PSK4U Exam Review
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Anatomy
How living things are structured or put together (organized)
Physiology
Study of body processes: growth, metabolism, reproduction, etc.
Kinesiology
Science dealing with the interrelationship of the physiological processes and anatomy of the human body with respect to movement
Exercise physiology
The sciences of human performance under physical stress and the relationship between physical activity and the structure and function of the human body.
Anatomical position
Standing with feet together, palms facing forward and head looking forward.
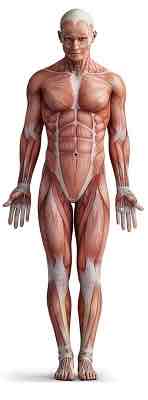
Sagittal plane + horizontal axis
Plane: divides body into a left and right side
Axis: goes right through the plane
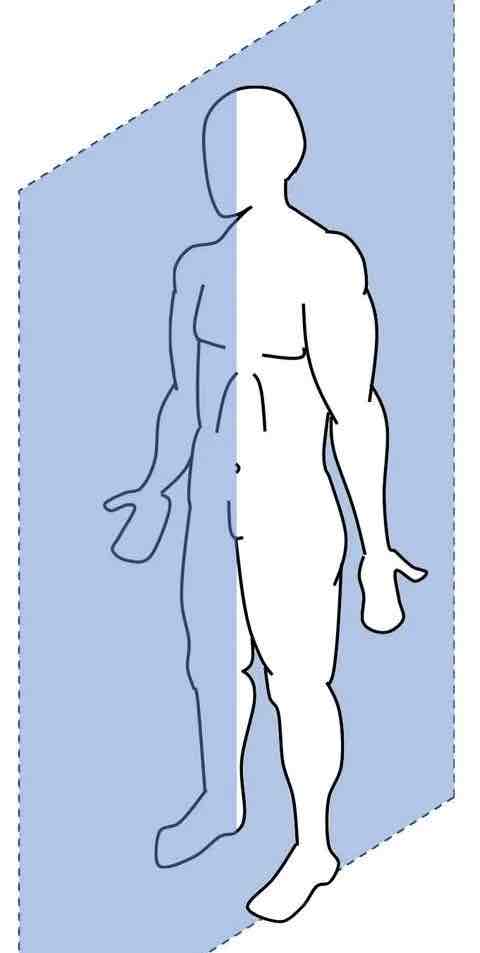
Transverse plane + Longitudinal axis
Plane: divides the body into a top and bottom section
Axis: goes through the plane (head to toe)
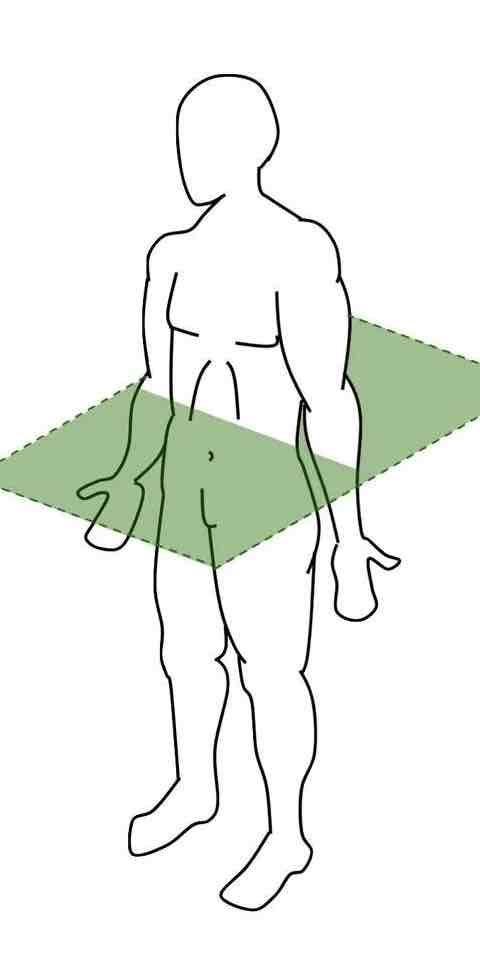
Frontal plane + antero-posterior axis
Plane: divides the body into a front and back
Axis: goes through the plane (front to back)
Lateral
Further away from the midline
Medial
Closer to the midline
Anterior (ventral)
Towards the front or the front surface of a body part
Posterior (Dorsal)
Towards the back or back surface of a body part
Superior
towards the top or top surface of a body part
Inferior
Towards the bottom or bottom surface of a body part
Proximal
towards the point of attachment of an extremity
Distal
further away from the point of attachment of an extremity
Palmar
Towards the front of the hand/foot or the front surface of the hand/foot
Dorsum
towards the back of the hand/foot or the back surface of the hand/foot
Superficial
more external / towards the surface (work from inside out)
Deep
more internal / further beneath the surface
Functions of the skeleton
1 - Give structure, support, stability
2 - Protection of important organs
3 - Some bones contain red bone marrow which produces all comps. of blood - plasma
4 - Store minerals (phosphorus and calcium
5 - Movement occurs to skeletal muscles
Long bones
Long arm and leg bones
Short bones
Primarily wrist and ankle bones
Flat bones
Flat and thin; scapula, skull, ribs
Sesamoid bones
Free floating bones encased in tendons (patella)
