Part 1
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Types of specificity of enzymes
Absolute Specificity
Group Specificity
Reaction Specificity
Stereospecificity
Linkage Specificity
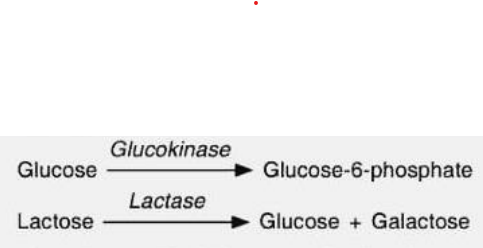
Absolute specificity
Types of specificity of enzymes
Act on only one substrate and catalyze one reaction
Most restrictive type of enzyme.
Not common.
Example is glucokinase which only binds to the substrate glucose to form G-6-P.
Another is Lactase (Hydrolase) , it will only recognize Lactose as its substrate and form form a product, glucose and galactose.
Group Specificity
Types of specificity of enzymes
Act on a specific bond or group of substrates.
Recognizes functional groups

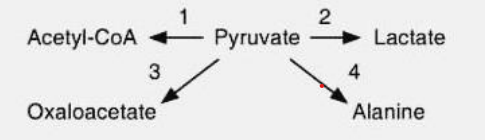
Reaction Specificity
Types of specificity of enzymes
Enzymes are specific for a particular reaction even through the substrate is same for each reaction.
The enzyme yung specific sakanya is the reaction of its catalase.
Here, regardless kung ano yung substrate, lets say we have 4 enzymes, and specific yung reaction niya, even if they have the same substrate, iba iba yung product na ma proproduce because they have different reactions.
Ex. Your pyruvate, if it passes the TCA we will form Acetyl Co-A
Ex. Pyruvate, passes anerobic glycolysis/fermentation = Lactic Acid
Ex. Pyruvate, passes TCA, gluconeogenesis = Oxaloacetate
Ex. Pyruvate, passes Amino acid metabolism = Alanine
Stereospecificity
Types of specificity of enzymes
Act on only one type of stereoisomer
Ex. Your L amino acid oxidase, it will only recognize the “L” amino acid but never the “D” amino acid.

Linkage specificity
Types of specificity of enzymes
Involves a particular type of bond, irrespective of the structural features in the vicinity of the bond.
Most general
Kahit iba iba pat ira structure as long as ma recognize niya na bond na yun na specific sa kanila, then kaya niyang ma recognize ito nga substrate as its substrate and it can catalyze the rxn.
Take note
What conditions capable in destroying your enzymes?
High Temperature
High Acidity, and Alkaline
Because they will denature.
Use of enzyme?
Catalase, they speed up.
Where is the catalytic site of an enzyme?
Active site.
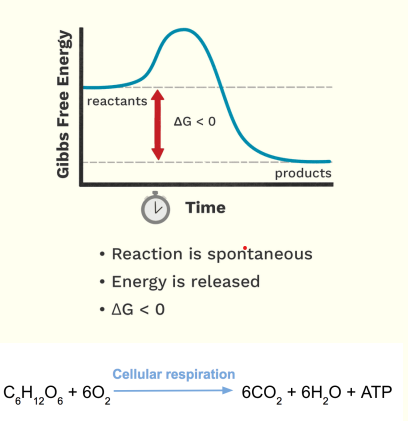
Exergonic Reaction
For a reaction to occur we need “Energy”.
In biological system, we call this energy as “Gibbs free energy”.
For us to know on how to catalyze the reaction, we need to take note the 2 important properties;
Free energy difference between the product and the substrate.
Free energy difference is denoted by a Delta G.
This will determine if the reaction will become spontaneous or not.
Energy required to produce a product.
Picture:
Let’s go to the free energy difference, in here you will observe higher yung free energy ng Reactant compared sa Product, so this is the free energy difference.
Now, pag higher yung free energy ng Reactant sa Product. The free energy difference is < 0.
If it is < 0 it is Negative.
If it is negative, the reaction can proceed spontaneously, because it is stable.
kaya niya mag occur independently without the need of an input of energy.
Ang mangyayri dito, di niya need ng energy because mag rerelease siya ng energy
Sino ba ang may mga ganitong reaction? Anabolic or Catabolic?
Catabolic
Ex. Cellular respiration, what are the reactants? It needs Glucose, CO2= H20 and O2 and ATP.
Catalase, this is capable of breaking your hydrogen peroxide forming O2 and H20.
Just remember, mostly catabolic reactions are exergonic, because they release energy.
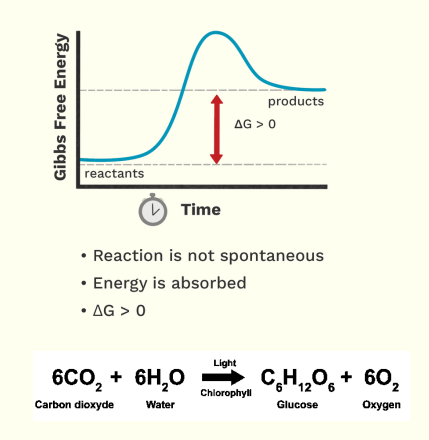
Endergonic Reaction
Now in here it is opposite, here there is a small free energy of the reactant compared to product.
If ganito siya, the Free energy difference is greater than 0
This means positive
If its positive the reaction cannot proceed independently, it is unstable.
We’ll need an input of energy, that is why energy here is absorbed.
Ex. Anabolic reactions such as Photosynthesis. We need H20 - CO2 and the energy is sunlight producing 02 and glucose.
Why is it anabolic? its because we formed a big biological molecule which is your sugar.
Take Note
The function of a catalyst is to INCREASE THE RATE OF A REACTION.
Catalysts DO NOT affect reaction equilibria.
How can we say that the reaction is at equilibrium?
There is no net change in the concentration of your reactant and product.
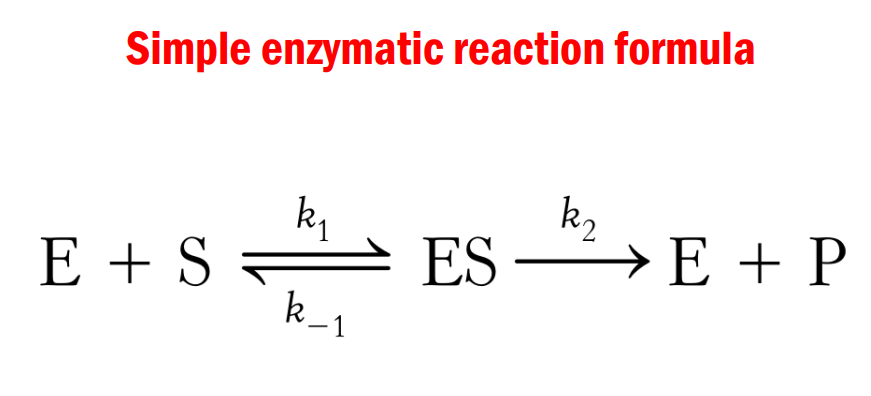
Simple Enzymatic reaction formula
This part is the enzyme substrate complex, this is formed when the enzyme and substrate binds.
Now your your ESC no longer a substrate but not yet a product.
So here you will observe it is still reversible. Pag hindi ma meet ang energy required then your ES they can revet or dissociate, If ma meet an energy demand then it can proceed to this, we can form a product.
Remember that in enzymes they are not consumed in the reaction that they are catalyzed.