Cell structure & intracellular transport
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
eukaryotes vs prokaryotes, functions of organelles, microscopy (light fluorescent and EM), subcellular fractionation and flw cytometry, nuclear transport, membrane transport and vescicular transport
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
what three properties does any living thing need to have? (GMR)
growth, metabolism and reproduction
organisms which have a nucleus are classed as…?
eukaryotic
organisms which do NOT have a nucleus are classed as…?
prokaryotic
prokaryotic membranes are composed of which three layers?
capsule, cell wall and plasma membrane
the plasma membrane controls … with the outside world
communication
what is the name of the area in prokaryotes which contains DNA?
nucleoid
the ER is responsible for the synthesis of the majority of which two biomolecules?
lipids and proteins
golgi is responsible for … of lipids and proteins (3 words)
modification, sorting and packaging
endosomes are responsible for sorting of … material
endocytosed
peroxisomes are responsible for oxidation of … molecules
toxic
lysosomes are responsible for intracellular …
degradation
prokaryotes have a cell wall made of which molecule?
peptidoglycan
peptidoglycan is a polymer of… (2 things)
amino acids and sugars
3 techniques used in the lab to study cell structure and function
subcellular fractionation, microscopy and fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS)
three types of microscopy
light, fluorescence and electron microscopy
two types of electron microscopy (TEM and SEM)
transmission and scanning EM
type of EM which looks at thin cross sections of tissue by passing a beam of electrons through the sample → 2D image obtained
transmission EM
type of EM which scatters electrons off the surface of the sample (used to look at surface details of cells) → 3D image obtained
scanning EM
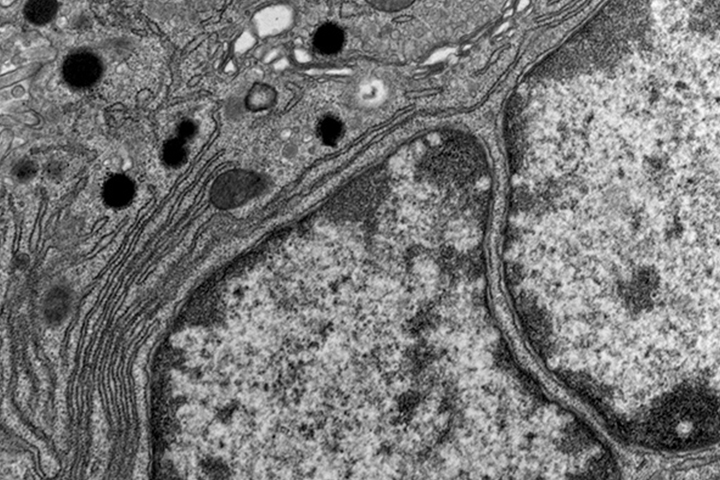
what type of microscopy is this?
transmission EM

what type of microscopy is this?
scanning EM
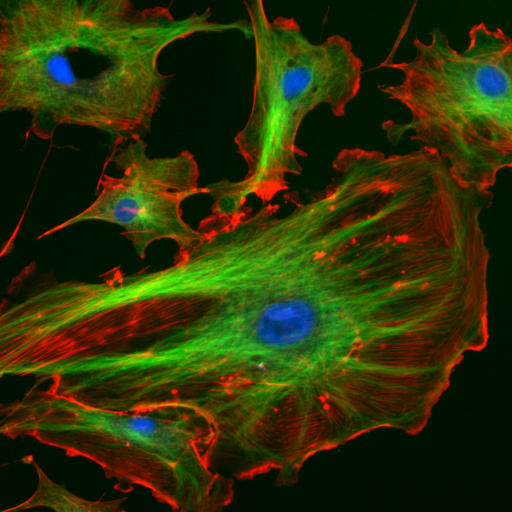
what type of microscopy is this?
fluorescence microscopy
type of microscopy that examines fluorescent substances in a microscope by illuminating the specimen with short-wavelength light?
fluorescence microscopy
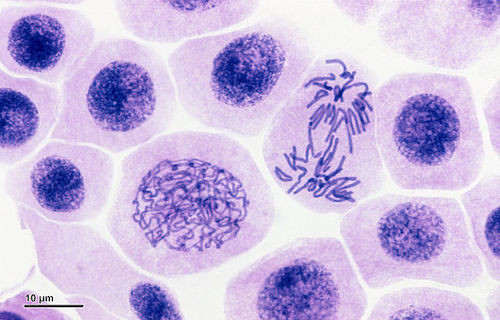
what type of microscopy is this?
light microscopy
technique used to isolate cellular components through centrifugation of lysed cells and through successive centrifugations at increasing RCFs (relative centrifugal forces)
subcellular fractionation
a technique which uses laser beams to determine the characteristics of cells?
