Introduction to Database Systems and Management
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Data
Data consists of raw facts.
Information
Information is the result of processing raw data to reveal the meaning of data.
Knowledge
Knowledge implies familiarity, awareness, and understanding of information.
Accurate Information
Accurate, relevant, and timely information is the key to good decision-making.
Data Management
Data management is a discipline that focuses on the proper generation, storage, and retrieval of data.
Database
A shared, integrated computer structure that stores a collection of end-user data and metadata.
End-user data
Raw facts of interest to the end user.
Database Management System (DBMS)
A collection of programs that manages the database structure and controls access to the data stored in the database.
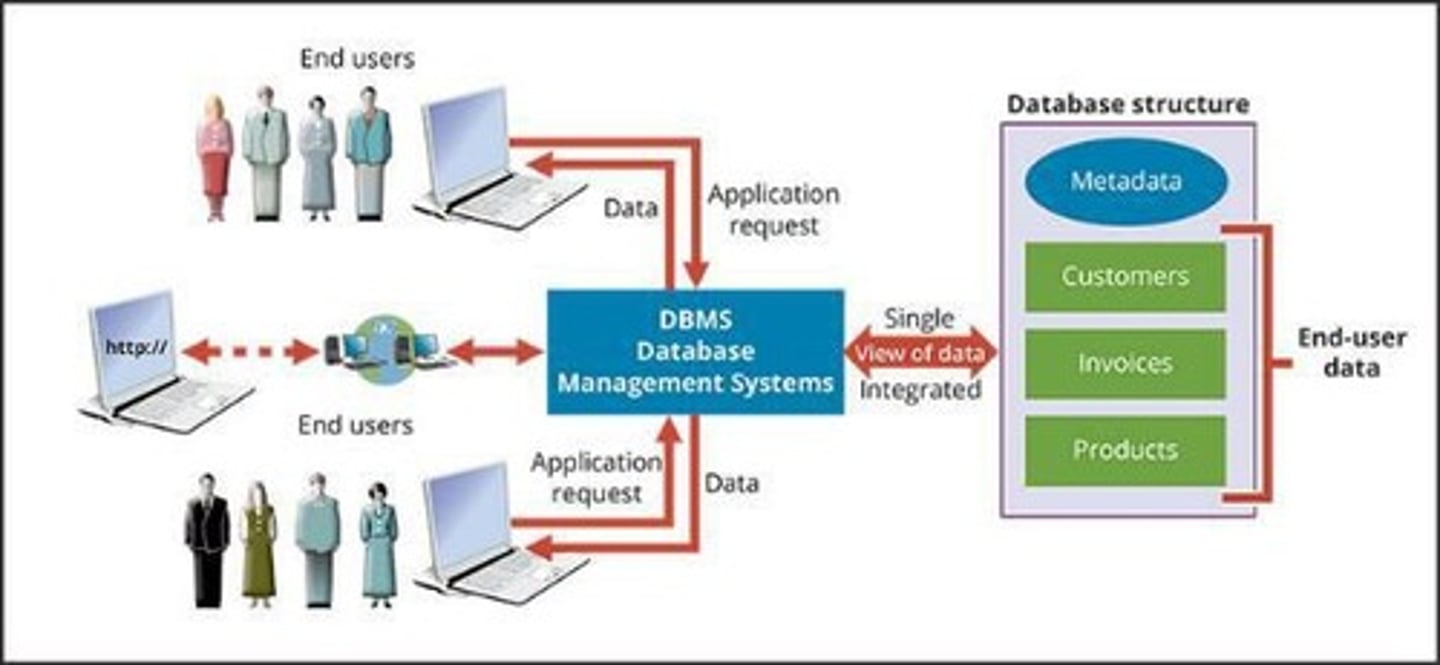
Metadata
Data about data, through which the end-user data is integrated and managed.
Single-user database
A database that supports one user at a time.
Desktop database
A single-user database on a personal computer.
Multiuser database
A database that supports multiple users at the same time.
Workgroup database
A multiuser database that supports a small number of users or a specific department.
Enterprise database
A multiuser database that supports many users across many departments.
Centralized database
A database that supports data located at a single site.
Distributed database
A database that supports data distributed across different sites.
Cloud database
A database created and maintained using cloud data services.
General-purpose databases
Databases that contain a wide variety of data used in multiple disciplines.
