Lecture 24 Non-Electrolytes and Electrolytes
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Define osmotic pressure. Define colligative properties. Demonstrate the difference between an electrolyte and non-electrolyte. Judge the difference between isosmotic, hypoosmotic, and hyperosmotic solutions. Distinguish the difference between isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions. Interpret the differences between isotonic and isosmotic. Recognize that isosmotic solutions can be formed by mixing of isosmotic solutions. Understand equations for isosmolarity for calculations in preparation for PHAR 433. Articulate the concepts of electrolyte amount (y) and electrolyte concentration (Y).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Colligative properties depend on the _____ of particles in a solution.
number
True or false: Electrolytes typically solubilize into 1 particle.
False. Nonelectrolytes
True or false: Electrolytes ideally dissociate upon solubilization based on the number of ions in the molecule.
True!
True or False: The number of particles is always what would be predicted using ideal conditions/theory.
False —> using ideal conditions/theory does not always predict the number of particles
What is isotonicity based on?
It is based on the transport of water in response to the fluid in which they are placed.
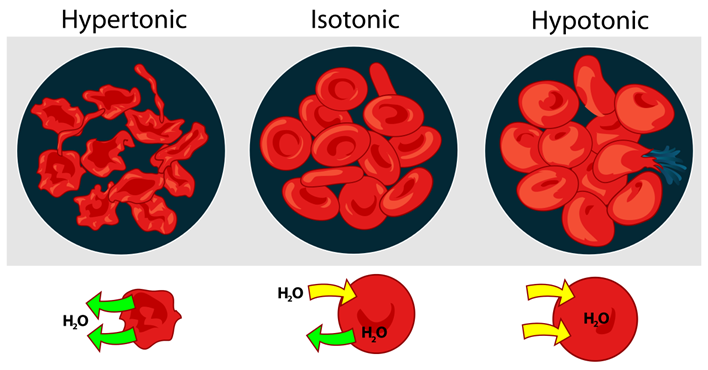
True or false: A way to measure isotonicity is to use cells (sheep blood)
True! ) Any cells work but can give different results.
What is a colligative property?
It is a property that depends on the # of particles (molecules or ions) dissolved in a solvent.
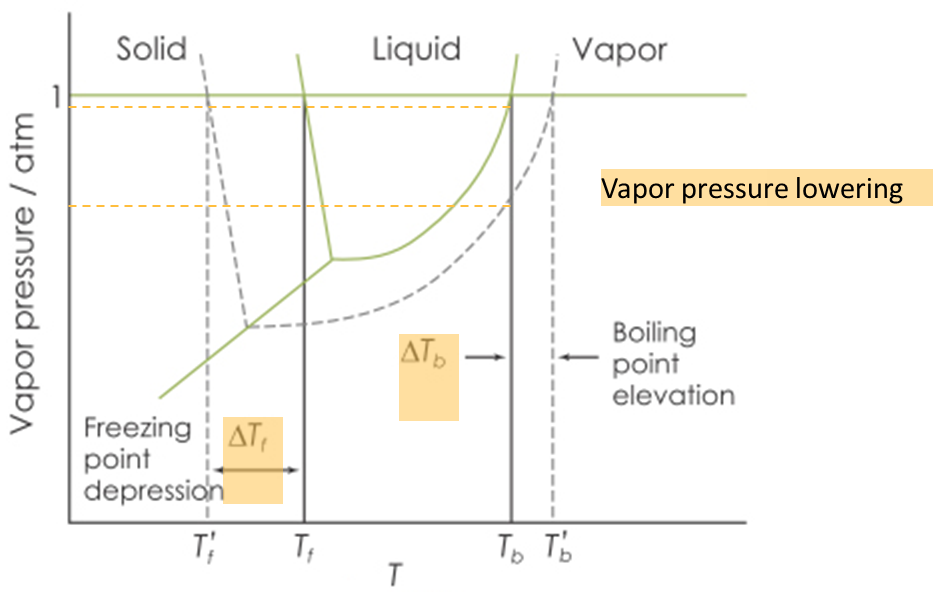
Green line —> normal solvent
Black-dashed lines —> when adding solvent to solution
What happens to freezing point depression?
a. gets raised
b. gets lowered
b. gets lowered

Green line —> normal solvent
Black-dashed lines —> when adding solvent to solution
What happens to boiling point elevation?
a. gets raised
b. gets lowered
a. gets raised
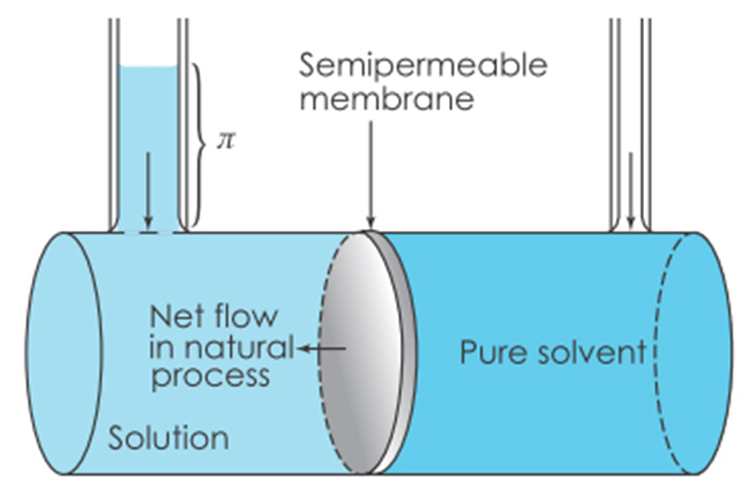
True or false: The pressure that is needed to push the water back through the membrane against gravity.
