FPD- pontic design
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
consequences of tooth loss
adjacent teeth may drift/tilt mesially/distally
the opposing tooth may retrude into the edentulous space
premature contacts may be created during protrusive movement
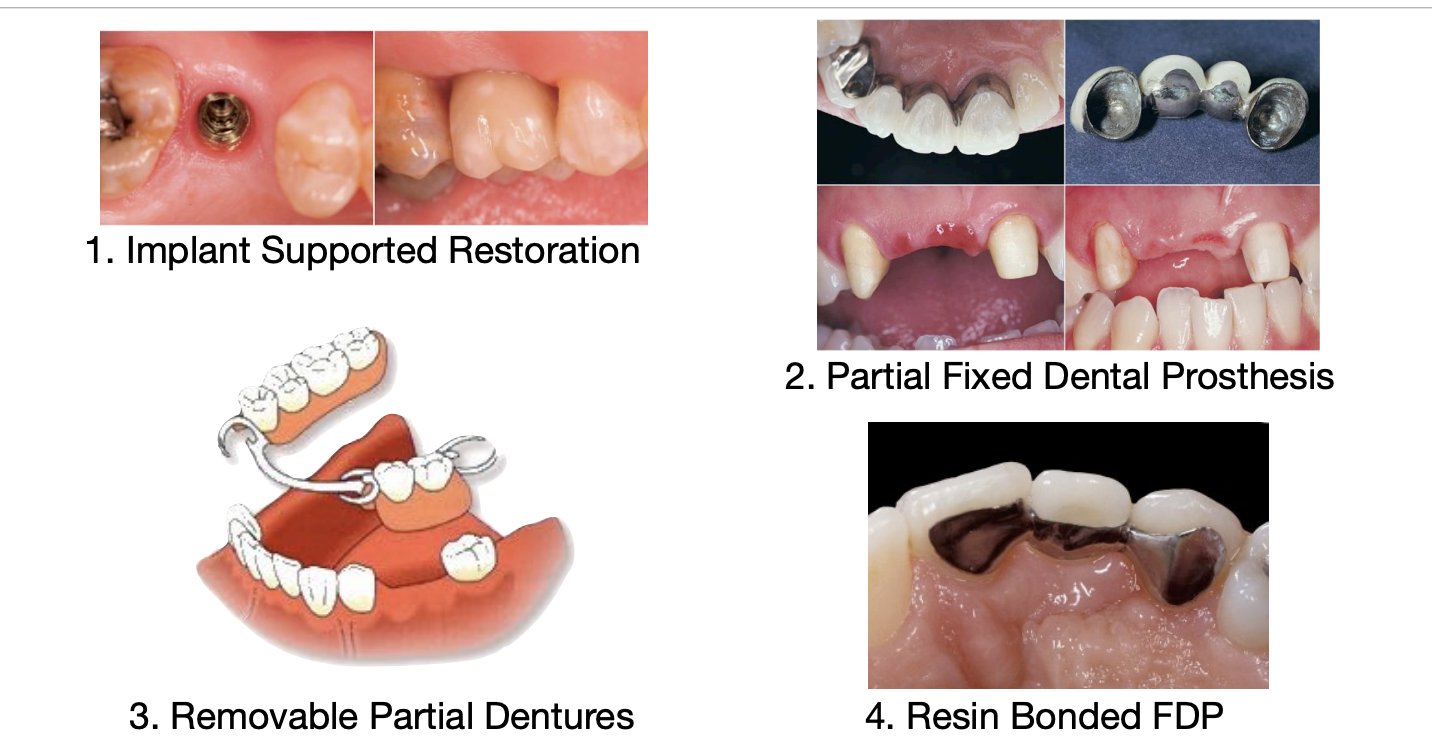
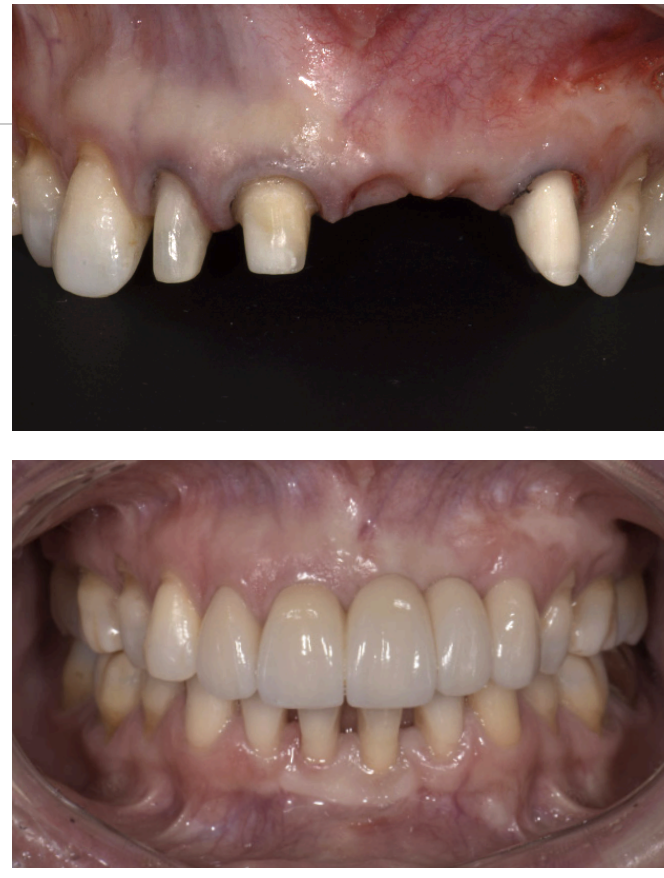
options for replacing missing tooth/teeth
implant supported restoration
partial fixed dental prosthesis
removable partial denture
resin bonded FDP
what is usually the first choice of replacing a missing tooth
implants
sometimes pt can decline implants, what tooth replacement would you offer to the pt next
FPD- fixed partial denture (bridge)
what might be some reasons a pt would decline implants/wouldn't be a good candidiate
declines surgery
hx of failed implants
limited finances
adjacent teeth on edentulous space already require complete coverage
pt desires quick tx completion
dentists should avoid indiscriminate preparation of healthy unrestored teeth to replace missing teeth because…
FPDs can increase the risk of future complications
what are the main components of a fixed partial denture (FPD)
retainer
pontic
connector
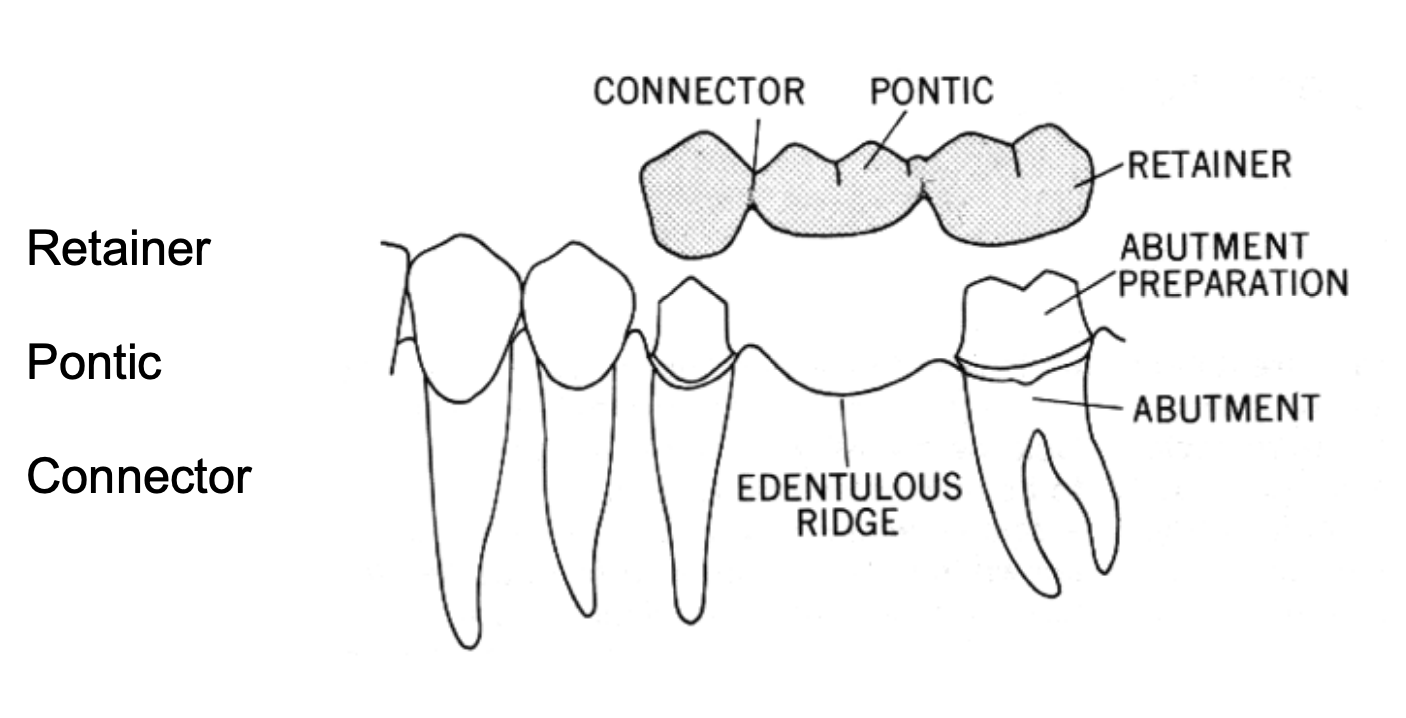
what is the abutment in a FPD
a tooth, a portion of a tooth, or that portion of a dental implant that serves to support and/or retain a prosthesis (tooth that supports the FDP)
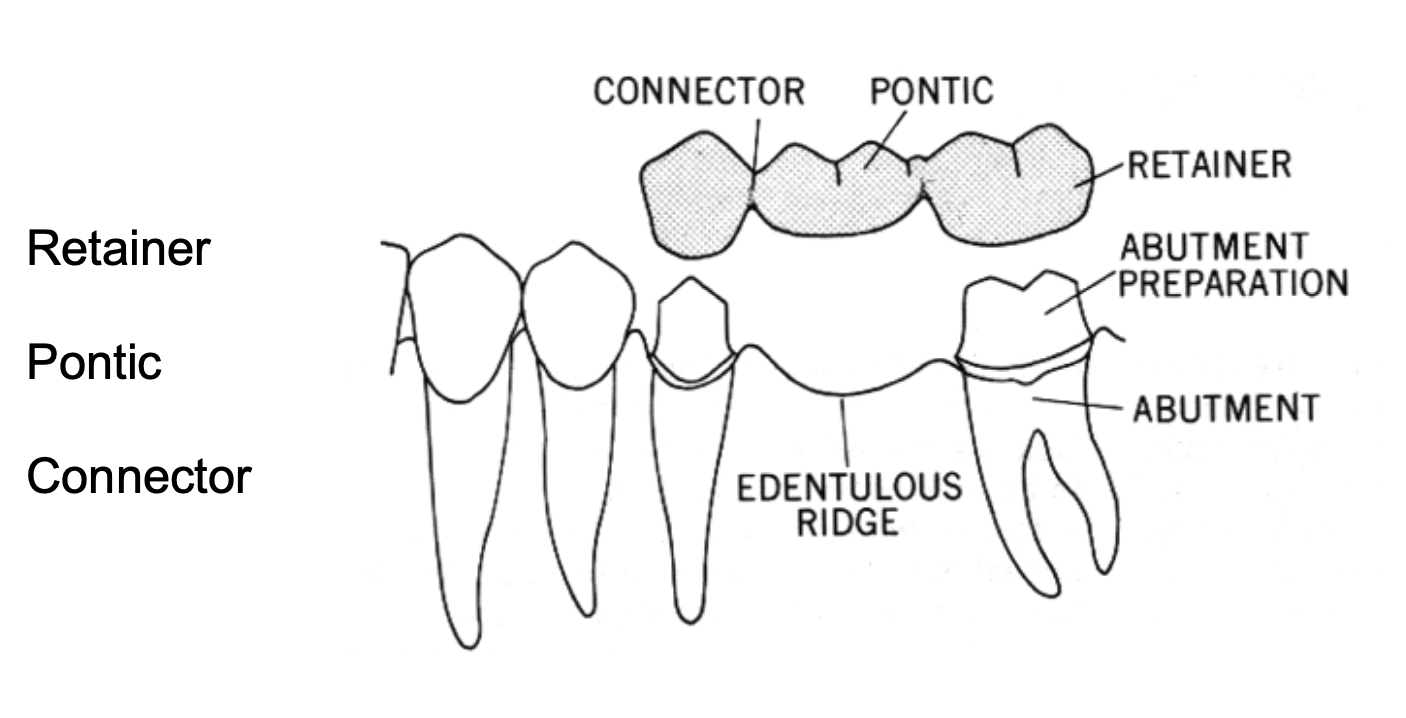
what is the retainer in a fixed partial denture
any type of device used for the stabilization or retention of a prosthesis- part of the FDP cemented or luted to the abutment
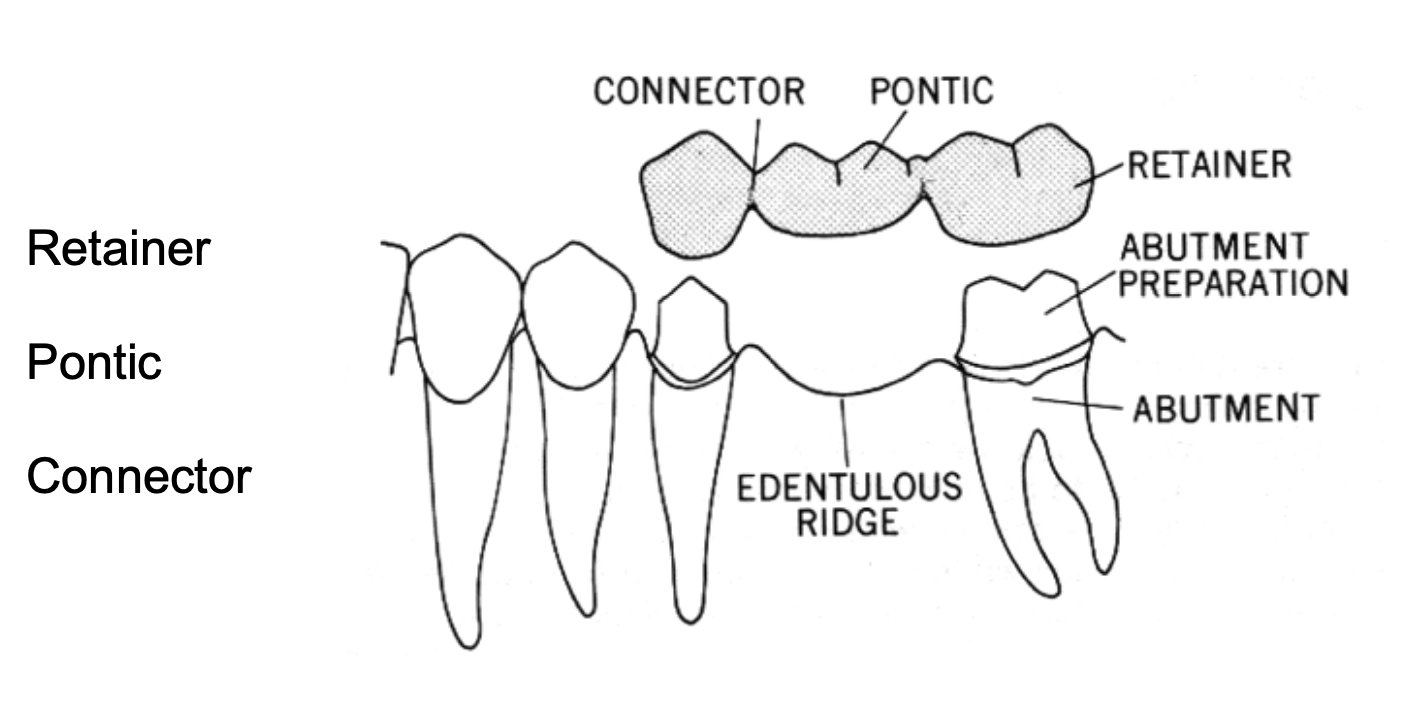
what is the retainer in a fixed dental prosthesis
the part of a fixed partial denture or fixed complete denture that unites the abutments to the remainder of the restoration
what is the pontic in a FPD
an artificial tooth on a fixed dental prosthesis that replaces a missing natural tooth, restores its funx, and usually fills the space previously occupied by the clinical crown
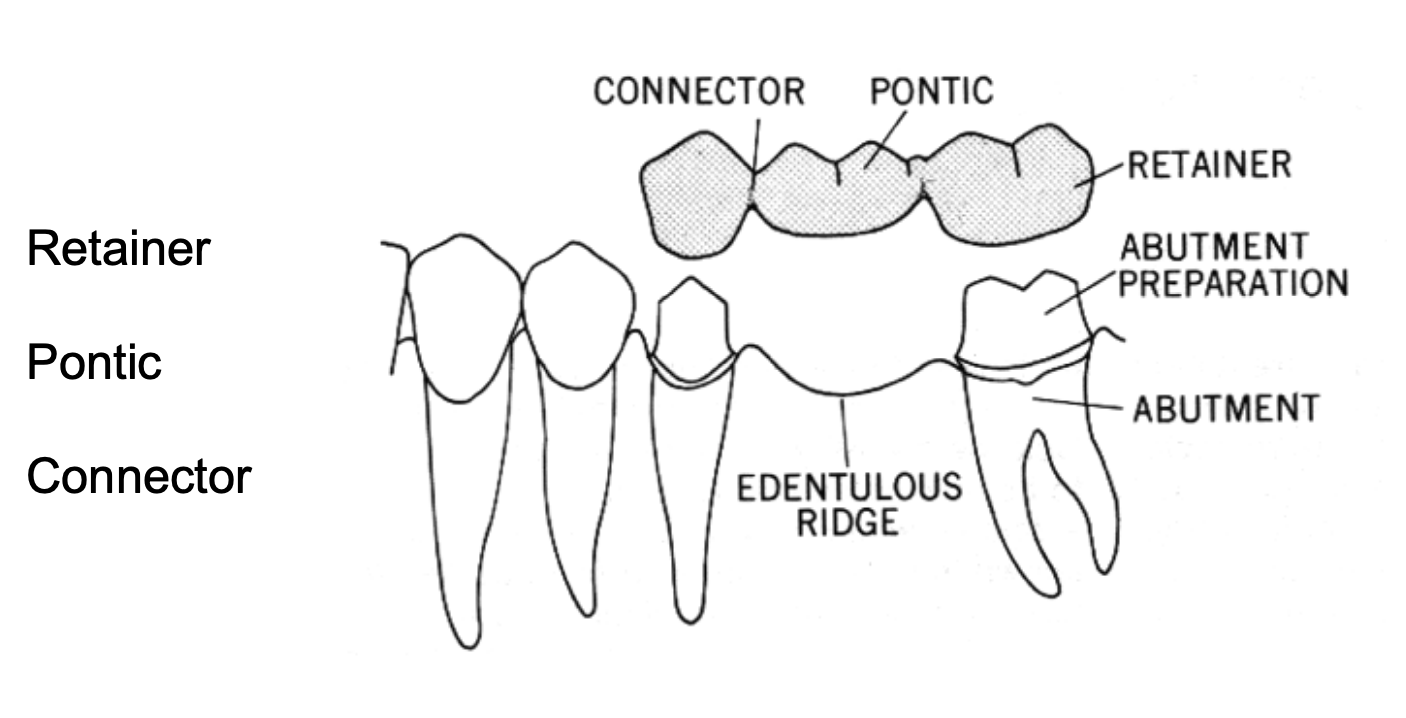
what is the connector
