Lecture 6 - Chromatin and DNA Damage Repair
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 335 - Radiobiology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What are the two roles of chromatin
it is used as a signalling and docking platform
what is the general definition of a nucleosome
DNA wrapped around histones
how many histones make up a nucleosome
8 histones, thus nucleosomes are also called histone octamers
what histones make up the nucleosome
2 x H2A
2x H2B
2x H3
2x H4
What is the DNA between nucleosome beads called?
Linker DNA
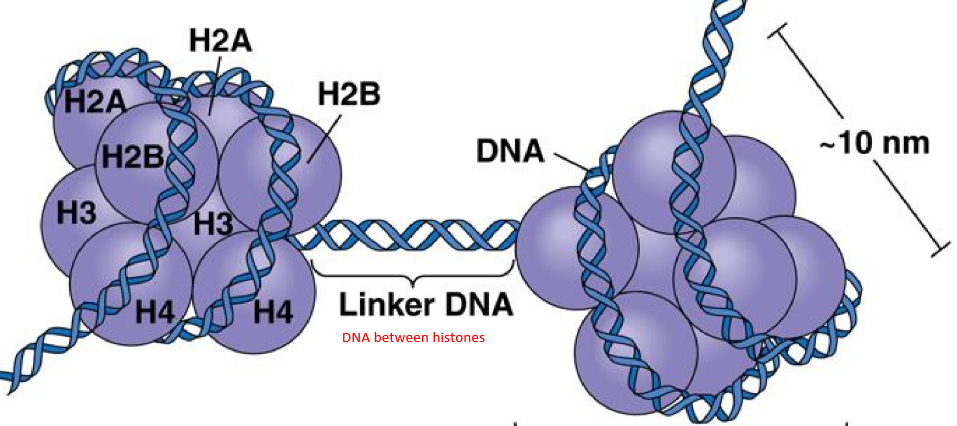
what components make up a nucleosome bead
8 histone molecules and 146 base pairs of DNA
What is the affect of nucelosomes on ionizing radiation damage
clustered lesions
spurs and blobs of ionization events have increased probability of having DNA damage if it wrapped around a nucleosome
what is heterochromatin
tightly wrapped chromatin, so tight that transcription factors cannot get to the DNA, so these sequences are not transcribed
What is Euchromatin?
loosly wrapped chromatin, transcription factors can reach DNA and attach machinery

How does DSB repair differ between euchromatin and heterochromatin?
DSB in heterochromatin are repaired slower and involve different signalling
