Ch. 13: Psychological Disorders
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Schizophrenia
breakdown in thinking and poor emotional response
prevalence = 1.1%
equally split between genders
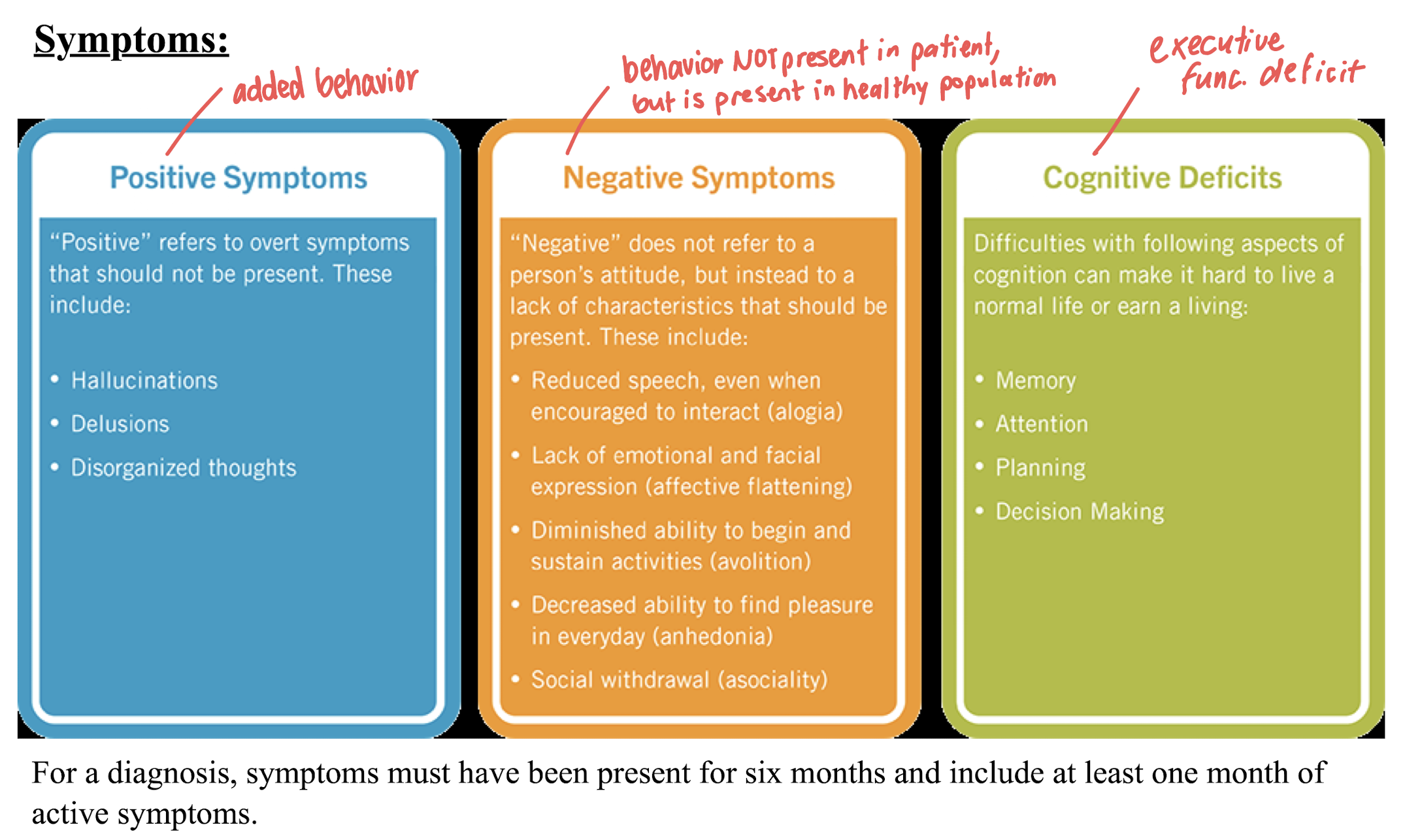
pos, neg, cog symptoms of Schizophrenia
pos = added behavior
neg = behavior not present in patient, but is present in healthy pop.
cog = executive func. deficit
genetic/environmental causes of Schizophrenia
Genetic:
DISC 1: disrupted in Schizophrenia on chromosome 1
Environmental:
place/time of birth
infection of mother during pregnancy
stress from mom during preg.
