Cardiovascular and Respiratory Test
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What are arteries
Always carry blood away from the heart
Usually oxygen rich (except pulmonary artery)
Walls are thick, elastic, and muscular
Don’t have valves
What are veins
always carry blood to the heart
Usually oxygen poor (except pulmonary vein)
Walls are thin, not elastic, with little muscle
Have valves to prevent backflow
What are capillaries
Connect arterioles and venules
Walls are only one cell thick
Exchange of materials between blood and body cells occurs through it
Don’t have valves
What is the order of blood flow through the vessels? (Start at heart)
Heart - artery - arteriole - capillary - venule - vein
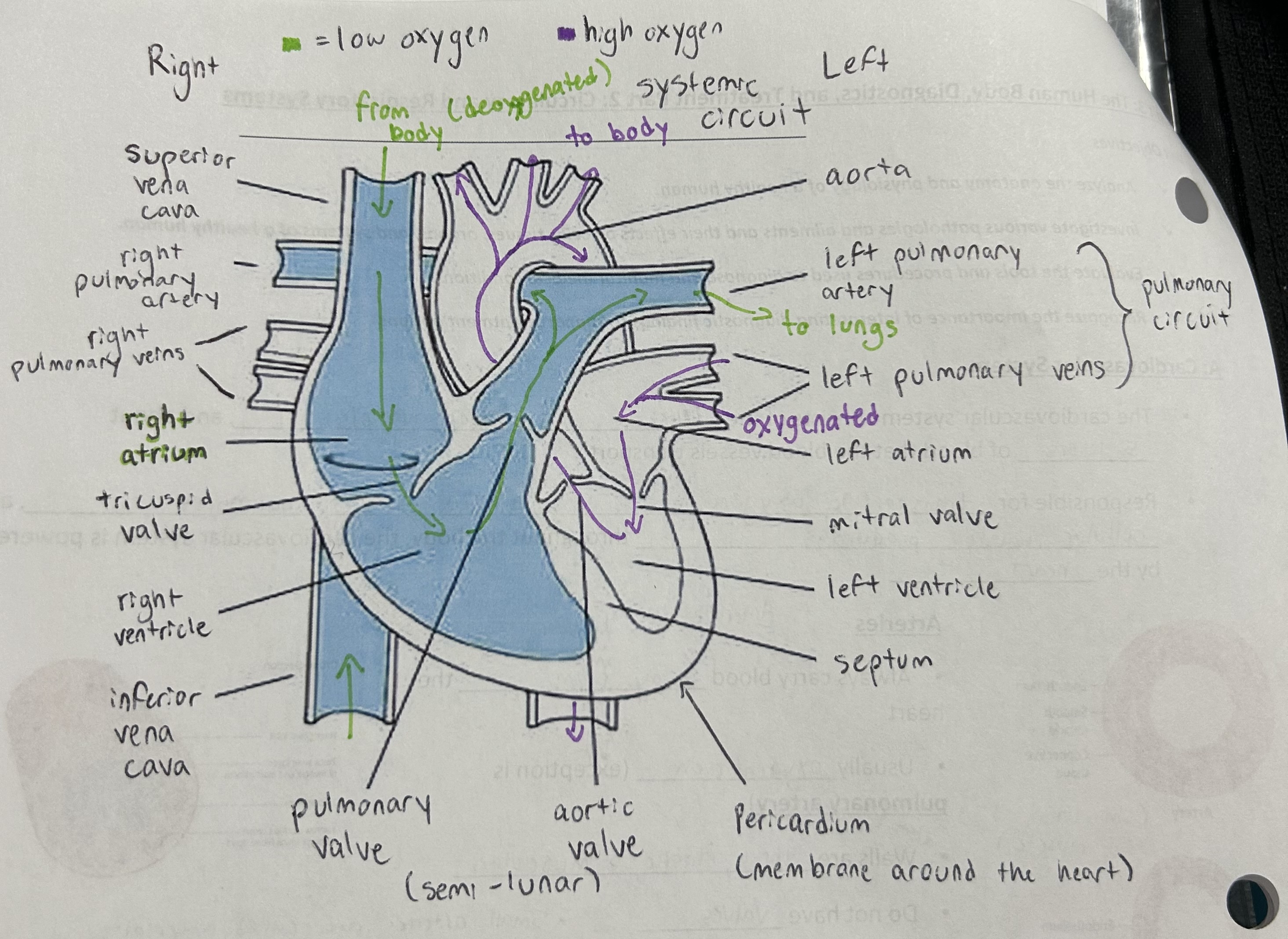
Heart diagram and blood flow
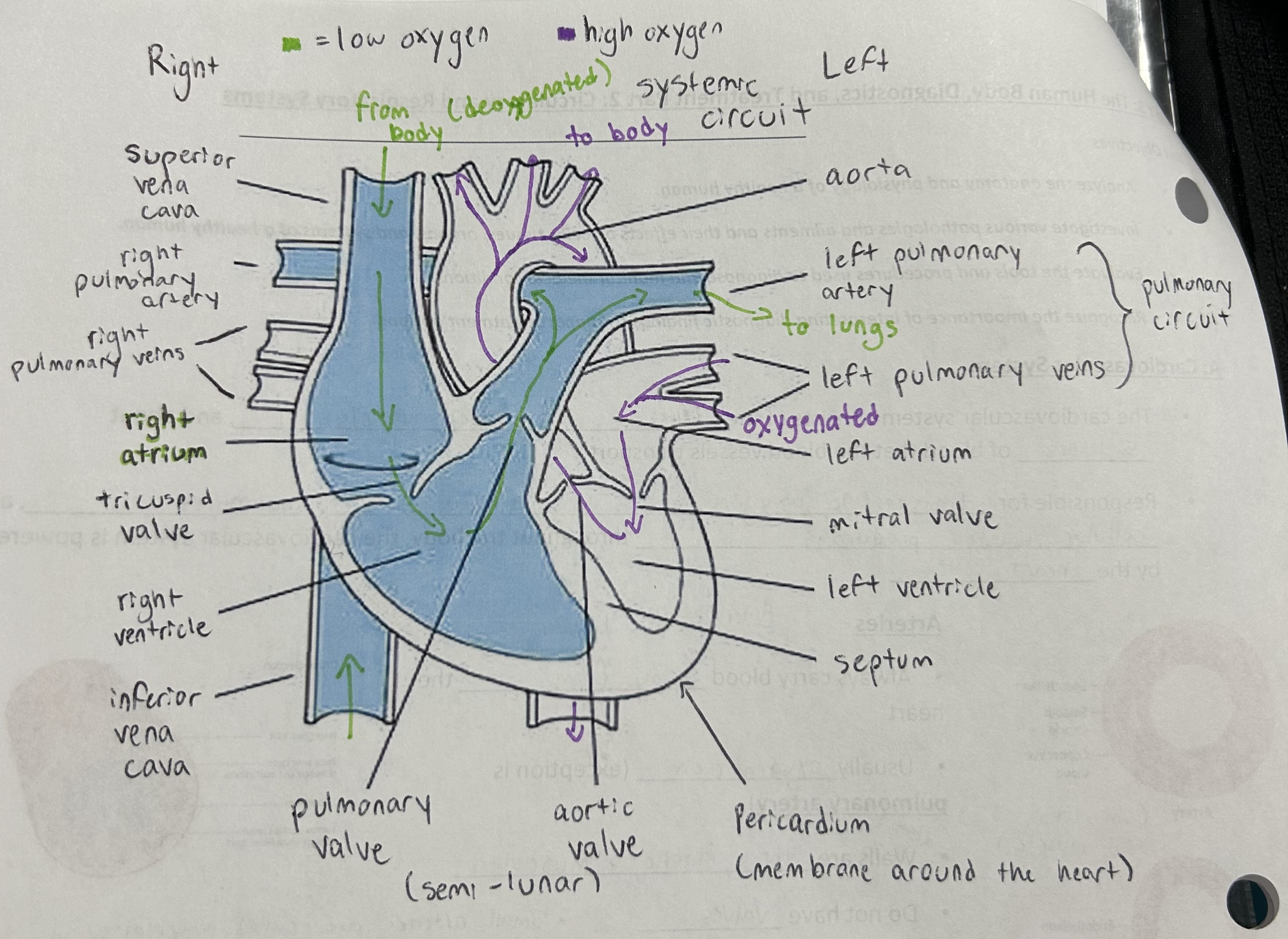
What are the lub/ dub sounds that we hear
Lub/ S1
Blood is going out to the arteries. Ventricles are contracting and pressure is high. Tricuspid and mitral valves snap shut
Dub/ S2
Blood is refilling the relaxed ventricles. Pressure is low. Pulmonary and aortic valve snap shut
Systemic and pulmonary circulation
Superior + inferior vena cava - right atrium / tricuspid valve / right ventricle / pulmonary valve / pulmonary artery - lungs - left pulmonary veins - left atrium / mitral valve / left ventricle / aortic valve / aorta - body
What is the average heartbeat?
72 bpm at rest/ 100,000 beats per day
What is systole?