in fixed dental prosthodontics, the portion of a fixed dental prosthesis that unites the retainer(s) and pontic(s)
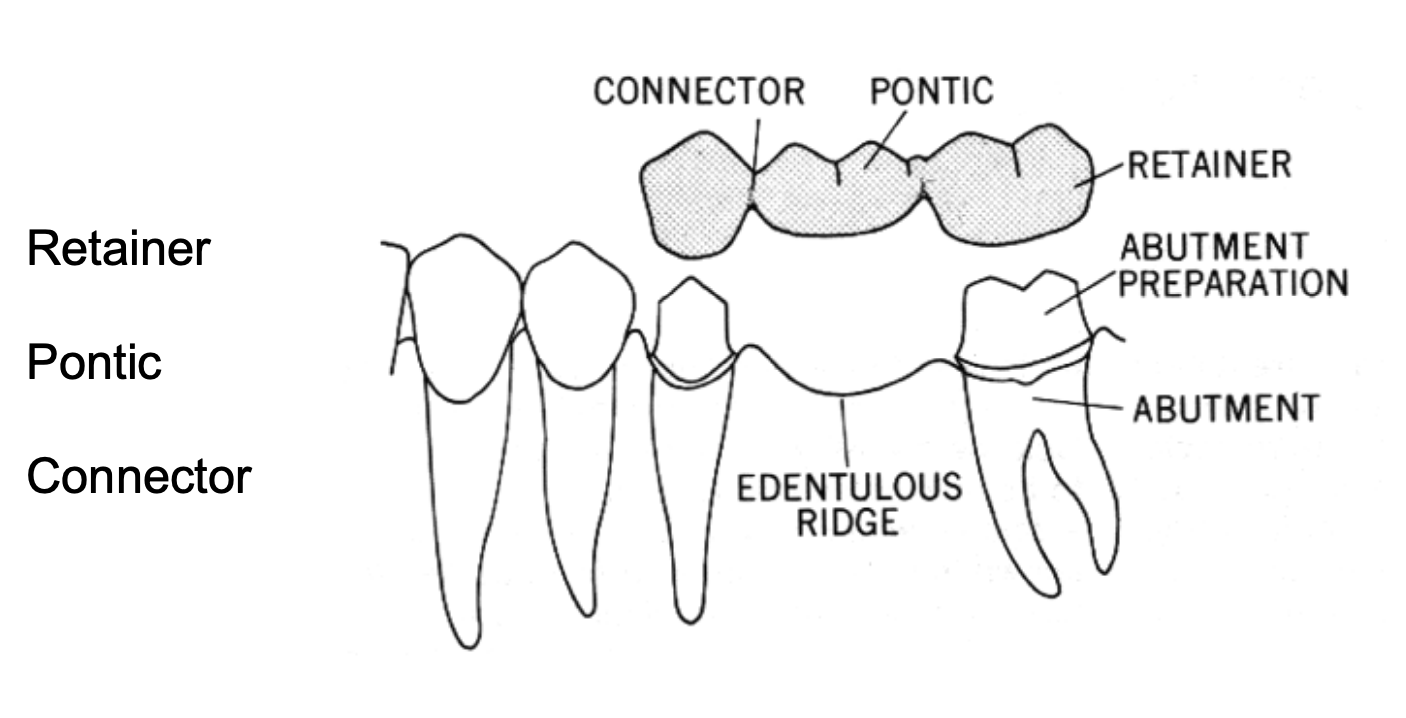
when considering FPD as tx, what should be evaluated
potential abutment teeth
super-erupted teeth
mesially or distally tilted adjacent teeth to edentulous area
when considering FPD as tx, what should be examined when looking at the potential abutment teeth
root shape
periodontal tissue
crown:root
if RCT → ferrule
quality and extension of caries/restoration
height/width of edentulous area at MIP
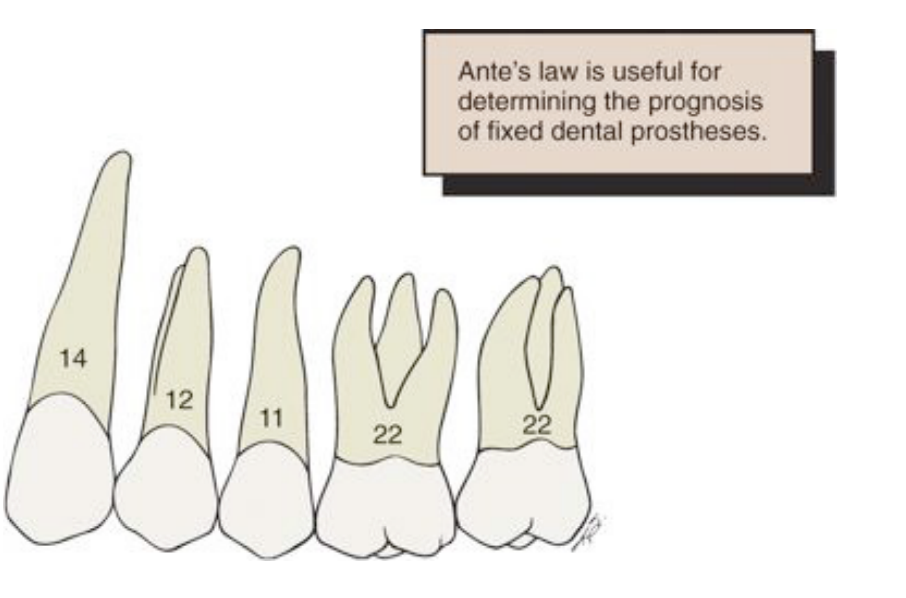
what Law is thought about when looking at root surface area
Ante’s law
what is Ante’s law
root surface area of the abutments should be more than the root surface area of the teeth being replaced
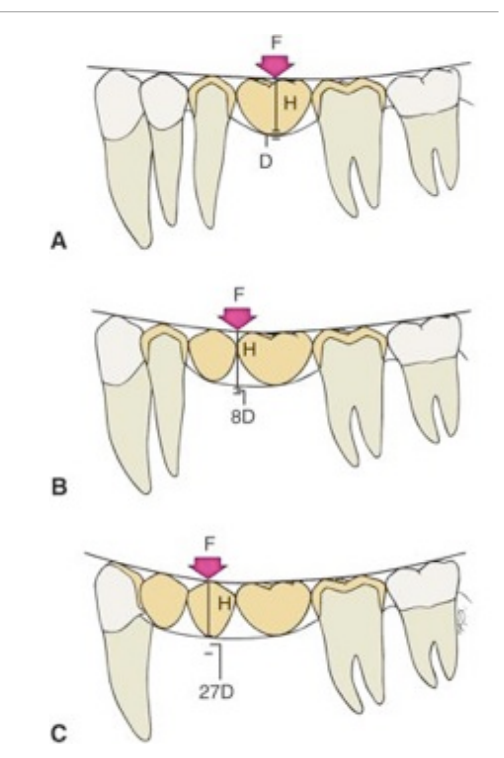
what Law is thought about when thinking of span length
Law of Beams
what is the Law of Beams
span of edentulous site: bending or deflection varies directly with the cube of the length and inversely w the cube of the occlusogingival thickness of the pontic
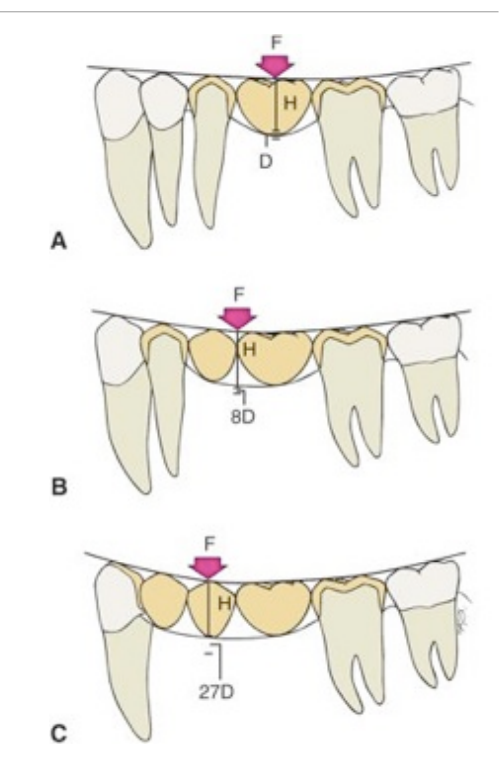
according to the Law of Beams, excessive flexing under occlusal loads can cause…
premature failure
fx of porcelain veneer
connector fx
loosening of a retainer
tooth mobility
unfavorable soft tissue response
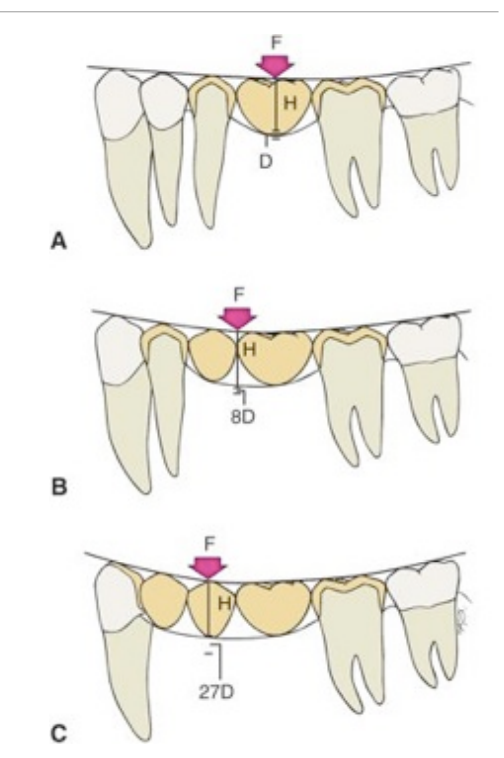
according to the Law of Beams, ______________ is a common contraindication for FDP
excessive span length
ranks these from most to least prognosis
FDP w 2 pontics in anterior region
FPD w 1 pontic
FPD w 2+ pontics in posterior region
FPD w 1 pontic > FPD w 2 pontics in anterior region > FPD w 2+ pontics in posterior region
what are the exceptions to a longer span length in FPD
when the FPD is opposing a complete denture → occlusal loads tend to be lower
a successful FPD in the mandibular anterior region includes a 6-unit FPD from canine to canine
what is a cantilever fixed partial denture
where only one side of the pontic is attached to one or multiple retainers
what is a classic popular example of a cantilever FPD
a lateral incisor pontic attached to only the adjacent canine retainer
cantilever FPDs can be made out of….
