Introduction to the heart and principles of hemodynamics
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what is cardiac output?
total volume of blood flow through the circulation
how do we calculate cardiac output (CO)?
CO = heart rate x stroke volume
For a resting heart rate ~72 beats per min and stroke volume* ~ 70 ml/beat, what is the cardiac output (CO)?
CO = 72 beats/min x 70 ml/beat = 5040 ml/min
what is stroke volume?
amount of blood ejected from either the right or left ventricle in one beat
maximum heart rate is approximately …?
220 - your age
for a 20-year-old person, maximum HR would be?
about 200 beats/minute
(220 - 20 years old = 200)
what is the effect of exercise on the heart?
intense exercise can cause stroke volume to almost double
Thus, for example, a moderately exercising individual could have a cardiac output = 150 beats/min x 100 ml/beat = 15,000 ml/min
When you exercise, it automatically adjusts its output to provide adequate blood flow to meet the body’s needs
With endurance training, the heart can increase its size and force of contraction
Your heart at rest pumps approximately your entire blood volume every (time) of your life
minute
what is the heart enclosed in?
pericardium (fibrous sac that is interspersed with fat)
the heart is hollow muscular organ weighing approximately ___ gm and is about the size of …?
300
one’s fist
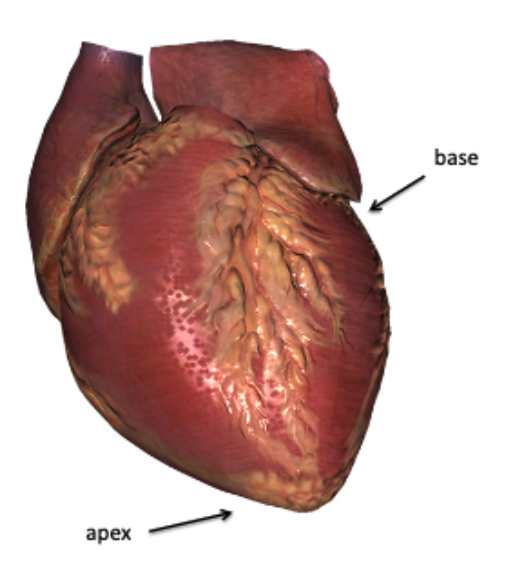
The heart is shaped like a ________ and rests on the diaphragm between the two lungs. The apex of the cone points to the right/left.
blunt cone
left (about 2/3 of the entire organ is to the left of the midline)
how is the right atrium, ventricle, and chambers positioned? left side?
The right atrium and ventricle, chambers that receive blood and then pump it, respectively are facing you.
The left atrium and ventricle are rotated so that they face the left side of the body
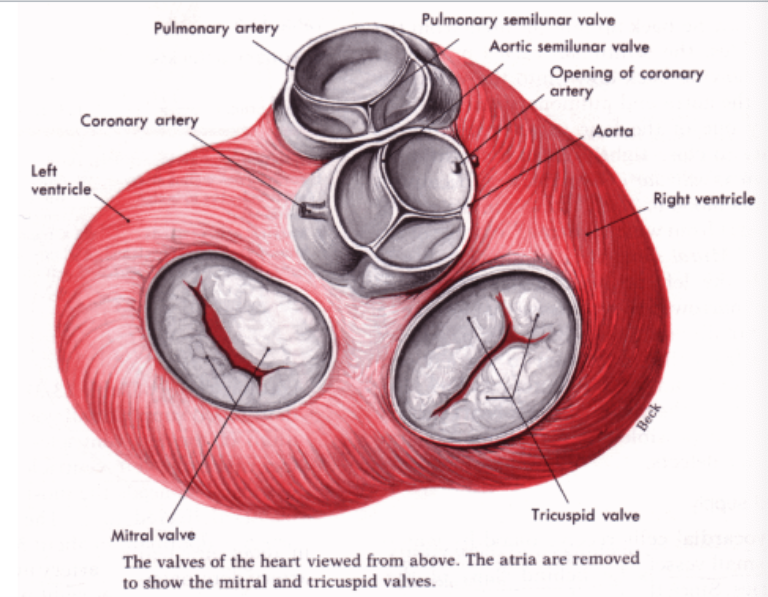
the aorta carries blood to…? what about the pulmonary trunk?
aorta → whole body (systemic)
pulmonary trunk → lungs
The right side pumps blood through the…? , the left pumps blood through the …?
lungs (pulmonary circulation)
other tissues of the body (systemic circulation)
the heart is actually 2 pumps arranged side-by-side. each pump has 2 chambers. what are they?
atrium- receives blood from veins and delivers it to the ventricles
ventricle- the thick-walled pumping chamber
the right and left pumps of the heart are separated by …?
