Ancient Egypt
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
characteristics of ancient Egypt
funerary objects dominate, including large scale sculptures, stone architecture, tomb artifacts; all in service of the god-like pharaoh
strict Egyptian stylistic conventions are only applied to gods and pharaohs
subjects of lesser status lack idealization
old kingdom
pharaoh was a god-like king ruling over its people
basic military systems (no professional armies, everyone fights)
basic education systems (illiterate)
basic economy, no middle class (most are poor)
pharaohs buried in pyramids
capital city of Memphis
new kingdom
pharaoh was a leader in both government and military, involved in religious practices
new weapons, very strong military
empire
strong economy and middle class
pharaoh buried in the Valley of Kings
capital city of Thebes

Palette of King Narmer (old kingdom)
slate/sandstone
use of registers (standard of ur)
related to naram sin
narrative of the unification of upper and lower egypt
has white crown of upper Egypt and red crown of lower Egypt
earliest known depiction of Egyptian king
ritual/votive object
hierarchy of scale
Narmer is idealized with lean and strong physique, vines and muscles accentuated
palette used to prepare farmers eye makeup (commemorative)
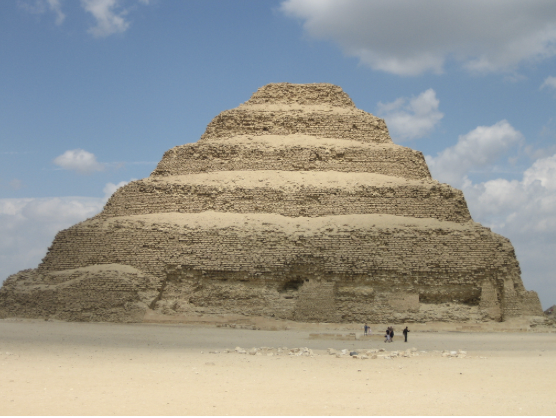

stepped pyramid (old kingdom)
pyramids are used to prevent grave-robbing of pharaohs
moves towards the heavens (like ziggurats, but funerary)
limestone
patron: djoser (loser)
1st architect: Imhotep
Egyptians believed that bodies needed to be mummified and protected for the afterlife
Ka = soul, pyramid was a tomb for the Ka to rest
Egyptians had been entombing people in high rank of mastabas, but Imhotep upgraded these mastabas into pyramids
meant to protect King Djoser’s mummy and symbolize his god-like power
pharaoh buried under the pyramid
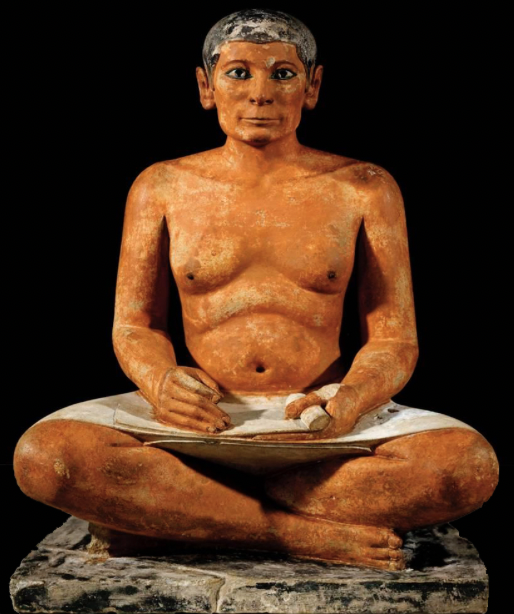

seated scribe (old kingdom)
painted limestone
non royal official of lower rank
shown by the sagging chest and soft bulging belly (not idealized)
shows that formality is relaxed and realism has increased when the human’s subject importance is low
created for a tomb at saqqara as a provision for Ka (funerary)
not a portrait of an actual person, scribes in general
holds a papyrus in his lap, writing instrument now missing
not idealized, low status
used to write down stories of pharaohs life and guide them into the afterlife
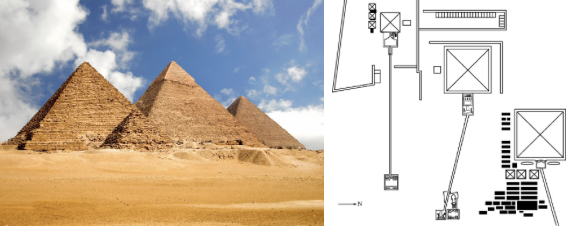
great pyramids of giza (old kingdom)
giant monuments for pharaohs Khafre, Menkaure, and Khufu (largest pyramid)
three smaller pyramids around Khufu’s wives and mastabas for nobles
each pyramid has a mortuary complex adjoined to it
pharaoh is buried in the pyramid rather than under it (stepped pyramid)
openings inside the pyramid to allow souls of the pharaohs to escape
each side of pyramid is oriented towards a point on the compass (like ziggurat, but funerary)
bodies were sent down the Nile River for everyone to see, each pyramid has a formal pathway used for carrying the pharaoh’s body to the pyramid

great sphinx: (old kingdom)
sphinx: animal with a human head (so also a lamassu)
limestone
might be a portrait of Khafre
cats highly respected and admired in Egypt
similar to images of a sun god
appears to be protecting pyramids behind it (apotropaic)
very general carvings, not as exact as some smaller sculptures