metal-ceramic
ceramic materials- zirconia
in an unideal situation: what do you do when the FPD is replacing either a maxillary or mandibular canine tooth
the small lateral incisor may be splinted to the central incisor to prevent lateral drift of the FPD
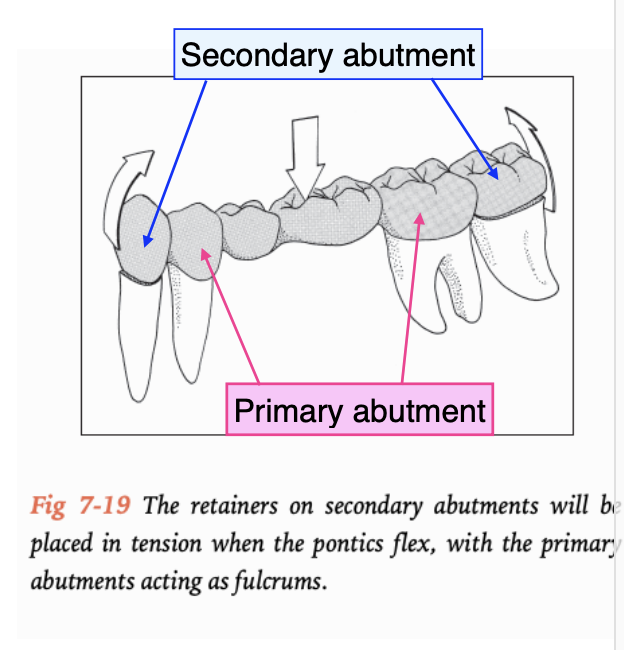
in an unideal situation, sometimes you need to double-abutt, what are the requirements for the secondary abutment
must have at least as much root surface area and as favorable a crown:root as the primary abutment
retainers on secondary abutment must be at least as retentive as the retainers on the primary abutments
what 3 things should be evaluated in a metal-ceramic restoration framework design
margin
occlusion
proximal contacts
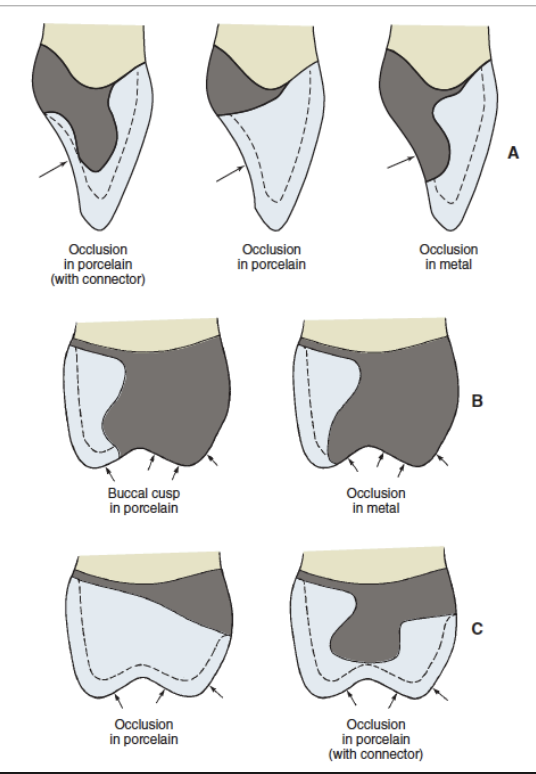
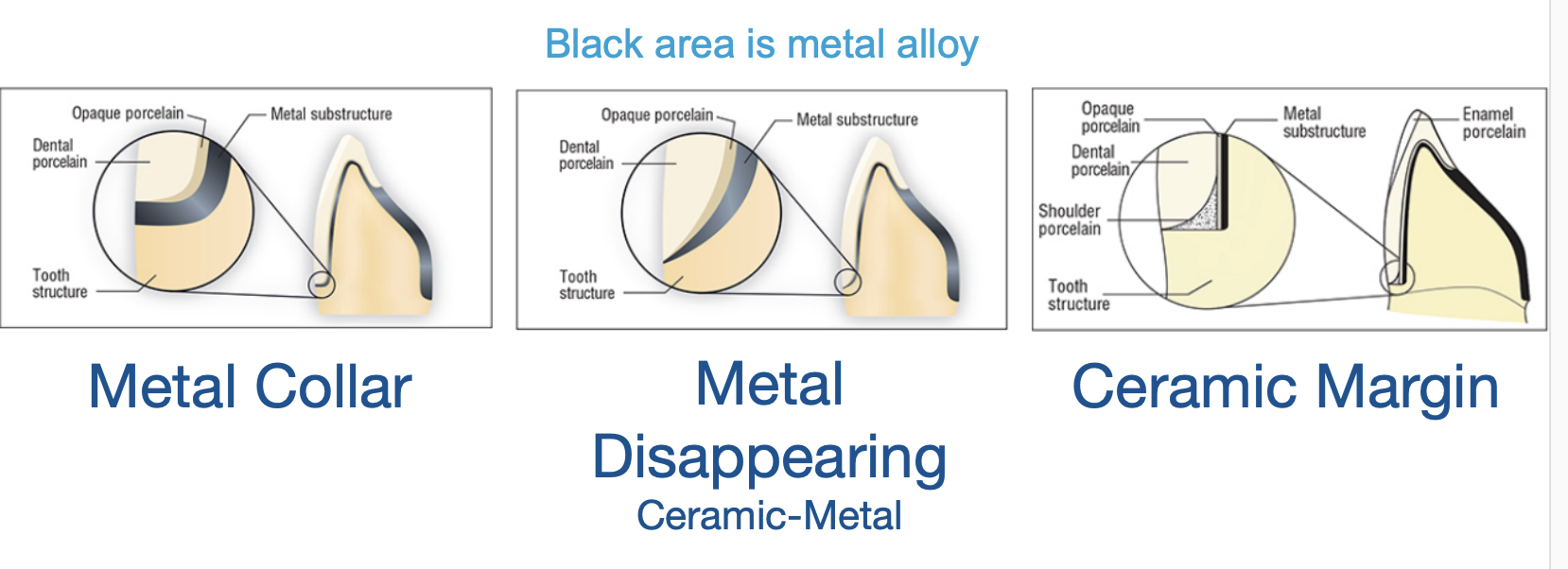
what are the 3 designs for margin or metal ceramic crown
metal collar
metal disappearing
ceramic margin
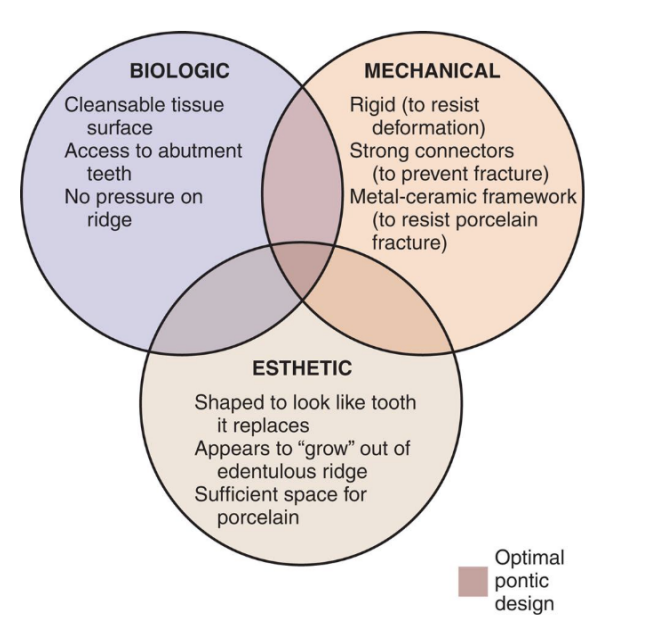
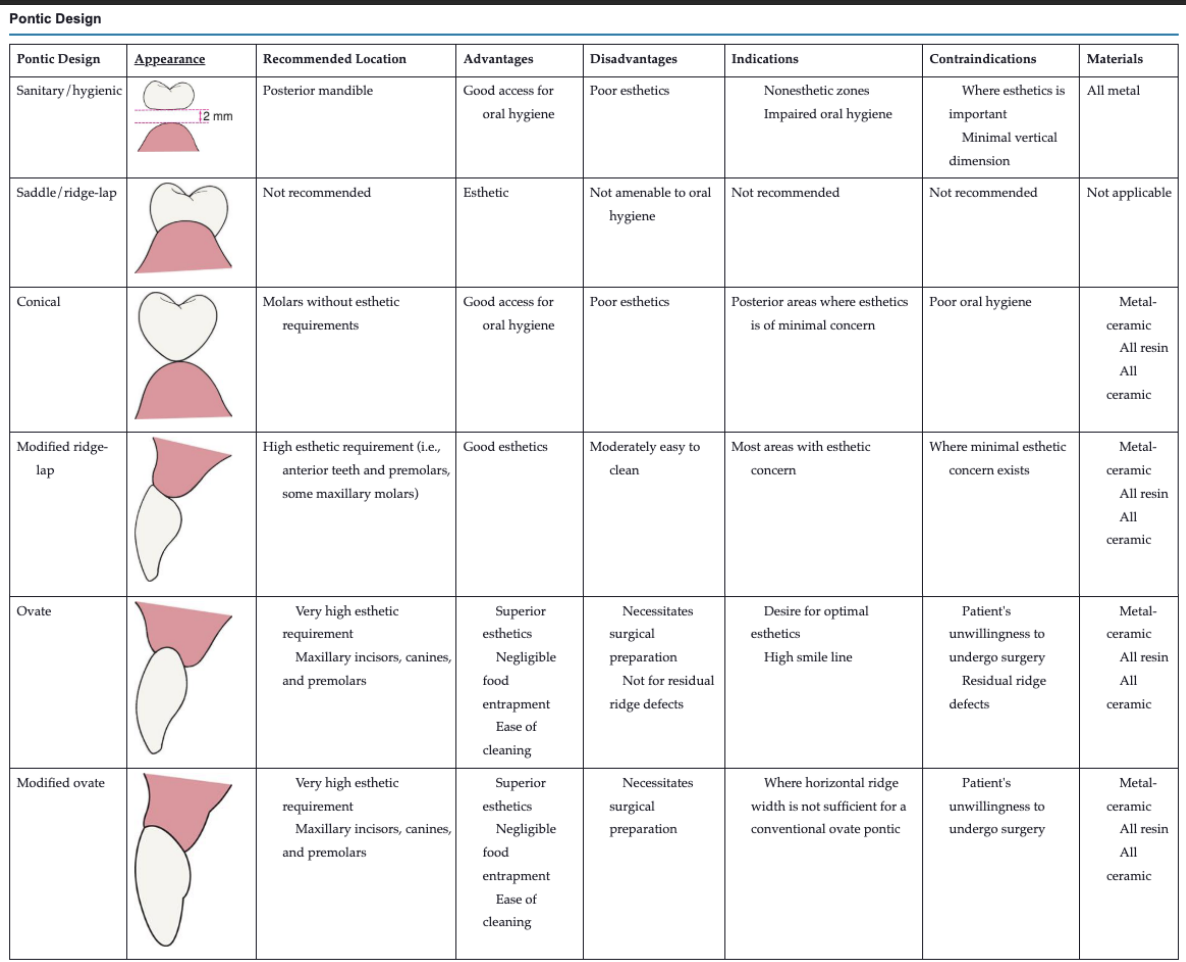
an optical pontic design should have what 3 components
biologic
mechanical
esthetic
___________________ may prove especially valuable for determining optimal pontic deisgn
diagnostic cast and waxing procedures
what should be in your pre-treatment assessment for FPD
pontic space
residual ridge contour
surgical modification
gingival architecture preservation
what do you want to look at for pontic space
mesial-distal
bucco-lingual width
occluso-gingival height
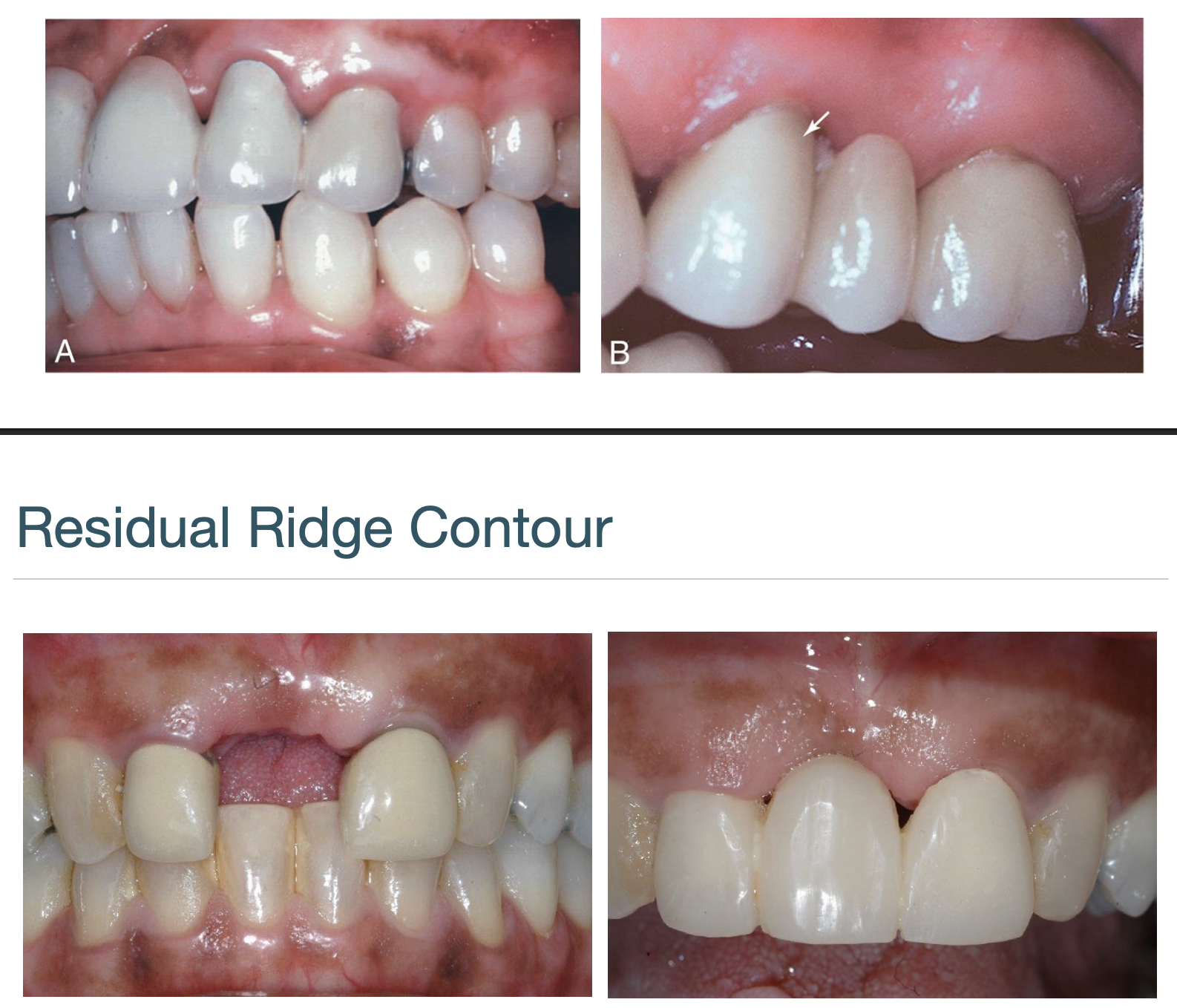
what to use to evaluate/grade the residual ridge contour
siebert residual ridge classification- I, II, III

siebert residual ridge C-I defects
faciolingual loss (horizontal loss) of tissue width w normal ridge height
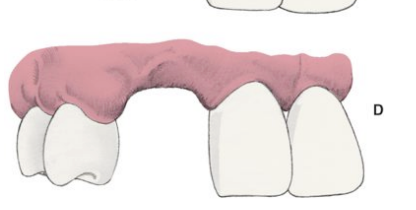
siebert residual ridge C-II defects
loss of ridge height (vertical loss) w normal ridge width