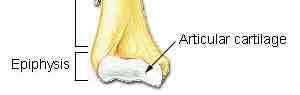
Long bone: Epiphysis + articular cartilage
Ends of long bones, part which connects with articular cartilage; friction free movement, protective covering
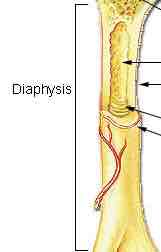
Diaphysis
Shaft of long bones, may consist of medullary cavity and bone marrow
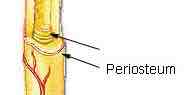
Periosteum
Outer surface of the entire bone, point of attachment for tendons and ligaments
Compact bone
Dense hard bone to withstand lateral forces, thick in shaft and thin at ends

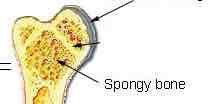
Cancellous / spongey bone
Spaces between the matrix of bone - resists weight bearing forces. thick in epiphysis and minimal in diaphysis
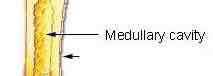
Medullary cavity
Filled with yellow and red bone marrow, blood cell production occurs here
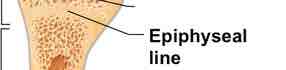
Epiphyseal plate
Growth plate where longitudinal growth occurs until the end of puberty
Ossification
The process of new bone formation, bones can grow longer and wider during puberty.
Osteoblasts release gelatin substance inside of cartilage matrix, hardens and creates bone.
Re-modelling
Further changes in bone occur due to this process
Osteoclasts break down old or damaged bone into its biochemical components
Simple fracture
No separation of bone “hairline fracture”

Compound fracture
Separate pieces are evident; “transverse fracture”
bone can break through skin, extra damage to other tissues due to movement

Communited fracture
Shattered into multiple pieces

Smooth muscle
Found as walls of visceral organs; stomach, intestines, bladder, walls of arteries, etc.
Involuntary, no striations, perform slow and substances contractions
Cardiac muscle
Only in the heart, striated, involuntary movements
Skeletal muscle
Attached to and covers bony skeleton
longest muscle cell types, striated, voluntary movement, easily tired
EEICC
Extensibility - ability to be stretched
Elasticity - ability to return back to normal length
Irritability - ability to respond to stimulus
Contractibility - ability to actively shorten
Conductivity - ability to transmit nerve impulses
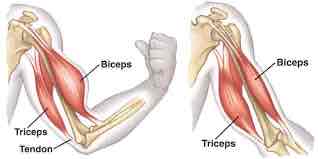
Agonist + antagonist
Muscle groups occur in pairs, working with and against each other.