birth problems
brain structures affected in Schizophrenia
enlarged ventricles = loss of neurons in adjacent areas
disorganization of cells in hippocampus
reduced activity of frontal cortex
loss of gray matter (too much synaptic pruning) in adolescent
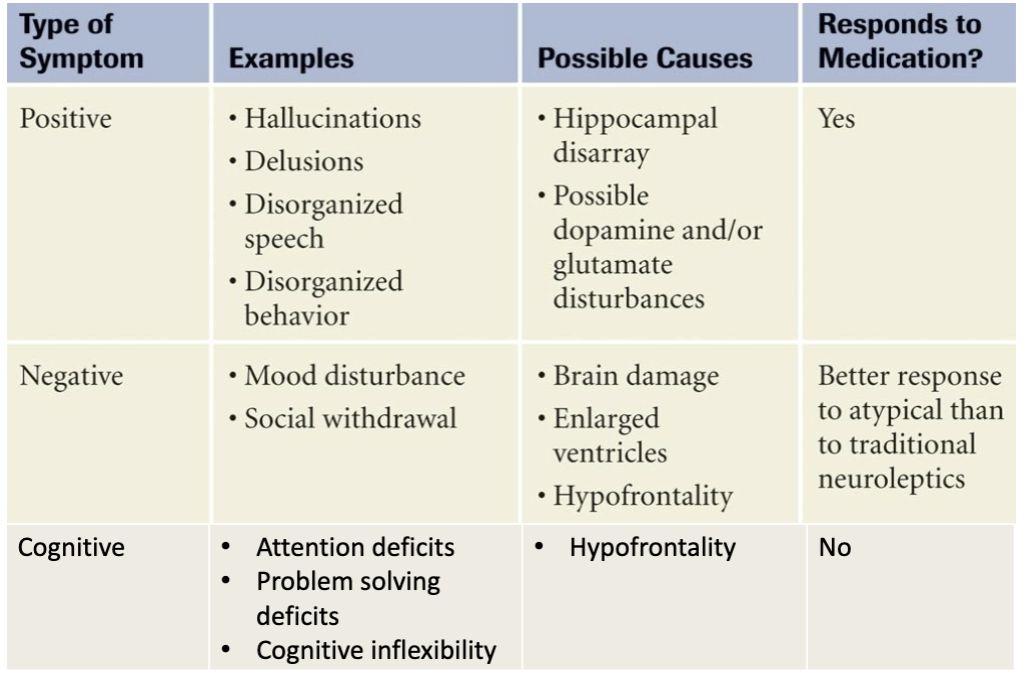
biochemistry of schizophrenia
too much dopamine (positive symptoms)
reduced activity of NMDA (glutamate receptors)
treatment of schizophrenia
typical antipsychotics: dopamine antagonist
binds to dopamine receptor → dopa cannot bind → no effect on post synap.
reduces pos symptoms