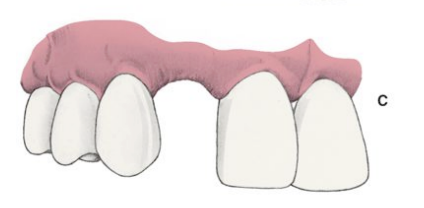
siebert residual ridge C-III
a combination of loss in both dimension (horizontal and vertical loss)
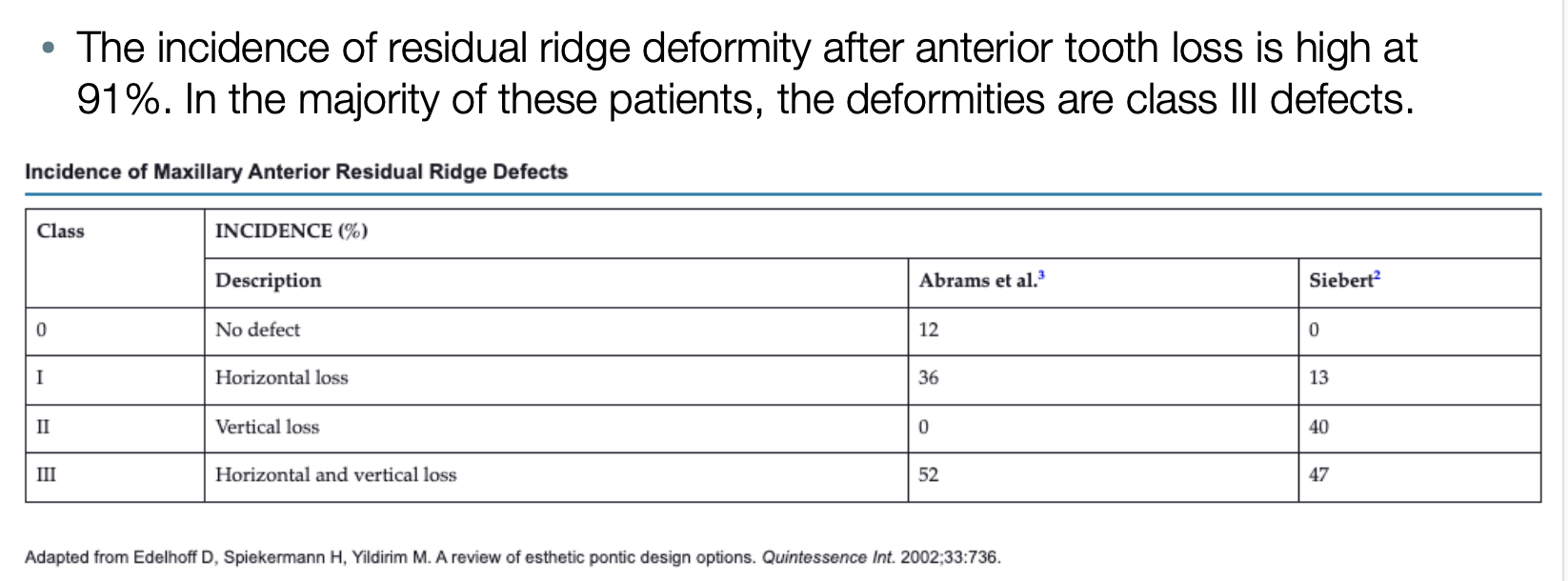
the incidence of residual ridge deformity after anterior tooth loss is high at ___%. the majority of these pts are within the C-____ defects
91%; C-III defects
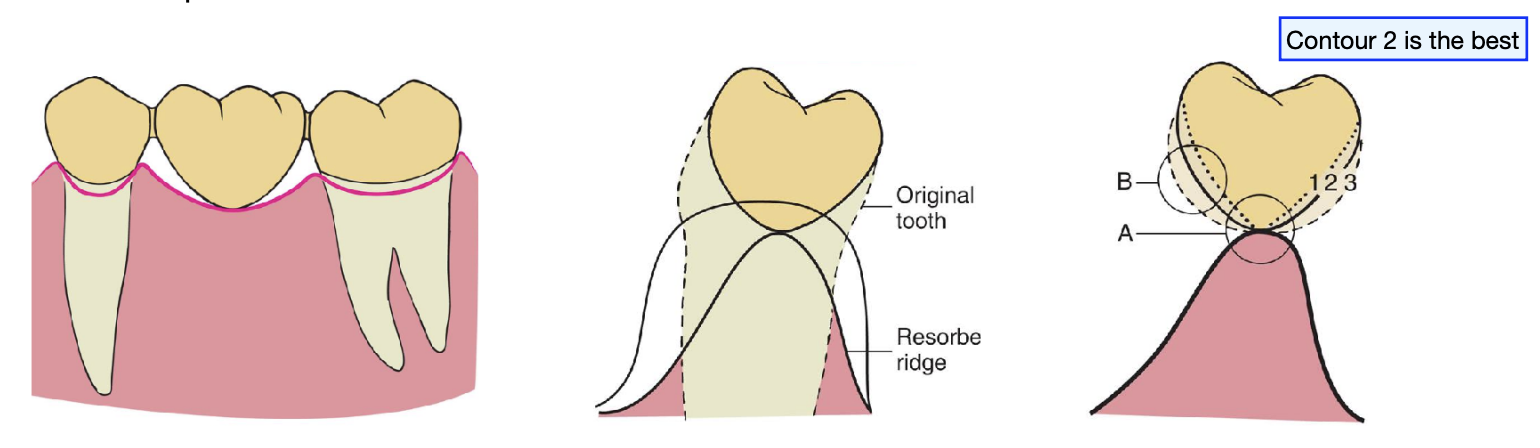
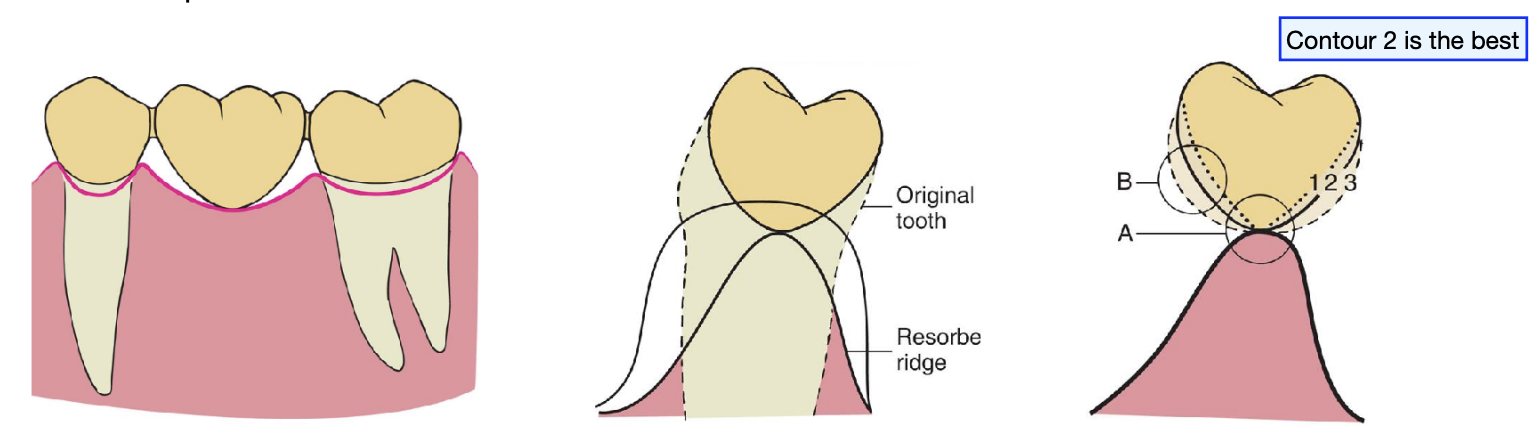
loss of residual ridge contour may lead to…
unesthetic gingival embrasures (black triangles), food impaction, and percolation of saliva during speech
correction of ridge defects can be done through surgical modifications such as…
soft tissue grafts
pedicle graft procedure: roll flap procedure
free graft procedure: pouch graft procedure, interpositional graft procedure, onlay graft procedure
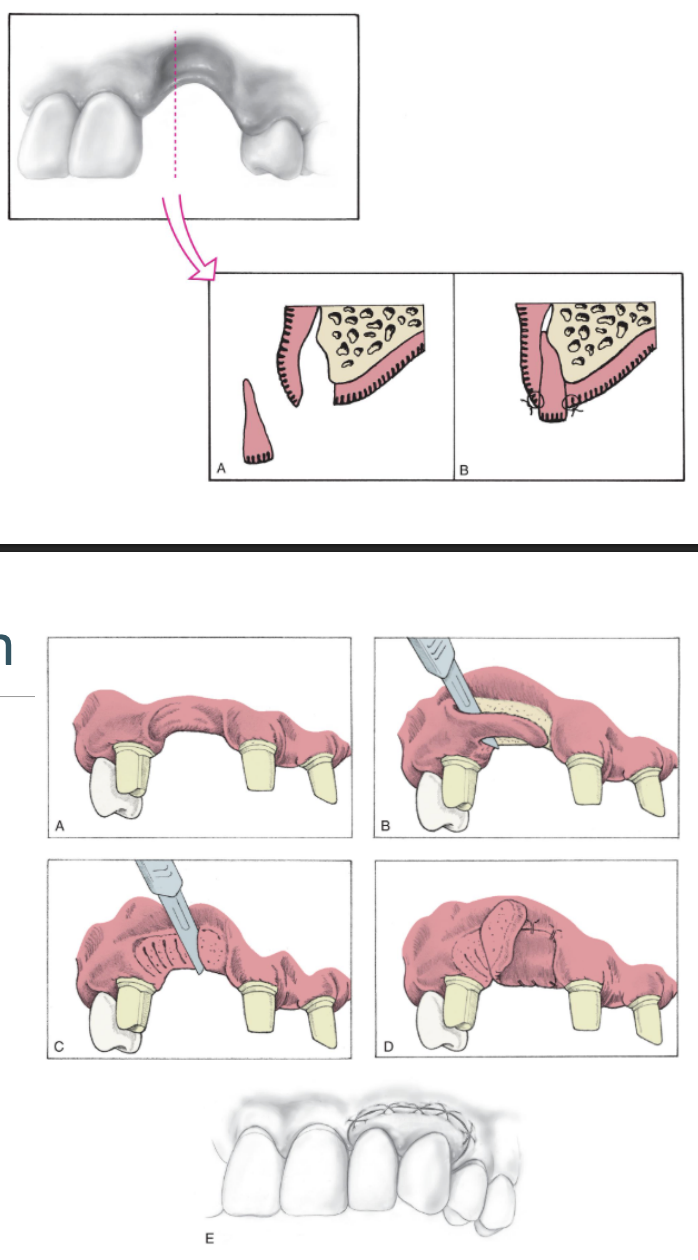
what soft tissue graft could you do for C-I defect
roll technique (top pic)
pouch technique (bottom pic)
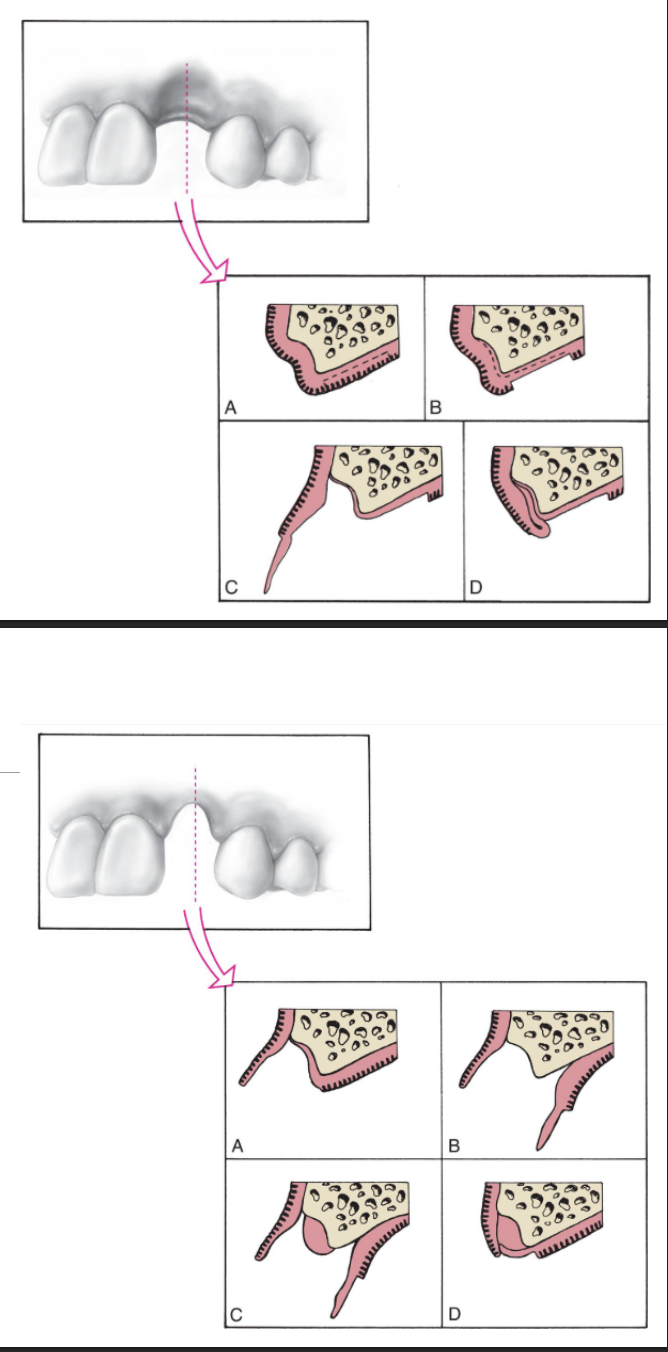
what soft tissue graft could you do for a C-II and C-III defect
interpositional graft (top pic)
onlay graft (bottom pic)
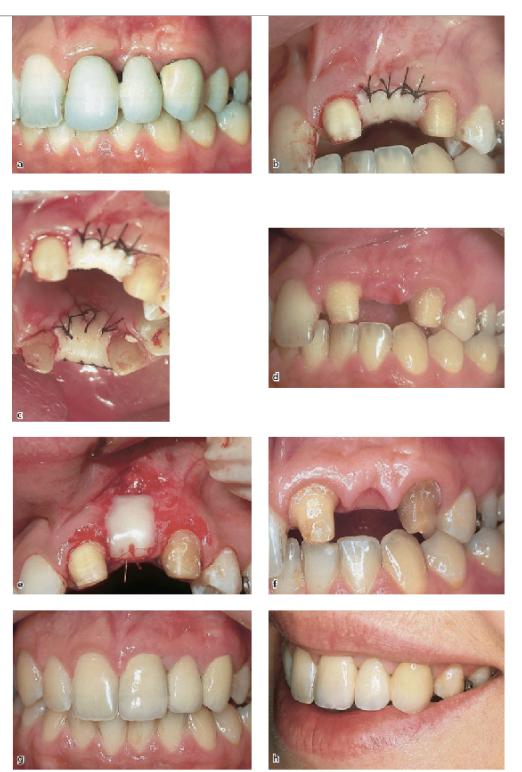
describe the gingival architecture preservation
immediate restoration and periodontal intervention at the time of tooth removal
preparing the abutment before ext
fabricate an interim FPD indirectly, ready for immediate insertion
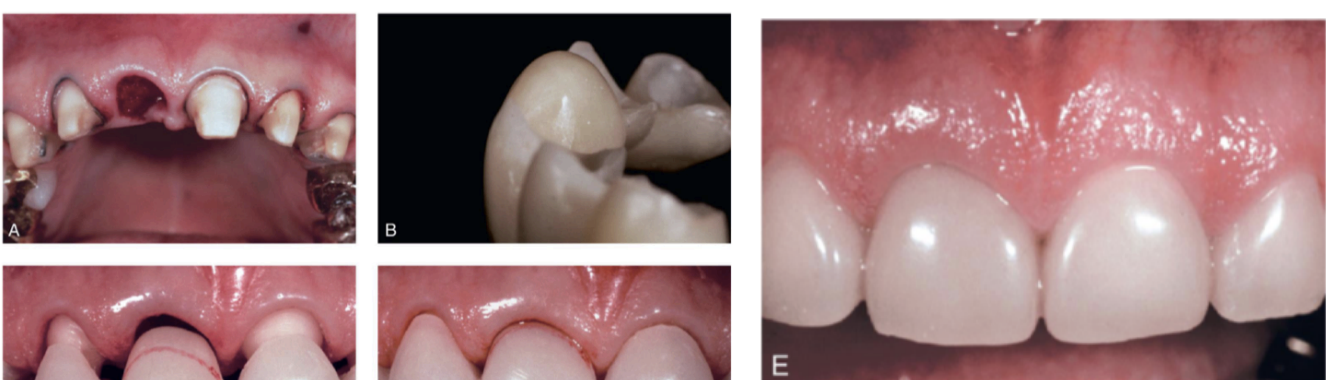
you want ___ mm apical to facial free gingival margin for gingival architecture preservation
2.5 mm
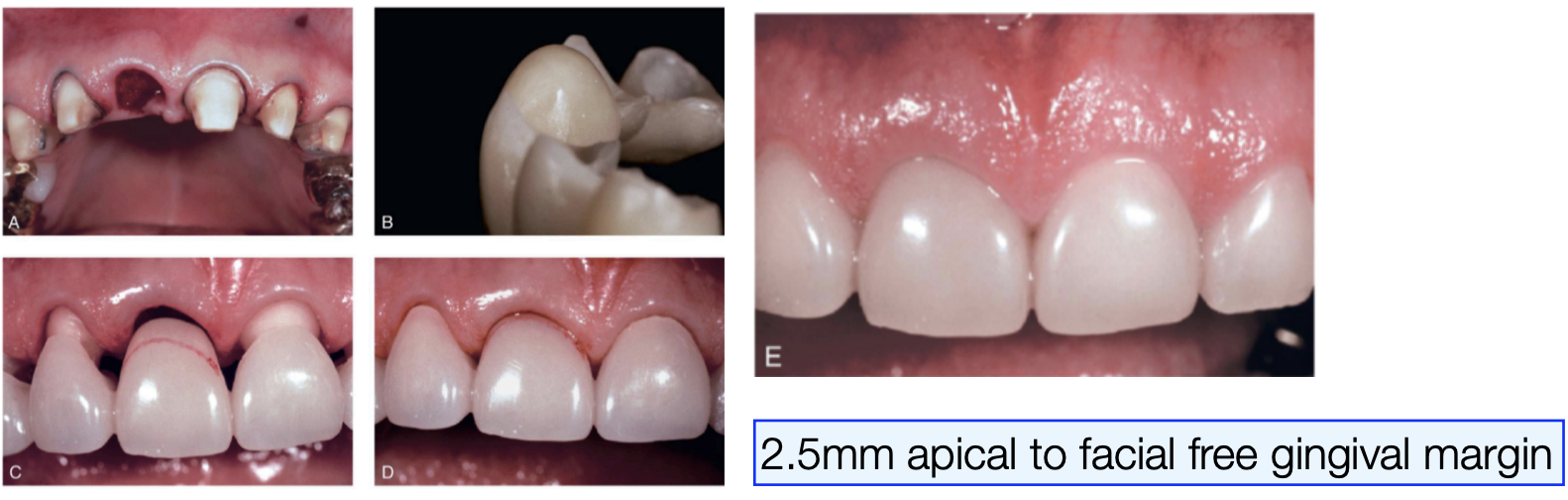
the contour of the ______ tissue side of the pontic is critical and must conform to within __ mm of the interproximal and facial bone contour to act as a template for healing
ovate tissue; 1 mm
the interim restoration should be highly __________
polished