Agonist: Primary joint mover (i.e. biceps)
Antagonist: Acts against the agonist to return the joint to original position
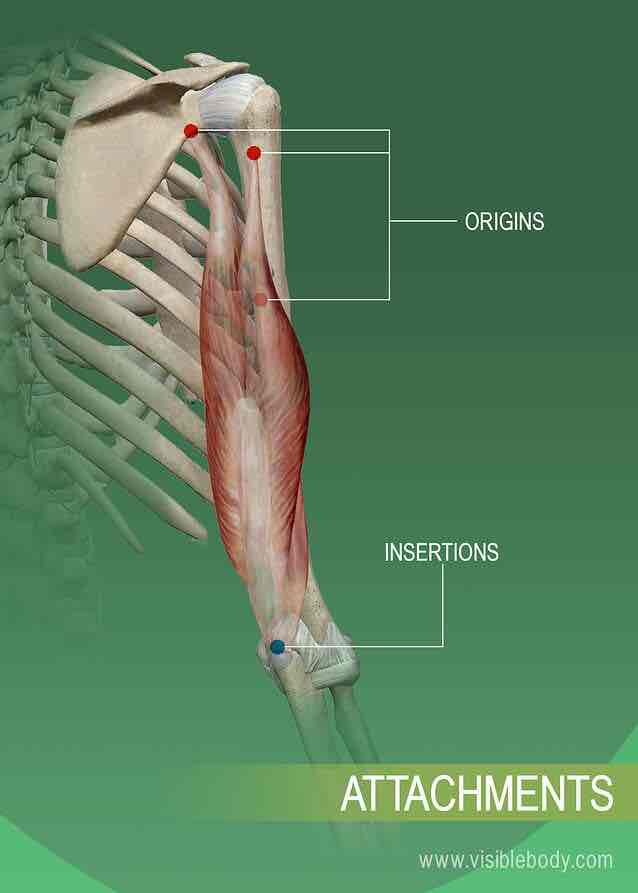
Origin, insertion, function
Origin: proximal attachment, muscle attaches to the areas closest to the axial skeleton
Insertion: distal attachment, muscle attaches to the area furthest from the axial skeleton
Function: action / motion; what the muscle does when activated in a certain position
Concentric contraction
Muscle fibres shorten while performing a movement
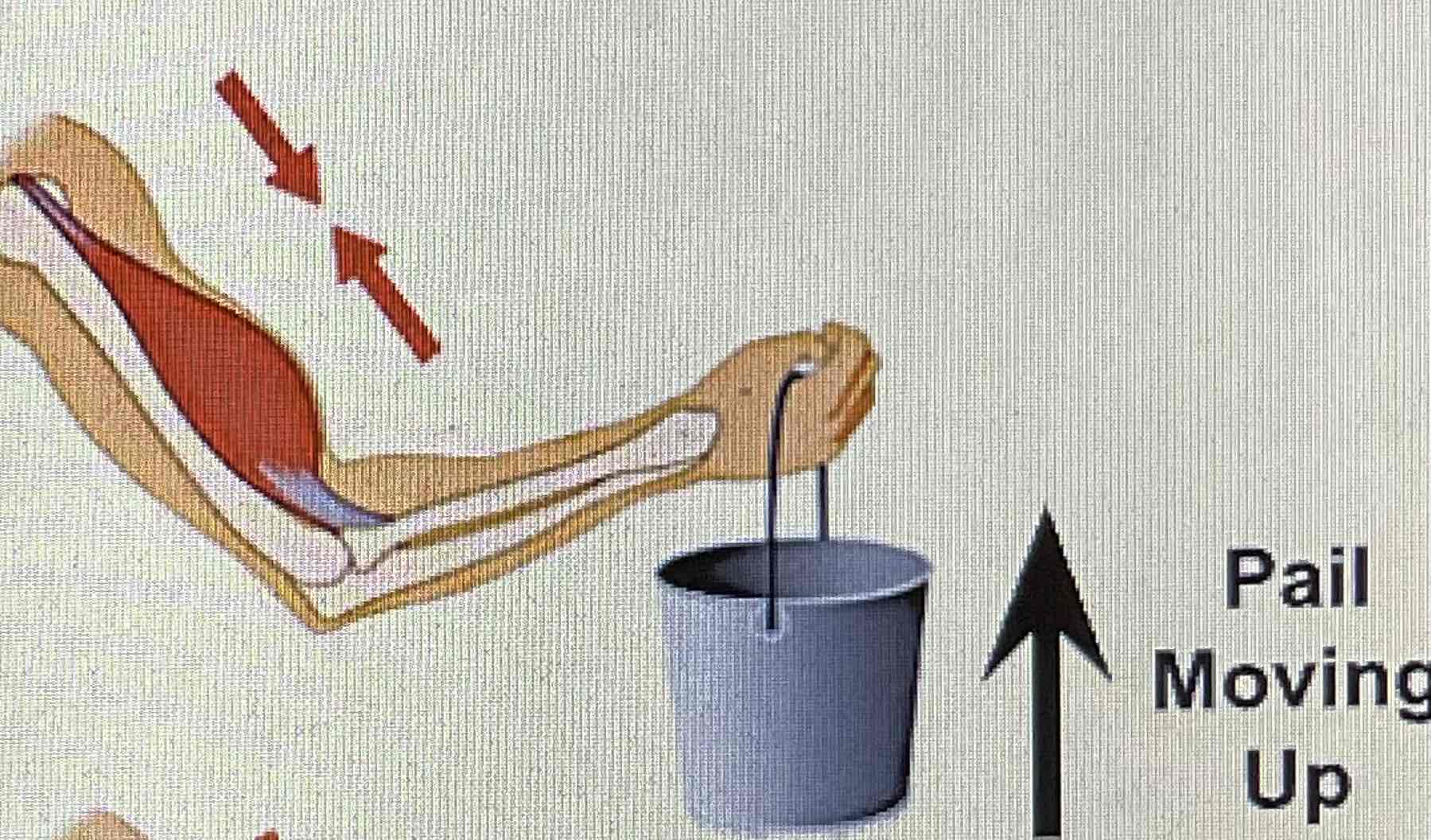
Eccentric
Muscle fibres lengthen while performing a movement
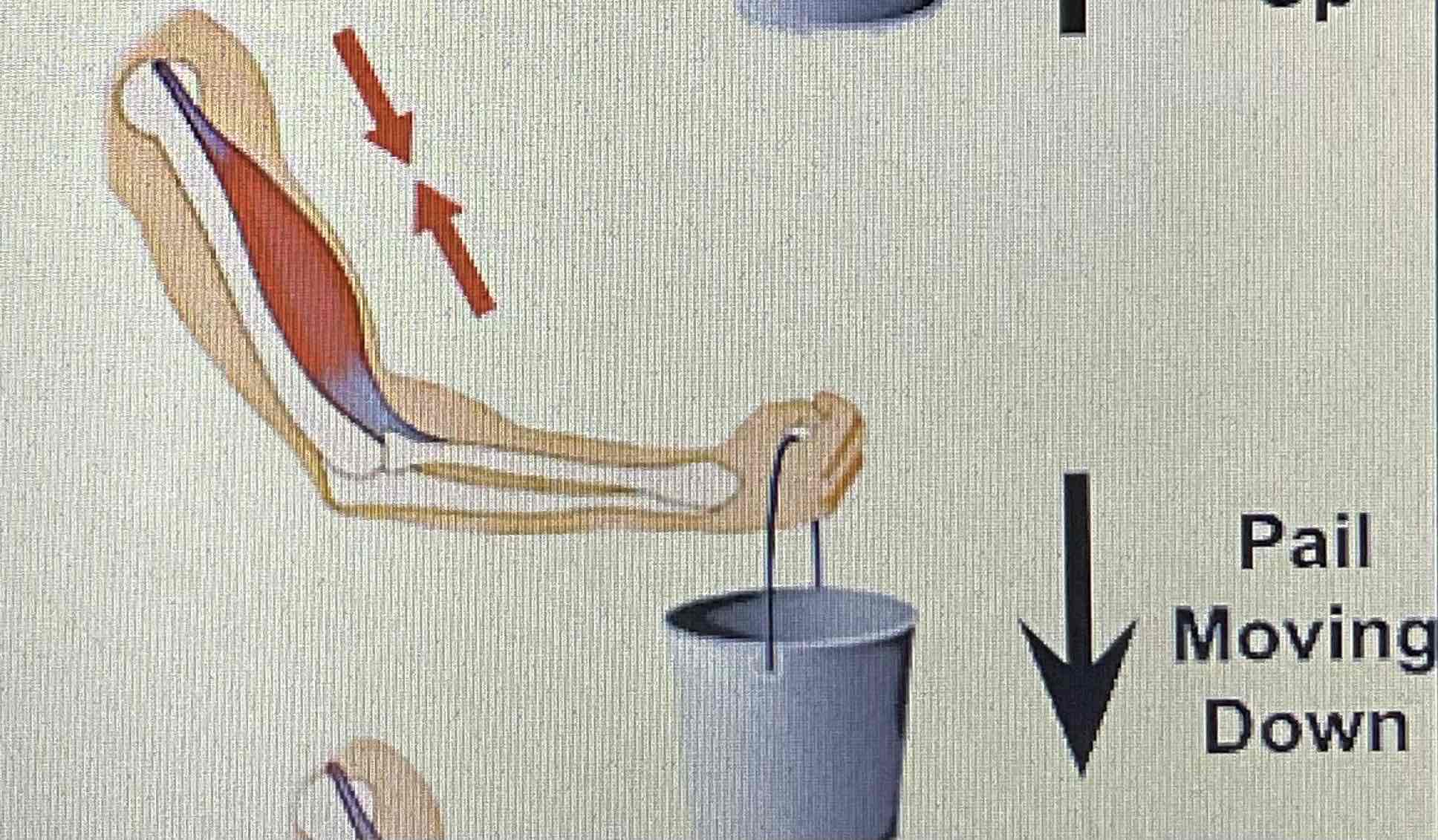
Isometric
Muscle fibres do not change in length, hold steady movement
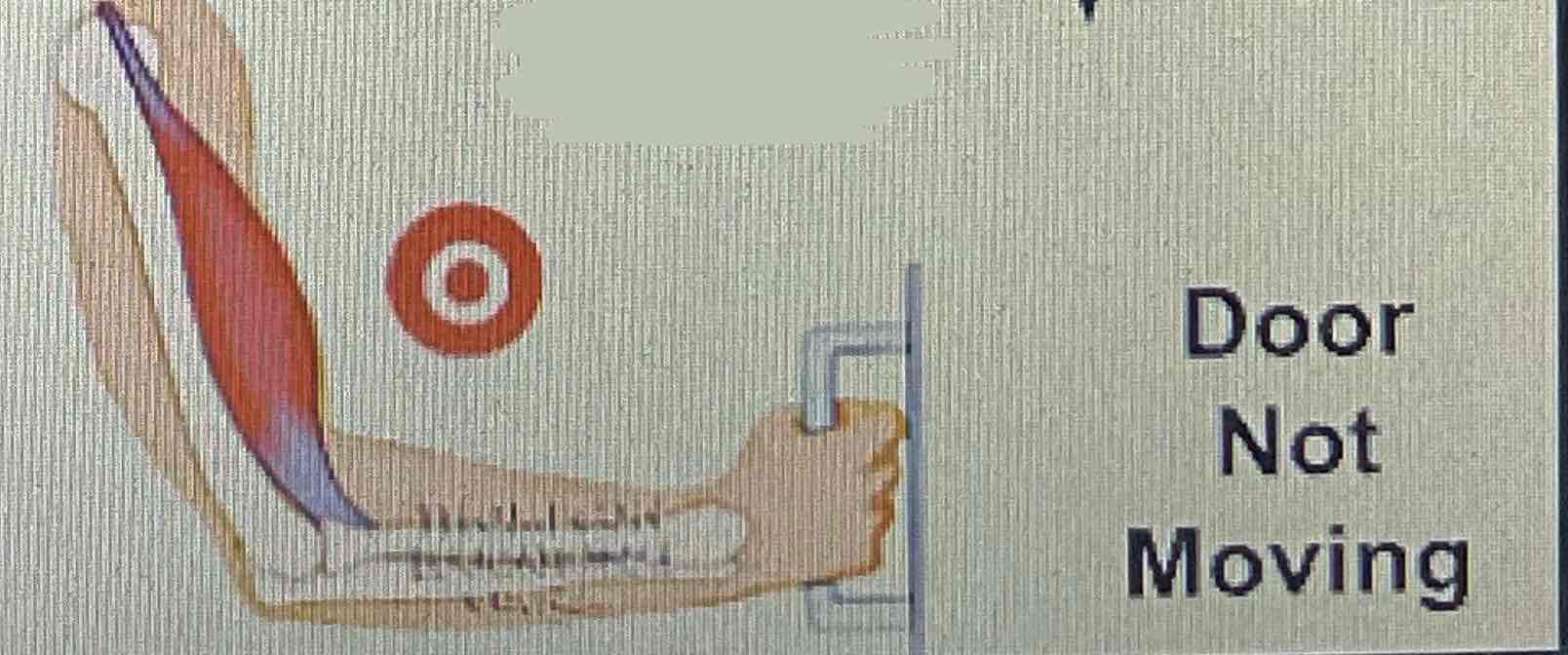
Isotonic exercise
Controlled shortening and lengthening of the muscle (intervals)
Isometric exercise
No motion - muscle fibres maintain a constant length throughout a contraction
Isokinetic exercise
Use of machines to control speed of contractions (combination of isotonic and isometric training)
Sliding filament theory
1: brain sends a signal from motor cortex to decide to move extremity
2: signal travels through the spine and branches off to extremity
3: signal goes through motor nerve and makes its way to the axon terminal
4: acetylcholine is produced and released to receptors, impulse down sarcolemma
5: Calcium ions (Ca2+) stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum start to travel towards myofilaments
6: Calcium ions bind to troponin
7: Ions cause tropomyosin to unravel the binding sites on the actin
8: myosin heads move towards the binding sites from the cross bridges and attach