Discipline-specific databases
Databases that contain data focused on specific subject areas.
Operational database
A database designed to support a company's day-to-day operations.
Analytical database
A database that stores historical data and business metrics used exclusively for tactical or strategic decision making.
Data warehouse
A component of an analytical database that stores data in a format optimized for decision support.
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP)
A set of tools for retrieving, processing, and modeling data from the data warehouse.
Business intelligence
A comprehensive approach to capture and process business data to generate information that supports decision making.
Unstructured data
Data that exists in its original (raw) state.
Structured data
Data that is the result of formatting unstructured data to facilitate storage and use.
Semistructured data
Data that has already been processed to some extent.
XML database
A database that supports the storage and management of unstructured XML data.
Extensible Markup Language (XML)
A language used to represent data elements in textual format.
NoSQL
A new generation of DBMS that is not based on the traditional relational database model.
Database design
Activities that focus on the design of the database structure that will be used to store and manage end-user data.
Data
Raw facts, such as a telephone number, a birth date, a customer name, and a year-to-date (YTD) sales value.
Field
A character or group of characters (alphabetic or numeric) that has a specific meaning. A field is used to define and store data.
Record
A logically connected set of one or more fields that describes a person, place, or thing. For example the fields that constitute a record for a customer might consist of the customer's name, address, phone number, date of birth, credit limit, and unpaid balance.
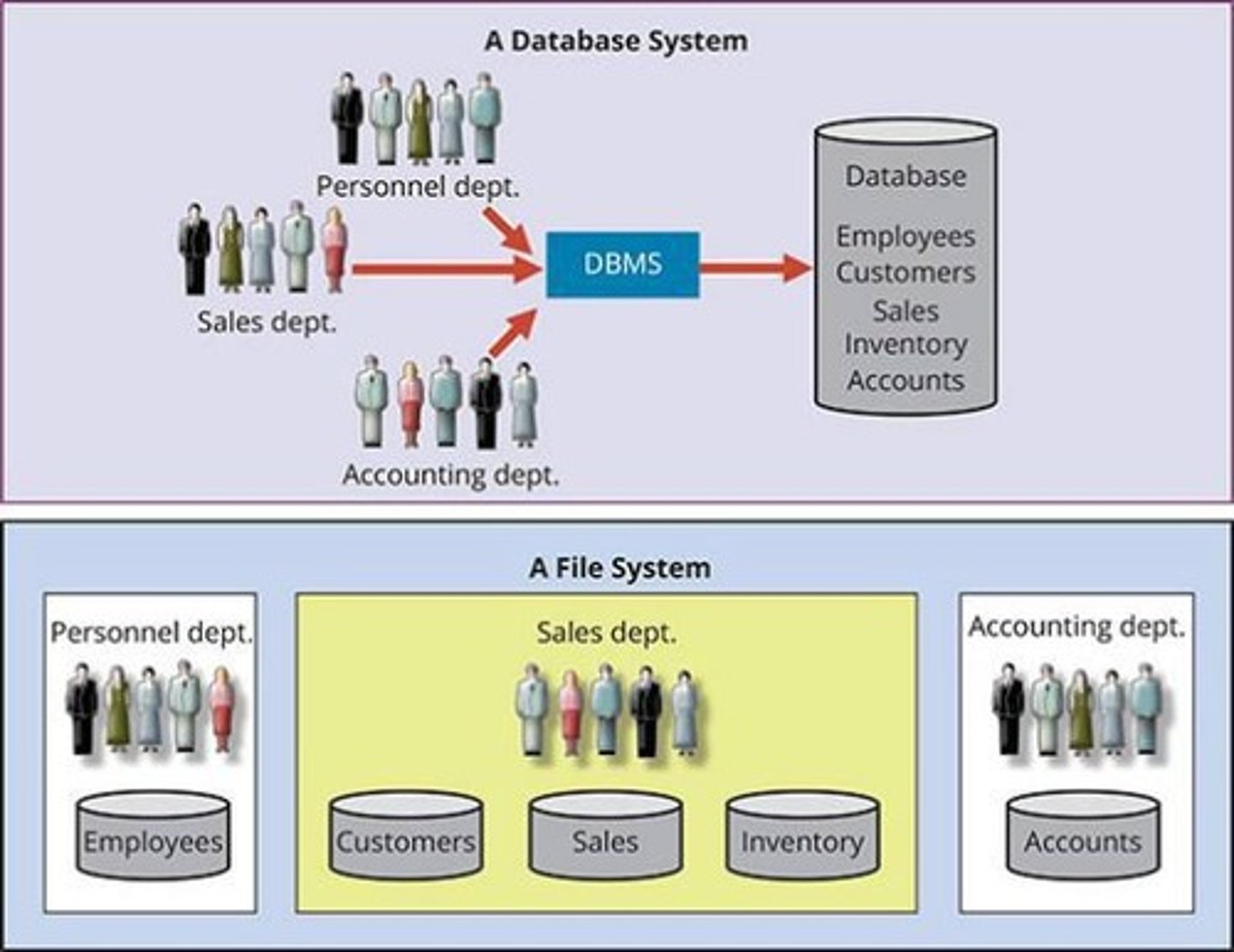
File
A collection of related records. For example, a file might contain data about the students currently enrolled at Gigantic University.