The contraction of ventricles were pressure on the arteries is high
What is diastole?
Relaxation of the ventricles where the pressure on arteries is low
What is a PET scan? How does it work? Advantages? Disadvantages?
A PET scan is an imaging technique used to look at the heart.
A radioactive tracer is injected and pairs of gamma rays are detected when the tracer accumulates and active cells.
It can detect diseases at early stages, assess a treatments effectiveness, and pinpoint hidden issues
Can cause radiation exposure to fetus/infants, and can be potentially inaccurate for people with diabetes
What is an echocardiogram? How does it work? Advantages? Disadvantages?
An ultrasound that checks the structure and function of the heart.
It uses a transduce to send high frequency, sound waves into the chest, which bounced off of the heart structures and return as echoes; a computer, then translates these returning sound waves into real time, moving pictures on a screen, showing the heart shape, size, and function
Provide provides a detailed, non-invasive look at the heart structure and function
Can cause mild chest discomfort or mild reactions to the contrast dye
What is an aortic dissection?
A tear in the aorta’s walls or in the aortic valve
What is coronary heart disease?
Plaque buildup in the arteries, causing restricted blood, oxygen, and nutrition flow to the heart
Components of blood
Red blood cells
The most numerous of the blood cells and is produced in the bone marrow, particularly in the ribs and vertebrae. It has no nucleus or mitochondria and its life expectancy is 24 months. Contains hemoglobin, which is responsible for the transport of oxygen.
White blood cells
Make up a very small percentage of the total number of cells in the bloodstream, but have important functions in the bodies immune system
Platelets
Responsible for the clotting of blood and the formation of scabs. Do not contain a nucleus and only survive in the body for up to a week.
Plasma
The liquid portion of the blood that makes up about 55% of the bloods volume. It’s a mixture of water, proteins, and dissolve substances. It is the transportation medium for those substances.
What are antigens and antibodies?
Antigen is a type of protein found on the surface of red blood cells. The two major kinds of antigens are A and B.
Antibodies caused the body to form defensive proteins for protection if foreign proteins (antigens) appear. The two major kinds of blood antibodies are anti-A and anti-B.
What is agglutination?
It is the clumping together caused when an anti antibody acts on an antigen ex. Antigen A + anti-A = clumping.
What are the different blood groups?
A(+&-), B (+&-), AB(+&-), O(+&-)
What blood type can donate to who?
A - A & AB
B - B & AB
AB - AB
O- all ( universal donor)
What blood type can receive from who?
A - A & O
B - B & O
AB - all ( universal recipient)
O - O
What is RH factor and incompatibility?
Factor-
(+) having the protein
(-) don’t have the protein
Incompatibility
