Plant Organisation - The Leaf
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
What is a leaf?
The leaf is a plant organ adapted specifically for photosynthesis
2
New cards
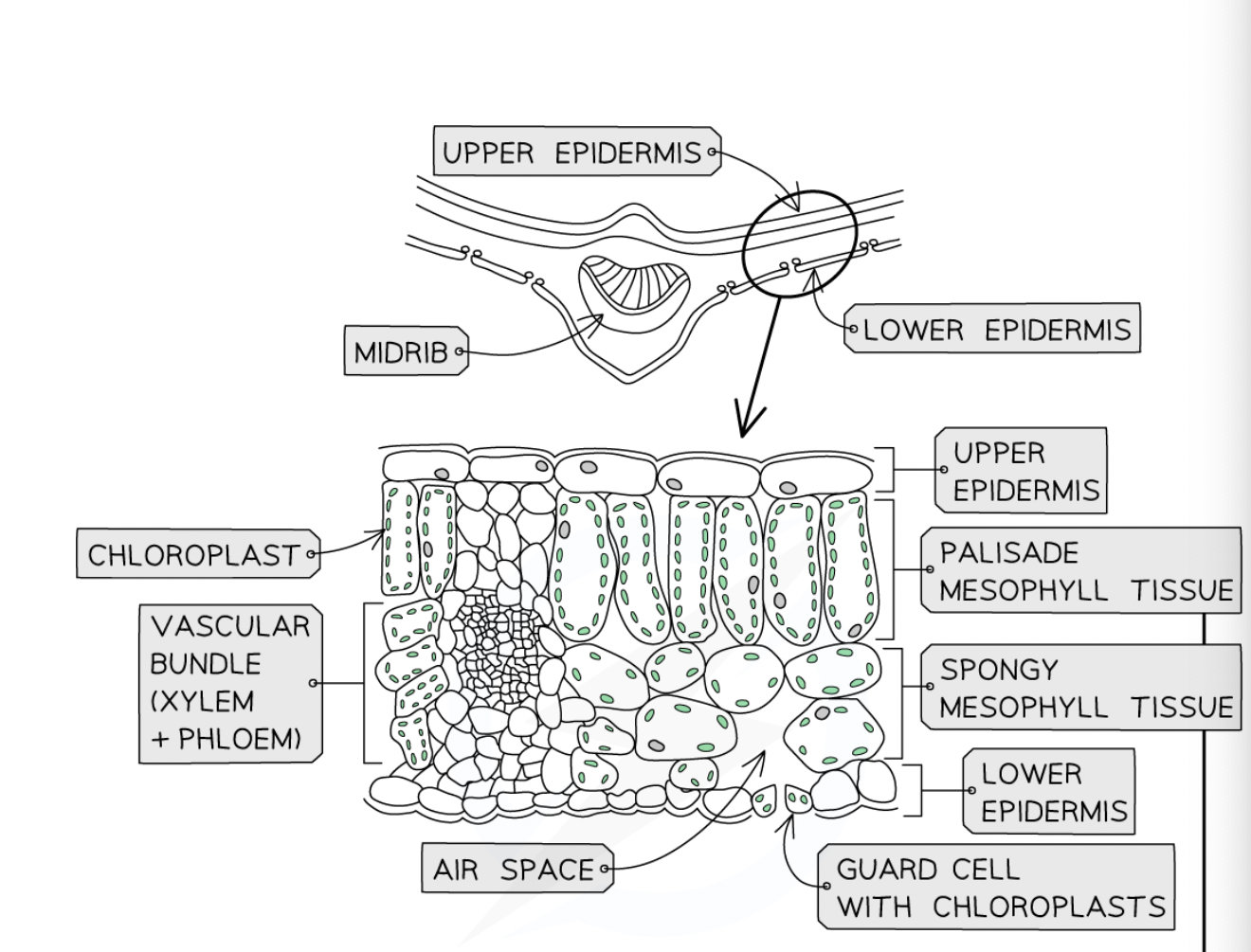
What is on top of the leaf structure?
waxy cuticle
3
New cards
What is below the top waxy cuticle?
upper epidermis
4
New cards
What is below the upper epidermis?
palisade mesophyll layer
5
New cards
What is below the palisade mesophyll?
spongy mesophyll
6
New cards
What is below the spongy mesophyll?
lower epidermis
7
New cards
What is part of the lower epidermis layer?
guard cells
8
New cards
What is above the guard cells?
air space
9
New cards
What runs through the side of the spongy mesophyll layer?
vascular bundle (xylem and phloem)
10
New cards
structure of a leaf
here
11
New cards
What are some adaptions of the leaf? (10)
Large surface area, thin, chlorophyll, network of veins, stomata, epidermis is thin and transparent, waxy cuticle, palisade layer at top of leaf, air spaces, vascular bundle
12
New cards
purpose of large surface area as an adaption?
Increases surface area for the diffusion of carbon dioxide and absorption of light for photosynthesis
13
New cards
purpose of thin as an adaption?
Allows carbon dioxide to diffuse to palisade mesophyll cells quickly
14
New cards
purpose of chlorophyll as an adaption?
Absorbs light energy so that photosynthesis can take place
15
New cards
purpose of vein network as an adaption?
