Maya Civilization
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
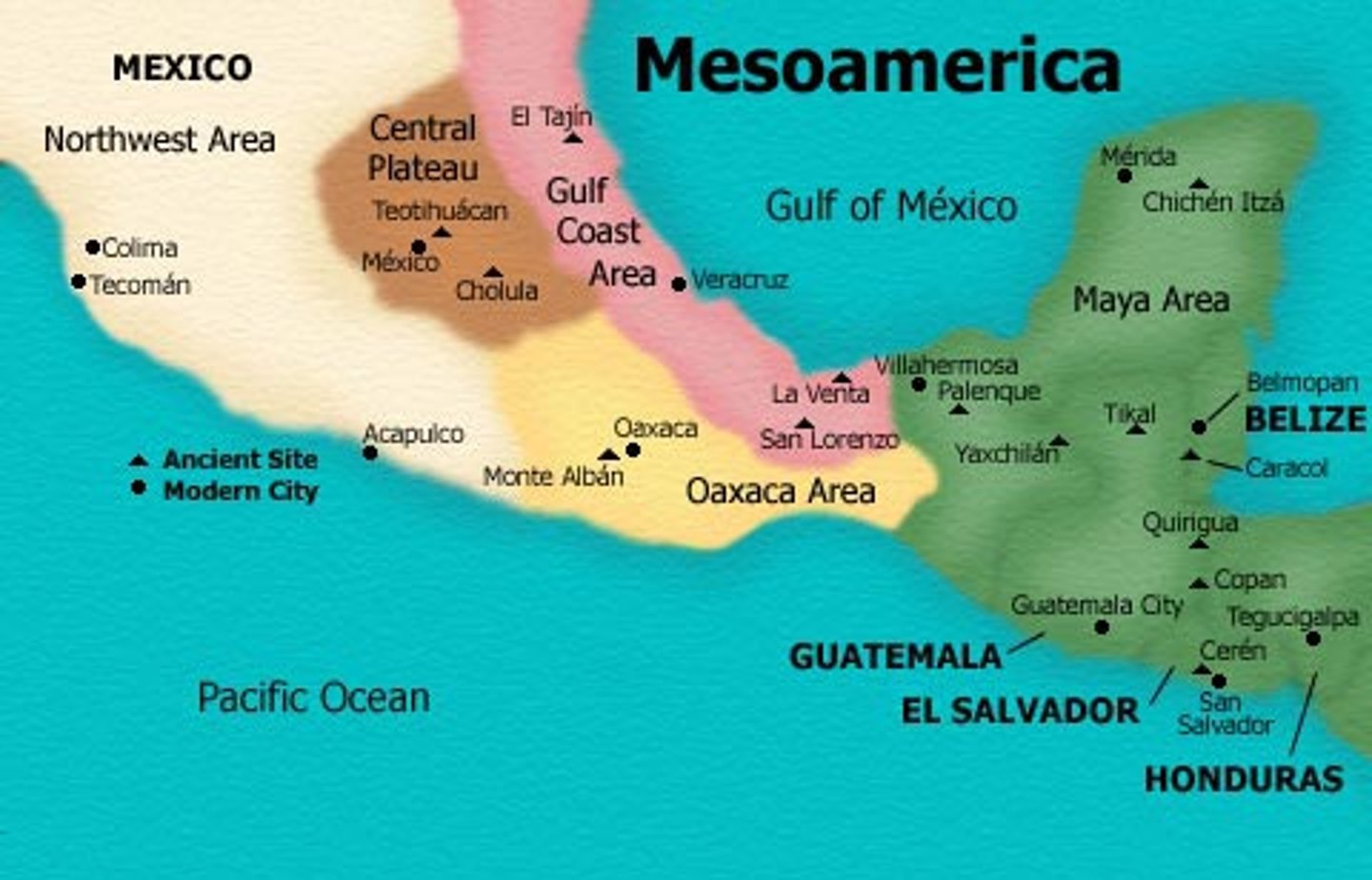
Geographic Region: Maya Civilization
Tropical rainforests in Mesoamerica.
Mesoamerica
present-day southern Mexico and northern Central America.