the interatrial and interventricular septa
The two sides are arranged in series so that the output of one side returns to the other. Thus…?
both sides must have the same output
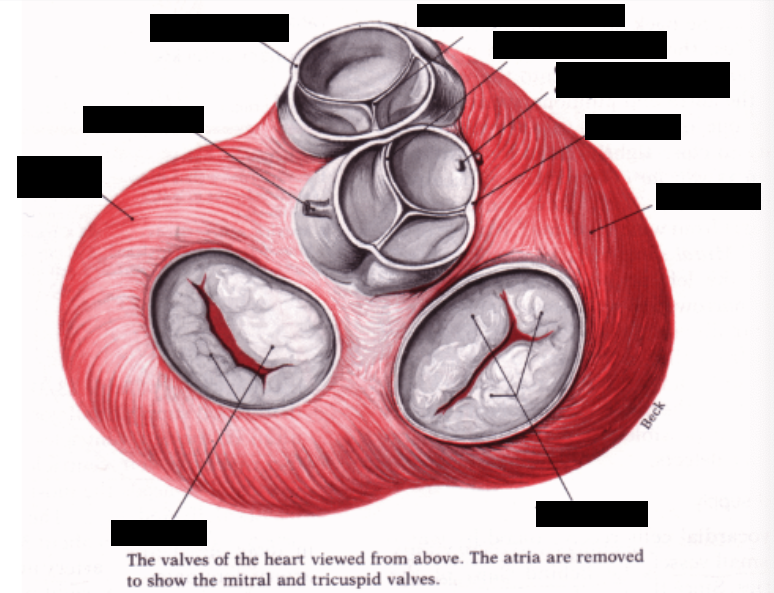
what is the function of valves?
keep blood moving in right direction
where are chordae tendinae attached?
underside of mitral and tricuspid valves
papillary muscles in ventricular wall
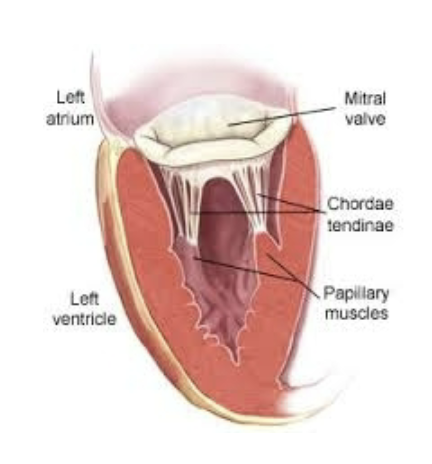
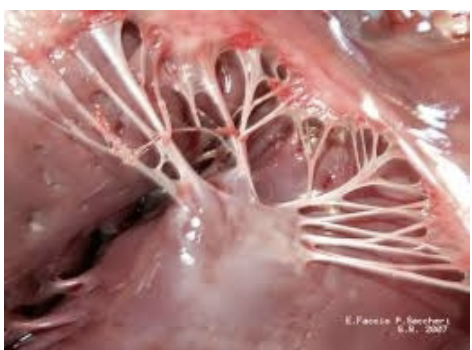
what is the function of chordae tendinae?
When mitral and tricuspid valves close, the cordae tendinae become taut and prevent the valve cusps from everting into the atria (prevent retrograde flow of blood)
what are the layers of the heart?
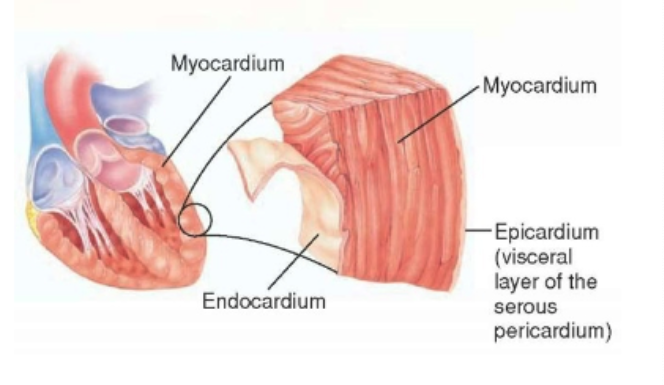
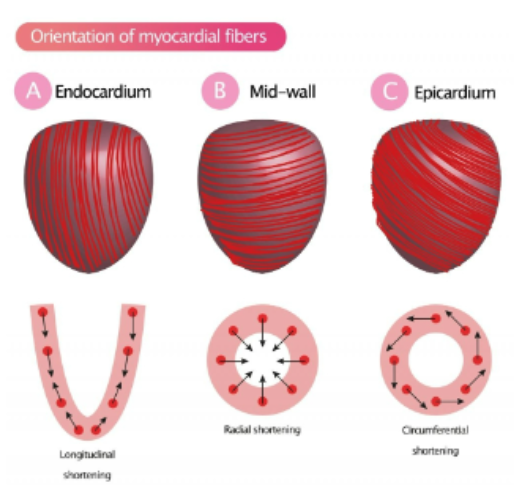
Bundles of fibers encircle the heart and have circular, longitudinal and oblique orientations
This allows for what?