9: myosin heads use ATP to pull on the actin, causing shortening of the muscle fibres
10: process continues until brain stops sending signals or the muscles are incapable of continuing
11: Ions return back to sarcoplasmic reticulum
What is a joint?
Points of contact (articulations) between two connected bones. Hold bones together and allow flexibility for movement
6 types of articular joints
1: ball and socket (hip)
2: hinge (elbow)
3: saddle (thumbs)
4: gliding (ankle)
5: pivot (cervical spine)
6: ellipsoid (wrist)
Tendons
Composed of collagen, attach muscle to bone, vascular
Ligaments
Tough bands of white and fibrous tissue, attach bone to bone, avascular
Common sports injuries
strains, pulls, tears
tendinitis (inflammation)
dislocations (bone displacement)
separations (ligaments tear)
cartilage (torn)
shin splints (membrane of periosteum tears)
Proper treatment for injury
Pressure: tensor wrap
Ice: placed on affected area
Elevate: to reduce swelling
Restrict: tensors, slings, or crutches
Carbohydrates
glucose and glycogen
Glycogen
stored glucose found in muscles and liver
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
the energy “currency” for the entire body
created in mitochondria and cytoplasm
resynthesizes aerobically and anaerobically
Aerobic vs Anaerobic
Aerobic: uses oxygen, occur in mitochondria, breaks down glucose
Anaerobic: no oxygen, use chemicals and enzymes, occur in sarcoplasm, short lived energy
Lactic acid
Chemical produced during strenuous exercise (lack oxygen), causes burning feeling in muscles
Lactate threshold
The exercise intensity at which lactic acid begins to accumulate exponentially, occurs at ~4-5mmol
Myoglobin
Protein in muscles which releases oxygen during periods of high demand, to ensure muscles have enough oxygen
