Unit 2 AOS 1
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Area of Study 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Economic Growth
An increase in the real value of goods and services produced in the economy (GDP) from one year to the next.
Macroeconomic Activity
Production, income and expenditure that takes place across the whole economy.
Production
Total value of goods and services that are produced in an economy.
Income
The flow of money or other economic benefits received by an individual, household, or business.
Expenditure
Total spending undertaken on the goods and services being produced.
Material Living Standards
The access individuals have to goods and services in a society.
Non-material Living Standards
Overall wellbeing and happiness including quality-of-life factors not factored in material living standards, like environmental quality, crime rates, personal freedom, public health, leisure time, and social well-being.
Formula for GDP and Aggregate Demand
C + I + G1 + G2 + (X - M)
or
C + I + G + (X - M)
5 Sectors of the 5 Sector Flow Model
Household/Consumer Sector
Business/Producer/Firm Sector
Financial Sector
Government Sector
Overseas Sector
3 Leakages in 5 Sector Flow Model
Savings
Taxes
Imports
3 Injections in 5 Sector Flow Model
Investment
Government Spending (G1 and G2)
Exports
Aggregate Demand
The total demand for goods and services within a particular market over a period of time.
In this course, it’s based on Australia.
C Component
Consumer Spending/Consumption:
Any spending by households and consumers.
I Component
Investment Spending
Any business or financial investment in plant, equipment, factors of production or economic resources.
G1 Component
Government Consumption:
Payments made by the government on consumption items like wages or Centrelink.
G2 Component
Government Investment:
Payments made by the government on capital items (such as new buildings, roads or capital).
X Component
Exports:
Any good or service sold overseas
(In this course, a good sold from Australia to overseas)
M Component
Imports:
Any good or service purchased from someone overseas
(In this course, a good bought from Australia by someone overseas)
Economic Cycle/Business Cycle/Trade Cycle
Series of economic contractions and expansions that an economy experiences over time with alternating periods.
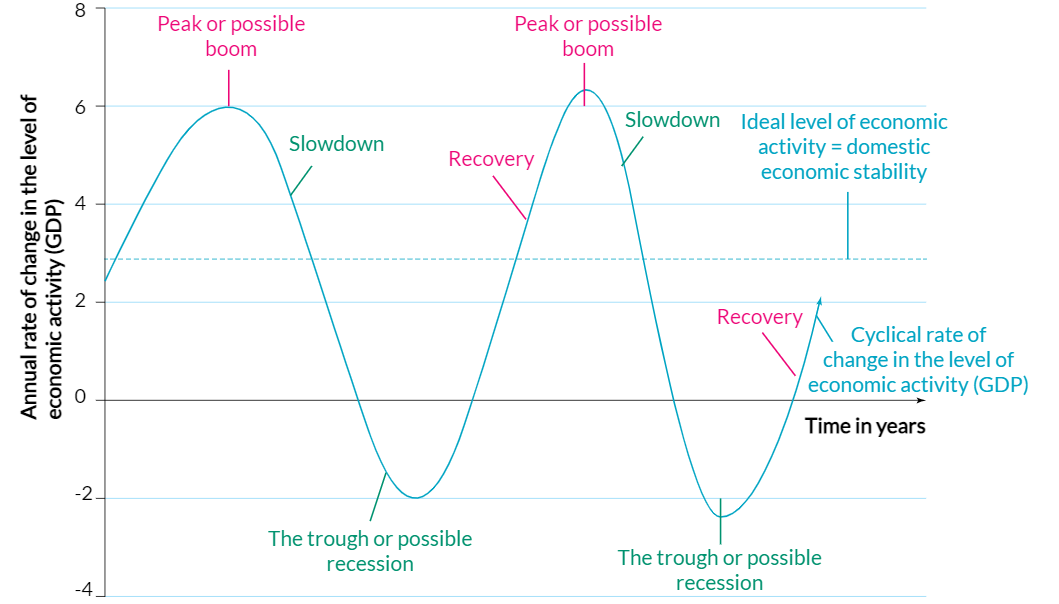
4 Phases of Economic Cycle/Business Cycle/Trade Cycle
Peak/Boom
Slowdown (Contraction)
Trough (Could be recession)
Recovery (Expansion)
Peak/Boom
The 1st period of the economic cycle where GDP is growing at its fastest rate and at its highest after a recovery but before a slowdown (contraction).