approximately after 1 month of healing, oral hygiene access is improved by recontouring the pontic to provide __ to __ of relief from the tissue
1-1.5 mm
when the gingival levels are stable, approximately ____________ after healing, the definitive restoration can be fabricated
6-12 months
options for gingival architecture preservation
bond the ext tooth to the adjacent tooth
socket preservation- graft
secondary surgical augmentation later down the line
ortho extrusion
root submergence techniques
if bone levels are compromised before or during ext, to preserve the sockets, they can be grafted w an __________ material
allograft
types of allograft material
hydroxyapatite
tricalcium phosphate
freeze-dried bone
rarely can socket preservation completely preserve the alveolar ridge frame, ________________ may still be necessary for some pts
additional surgical augmentation of the ridge
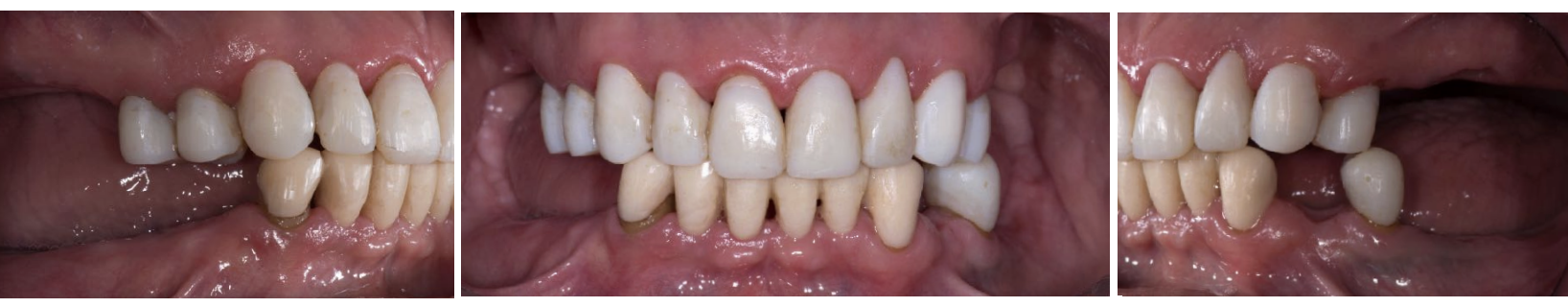
how does ortho extrusion aid in gingival architecture preservation
as teeth are extruded, apposition of bone occurs at the root apex, thereby filling the socket w bone as the tooth is slowly ext orthodontically
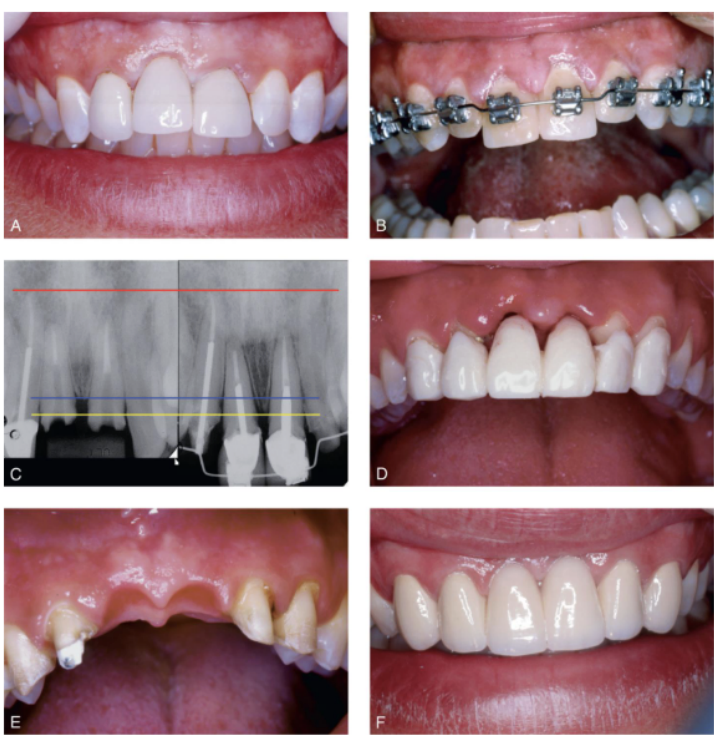
disadvantages of ortho extrusion aiding in gingival architecture preservation
additional time and expense
endodontic tx necessary beforehand
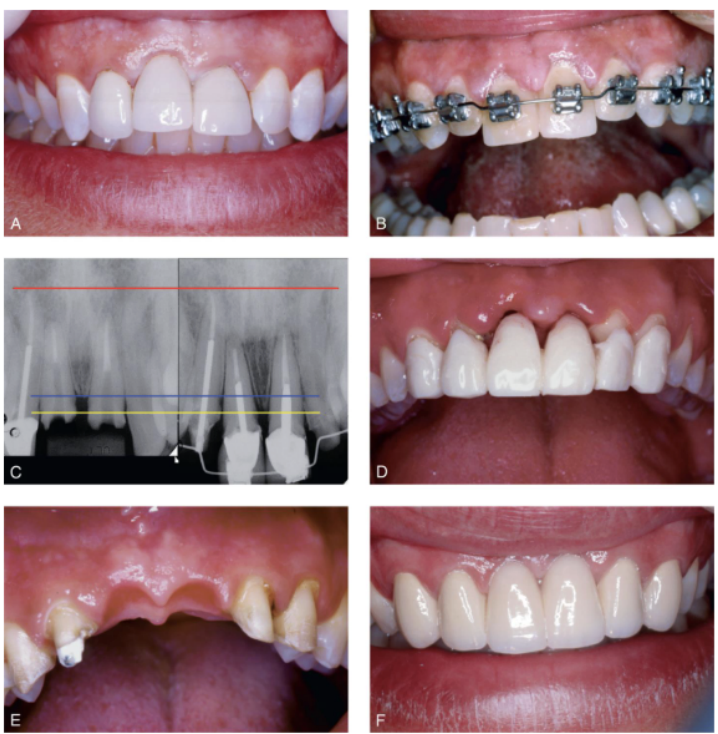
________________ technqiues hav been recommended to preserve alveolar bone height
root submergence techniques
pontic selection depends primarily on ________ and ________
esthetics and oral hygeine
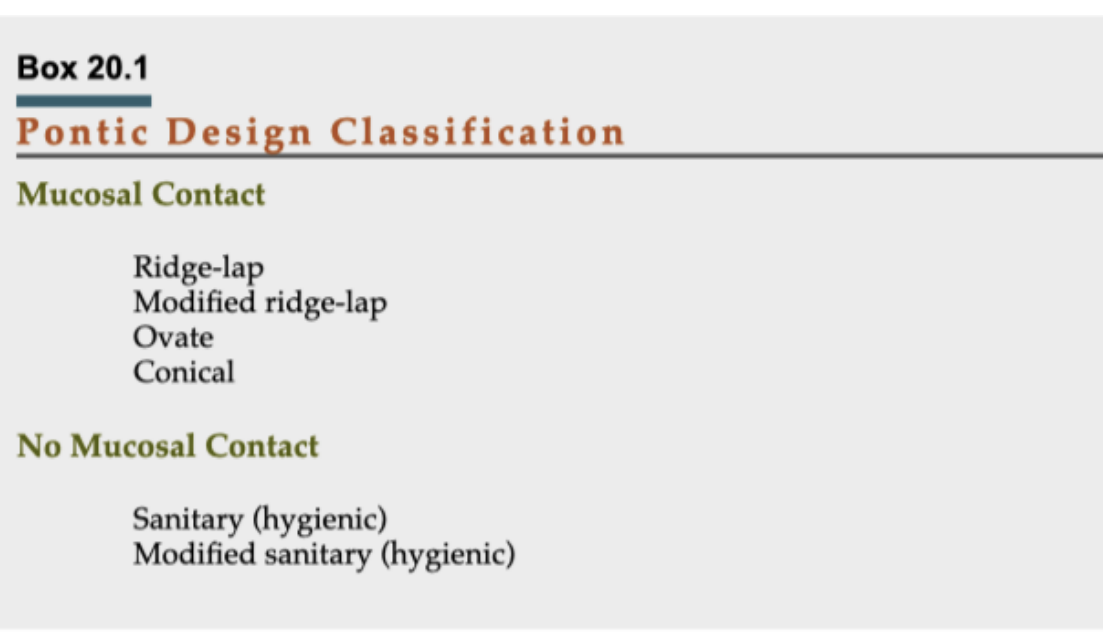
pontic densign classification
mucosal contact
no mucosal contact
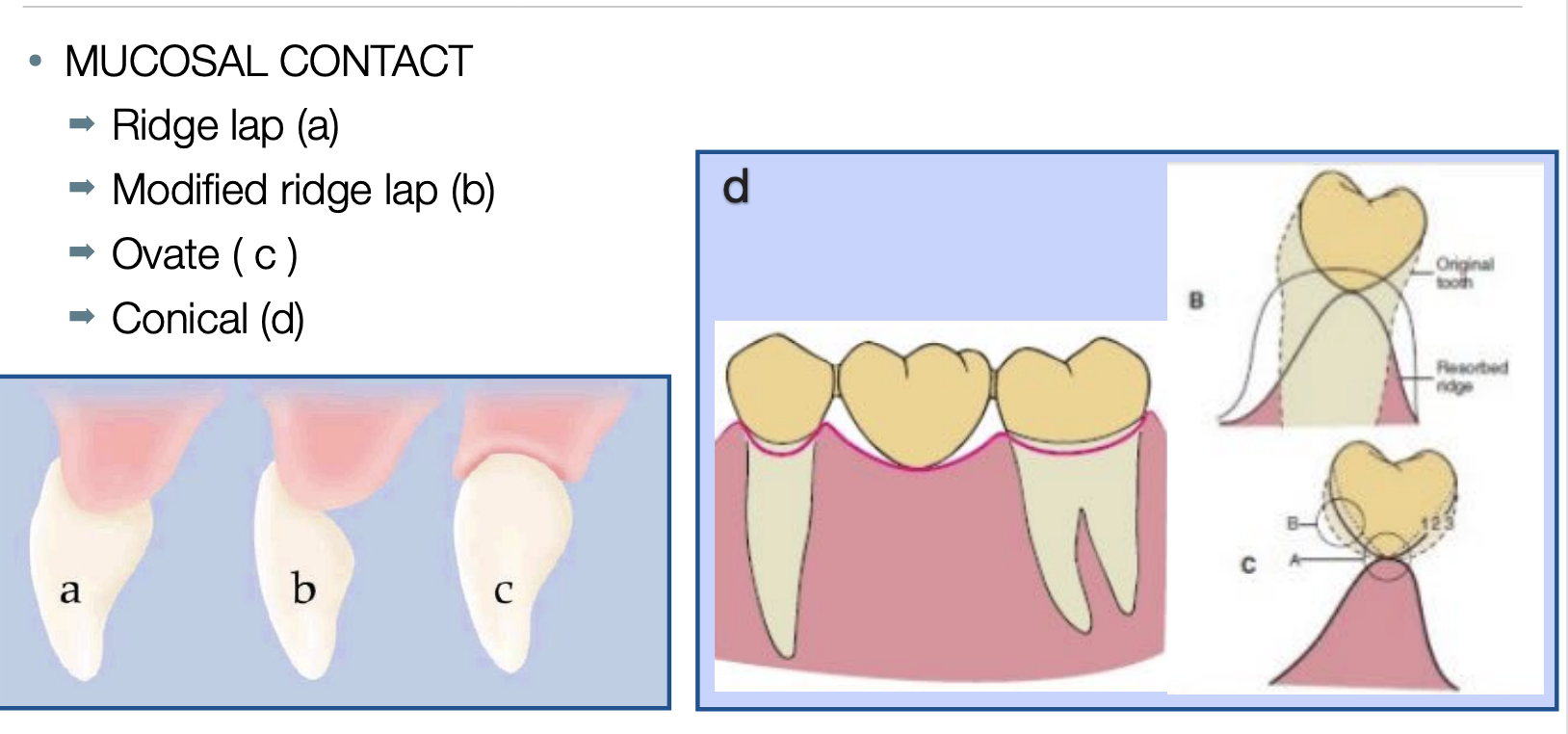
pontic classification sunder mucosal contact
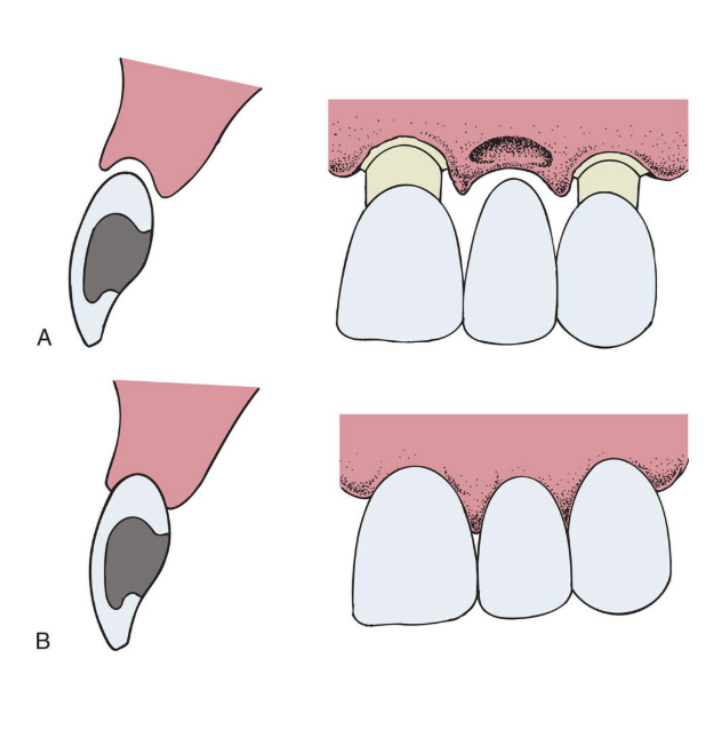
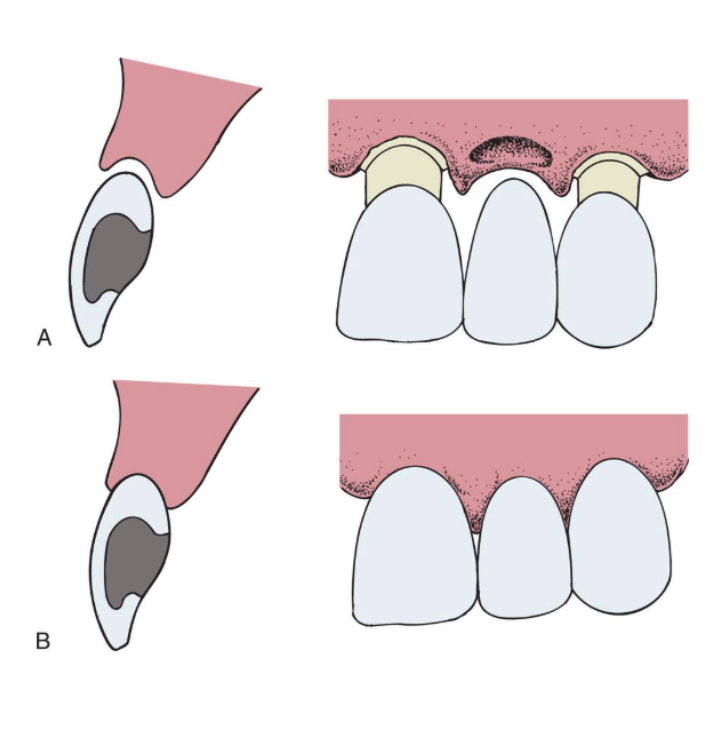
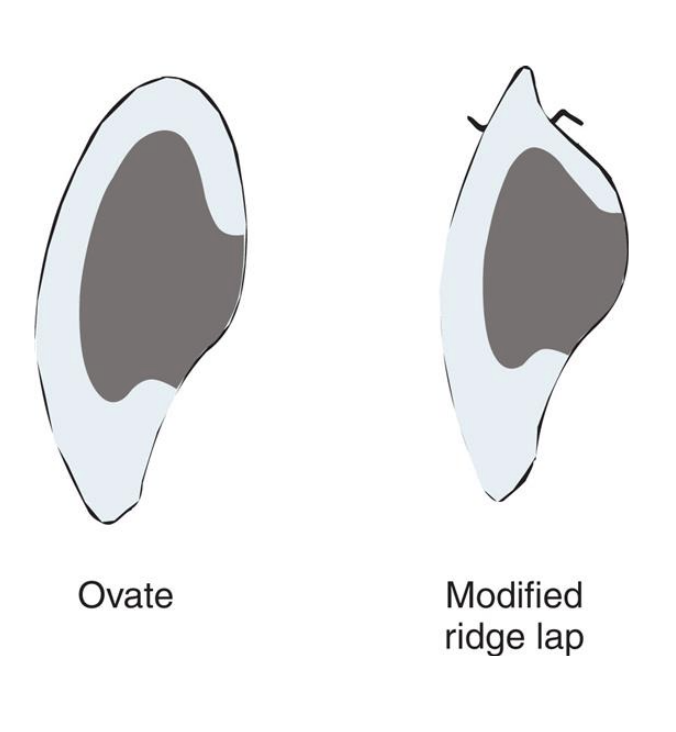
ridge-lap