atypical antipsychotics: serotonin agonist; ACh receptor agonist
improve negative symptoms
Schizophrenia symptoms table
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) symptoms
insomnia/hypersomnia
restlessness or feeling slowed down
significant weight lost or gain
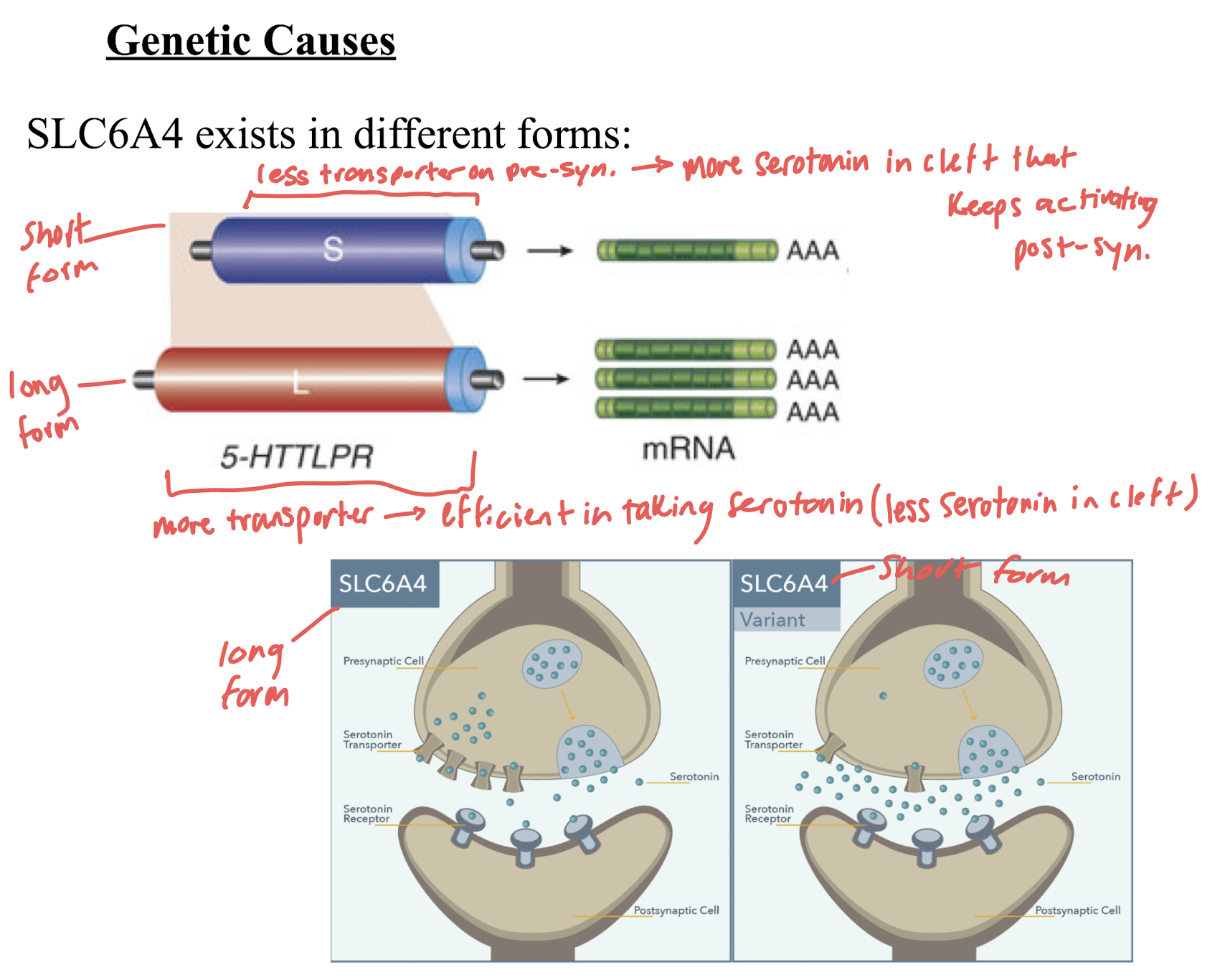
genetic causes of MDD
serotonin transporter allele:
short: less transporter on pre-synap. → more serotonin in cleft → keeps activating post-synap. → incr risk of MDD
long: more transporter → efficient in taking serotonin → less serotonin in cleft
overactivation of amygdala
environmental causes of MDD