Farming techniques
cleared patches of rain forest to plant crops and dug canals to bring water
Population of Maya cities
home to as many as 100,000 people
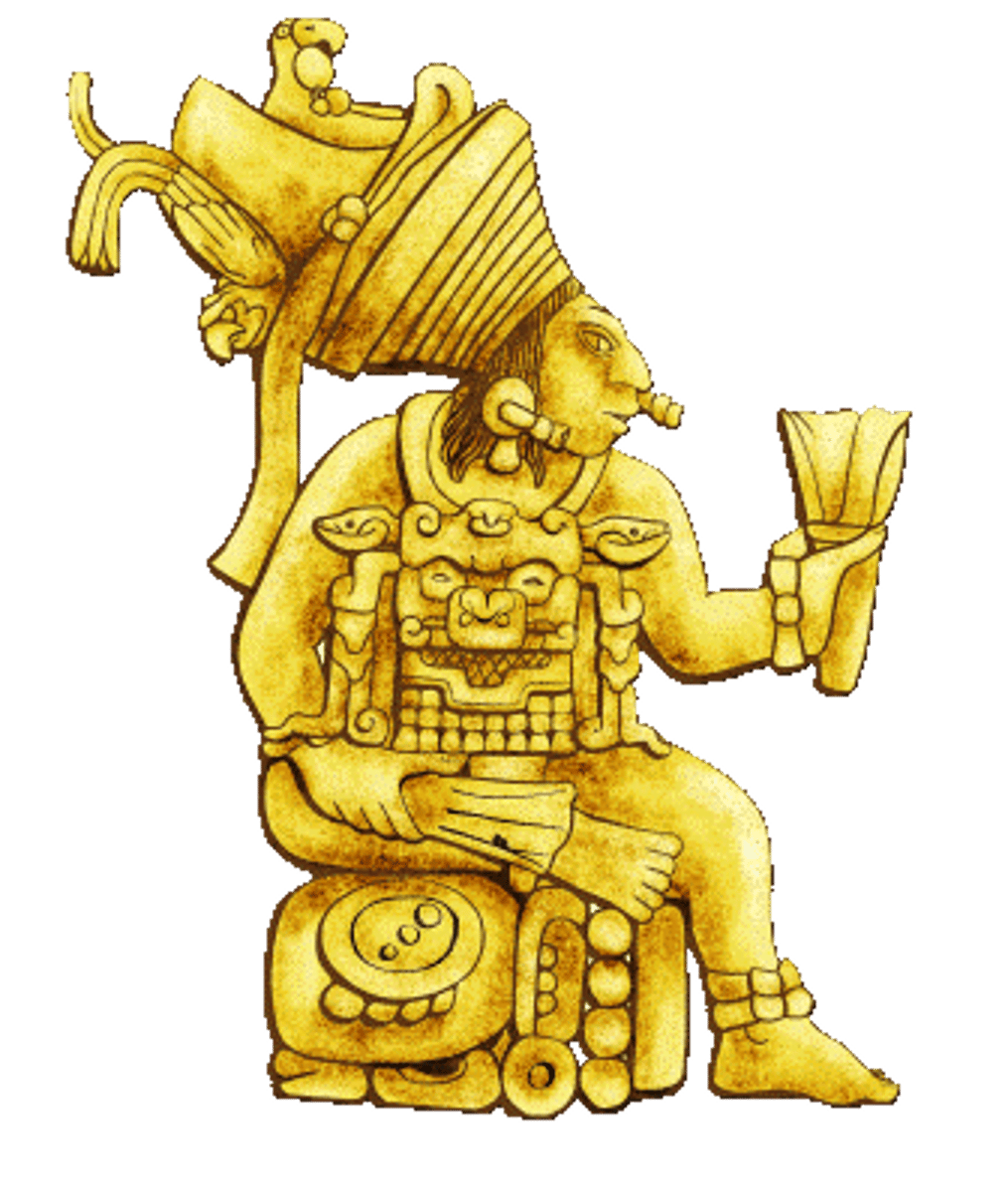
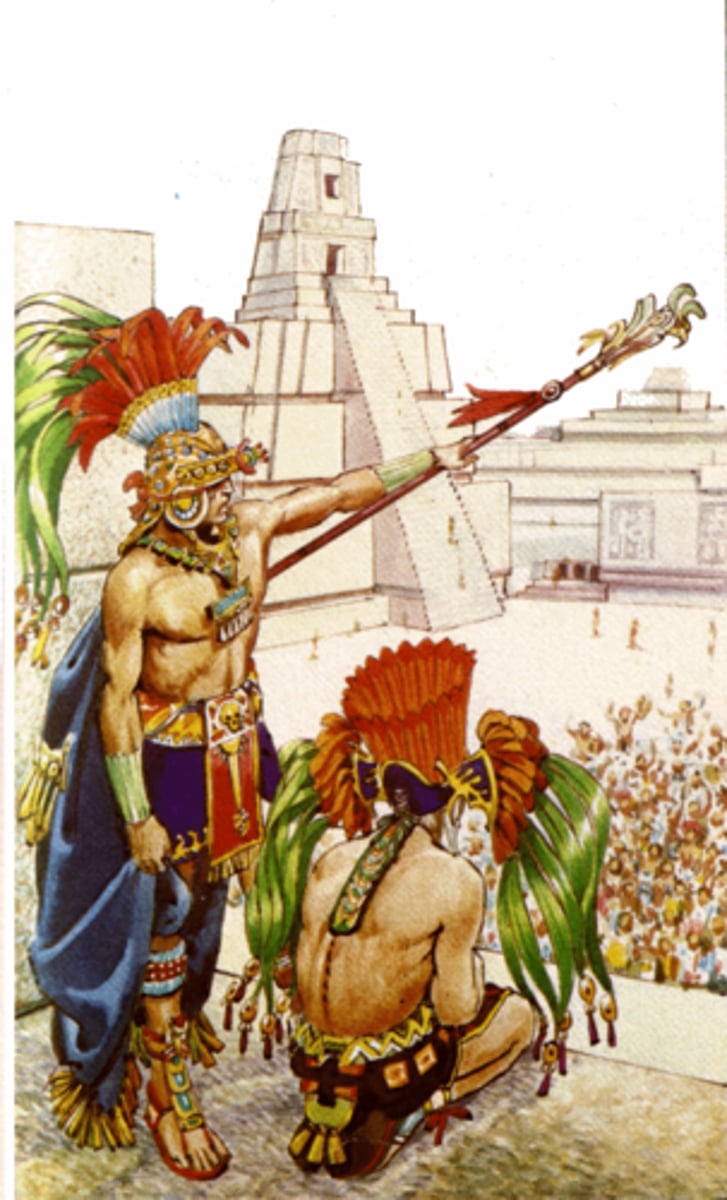
Maya ruler
believed to have god-like powers
most important religious figure

Maya social structure
top class: rulers, priests, high-ranking officials
middle class: lower-ranking officials, traders, skilled workers
bottom class: farmers
Maya gods
represented forces of nature such as the sun, moon, and rain.