allows for the blood to be propelled towards the base of the ventricles and into the aorta and pulmonary artery.
what is the orientation of myocardial fibers in the endocardium? mid-wall? epicardium?
myocardial cells are connected end-to-end by…?
intercalated disks
(individual cells are arranged into fibers that branch)
what electrically connects myocardial cells?
gap junctions
what formula can be used to calculate flow through a tube?
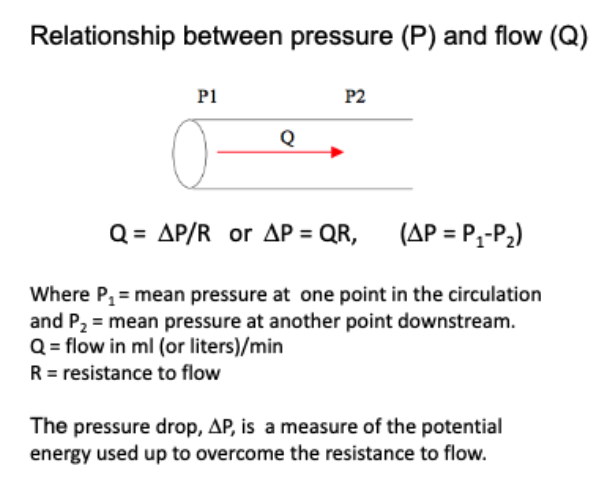
what formula can be used to calculate blood flow through the vascular system?

what is total peripheral resistance (TPR)?
frictional resistance to blood flow provided by all the vessels between the aorta and right atrium
how are parallel resistances calculated?
(reciprocal)
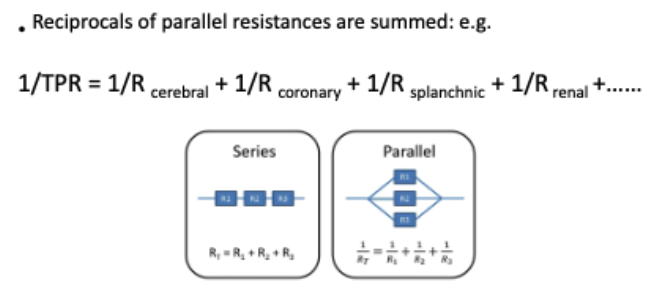
how are resistances in series calculated?

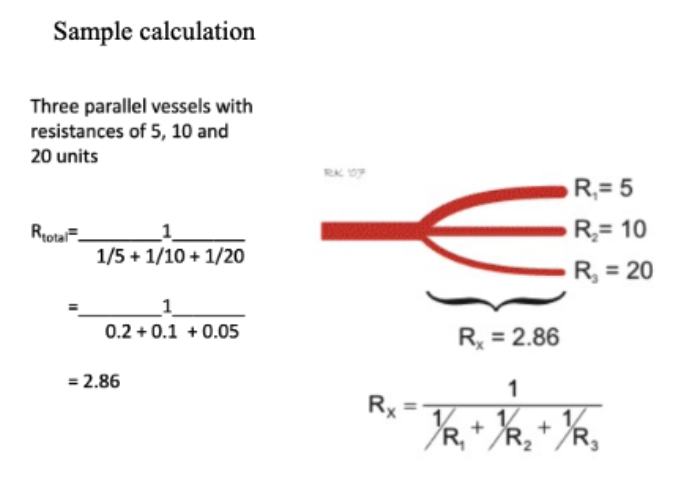
what is the resistance of 3 parallel vessels with resistances of 5, 10 and 20 units?
what factors contribute to resistance?
viscosity, length of tube, radius of tube
of the factors that contribute to resistance, which ones are subject to change?
n the circulation, n and l are essentially constant, but r can change owing to vasoconstriction and vasodilation
Since r is raised to the 4th power, a small change in radius has a large effect on flow; e.g. a 5% increase in radius produces > 20% increase in flow at the same P
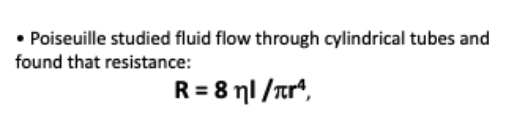
what is Poiseuille’s equation?

what is the flow equation according to Poiseuille?