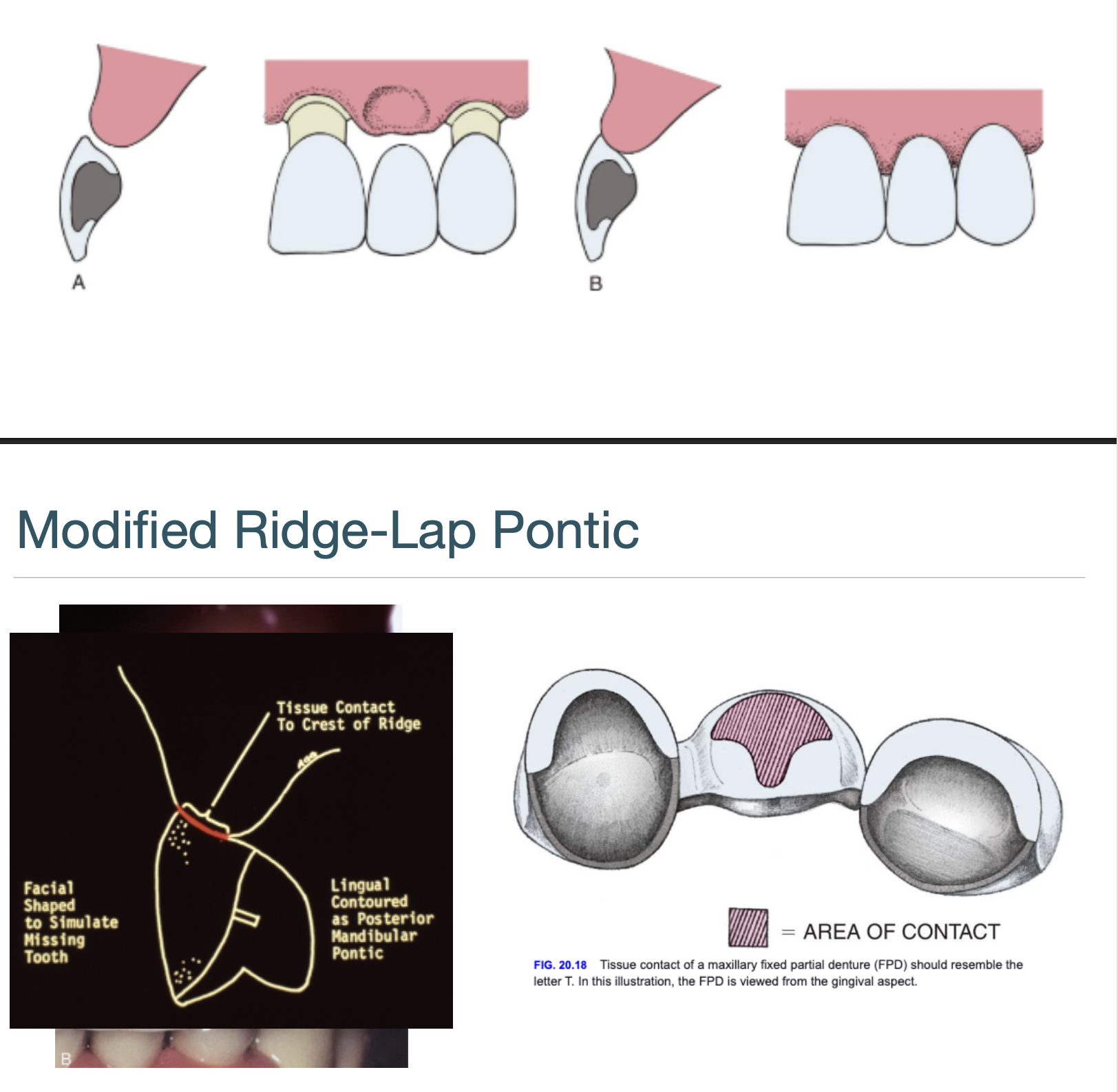
modified ridge-lap
ovate
conical
pontic classification under no mucosal contact
sanitary (hygienic)
modified sanitary (hygienic)
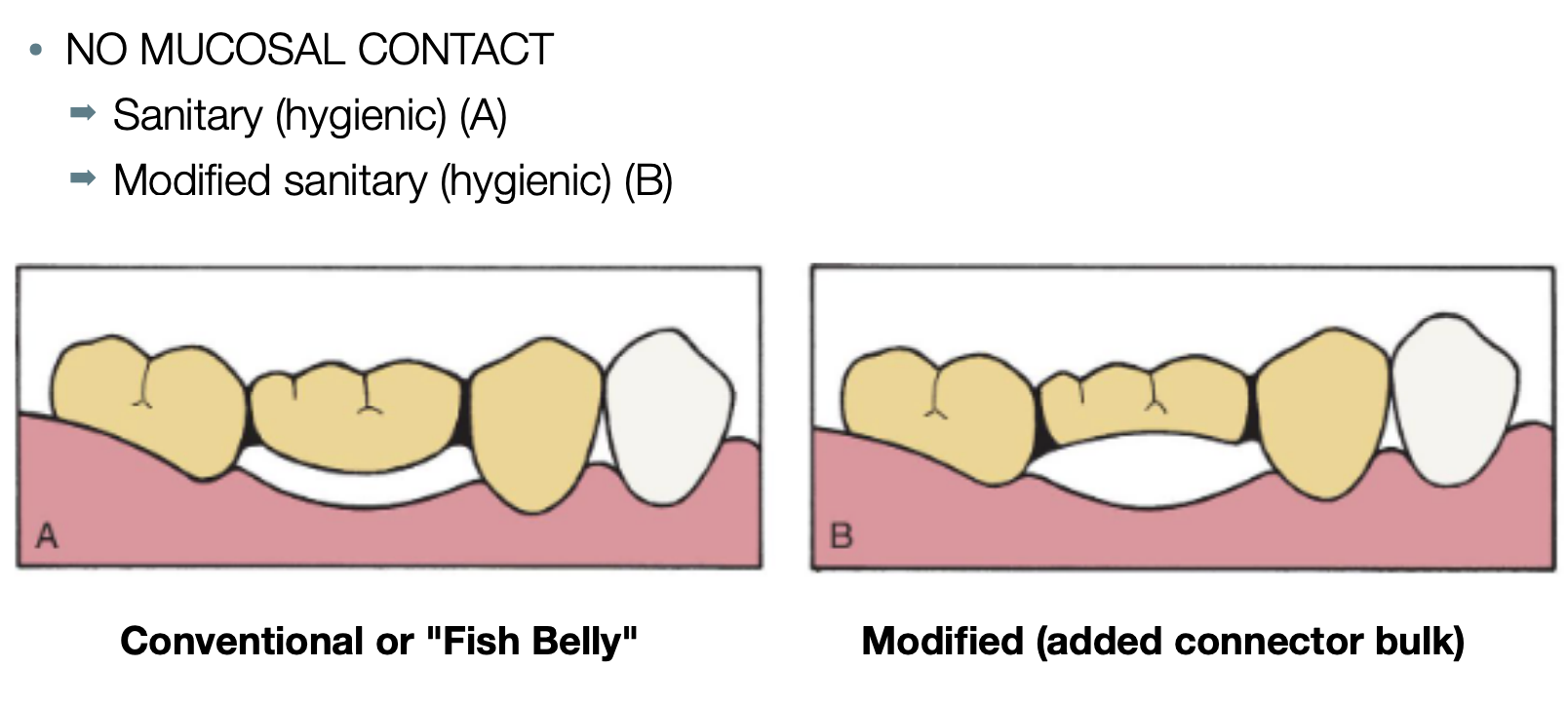
_________ or _______ designs should be avoided because the concave gingival surface of the pontic is not accessible to cleaning w dental floss
saddle or ridge-lap designs
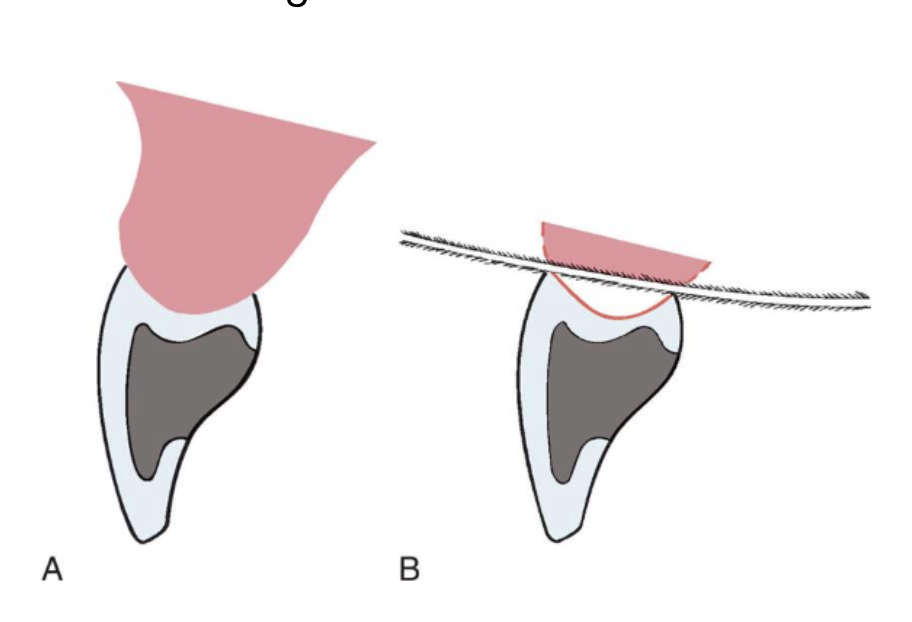
the saddle or ridge-lap designs can lead to
plaque accumulation
tissue inflammation
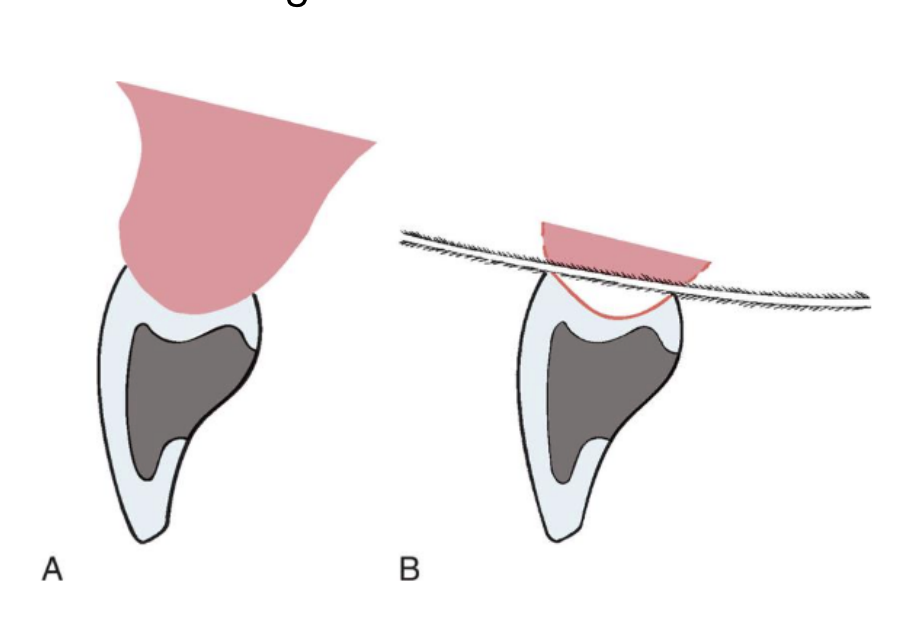
the modified ridge-lap pontic combines ________ with easy ___________
esthetics w easy cleaning
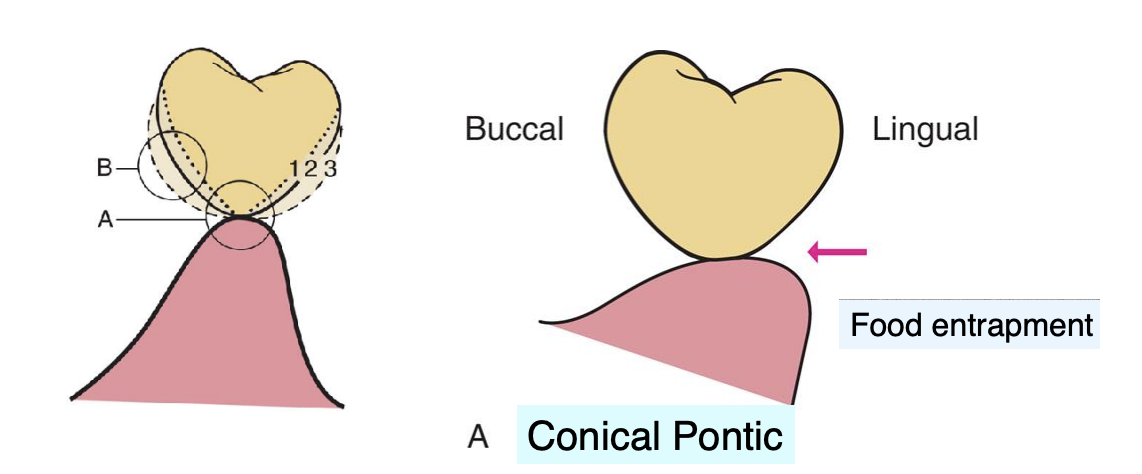
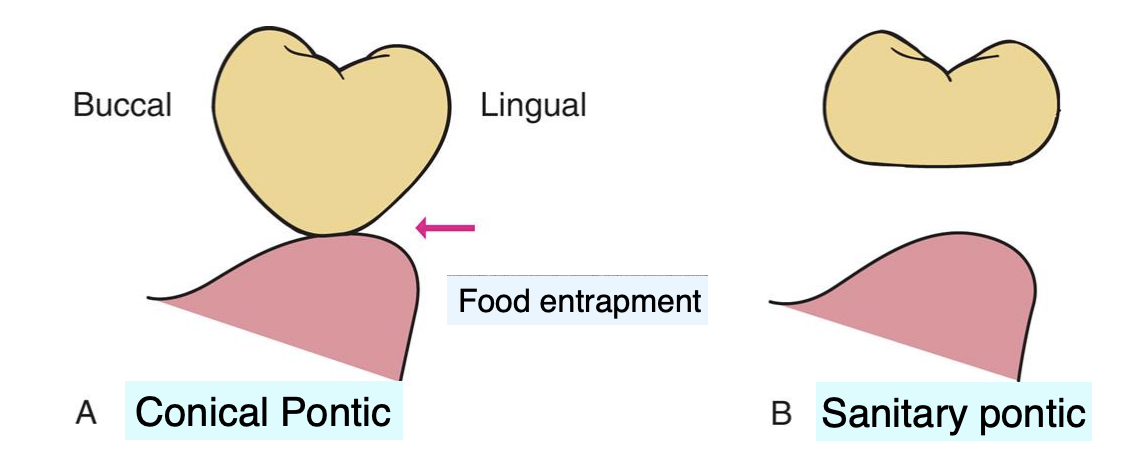
describe the design of the conical pontic
egg shaped, bullet-shaped, or heart shaped
one point of contact
pro of conical pontic
easy to clean
indication for conical pontic
mandibular posterior teeth: esthetic is a lesser concern
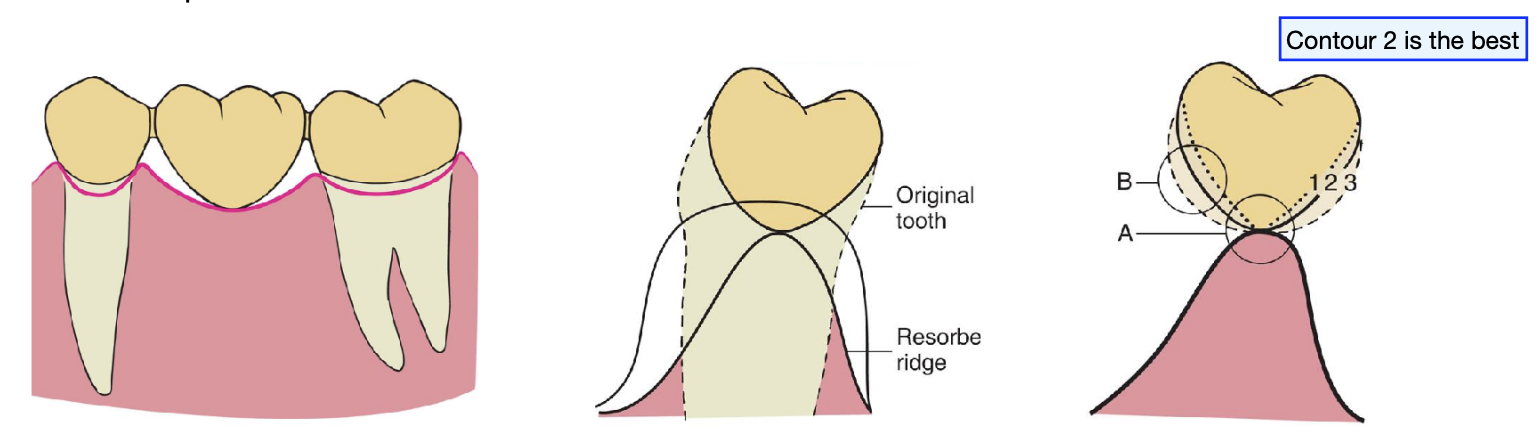
contraindications for conical pontic
unsuitable for broad residual ridges (bc the emergence profile associated w the small tissue contact point may create areas of food entrapment)
the __________ pontic form may be a better alternative than the conical pontic
sanitary pontic
describe the design of the ovate pontic
emerges from the gingiva, very esthetic
pros of ovate pontic
most esthetic
stronger than modified ridge-lap pontic
not susceptible to food impaction
easy to clean
con for ovate pontic
need for surgical tissue management/surgical augemntation of soft tissue → socket preservation techniques should be performed at the time of ext
why is the ovate pontic stronger than the modified ridge-lap pontic
the broad convex geometry makes it stronger because the porcelain at the gingivofacial extent of a pontic is supported
what is prosthetic biologic width