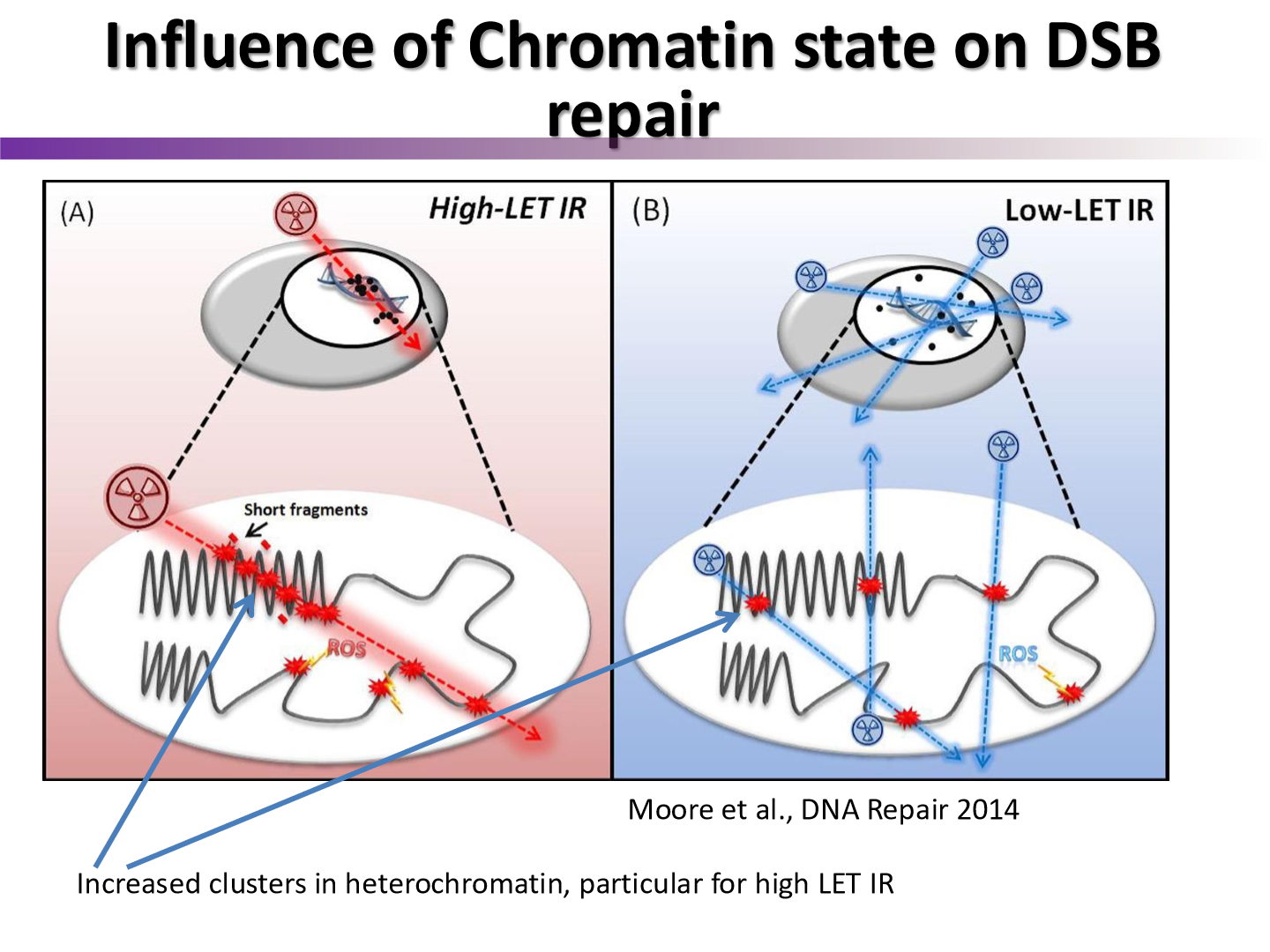
what effect does heterochromatin have on radiation damage, particularly for high LET radiation?
heterochromatin will have more damage clusters than euchromatin
How can euchromatin be converted into heterochromatin?
Via covalent modifications
when DNA is methylated (add CH3), HP1 protein compacts DNA down
How are tumor supressors inactivated?
Accidental methylation
if a methyl group is added to an euchromatin DNA section that contains a tumor supressor, it is coiled up into heterochromatin and inactivated
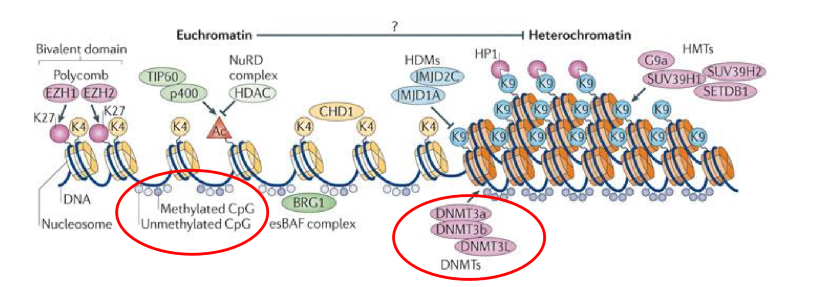
how can the nucleosome be remodeled if DNA damage is identified in a dense compact section?
Sliding
slide nucleosome away to make DNA accessible
Ejection
kick nucleosome off of DNA strand
H2A/H2B ejection
kick certain portions off of nucleosome
H2A/H2B dimer replacement
adding new dimer may make it easier to reach certain DNA section
what is epigenetics
a field of study focused on changes in DNA that do not involve alterations to the underlying sequence, but via chemical modifications that change the degrees to which genes are turned on and off.
such as DNA methylation of nucelosomes
what are some other modifications that can be done to chromatin/histones?