Maya priests
job was to mark time so that festivals and ceremonies were held on the right day

Hieroglyph
symbol that represents a word, idea or sound

Advances in science
study of stars and planets (astronomy), concept of zero (math), accurate calendars
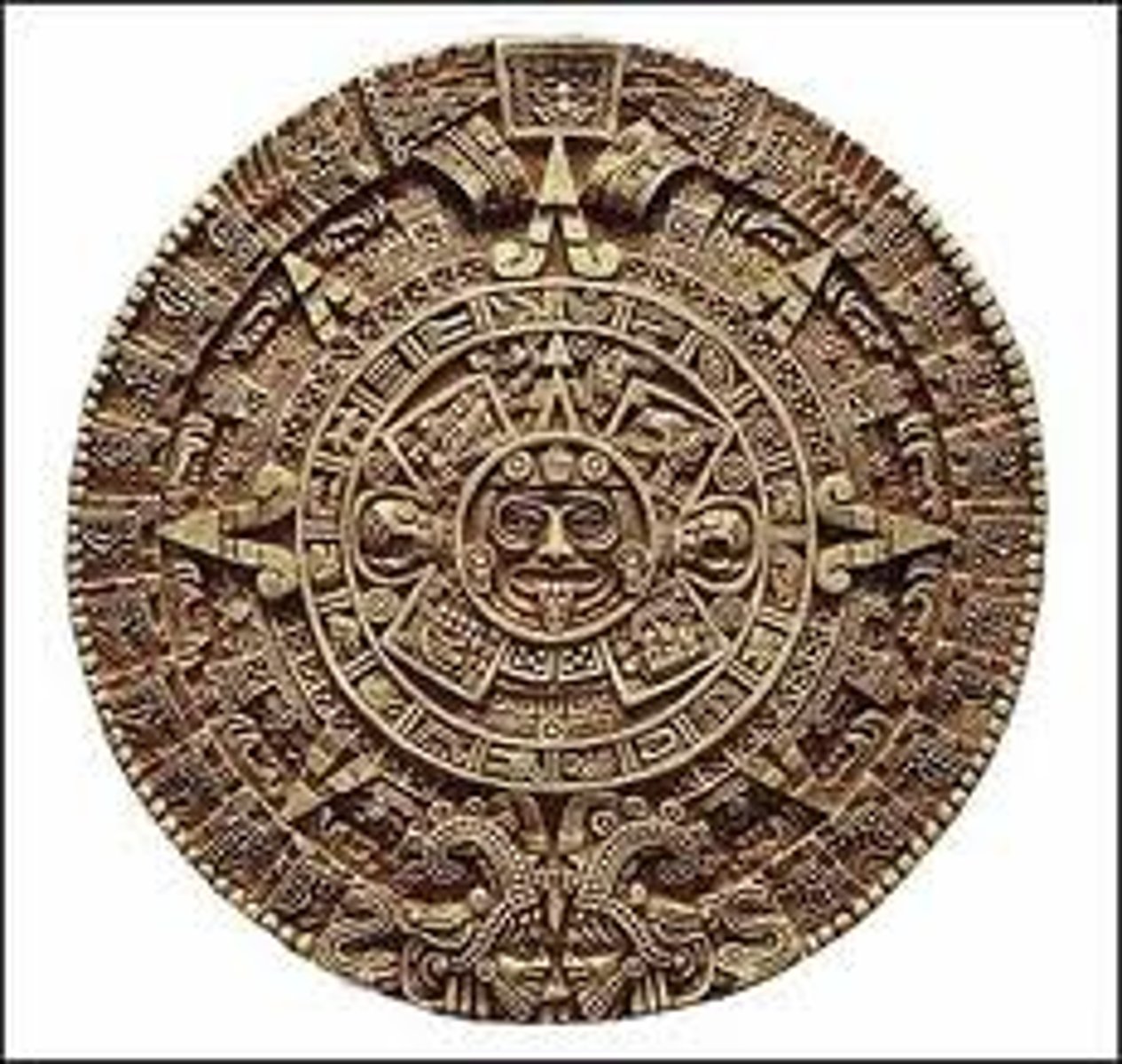

Maya art
fine pottery, bone carvings, jewelry, paintings
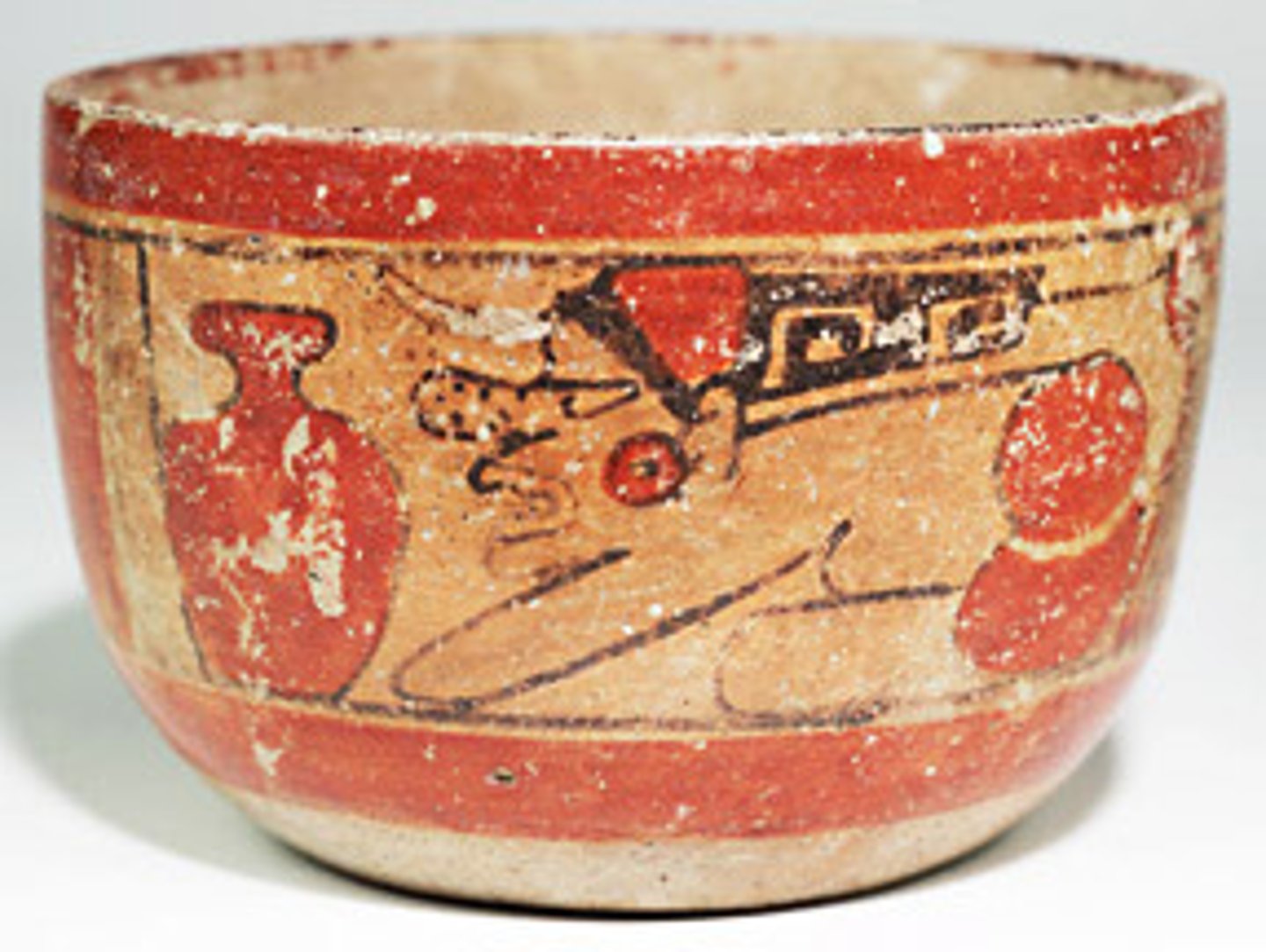

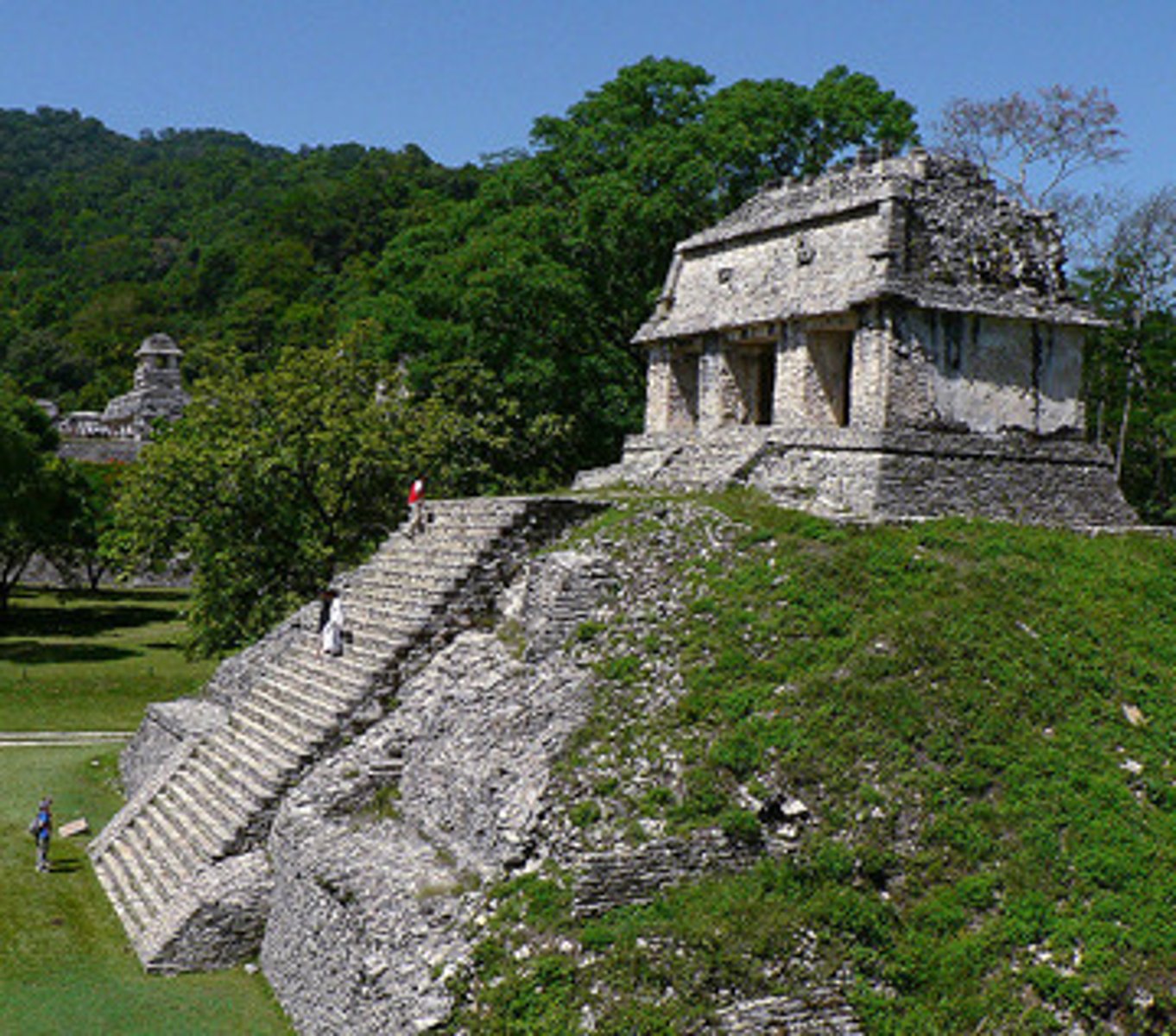
Maya city centers