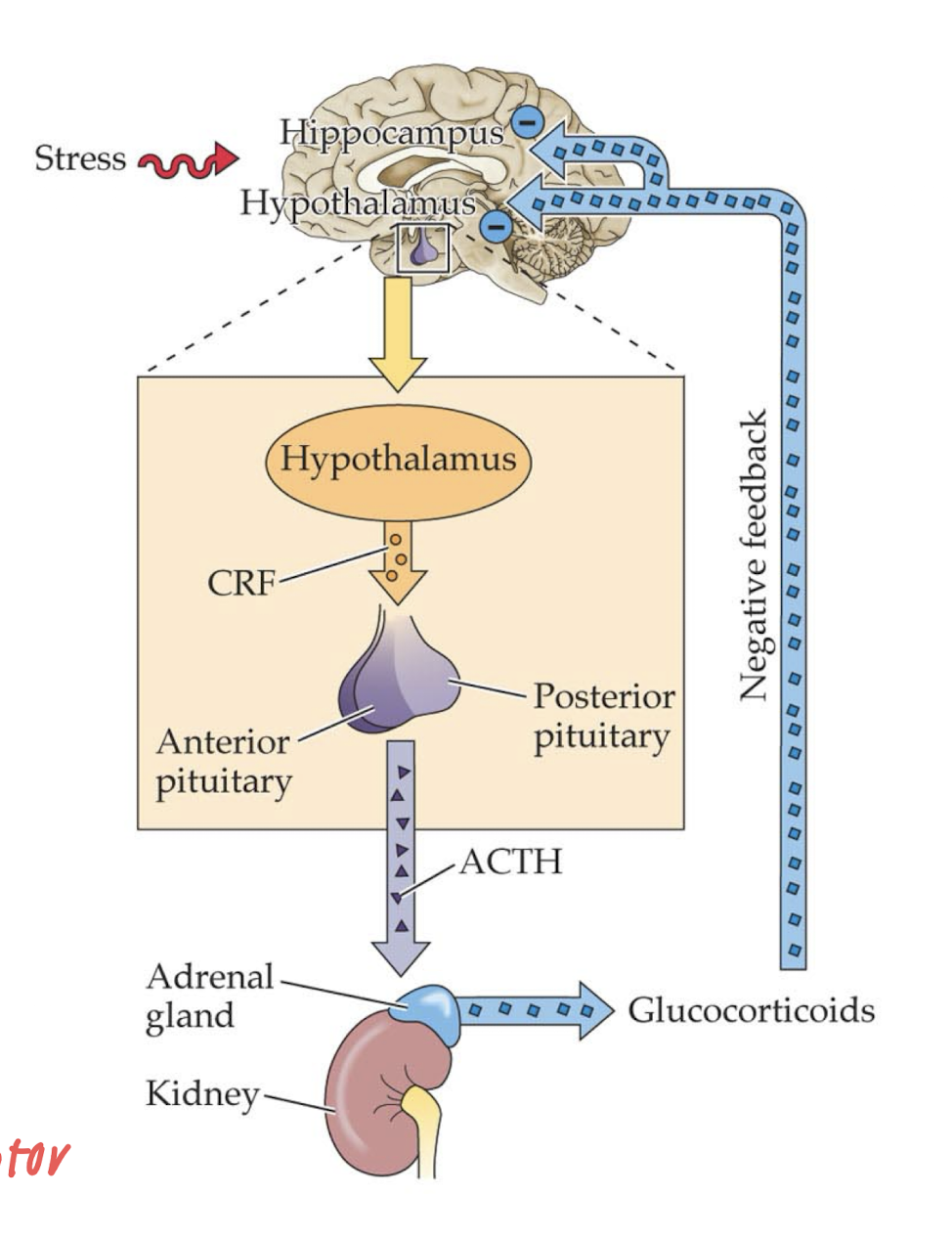
stress
HPA axis: stress → pituitary → adrenal gland → cortisol → negative feedback → deactivate hypothalamus
brain structures affected in MDD
decreased volume of hippocampus (less neurogenesis)
decreased activity of ACC
increased activity of amygdala
abnormal communication between frontal cortex and limbic system
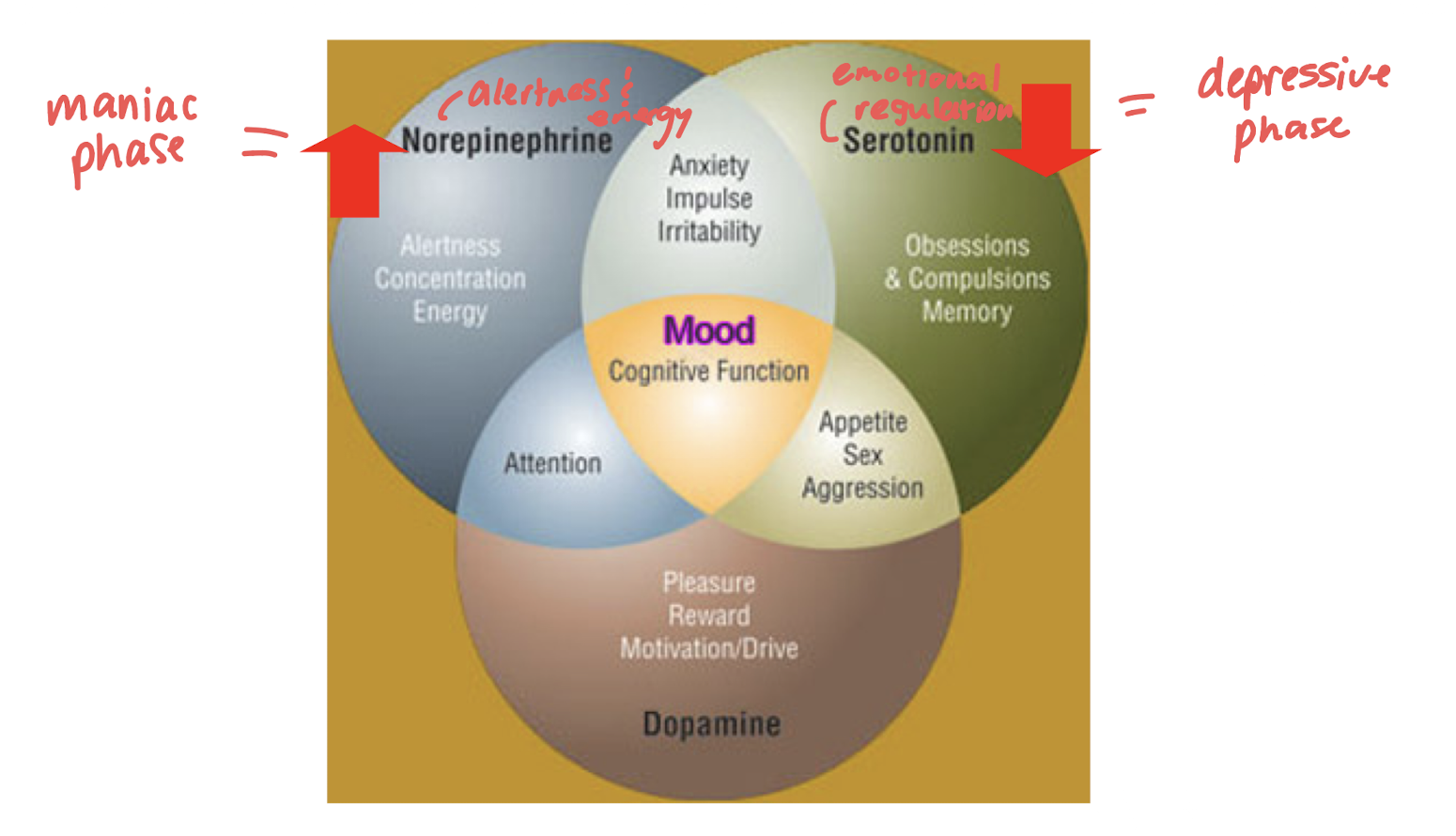
biochemistry of MDD
norepinephrine = alertness and energy
serotonin = anxiety, obsessions, compulsions
dopamine = attention, motivation, pleasure, reward, interest in life