flow cytometry
machine which has a fluidic system that transports the cells from a test tube into a narrow stream of fluid, where cells are passed individually through a laser beam
flow cytometer or fluorescent activated cell sorterer (FACS)
in flow cytometry cells are separated based on properties such as… (3 examples)
size, granularity and protein expression
what is the name of the membrane which encloses the nucleus?
nuclear envelope
is the nuclear envelope a single or double membrane?
double
a sequence of amino acids known as the … on the protein is used to direct proteins to their final destinations
signal sequence
KDEL is the signal sequence (or retential signal) which directs proteins to or tells them to stay in which organelle?
the ER
KDEL stands for which amino acids
lysine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid and leucine
during protein transport through nuclear pores, the pores act as …
selective gates
during protein transport across membranes, proteins get unfolded and are transported via…
protein translocators
during protein transport by vesicles, what membrane related process allows proteins to enter organelles?
membrane fusion
what type of molecules can freely diffuse through nuclear pores between the nucleus and cytosol?
small water soluble molecules
what is the name of the signal sequence proteins in the cytosol must have to enter the nucleus?
nuclear localisation sequence (NLS)
are proteins that are transported into the nucleus unfolded or folded?
folded
proteins which form the nuclear pore complex
nucleoporins
long, stalk-like structures which project from both sides of a nuclear pore
protein fibrils
on the nuclear side, protein fibrils form a structure in what shape?
basket like
does nuclear transport require energy?
yes
a protein which contains the nuclear localisation sequence (NLS) binds to … receptors and is guided to the nuclear pore
nuclear transport receptors
the nuclear transport receptor interacts with which structure or the nuclear pore to guide the protein to the pore?
protein fibrils
what happens to the nuclear transport receptor once it has delivered the NLS-containing protein to the nucleus?
it returns to the cytosol
which nucleotide triphosphate molecule does nuclear transport utilise?
GTP
complex of which two molecules binds to the nuclear transport receptor (NTR), causing it to release the NLS-protein?
ran-GTP
after the ran-GTP and NTR complex is transported back to the cytosol, ran-GTP gets hydrolyzed to …
ran-GDP
what happens when ran-GTP is hydrolyzed to ran-GDP?
the NTR is released

name of the translocase complex on the OM of the mitochondria, which recognises and binds mitochondrial signal sequences to initiate protein import
translocase of the outer membrane (TOM)
do proteins cross the mitochondrial membranes folded or unfolded?
unfolded

which translocase complex facilitates import of protein through the IM of the mitochondria?
translocase of the inner membrane (TIM)
what happens to the protein when it enters the mitochondrial matrix?
it is refolded and the signal sequence is removed
which proteins aid with translocation and refolding during mitochondrial protein import?
chaperone proteins
which enzyme cleaves the signal sequence off proteins when the enter mitochondria?
signal peptidase
proteins which are destined for which organelles first enter the ER? (GEELS)
golgi, ER, endosomes, lysosomes and cell surface
which structures transport proteins out of the ER?
vescicles
which two things direct a ribosome translating an ER protein to the ER membrane?
the signal sequence and the signal recognition particle (SRP)
what is the name of the channel which lets soluble proteins get translated directly into the ER lumen
translocation channel
what is the name of the enzyme which cleaved the signal sequence off proteins once they are in the ER
signal peptidase
what is the name of the two sequences membrane proteins have which allows them to become embedded in the membrane
hydrophobic stop transfer sequence and hydrophobic start transfer sequence
which sequence on the transmembrane proteins halts the insertion process (of moving through the channel), causing the protein to be anchored in the membrane instead of being fully translocated across it
hydrophobic stop transfer sequence
which sequence initiates the insertion of a protein into the ER membrane (aka initiates the movement through the channel)
hydrophobic start transfer sequence
what are the two types of proteins moved from the cytosol to the ER?
soluble and transmembrane proteins
out of soluble and transmembrane proteins, which completely cross the ER membrane and are released into the lumen?
soluble
out of soluble and transmembrane proteins which only partly cross the ER membrane and become embedded?
transmembrane
the signal recognition particle (SRP) binds to the ER signal sequence on a protein being translated. translation then slows down until the SRP binds to the … on the ER membrane
SRP receptor
in addition to directing proteins to the ER, the ER signal sequence functions to open the …
translocation channels
multi pass transmembrane proteins also contain which sequence?
internal signal sequence

vescicle budding is driven by the assembly of a …
protein coat
what are the two proteins which may compose the protein coat of a vescicle?
clathrin or coat protein complex (COP) proteins
vescicles originating from the ER or golgi destined for endosomes or lysosomes are generally coated with which protein?
clathrin
vescicles shuttling between the ER and golgi are generally coated with which proteins?