Pyruvate
A byproducts of glycolysis, creates more ATP in the presence of oxygen
Summary of energy systems

Types of muscle fibres
Type 1 (slow oxidative): generate energy slowly, fatigue resistant, aerobic system dependent
Type IIA (fast oxidative): intermediate fibres, high speed energy release, allow glycolytic capacity, can be transformed into type 1 fibres with endurance
Type IIB (fast glycolytic): store glycogen and high levels of enzymes, allow for quick contraction without need for oxygen, primary system is ATP-PC
Components of the nervous system
CNS: consists of brain and spinal cord
PNS: sensory and motor nerves —> somatic and autonomic —> sympathetic and parasympathetic
Autonomic nervous system
Involuntary movements, sympathetic sys; body’s reaction to stimulus. parasympathetic; returns body back to normal balance
Somatic nervous system
Voluntary movements, contains both afférent and efferent nerves, receives signals from outside world, action taken with motor response (reactions)
Proprioceptors
Specialized receptors located within tendons, muscles, and joints which provide information through the use of golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles
Paraplegia
Paralysis of both legs, mid thoracic-lumbar spinal injury
Quadriplegia
Paralysis of all 4 limbs, upper thoracic-cervical spinal injury
Major parts of the brain PART 1
Cerebrum: sensory + motor activites
Parietal: incoming info, determines position of body parts, pain and pressure
Frontal: problem solving, intellect, behaviour, personality, smell
Occipital: vision centre
Temporal: auditory and visual memories, speech and language
Major parts of the brain PART 2