Allows the transport of water to the cells of the leaf and carbohydrates from the leaf for photosynthesis (water for photosynthesis, carbohydrates as a product of photosynthesis)
16
New cards
purpose of the stomata as an adaption?
Allows carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf and oxygen to diffuse out
17
New cards
purpose of thin and transparent epidermis as an adaption?
Allows more light to reach the palisade cells
18
New cards
purpose of waxy cuticle as adaption?
to protect the leaf without blocking sunlight
19
New cards
purpose of palisade layer at top as an adaption?
Maximises the absorption of light as it will hit chloroplasts in the cells directly
20
New cards
purpose of air spaces in the spongy layer as an adaption?
Air spaces allow carbon dioxide to diffuse through the leaf, increasing the surface area
21
New cards
purpose of vascular bundle as an adaption?
Thick cell walls of the tissue in the bundles help to support the stem and leaf
22
New cards
what is the purpose of the structure of the leaf?
The structure of a leaf maximises the diffusion of carbon dioxide into the mesophyll cells for photosynthesis
23
New cards
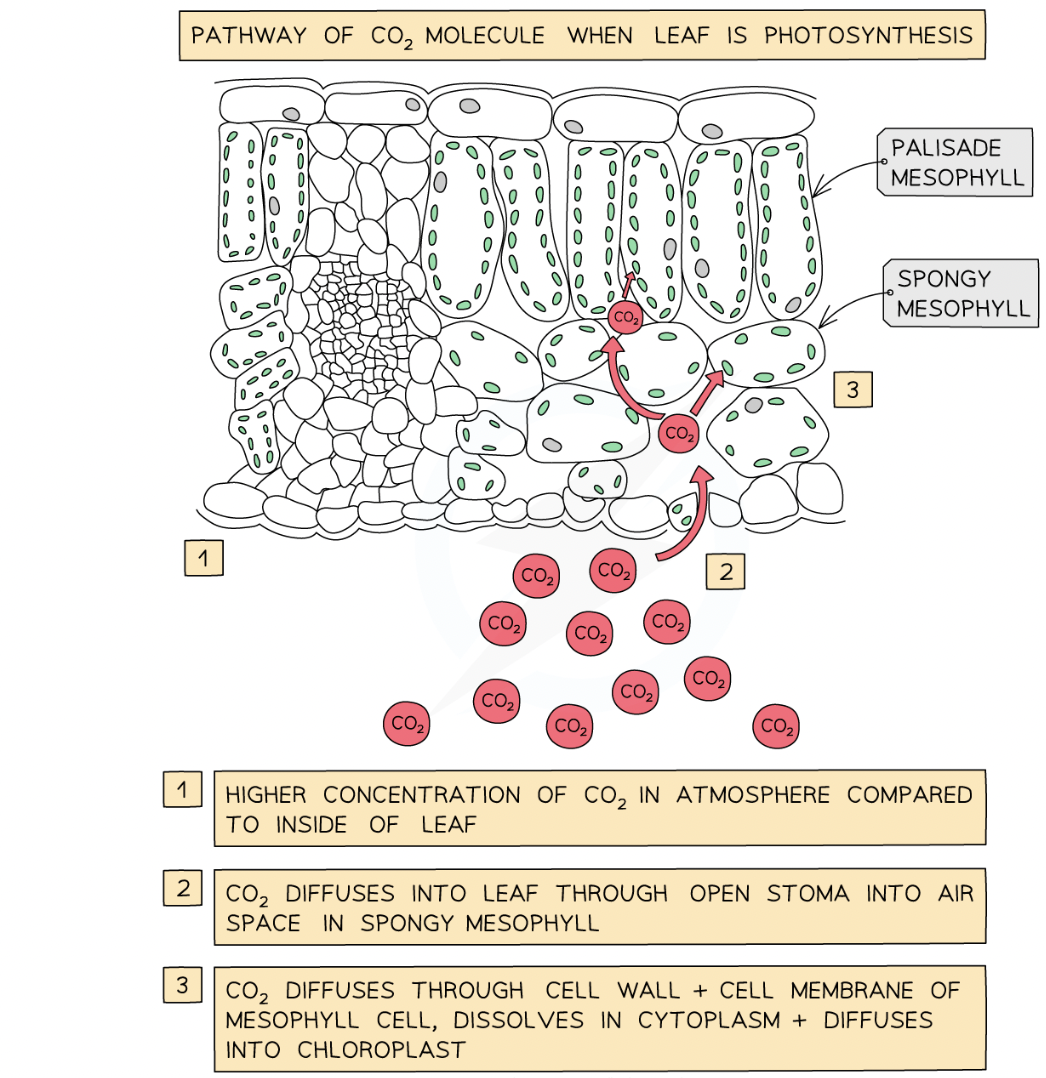
What is the pathway of carbon dioxide in the leaf?
1. in the atmosphere: higher concentration of carbon dioxide compared to inside the leaf
2. co2 diffuses into leaf through open stoma into air space in spongy mesophyll
3. co2 diffuses through cell wall + cell membrane of mesophyll cell, dissolves in the cytoplasm + diffuses into chloroplast
24
New cards
What does the structure of the leaf enable?
The structure of a leaf enables air to circulate within it to maximise the diffusion of carbon dioxide to the chloroplasts for photosynthesis