the thickness of tissue necessary between a pontic and the alveolar bone; 3.36 ± 0.6 mm
for the ovate pontic, when an adequate volume of ridge tissue is established, a _______ is sculpted into the ridge w…
a socket depression is sculpted; surgical diamonds, electrosurgery, or a dental laser
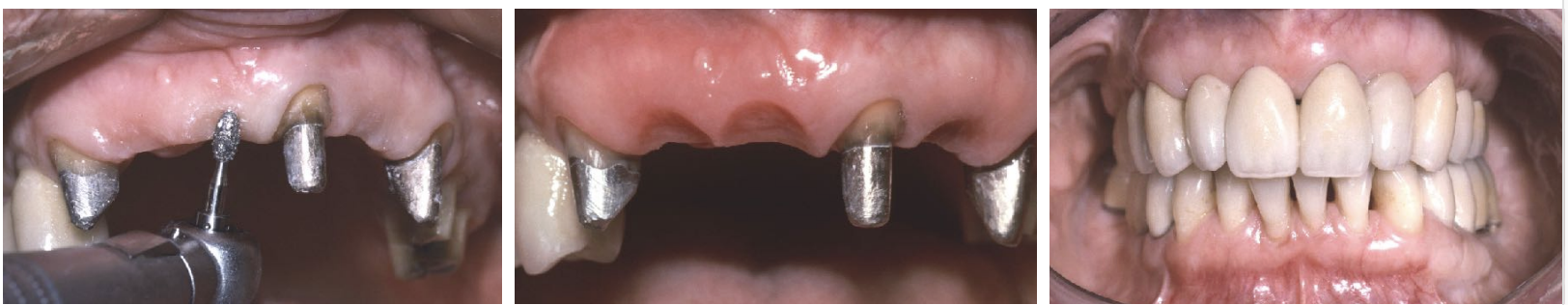
ovate pontic vs modified ovate pontic
ovate form with the apex positioned more facially on the residual ridge, rather than at the crest of the ridge
indication for modified ovate pontic
horizontal ridge width is not sufficient for a conventional ovate pontic
pros for sanitary/hygeienic pontic
easier plaque control
cons of sanitary/hygienic pontic
entrapment of food
poor esthetics
requirements for sanitary/hygienic pontic
>/= 2 mm ridge-to-pontic space
pontic O-G thickness >/= 3 mm
what are the available pontic systems
metal-ceramic
metal
ceramic
advantages of metal-ceramic pontic system
esthetics
biocompatible
advantages of metal pontic system
strength
straight forward procedure
advantages of `ceramic pontic system
best esthetics
biocompatible
disadvantages of metal-ceramic pontic system
difficult to fabricate if an abutment is not metal-ceramic
weaker than metal
disadvantages of metal pontic system
nonesthetic
disadvantages of ceramic pontic system
risk of fx
unable to be sectioned and reconnected
large connectors needed
indications for metal-ceramic pontic system
most situations
indications for metal pontic system
mandibular molars- especially under high occlusal force
indications for ceramic pontic system
high esthetic demand
contraindications for metal-ceramic pontic system
long span w high stress
contraindications for metal pontic system
where esthetics are important
contraindications for ceramic pontic system
long span w high stress
biological considerations for oral hygiene
cleansable tissue surface