stone buildings, wide plazas, ball courts

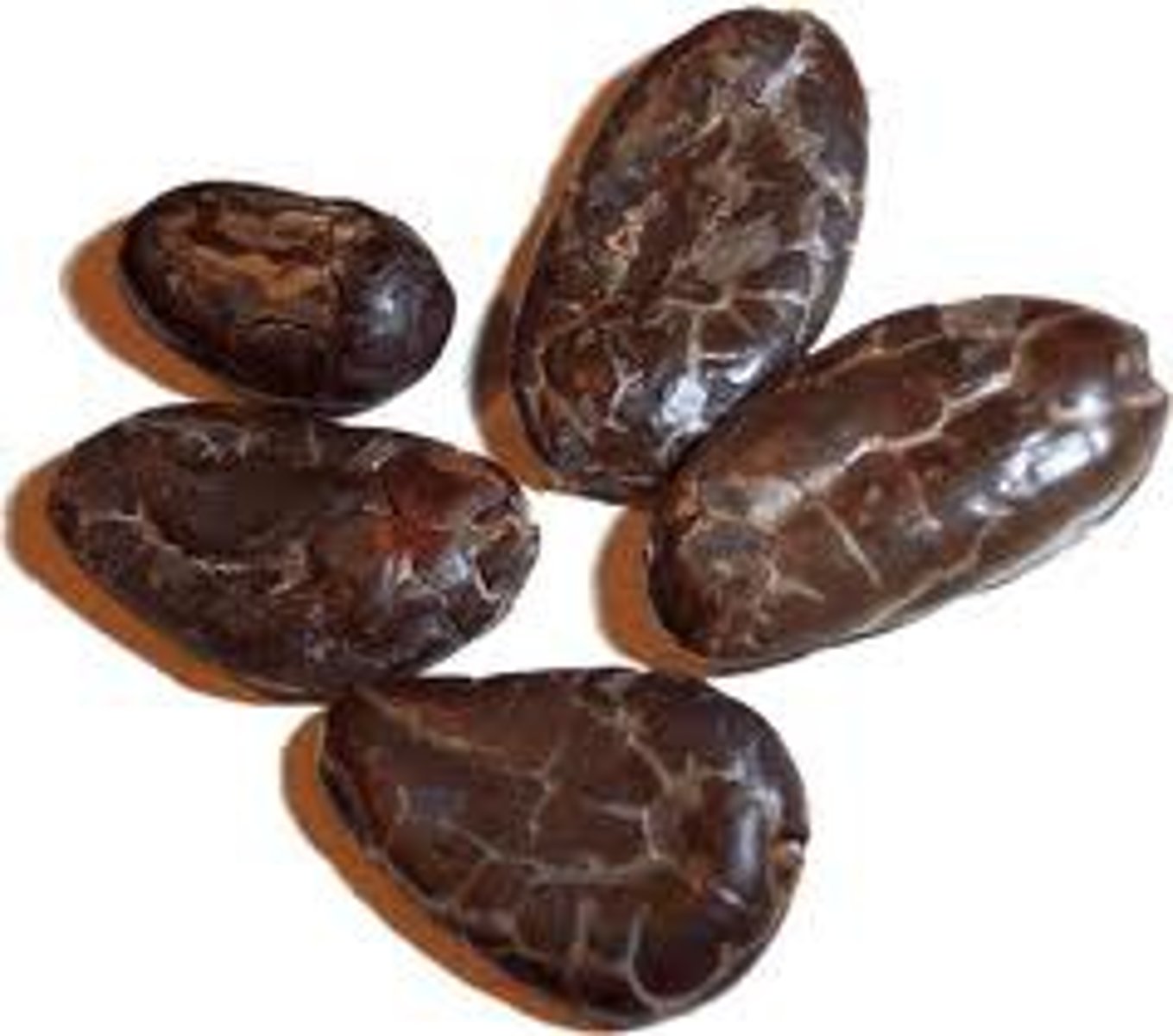
Goods traded
cacao or cocoa beans, animal skins, jade, dried fish, honey,

Features of a civilization