File System Problems
Challenges with file systems that affect information creation and accuracy, including lengthy development times, difficulty of getting quick answers, complex system administration, lack of security, limited data sharing, and extensive programming.
Structural Dependence
A condition where access to a file is dependent on its own structure, requiring all file system programs to be modified to conform to a new file structure.
Structural Independence
Exists when the file structure can be changed without affecting the application's ability to access the data.
Data Dependence
Occurs when all data access programs must change when data storage characteristics change.
Data Independence
Exists when data storage characteristics can be changed without affecting the program's ability to access the data.
Logical Data Format
How humans view the data.
Physical Data Format
How the computer must work with the data.
Data Redundancy
Exists when the same data is stored unnecessarily at different places, leading to poor data security, data inconsistency, data-entry errors, and data integrity problems.
Islands of Information
Term used by database professionals to describe scattered data locations.
Data Anomalies
Problems that arise from redundancy in data, including update anomalies, insertion anomalies, and deletion anomalies.
Database System
An organization of components that define and regulate the collection, storage, management, and use of data within a database environment.
DBMS
Database Management System, which eliminates most of the file system's data inconsistency, data anomaly, data dependence, and structural dependence problems.
Data Dictionary Management
A DBMS function that stores definitions of data elements and their relationships.
Data Storage Management
A DBMS function that creates and manages the structures required for data storage.
Performance Tuning
Ensures efficient performance of the database system.
Data Transformation and Presentation
A DBMS function that transforms entered data to conform to required data structures.
Security Management
A DBMS function that enforces user security and data privacy.
Multiuser Access Control
A DBMS function that ensures multiple users can access the database concurrently without compromising its integrity.
Backup and Recovery Management
A DBMS function that provides backup and data recovery to ensure data safety and integrity.
Data Integrity Management
A DBMS function that promotes and enforces integrity rules, minimizing redundancy and maximizing data consistency.
Database Access Languages
Languages provided by a DBMS for data access, allowing users to specify what must be done without having to specify how.
Structured Query Language (SQL)
The de facto query language and data access standard supported by the majority of DBMS vendors.
Database Communication Interfaces
Interfaces that a DBMS accepts end-user requests through.
Disadvantages of Database Systems
Include increased costs, management complexity, maintaining currency, vendor dependence, and frequent upgrade/replacement cycles.
Database Developer
Creates and maintains database-based applications, requiring programming, database fundamentals, and SQL skills.
Database Designer
Designs and maintains databases, requiring systems design, database design, and SQL skills.
Database Administrator
Manages and maintains DBMS and databases, requiring database fundamentals, SQL, and vendor courses.
Database Analyst
Develops databases for decision support reporting, requiring SQL, query optimization, and data warehouses skills.
Database Architect
Designs and implements database environments, requiring knowledge of conceptual, logical, and physical database design.
Database Consultant
Helps companies leverage database technologies to improve business processes and achieve specific goals.
Database Security Officer
Implements security policies for data administration, requiring DBMS fundamentals and data security technologies.
Cloud Computing Data Architect
Designs and implements infrastructure for next-generation cloud database systems, requiring knowledge of internet technologies and cloud storage technologies.
Data Scientist
Analyzes large amounts of varied data to generate insights, requiring skills in data analysis, statistics, and machine learning.