King Menkaure and his Queen (old kingdom)
idealized (high status)
found buried outside his period in Giza (not in situ)
women could be goddess Hathor (delivers someone into the afterlife), his mother, or his wife
greywacke
relief from a block of stone, not freestanding
queen has affectionate gesture, presenting her husband to the gods (pose showing marital status)
queen is not nude, wearing some sort of a skirt (reveals her form yet shows modesty)
menkaure has a greater stride than queen, showing willingness and confidence

temple of anun-re and hypostyle hall (new kingdom)
sacred space, also has a common area for fellowship
post and lintel construction
columns with lotus flowers on top
sandstone and mud brick
axial plan: center entrance that can be followed all the way to the most sacred space
hypostyle hall: large room with columns holding up the tall roof
clerestory: bunch of higher up sky lights or windows you can’t look through to let in natural life
columns have sunken relief: image is cut out from the background
after hypostyle hall, there is a sanctuary for upper class and priesthood, then the statue of amun-re is found in the deepest, most sacred part of the sanctuary
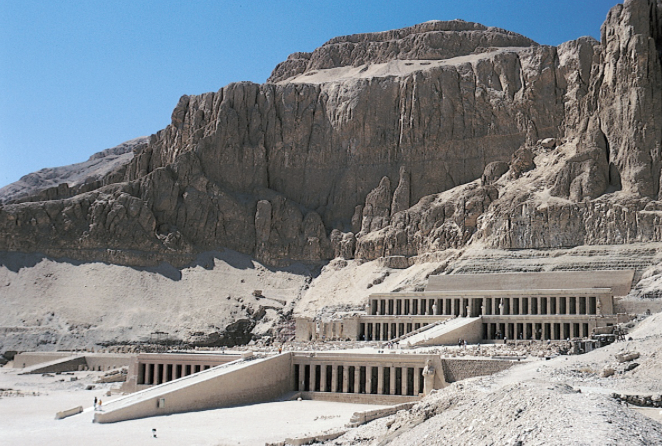

mortuary temple of hatshepsut (new kingdom)
hatshepsut is the first woman to hold power, to rule instead of 7 year old son
not funerary (she wasn’t buried there), but was used to memorialize her (shows major difference between old and new kingdom)
colonnade: columns holding up a terrace (to walk on, not a roof)
sandstone
coordinated with the natural setting of cliffs (blends with environment)
statues of hatshepsut line the ramps up to the most sacred part of the temple
most of statues and references of hatshepsut was destroyed by step-son
post and lintel construction

kneeling statue of hatshepsut with offering jars
feminine attributes minimized, male attributes accented, as males only had authority (broad shoulders, bare chested, false beard, kilt)
red granite
one of 200+ statues of her found at her mortuary temple
statue of her making an offering to Amun-Re (sun god)
a pharaoh only kneels for a god
she will not give up the throne until her death, keeps the title of pharaoh
first known female ruler, statue smashed by step-son trying to erase her from history
amarna period (during new kingdom)
1350-1370 (20 year duration)
revolution in art, culture, and society
pharaoh Amenhotep changes name to Akhenaton
traditional Egyptian religion replaced for monotheistic religion
the one god is Aton, symbolized by a sun disk
great temples emptied/priests abandoned
capital of amarna
Akhenaton claimed to be sole prophet of god/Aton
upon Akhenaten’s death priests reestablished the old Egyptian religion and culture