cities, well-organized government, workers with specialized jobs, established religion, system of writing, highly developed culture (art, architecture, music, etc.)
Agricultural Revolution
The time when human beings first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering.

3000 B.C.
The world's first cities appear in the Middle East.
250 A.D.
Maya civilization takes shape.
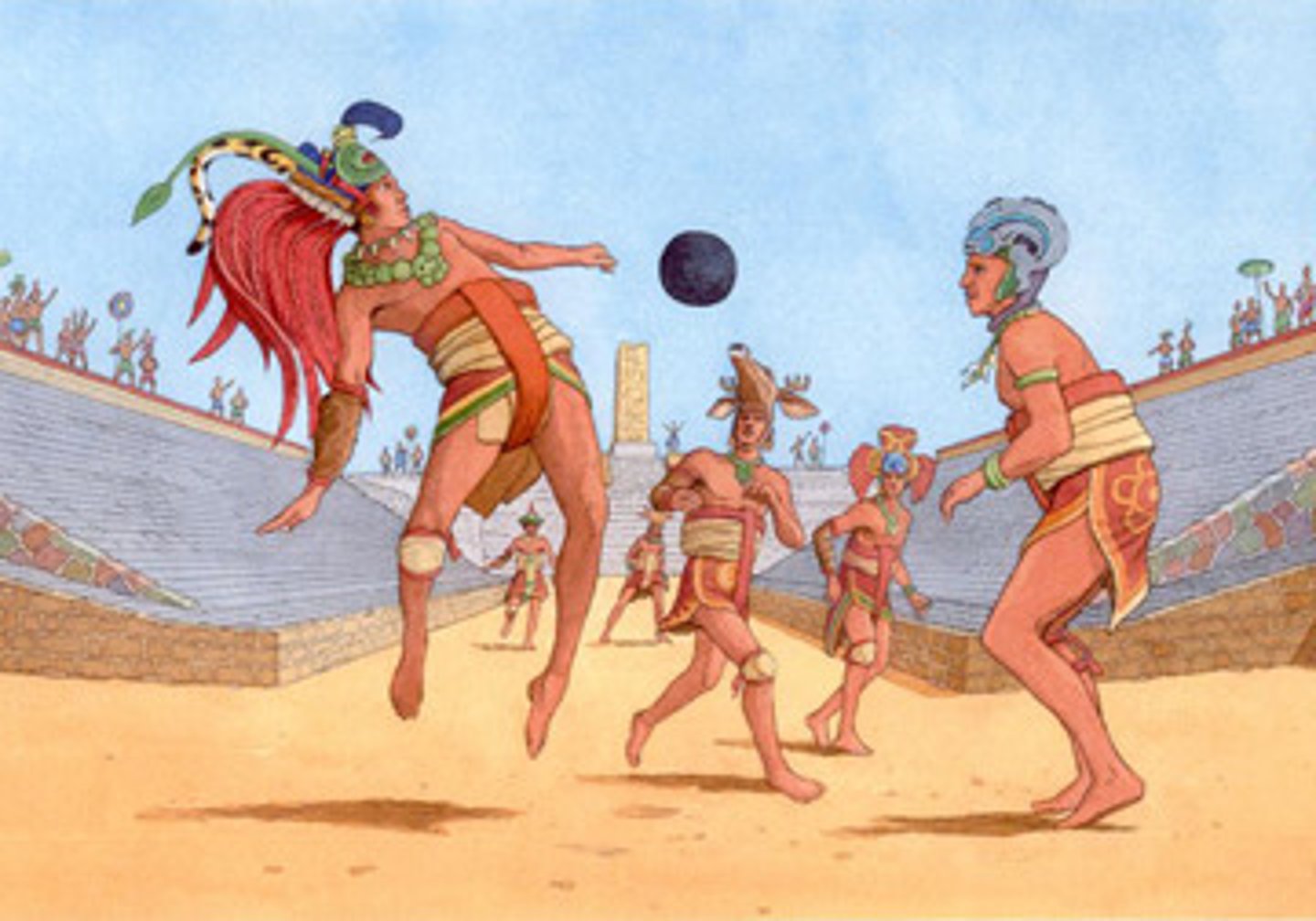
Maya Ball Game
Popular recreation

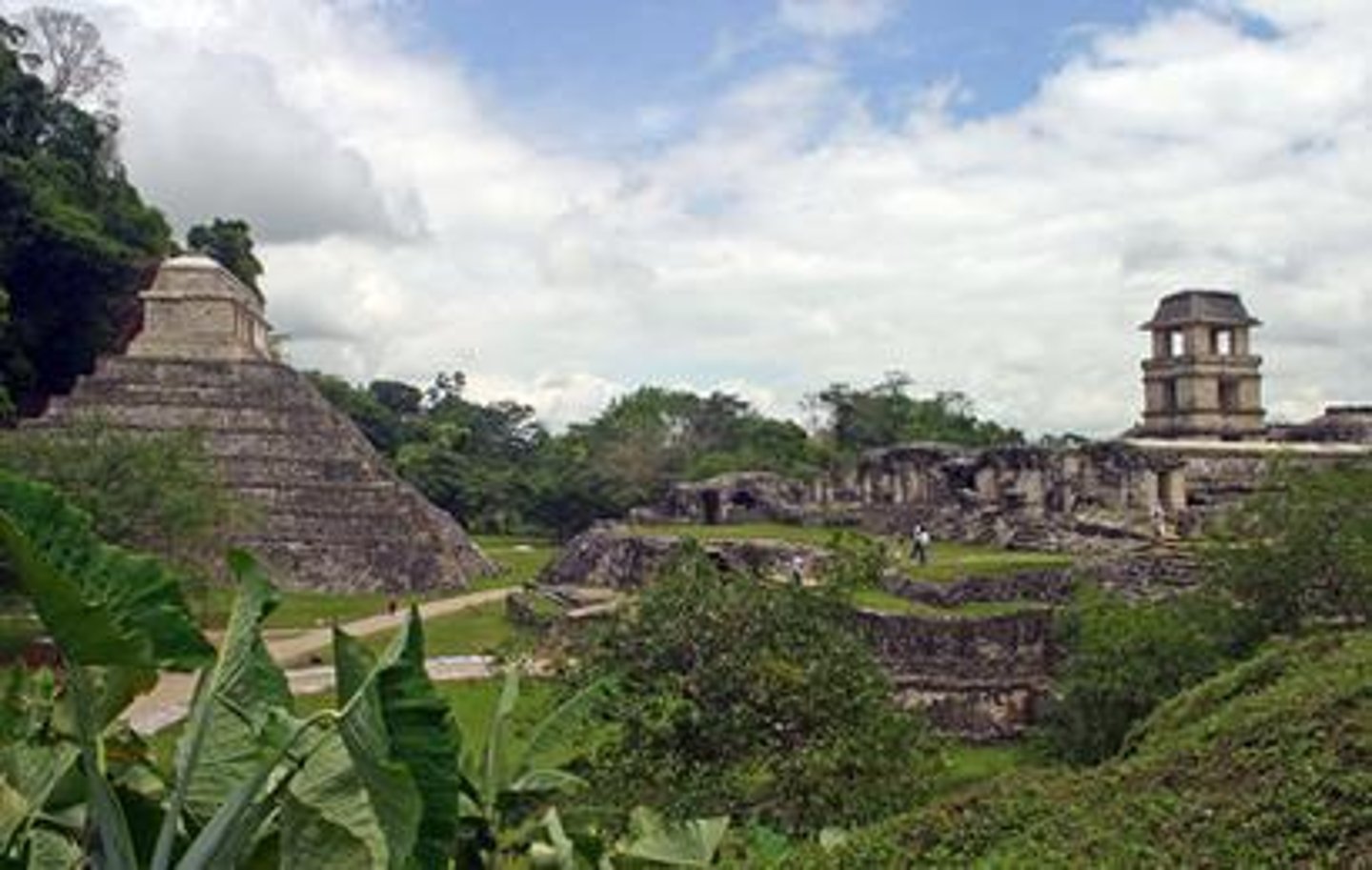