covalent modifications of histone tails or DNA
Nucelosome remodeling
Histone variants
Non-Coding RNAs
what are the 4 types of histone tail modifications
Acetylation
Phosphorylation
Methylation
Ubiquitination
what amino acids are responsibile for phosphorylation
serine and thereonine
what amino acids are responsible for methylation
arginine and lysine
what amino acids is responsible for acetylation and ubiquitination
lysine
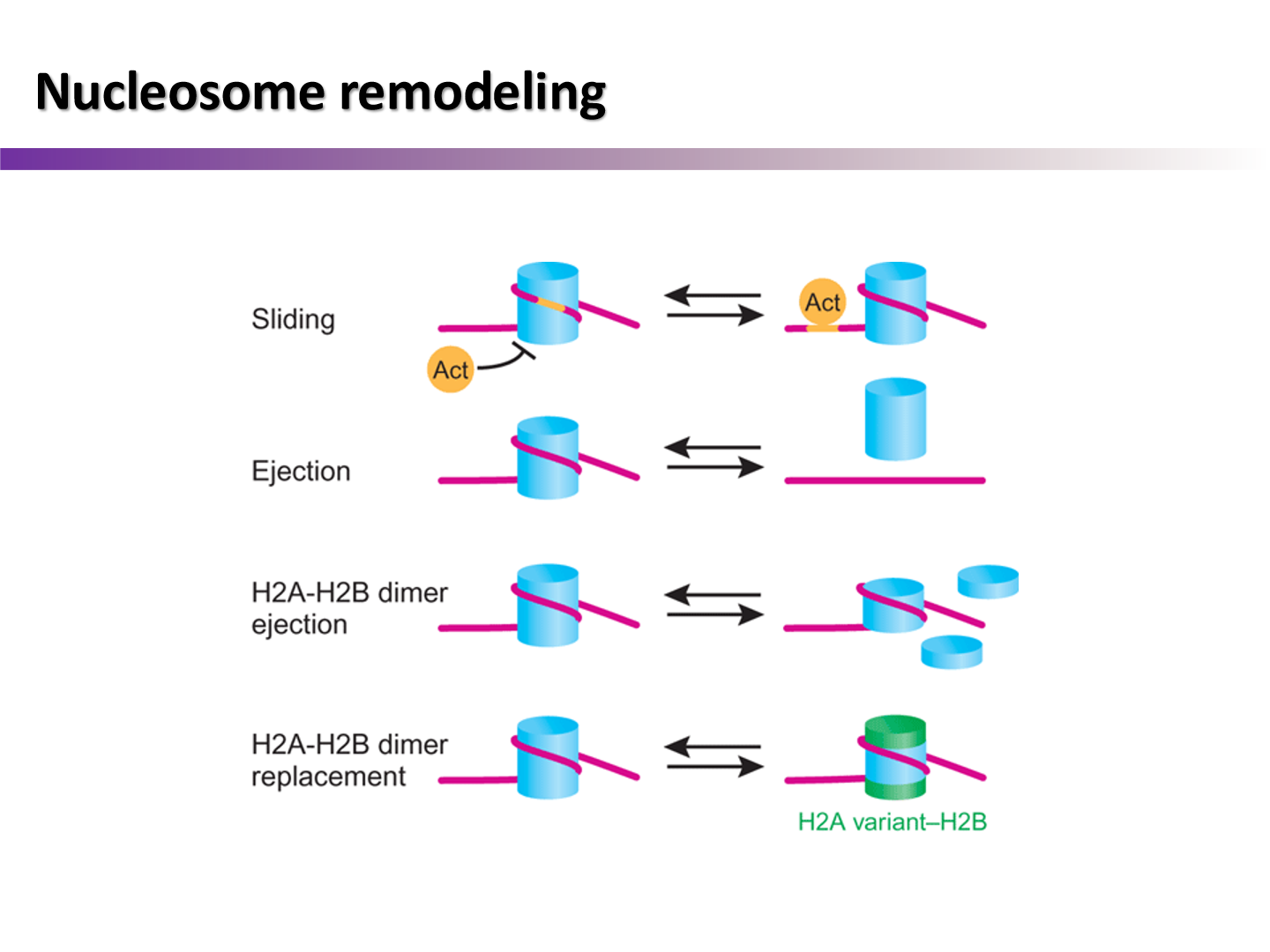
how does nucleosome remodling work
DNA around nucleosome is unravelled to be transcribed, and then ravelled back up again
how does non-coding RNA work?