Akhenaton from the temple of Aton (amarna period, new kingdom)
does not follow idealized norm of Egyptian kings (soft belly, feminine hips, arms and thighs, crown not as rigid)
androgynous features (both male and female)
sandstone
standard frontal pose of royal portraits
most likely an intentional break with artistic style
temple at Amun-Re at Karnak changed to temple of Akhenaton
this sculpture replaced the sculpture of Amun-Re in the temple
toppled and buried after his death, and priesthood restores original religion upon his death
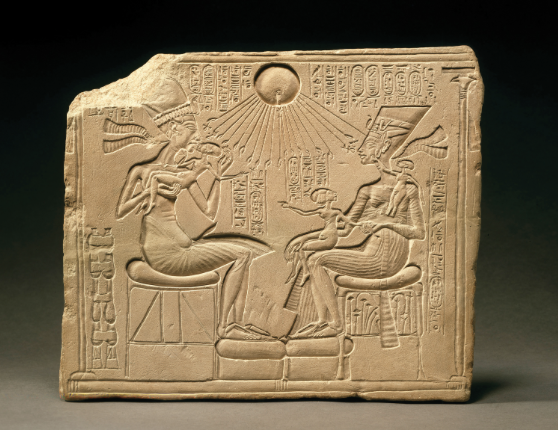

Akhenaton, Nefertiti, and three daughters (amarna period, new kingdom)
aton is sending ankhs (crosses with circles meaning eternal life)
god is giving life to both of them
not idealized bodies, not showing royal authority
body portrayed in similar fashion to sculpture of Akhenaton
curved bodies, prominent bellies
intimacy of family life
informal mood, odd for art portraying royals
limestone
sunken relief
perhaps from a private shrine
maintains Egyptian style of frontal torso with profile heads and lower body
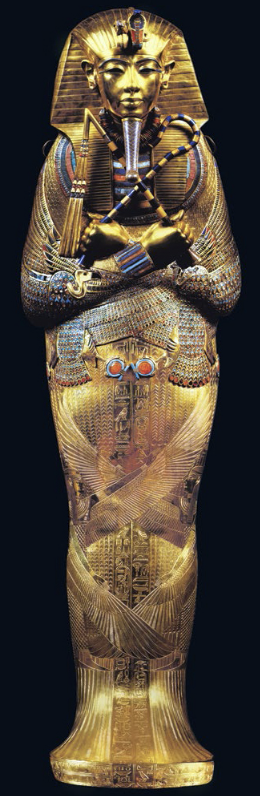
Tutankhamun’s tomb, innermost coffin (new kingdom)
becomes king at 9 after Akhenaton dies, but is dead at 19 and only served for 10 years
priesthood of Egypt was restored under him (he was a young ruler = easy to manipulate
sign of amarna period ending
his is the only tomb that was found without being raided
not a typical tomb, it was small
he died young, tomb was quickly put together as they didn’t expect him to die (not as developed as other tombs)
many broken bones on his mummy, maybe a tragic accident that killed him
made of pure gold and stones
discovered by Howard Carter in 1992, died 3 months later
coffin held mummified body of tut wearing a gold mask
over 140 objects placed with his mummy

temple of Ramses II (new kingdom)
preservation of art
a dam was built on the Nile (would have flooded the temple completely), so the UNESCO moved the whole mountain to preserve it in the 1960s
sandstone
four images of Ramses II at innermost part of the temple (sun shines directly there on two certain days)
most sacred part
similar in function to Hatshepsut’s mortuary temple
all the colossi (giant sculptures) at the front are of Ramses, smaller sculptures are of his family
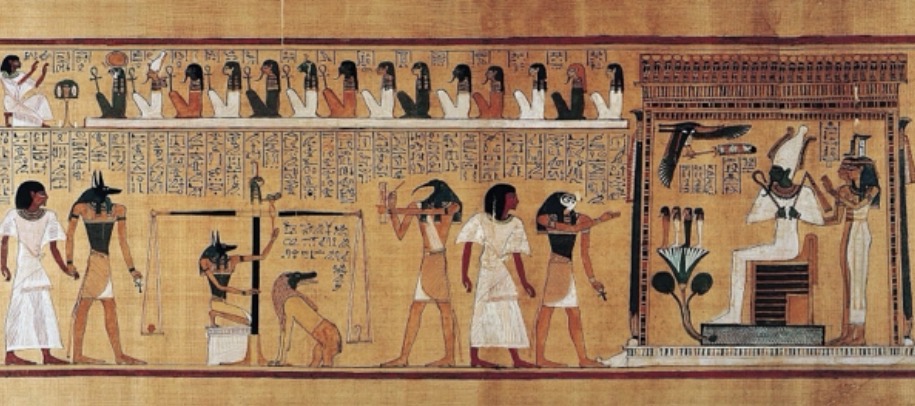

last judgement of Hu-Nefer from his tomb
narrative in function to show beliefs in how to get into the underworld
Osiris, God of the underworld
Hu-Nefer’s heart is put on a scale, but the feather weighs more than the heart, meaning that the heart is not heavy with guilt
in the animal is a mixture of crocodiles, lions, and hippos that kill humans
hu-nefer will be devoured by a hippo
painted papyrus school, book of the dead
compared to standard of ur