Pyramid
a structure with a flat base and sides shaped like triangles; Maya temples were built on top of these
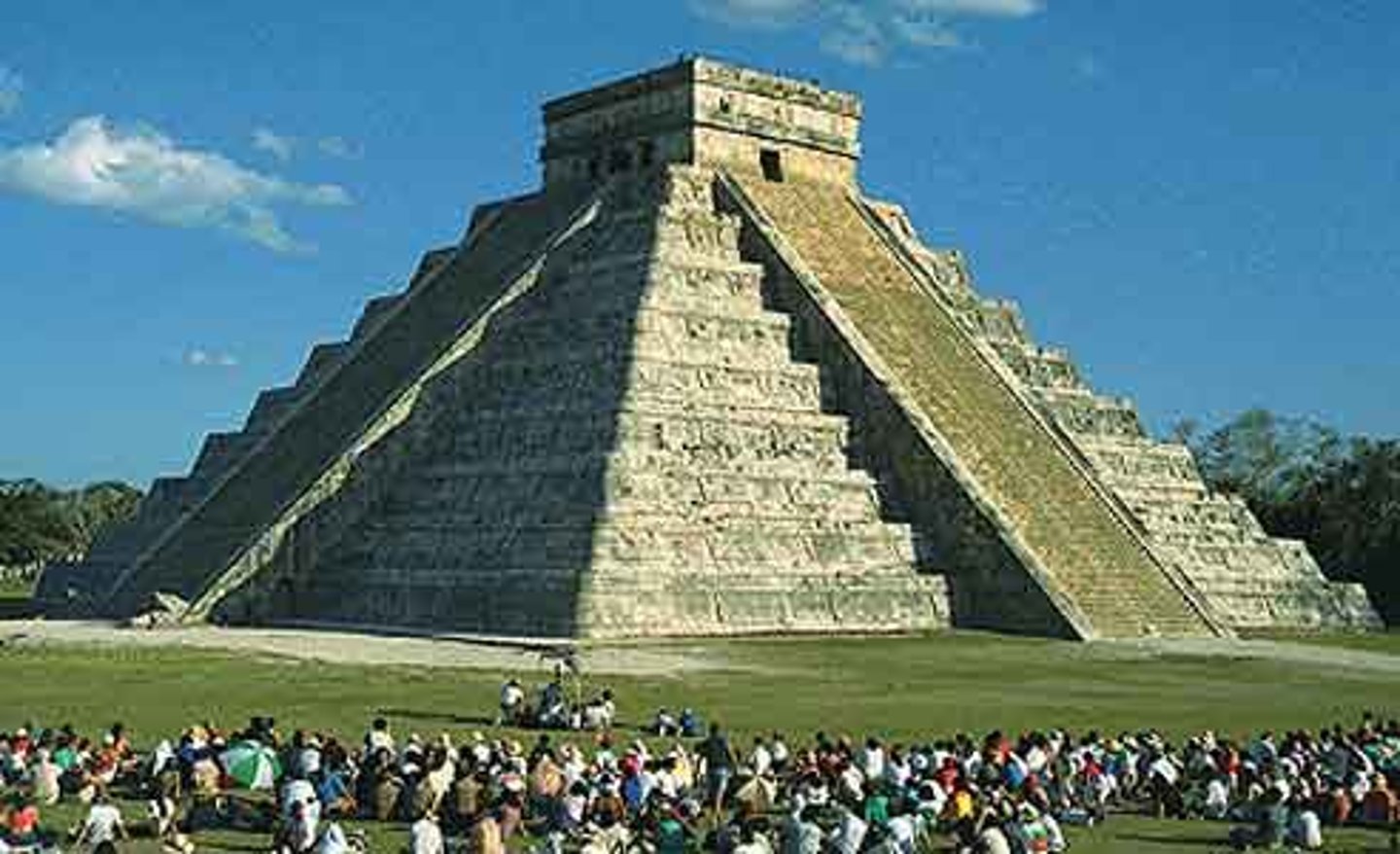

Maya buildings
constructed from large blocks of stone