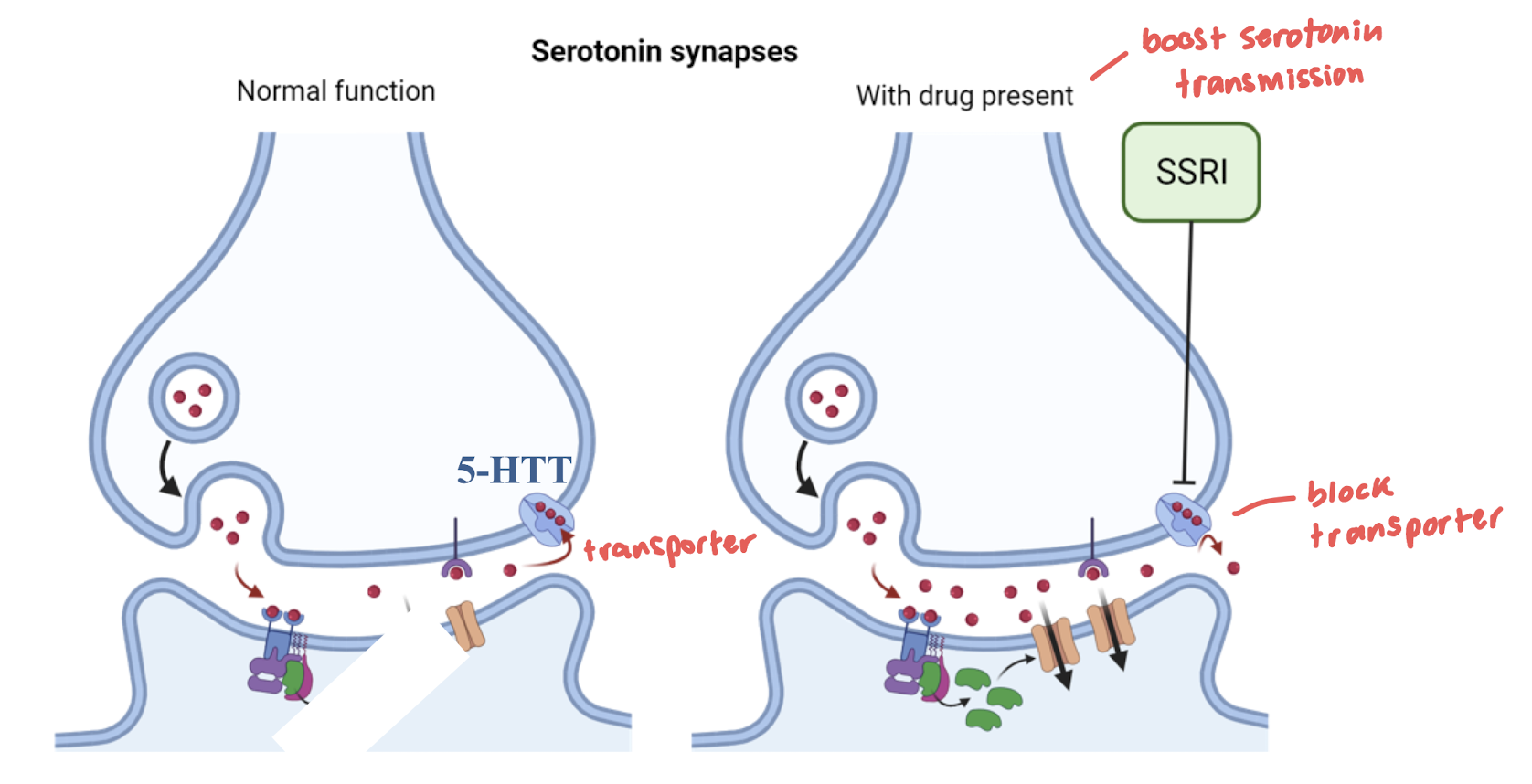
treatment of MDD
SSRI: boost serotonin by blocking transporter
brain stimulation:
symptoms of bipolar disorder (BD)
fluctuations in mood
distinct period of irritable mood
excessive energy
excessive involvement in pleasure seeking activities
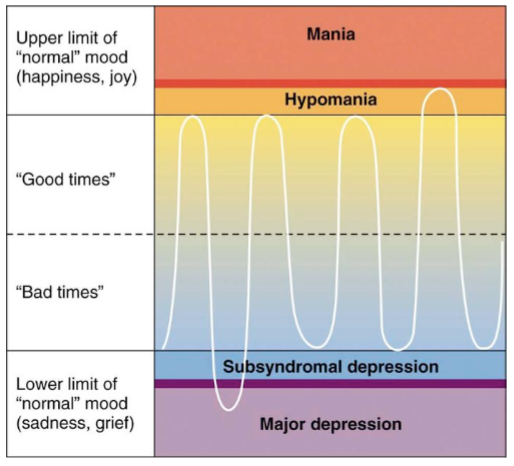
brain structures affected in BD
reduced hippocampal volume
elevated basal ganglia activity (manic phase)
increased amygdala volume and activation
overall increased activity in brain
biochemistry of BD
norepinephrine: incr alertness & energy (manic phase)
serotonin: decreased emotional regulation (depressive phase)
treatment for BD
mood stabilizers
anxiety disorders
excessive and persistent feeling of fear or worry that interferes w/everyday life
OCD
obsession = intrusive thoughts producing uneasiness, fear, or worry
compulsion = repetitive behaviors aimed to reduce associated anxiety
neural network affected in OCD
hyperactive cortico-striatal-thalamo-cortical loop (controls movement execution, habit formation, and reward)
PTSD
recurrent dreams, flashbacks, hyperarousal, and avoidance stimuli associated w/trauma, high lvls of vigilance, and an impairment in daily func.