RNA covers the chromatin/nucleosomes which inactivates it
what are histone variants?
histones like H2A and H3 for example are made up of different genes
so an H2A gene can be made with different genes, resulting in variants
what is the most important histone variant?
H2Ax
why is the H2Ax variant important?
when DSB damage is detected, ATM will actually phosphorylate the S139 section of H2Ax which can then be used for signaling and docking
activated H2Ax = gamma-H2Ax
Describe the activation process of H2Ax
At a DSB, MDC1 recognizes H2Ax and recruits ATM to phosphorylate H2Ax to become gamma-H2Ax
What is H2Ax focus formation?
H2Ax creates a platform for repair proteins and antibodies to attach to around the double strand break
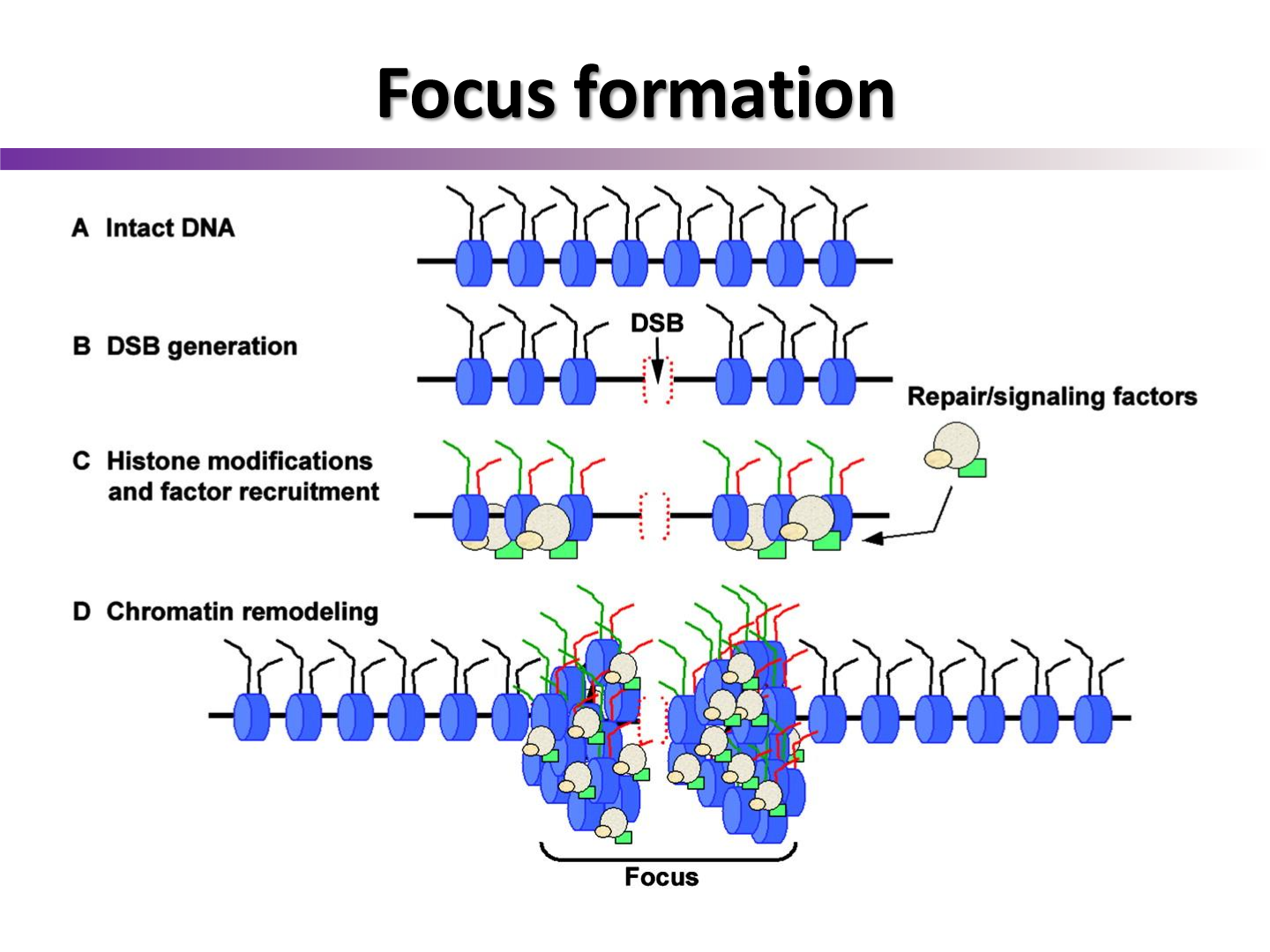
What else does gamma-H2Ax do?
