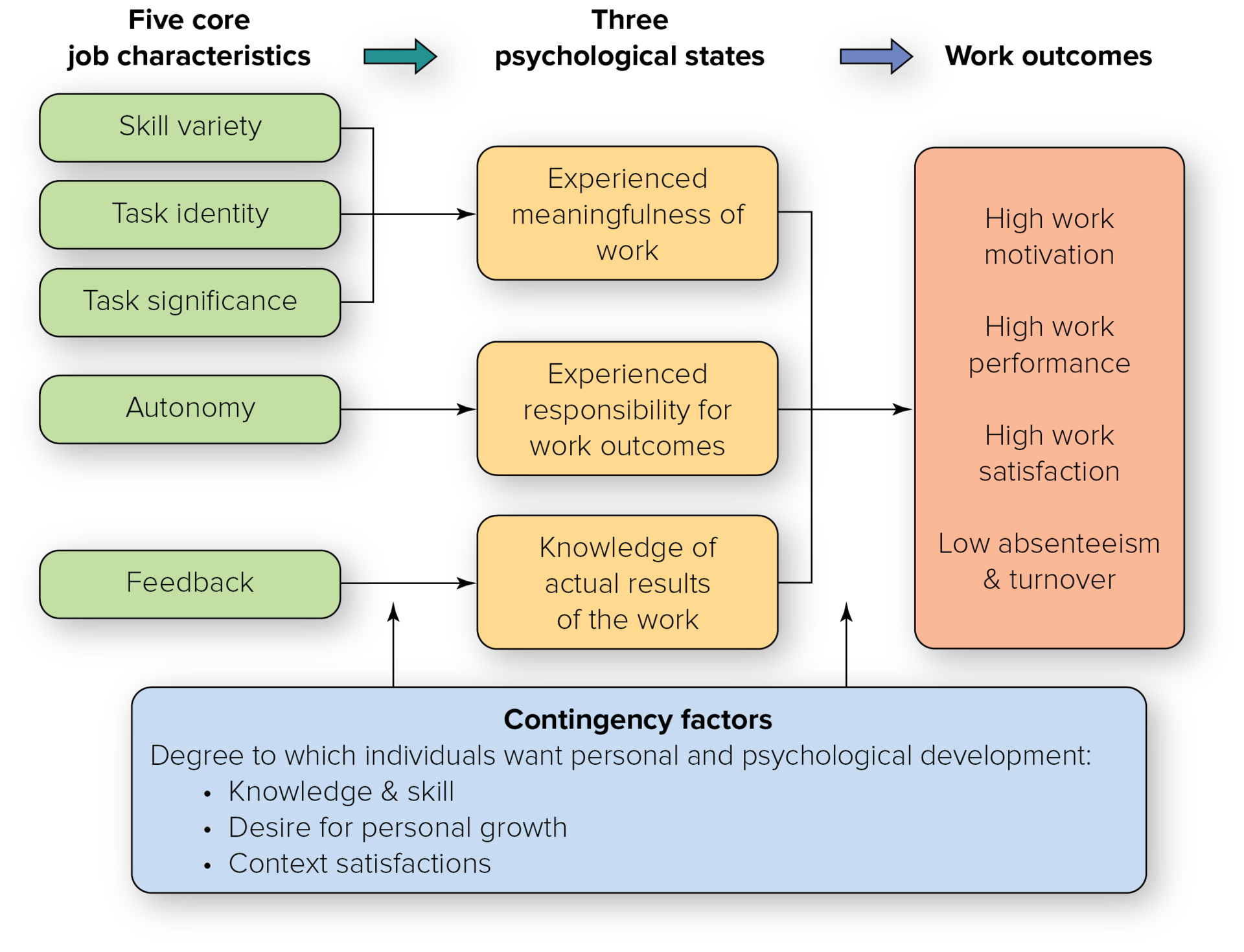
Prosocial Motivation
the desire to benefit others
Pros:
Social capital (coworkers trust prosocial motivated employees and see them having leadership potential)
Working harder (people work harder bc of fear of letting others down and anticipation others will be grateful for their efforts)
Working Together (prosocial motivation prompt ppl to share information with others)
Working Smarter (they gather and analyze information from multiple perspectives to create more creative ideas)
Working Safer (prosocially motivated prompts employees to share information with others)
B.F. Skinner’s Operant Conditioning
the process of controlling behavior by manipulating its consequences
Thorndike’s Law of Effect
behavior with favorable consequences tends to be repeated while behavior with unfavorable consequences tends to disappear
Reinforcement Theory
attempts to explain behavior change by suggesting that behavior with positive consequences tends to be repeated and vice versa
Reinforcement
anything that strengthens the likelihood that a given behavior will be repeated in the future
1. Positive Reinforcement
Negative Reinforcement
Extinction
Punishment
Positive Reinforcement
introduction of positive consequences to strengthen the likelihood that a particular behavior will occur again
Giving rewards as soon as possible
Be clear about what behavior is desired
Reward only desirable behavior
Negative Reinforcement
removal stimulus to strengthen the likelihood that a particular behavior will occur again in the future
Extinction
decrease the likelihood that a particular behavior will occur again in the future by ignoring it or making sure it is not reinforced
Punishment
decreases the likelihood that a behavior will occur again in the future by presenting something negative or withdrawing something positive
Punish only undesirable behavior
Give reprimands and disciplinary actions as soon as possible
Administer punishment in private
Pay For Performance
bases pay on one’s results
Piece Rate = employees are paid according to how much output they produce
Sales Commission = sales representatives are paid a percentage of the earnings the company made from their sales
Bonuses
cash awards given to employees who achieve specific performance objectives
Profit Sharing
distribution to employees of a percentage of the company profits
Gainsharing
distribution of savings or “gains” to groups of employees who reduced costs and increased measurable productivity
Stock Options = certain employees are given the right to buy the company’s stocks at a future date at a discounted price
Pay for Knowledge = employee pay to the number of job relevant skills or academic degrees they earn
Work-Life Benefits
initiatives and programs that employers implement in an effort to help employees balance the often competing needs of their work and home lives
Vacations, Sabbaticals, Flexible work arrangements, etc.