Occurs if an Rh negative mother is carrying an Rh positive embryo
The placenta may transfer the embryos’s blood to the mother, causing her blood to form antibodies
how does the body obtain oxygen, and why is it important?
Through the lungs and the blood received through the lungs
What is cellular respiration?
The metabolization of carbs, fats, and proteins to make ATP
Respiratory system diagram
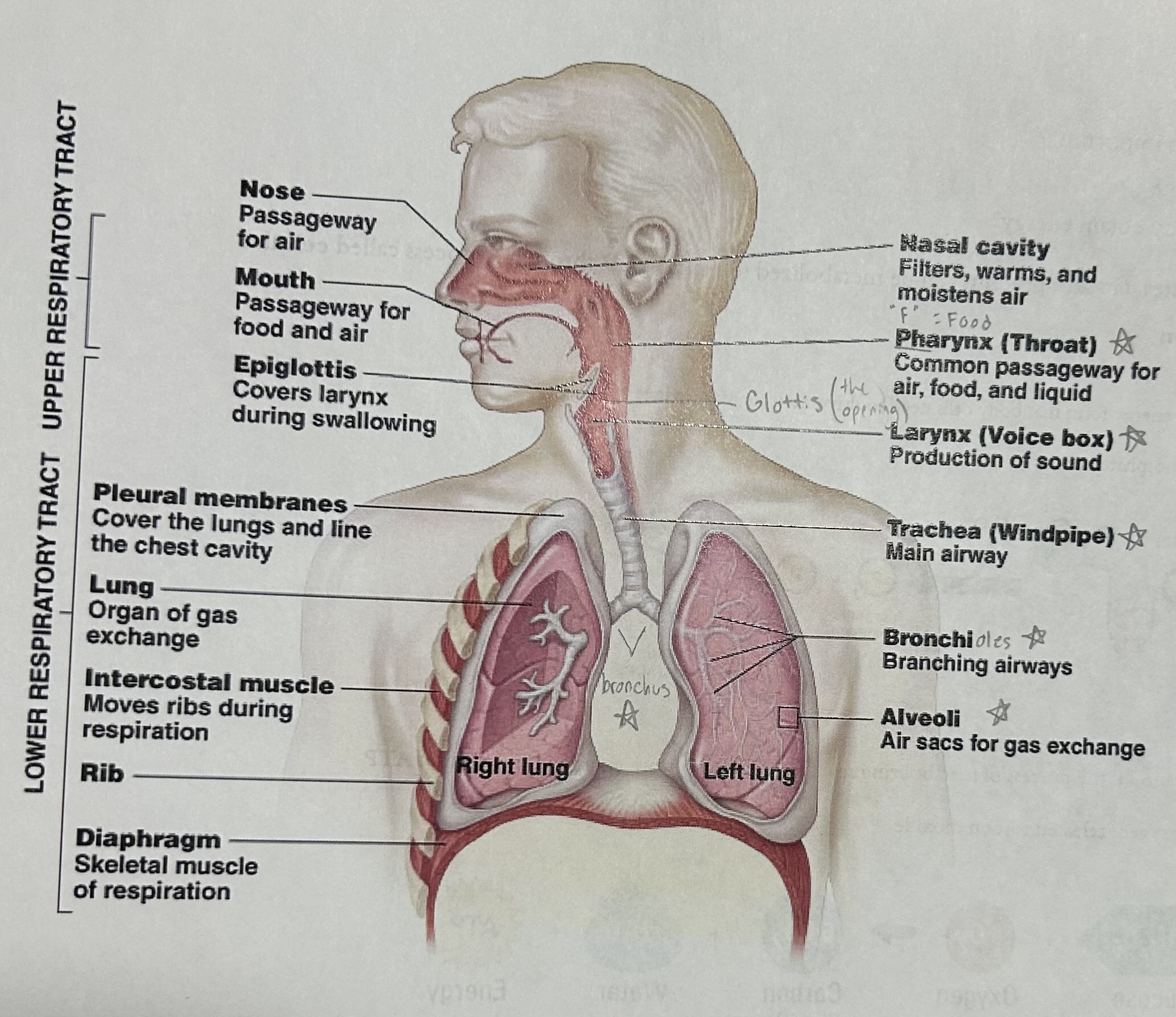
Nose and mouth function
Passage ways for air ( also food for mouth)
Pharynx (throat) function
The common passageway for air, food, and liquid
Larynx (voice box) function
The production of sound (voice)
Glottis function
The opening that covers the larynx during swallowing
Trachea (windpipe) function
The main airway (transports air to and from lungs)
Bronchus function
Two passage ways the branch into the lungs
bronchi / bronchioles function
The branching airways in the lungs
Alveoli functions
The air sacs for gas exchange
Diaphragm function
The skeletal muscle of respiration; it moves down as the ribs move up and out, enlarging the chest cavity so that the air outside your body is drawn inward
Lungs function
transports air to alveoli for gas exchange
Upper respiratory tract functions
Passageway for respiration
Receptors for smell
Filters incoming air to filter larger foreign materials
Moistens and warms incoming air
Resonating chambers for voice
Lower respiratory tract functions
Larynx: assists in sound production (voice)
Trachea: transports air to and from lungs
Bronchi: branch into lungs
Lungs: transports air to alveoli for gas exchange
Respiratory cycle
⭐️As the diaphragm moves down and the ribs move up and out, the chest cavity enlarges. The lungs blood pressure drops, drawing air in
Air passes through the nostrils, naval cavities, and into the pharynx
The epiglottis/ glottis protects the opening of the lungs. It opens to let air in but closes when food passes towards the esophagus
The trachea is the air passage that extends through the neck in front of the esophagus
Divides into two bronchus
Each bronchus leads to a lung where they branch off and end up as microscopic divisions
Respiratory gases diffuse into and out of the blood through the thin membranes of the tiny blood vessels and alveoli
Oxygen passes from the air sacs into the blood and carbon dioxide passes from the blood into the air sacs
Spirometer functions in measuring lung capacity ( tidal volume, vital capacity, inspiratory/expiratory reserve volume, residual volume)
It measures the amount of air inhaled and exhaled; checks respiratory and cardiovascular health
Tidal: the volume air inhaled in exhale in a single breath (normal breathing)
Vital: the maximum volume that can be exhaled after maximal inhalation (big breath in and release all air)
Inspiratory: the amount of air that can be inhaled beyond the tidal volume (breathe in all the way after breathing in normally)
Expiratory: the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled beyond the tidal volume (breathing out all the way after breathing out normally)