brain structures affected in PTSD
shrinkage of hippocampus
smaller hypothalamus → less glucocorticoid receptor → less efficient at negative feedback of hippocampus → more stress
over-activation of amygdala
decreased activation on prefrontal cortex
Autism Spectrum Disorder
varying degrees of difficulties in social interaction, nonverbal communication, and repetitive behavior
more prominent in men
causes of ASD
many genetic and environmental factors
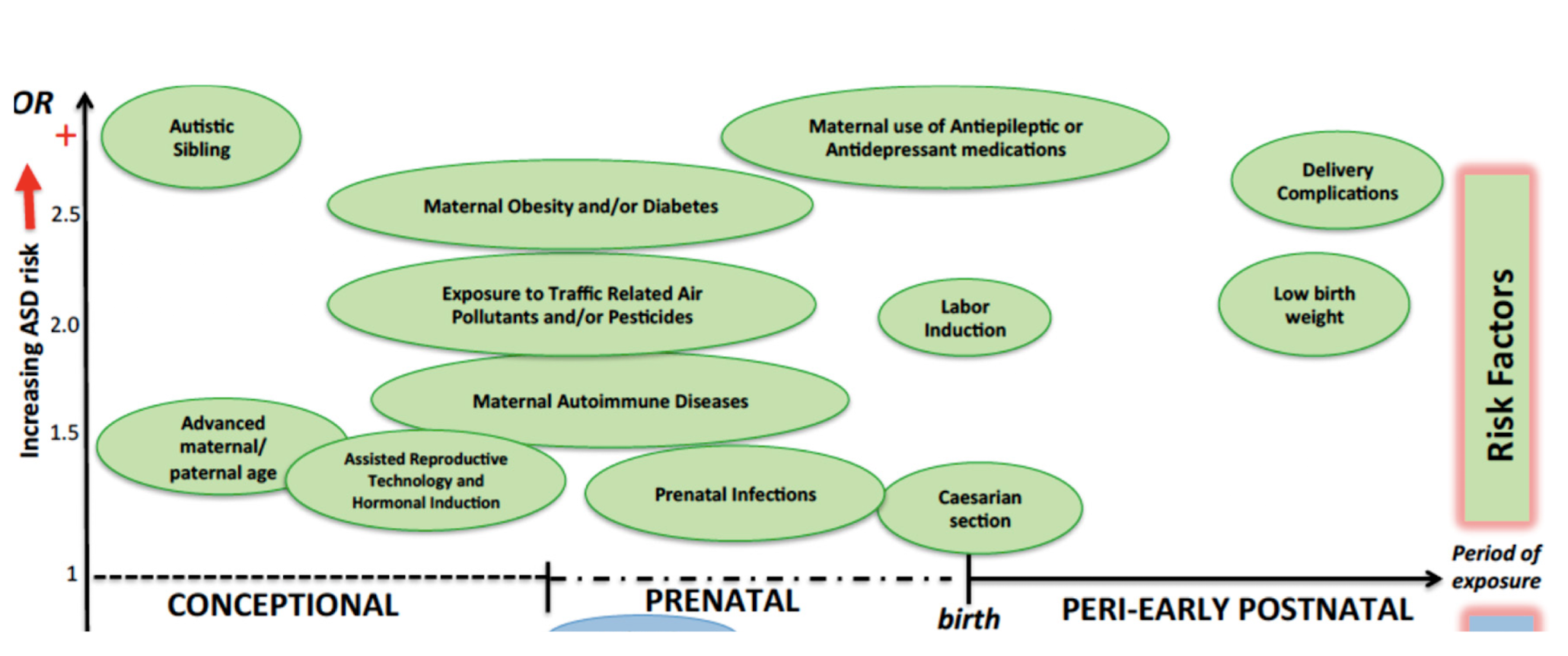
brain regions affected in ASD
excessive brain growth due to lack of synaptic pruning
smaller corpus callosum: comm. btwn hemispheres
amygdala: emotion and social behavior (abnormal func.)
cerebellum: motor activity balance, coordination (repetitive movement)
biochemistry of ASD
glutamate-GABA imbalance
low lvls of serotonin in brain; high lvls in blood
ADHD
significant problems of attention, hyperactivity, and/or acting impulsively that are not appropriate for one’s age
more boys diagnosed than girls
causes of ADHD
high genetic component
environmental factors
brain injurt
low birth weight
exposure to toxic environment
substance-use during pregnancy
premature delivery
brain regions involved with ADHD
reduced activity of prefrontal cortex
smaller basal ganglia = hyperactivity
biochemistry of ADHD
dopamine lvls reduced
treatment of ADHD
dopamine reuptake inhibitor = block reuptake transporter to boost dopamine