Cerebellum: “Little brain”, coordinates movements balance and posture
Major parts of the brain PART 3
Brain stem: All basic life functions
Major parts of the brain PART 4
Limbic system: controls emotions (Inside out)
Major parts of the brain PART 5
Reticular activating system: network of neurons connecting the parts of the brain
5 parts of reflex arc
a) Pain receptor
b) afferent (sensory) neuron
c) interneuron
d) efferent (motor) neuron
3) effector organ
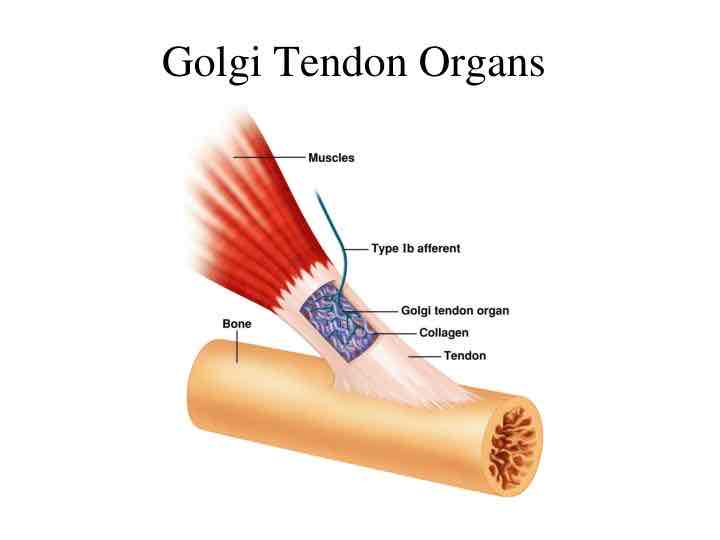
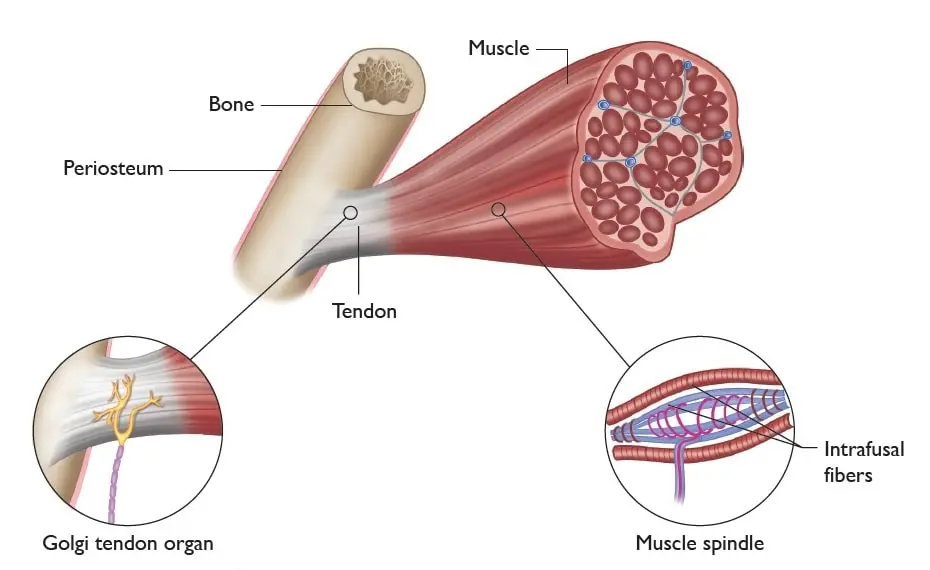
Golgi tendon organ
Where tendon meets muscle fibres, in series with muscle fibres, respond to changes/tension in muscle, one sensory neuron
Muscle spindles
In the centre of the muscle fibre, parallel to muscle fibres, respond to changes in muscle length, 2 sensory neurons
Types of tubes
Arteries: move blood away from the heart, oxygenated
Capillaries: responsible for gas + nutrient exchanges within tissues
Veins: return blood back to heart with one way valves
Types of pumps
Skeletal: muscle contractions pump blood back to heart with movement
Thoracic: changes in pressure due to breathing pushes blood from veins
Nervous: signals sent to veins, constriction allows for more blood to flow
Components of blood
Erythrocytes (rbc): made in bone marrow, carry O2 + CO2, transport nutrients and waste
Leukocytes (wbc): destroy foreign elements, critical in the function to the immune system
Platelets: regulate blood clotting
Hemoglobin: transports O2 from the lungs to the rest of the body
Frank-Starling Law
The heart’s ability to stretch and increase the force of contraction
How to increase O2 delivery
Increase in cardiac output
Redistribution of blood flow to different areas of the body (more = heart, muscles. less = kidney, digestive system)