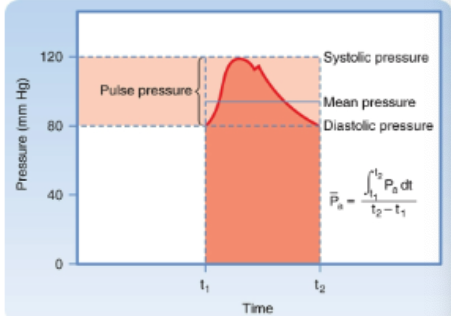
Aortic pressure fluctuates between the …? and …? when do each of these occur?
systolic pressure (SP) → when the ventricle contracts
diastolic (DP) → when it relaxes
when using the flow equation for blood flow, what value do we use for P1?
mean arterial pressure (represents the driving force averaged over the time of the heartbeat obtained from bisecting the integral of the pressure curve)
how is flow (Q) calculated?
Flow (Q) = Volume / Time; cm3 / min
how is velocity (V) calculated?
Velocity (V) = Distance / Time; cm / min
Velocity(V) = (Q/A) = cm/min
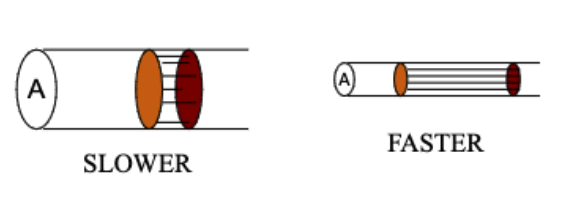
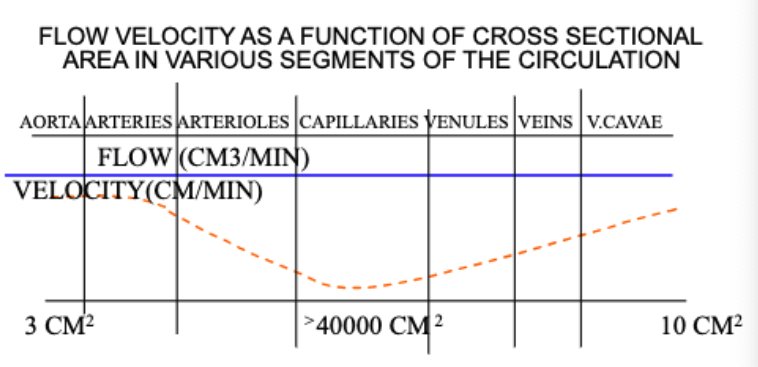
While the same total volume of blood (Q) flows through each segment of the circulation, the velocity of any given particle in the blood will vary inversely with the total cross-sectional area of that segment.
Thus, the lowest velocity of blood flow is through the…?
capillaries which allows time for exchange of fluid and solutes with the tissues
what is a non-invasive test that can be used to estimate your blood flow through blood vessels by bouncing high- frequency sound waves (ultrasound) off circulating red blood cells and measuring the frequency change in reflected sound?
Doppler ultrasound
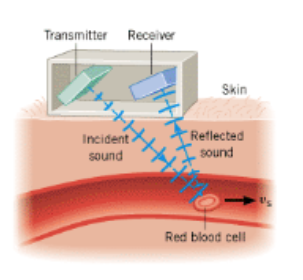
what information can we get from a Doppler ultrasound?
cardiac output minus coronary circulation

Pressure drop (change in P) is directly proportional to the …?
resistance in each segment of the vasculature
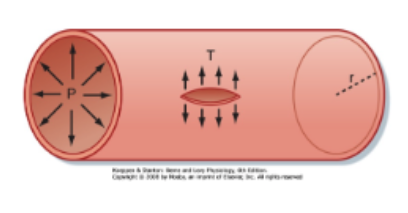
How can capillaries withstand pressures of 30-40 mmHg?
Law of Laplace
T=Pr
T: tension on vessels wall (force needed to prevent wall from splitting)
P: distending pressure
r: radius
what does the Law of Laplace tell us?
P = T/r
smaller blood vessel radius = smaller tention needed to balance the distending pressure
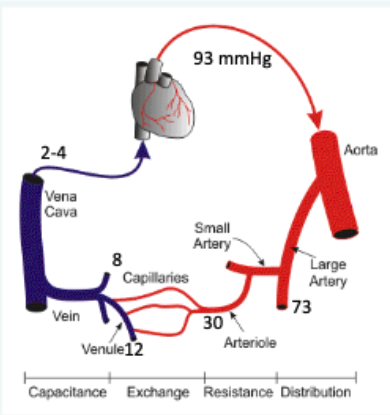
the greates change in P is in? greatest r?
arterioles