High levels of spending
High aggregate demand
Low unemployment rates
Slowdown (Contraction)
The 2nd period where the speed of rise in economic activity and GDP slows down after a peak but before a trough.
Trough
The 3rd period where economic activity and rate of GDP growth are at their slowest after a slowdown but before a recovery.
High rates of unemployment
Reduced incomes
Reduces purchasing power
Reduced living standards
Reduced levels of spending
Low aggregate demand
Recession
A trough lasting at least two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth, lasting 6 months.
Recovery (Expansion)
The 4th period where the rate in GDP starts to accelerate after a trough but before another boom/peak, repeating again.
Ideal Economic Activity/Domestic Economic Stability
The ideal, preferred and favourable level of economic activity between the peak and the trough. There is
An inflation rate between 2-3%
A GDP Growth rate between 3-4%
An unemployment rate between 4-4.5%
3 Types of Indicators
Lagging Indicators
Coincident Indicators
Leading Indicators
Lagging Indicators
Indicators of economic activity that indicates economic activity that occured some time ago.
Examples of Lagging Indicators
GDP Figures
Unemployment Rate
Inflation Rate
Weekly Earnings
Coincident Indicators
Indicators of economic activity which moves closely with actual change in economic activity.
Examples of Coincident Indicators
Share prices
Monthly retail sales
New car registrations
Leading Indicators
Indicators or predictors of future economic activity
Examples of leading indicators
Consumer confidence
Business confidence
Index of new housing approvals
Share Prices
Stock Prices
Returns on Bonds
GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
Final market value of all goods and services produced economy over a given period of time. Alternatively, it is the total 'value added' during each stage of the production process.
(In this course, it is based on Australia)
Factors Affecting Consumption Spending
Disposable Income
Consumer Confidence
Interest Rates
Population Growth
Government Budgetary Policies
Factors Affecting Private Business Investment
Business Confidence
Interest Rates
Company Tax Rates
Government Policies
Technological Advancements
Factors Affecting Government Spending
Unemployment Rate
Inflation Rate
Population Growth
Government Debt
Issues in the Nation
Factors Affecting Exports
Exchange Rate of Currency
Overseas Economic Conditions
Natural Disasters
Factors Affecting Imports
Exchange Rate of Currency
Local Economic Activity
Consumer and Business Confidence
Overseas Economic Conditions
Inflation Rates
Monetary Policy
Tools of the central bank (RBA in Australia) like interest rates, money supply and the cash rate.
Aggregate Supply
The total amount of goods and services that all producers in the country can make available over a period of time.
Shown on a PDF
Depends on factors of production and economic resources
Factors Affecting Aggregate Supply
Quantity of Factors of Production
Efficiency of Usage of Factors of Production
Climatic Events
Anomalies like pandemic lockdowns, wars and disruptions
Economic Policies
Factors Affecting Labour Resources
Demographics
Population’s Age Structure
Education, skills, and labour productivity
Investment levels
Factors Affecting Capital Resources
Interest Rates
Technology, Research, Development and Efficiency
Mineral Exploration
Factors Affecting Natural Resources
Mineral Exploration
Land Management
Climate Change and Weather Events
Factors Affecting Production Costs
Wage costs and labour productivity
Taxation
Government Investment on Infrastructure (G2)
Nominal GDP
The total value of all goods and services produced in an economy over a period of time does not account for inflation
Real GDP
The total value of all goods and services produced in an economy over a period of time accounting for inflation.
Benefits of Economic Growth
Employment and Opportunities
Increase in Material Living Standards
Increase in Non-Material Living Standards
Economic Development
Limitations in Real GDP
Doesn’t account for
Non-Material Living Standards
Black (Illegal) Market
Home production
Cash economy (transactions done with cash)
Volunteers
‘Guestimating’ occurs for
Farm production consumed on the farm
Accommodation Values
MAP (Measuring Australia’s Progress)
Collection of measures of living standards published periodically by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. The 4 main categories of measures are society, economy, governance and environment.