Functions of cardiovascular system
Delivers O2, fuel, nutrients to tissues
Removal of CO2 and waste products from tissues
Maintain body temperature
Prevention of infection
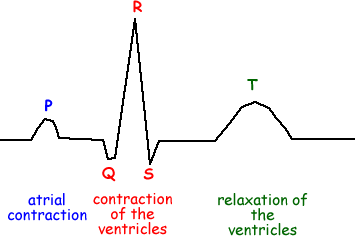
ECG conduction
P - SA + AV nodes + internodal pathways. conduction spreads through atria (depolarize)
QRS - conduction through ventricles (depol), resets atria (repolarization)
T - reset ventricles (repol)
Functions of respiratory system
Gas exchange between atmosphere and body cells
Supplies oxygen to the body through respiration
Exhalation gets rid of waste (CO2)
Internal respiration
Exchange of gases in the mitochondria during cellular respiration
External respiration
Exchange that occurs in the lung/capillary interface
VO2 max
Maximum amount of O2 that can be taken in and used for the metabolic production of ATP during exercise.
Testing: perform progressively more difficult exercise to exhaustion
good indicator of an athletes aerobic fitness
O2 deficit
When cells require more oxygen than is being consumed
tends to occur in the early stages of exercise when there isn’t enough ATP created
results in early athletic struggles when exercise demands are high
trained athletes experience less oxygen deficit due to efficiency
Excess post-exercise O2 consumption (EPOC)
Additional O2 taken in after exercise to compensate for the exercise
VO2 levels return to normal levels; ATP stores, phosphocreatine stores, convert lactic acid to pyruvate, removing excess heat (sweat)
Major physiological adaptations due to endurance training
Ability to ventilate: higher tidal volume and lung capacity
Respiratory muscles: increased endurance and strength of diaphragm and intercostals