it acts a signal amplifier
kinda acts like nodes of ranvier i think
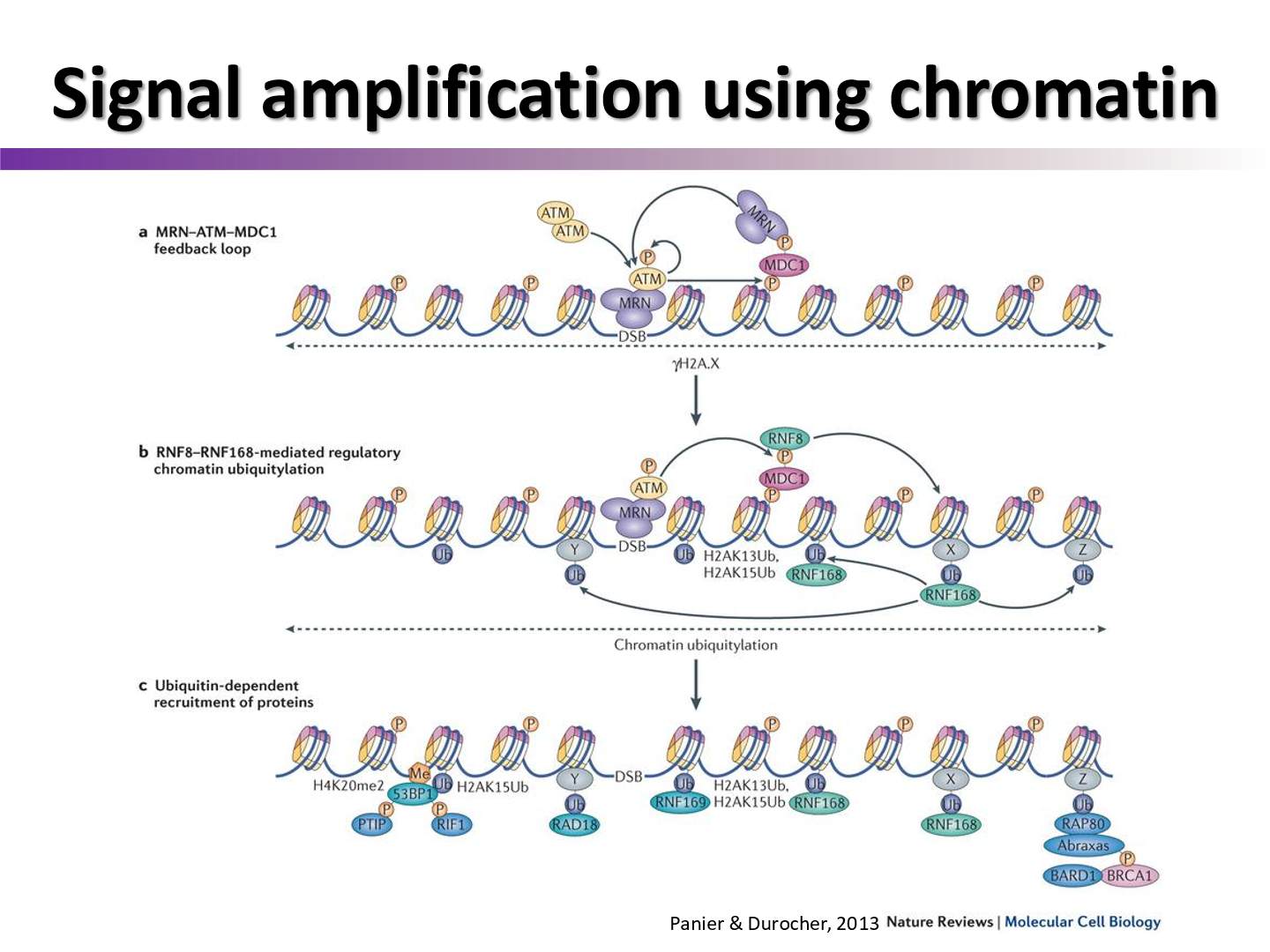
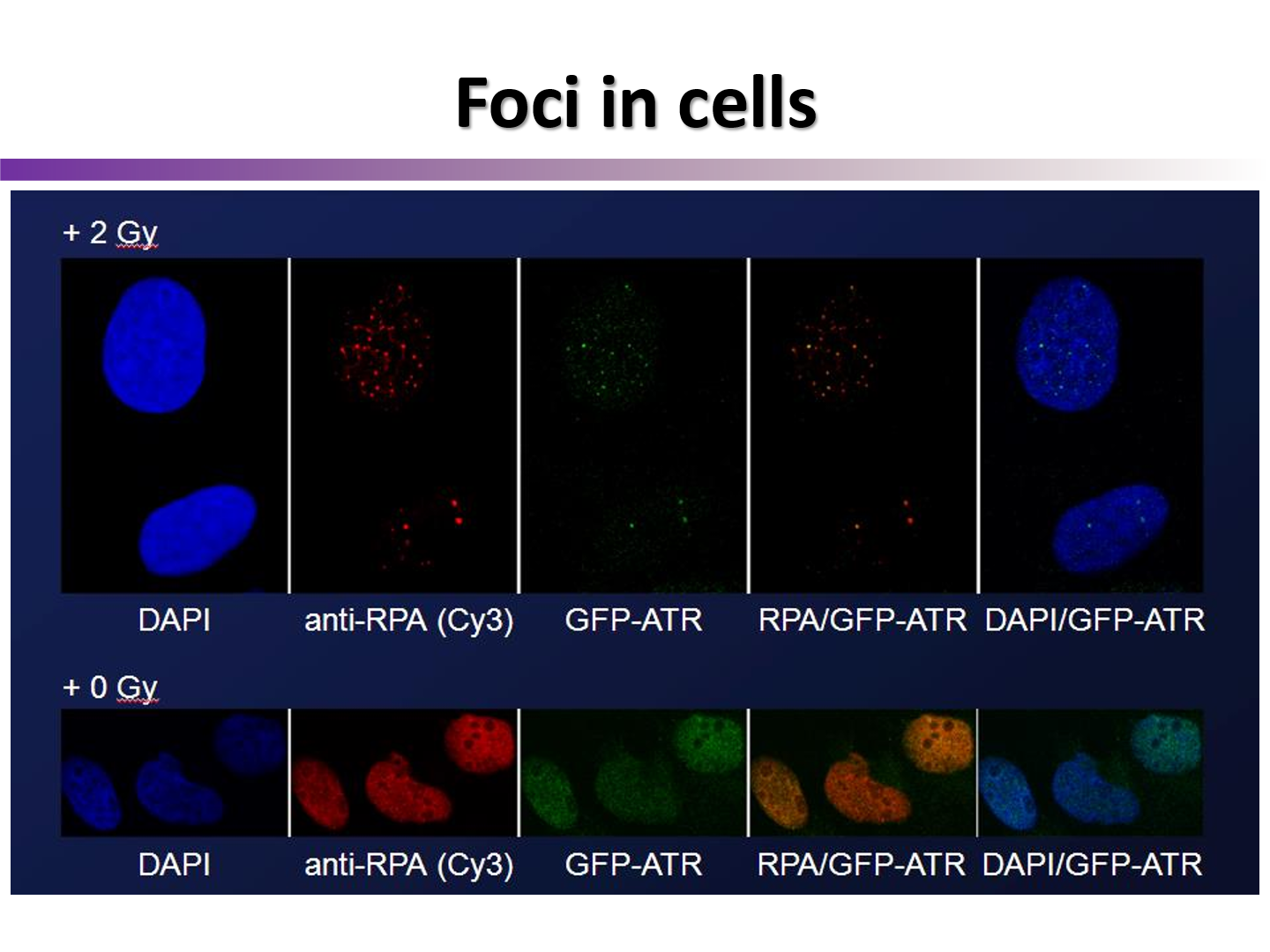
How can chromatin foci formation be used to show DNA damage in microscopy?
attach fluorescent IgG’s to the H2Ax focus, allowing us to see the amount of DNA DSB in a cell after irradiation