COP proteins
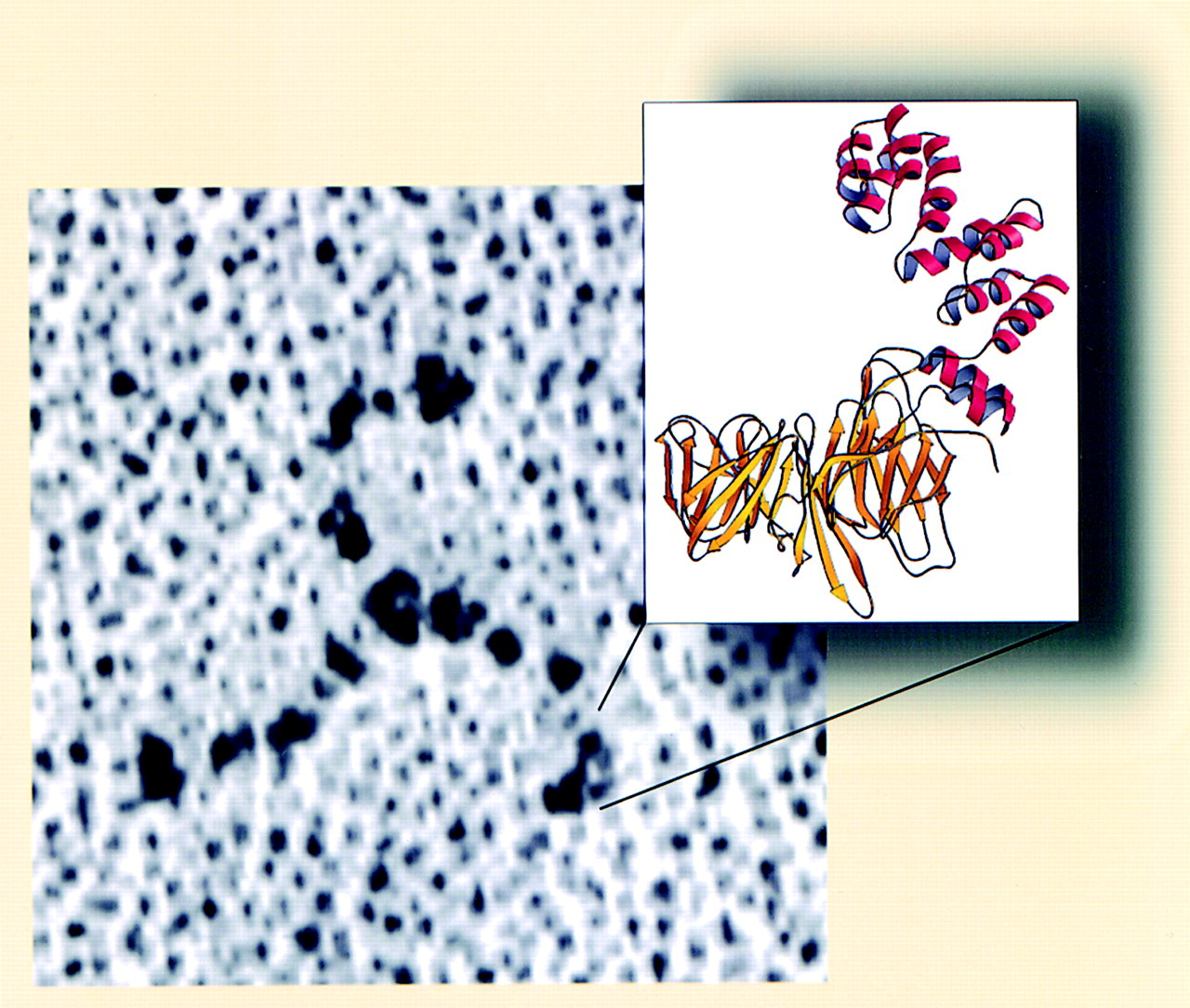
when clathrin molecules are free in the cytosol they shape what three-legged strucutre?
triskelions
what is the name of the proteins which mediate the contact between the receptors and clathrin molecules in vescicles?
adaptins
in general which 4 molecules are needed to form a vescice?
cargo, receptors, adaptins and clathrins
example of a protein which is constantly secreted from cells?
serum albumin
example of a protein which is secreted from cells only once an appropriate signal is received?
insulin
type of protein secretion from cells which is continuous?
constitutive secretion
what is the membrane mediated degradation of cellular components called?
autophagy
what is the membrane mediated uptake of bacterial cells and dead, damaged or infected cells called?
phagocytosis
what is the membrane mediated uptake of vescicles called?
endocytosis
which three membrane mediated processes all ultimately lead to the formation of a lysosome?
endocytosis, phagocytosis and autophagy
do all three; nuclear transport, membrane transport and vescicular transport require energy?
yes