Increase of capillaries and alveoli: capillaries around these new alveoli
Max VO2: increase efficiency of internal + external respiration, better use of O2
Macronutrients
Largest portion of food we eat and provide usable energy, important in body structure and function (cell membrane, DNA, etc.)
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
Micronutrients
Assist in biochemical reactions, tissue synthesis and energy systems
Vitamins
Minerals
Carbohydrates
Dominant source of energy, 4 cal of energy per carb
Simple carbs: digested and absorbed quickly; sugar, honey, junk, processed foods
Complex carbs: digested and absorbed more slowly; vits, mins, protein, fibre (bread, fruit, beans, pasta, veggies)
Proteins
Necessary for growth and repair body tissues (involved in almost all body processes)
10-15% of diet recommended
4 calories of energy per gram of protein
proteins broken down into amino acids; 9 supplied by foods, 11 already in our bodies
Complete proteins: foods containing all 20 amino acids (meat, cheese, eggs, quinoa, soy, milk)
Incomplete proteins: limited amounts of amino acids (most vegetable proteins)
Fats (lipids)
Insulate and protect vital parts of the body, provide large source of concentrated energy for low intensity activities
9 cals of energy per gram
Saturated fats: Meat, poultry, butter, lard, hard margarines (animal/processed foods)
tends to raise cholesterol + lipid levels in the blood (heart disease/blocked arteries)
Unsaturated fats: Olive, soybean, corn, sunflower, safflower, sesame oils
carries cholesterol and fat out of the bloodstream
Calories
Kilocalorie (kcal) is 1000 calories; it measures the amount of energy that food will produce as it passes though the body