access to abutment teeth (gingival embrasure)
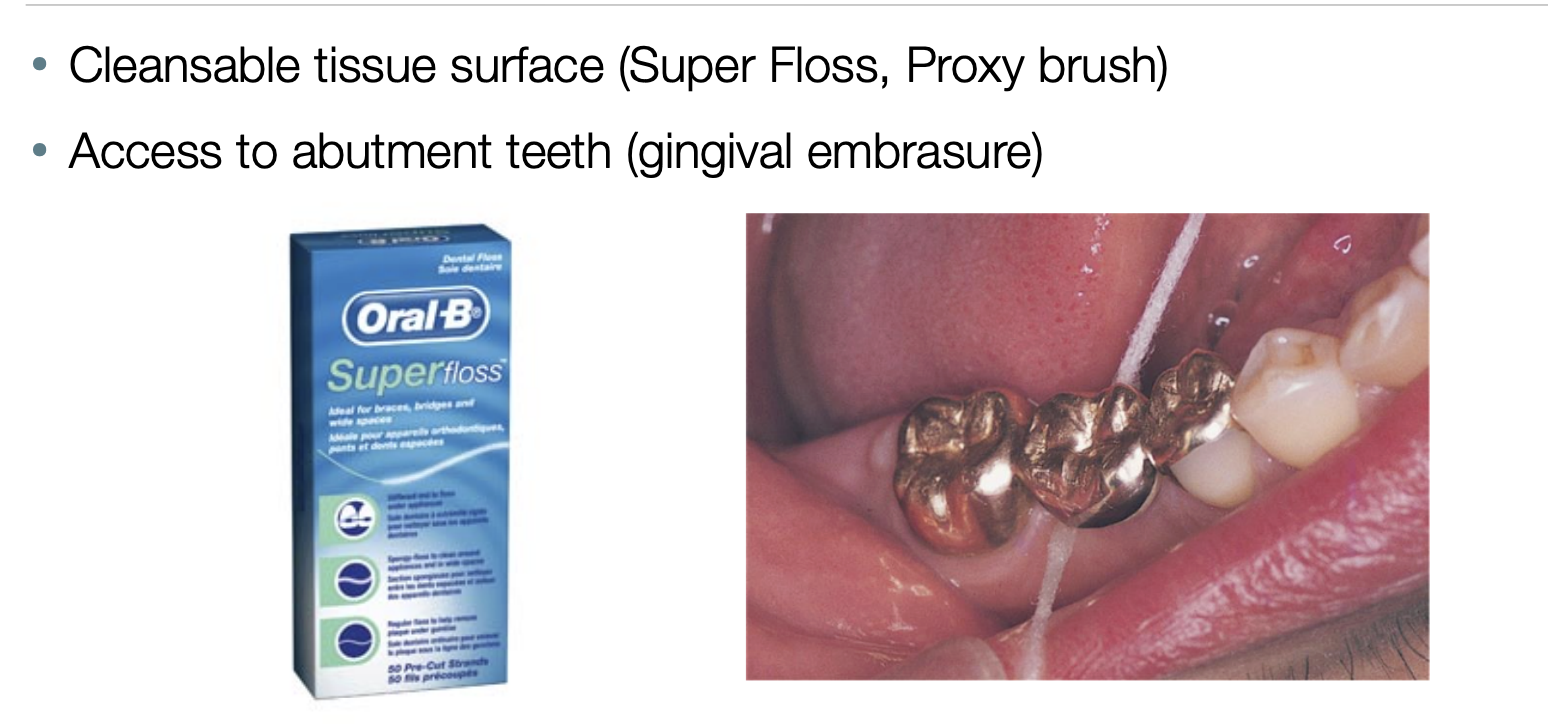
biological considerations fro pontic material
glazed porcelain is most biompatible
glazed porcelain looks smooth, BUT shows many voids and is rougher than either polished gold or acrylic resin under microscope
metal should be highly polished
zirconia is biocompatible, and the soft tissue response is SUPERIOR to other porous materials bc of its low bacterial colonization potential
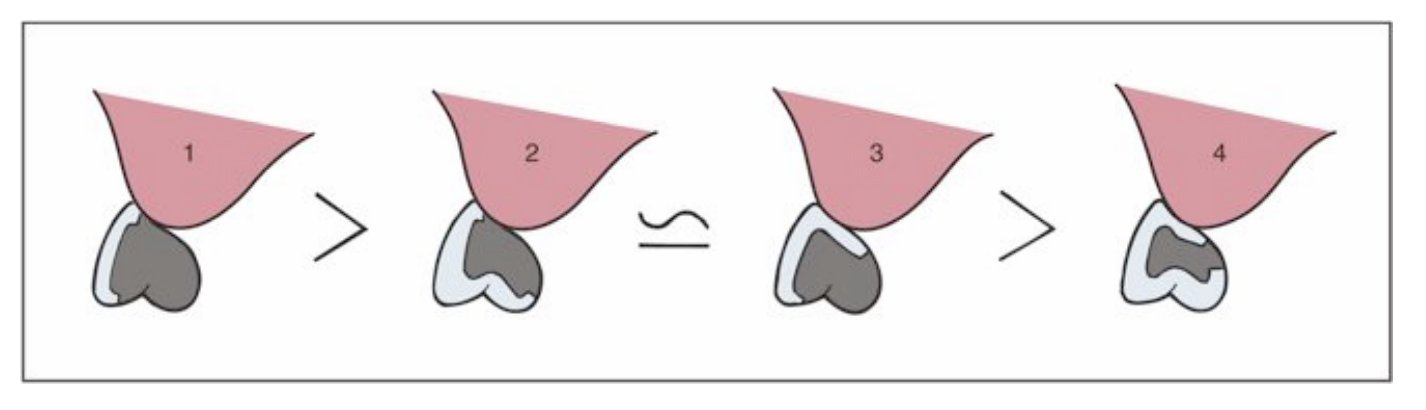
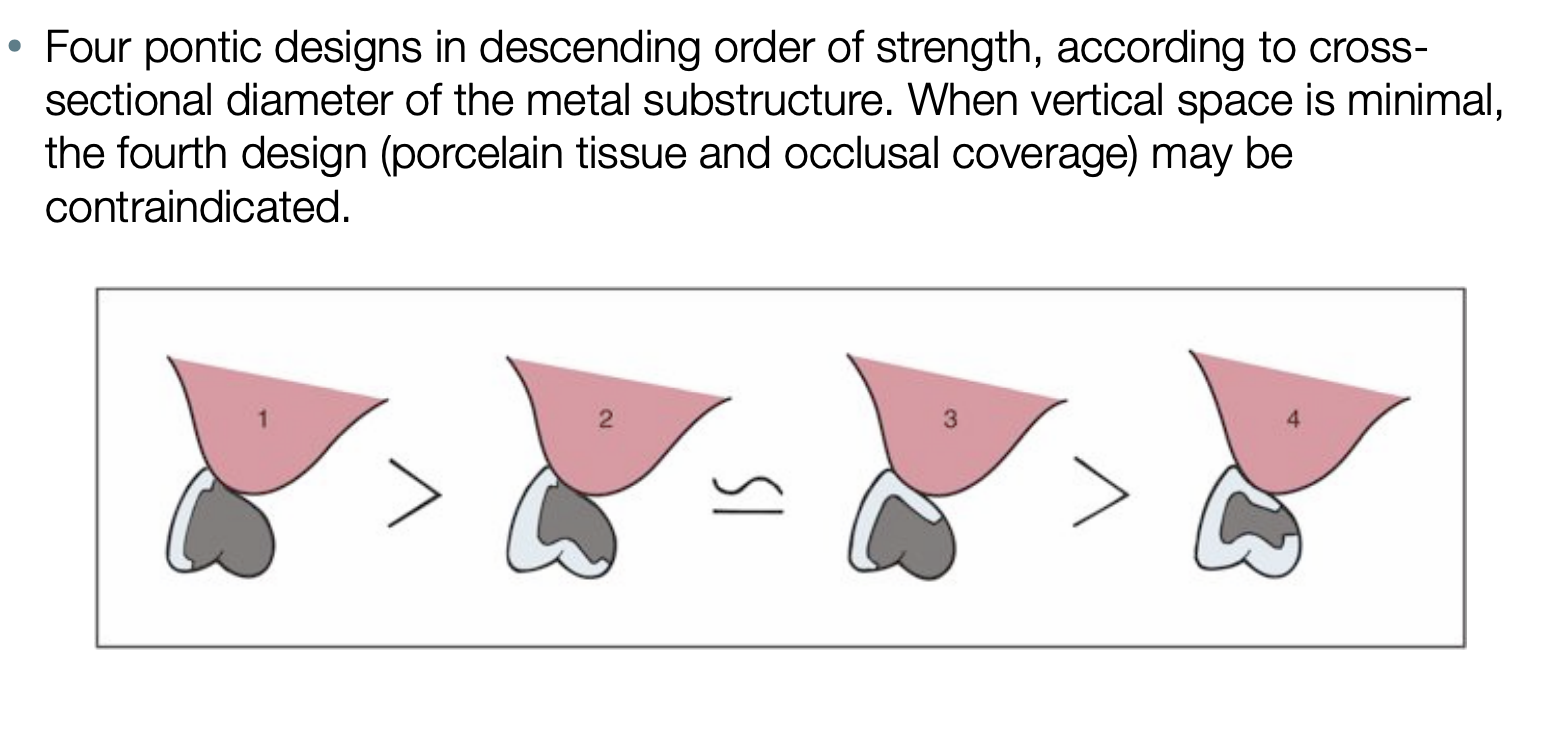
when vertical space is minimal, which design may be contraindicated
4: when looking at the sectional diameter of the metal substructure, it is the weakest
biological considerations for occlusal forces
recommend to reduce occlusal surface vs normal occlusal width
it is recommended to reduce occlusal surface vs normal occlusal width; what is the exception to this situation
where the residual alveolar ridge has collapsed buccolingually → reducing pontic width may be desiered and would thereby lessen the lingual contour and facilitate plaque-control measures
mechanical considerations when thinking of failure of FPD
may be caused by improper choice of materials, poor framework design, poor tooth preparation, or poor occlusion
long-span FPD are particularly susceptible to mechanical problems
__________ pontics have a high fx resistance which make it sutible to be used in long-span fixed restorations w multiple pontics and abutments
zirconia pontics
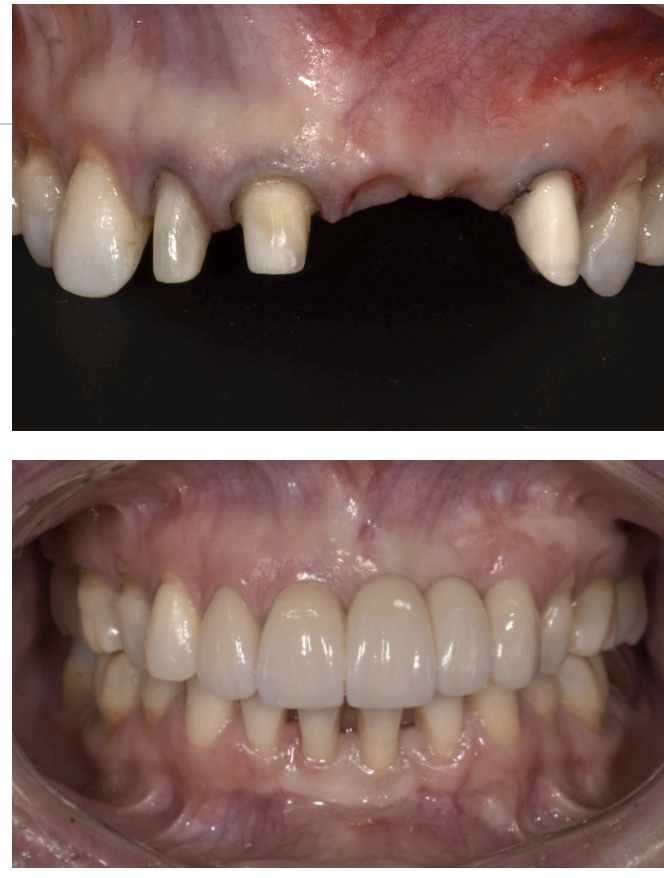
____________ is required for adequate strength for zirconia pontics, what affect does this have on the restoration
large connector size; diminishes the natural appearance and compromises the ability for oral hygiene maintenance
the metal-ceramic pontic framework must provude a uniform veneer of porcelain, approximately ___ mm
1.2 mm