True! Osmotic pressure = π
What is Osmolarity?
Osv = i * M
Osv Units: Osmol/L
It is the #of osmoles of solute per L of solution
i = particles formed per molecule (Osmol/mol)
M = molar conc. (mol/L)
What is Osmolality?
Osm = i * b
Osm Units: Osmol/kg
The # of osmoles of solute per kg of solvent.
more stable since mass doesn’t change with temp
i = particles formed per molecule (Osmol/mol)
b = molal conc. (mol/kg)
What would happen if we mixed 100 mL of 0.9% saline and 100 mL of D5W (5% dextrose)?
It would be isosmotic.
Mixing 2 isotonic/isosmotic solutions will result in an isotonic/isosmotic solution.
The solution would be 0.45% NaCl and 2.5% dextrose.
True or false: Dextrose is a non-electrolyte and the particles do not conduct electricity.
True! It does not readily ionize when dissolved/melted.
True or false: Sodium chloride is an electrolyte because it does conduct electricity. It is also a strong electrolyte.
False. It is not a strong electrolyte < 100% dissociation.
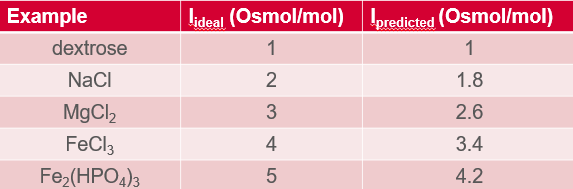
van’t Hoff = i
Non-electrolyte: i = 1
True or false: for strong electrolytes, ipredicted = # of ions formed on dissociation and is typically <iideal
False. This rule applies for weak electrolytes
Which of the following is NOT true about van’t Hoff’s factor?
a. van’t Hoff’s i is not a constant
b. van’t Hoff’s i is always predictable at times
c. van’t Hoff’s i’s have been measured or can be estimated
b. van’t Hoff’s i is always predictable at times
it is not always predictable
What is the valence (v)?
The absolute value or charge
# of electrons (e) that are present (-) or missing (+) compared to the uncharged state
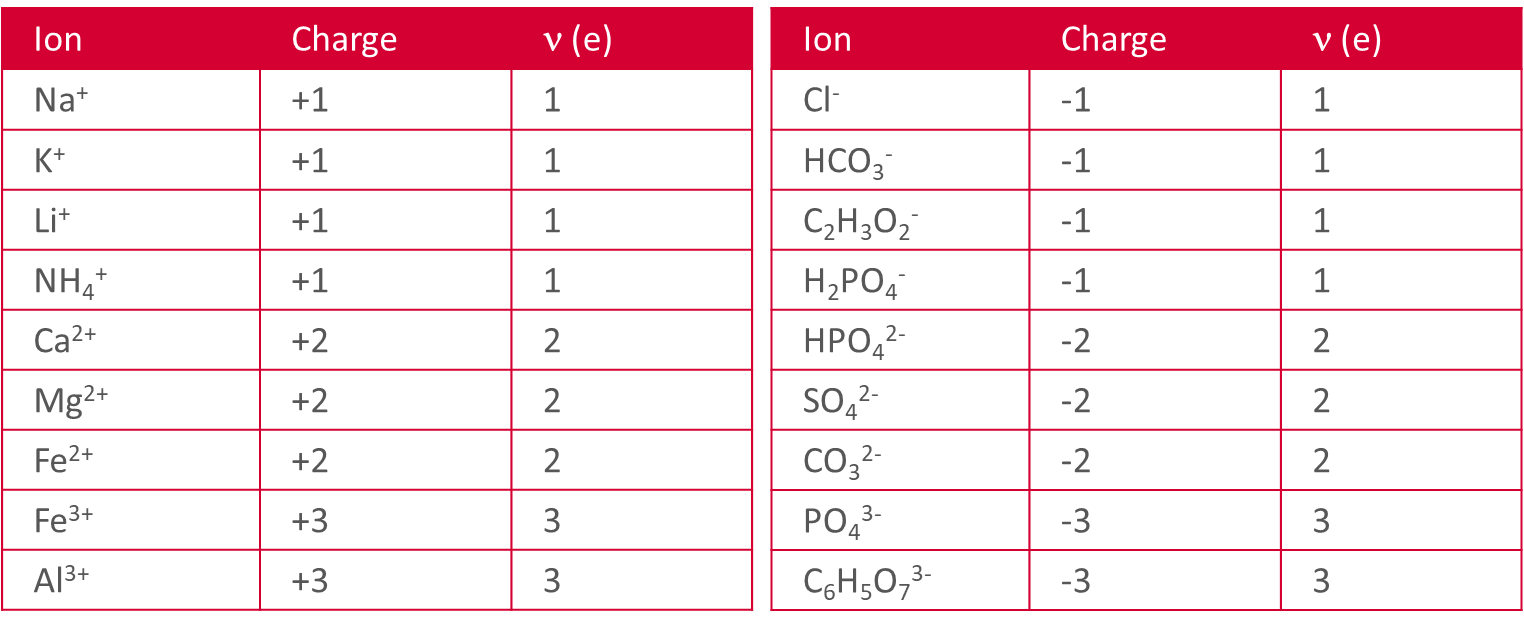

v , ψ, Ψ
What do these symbols mean?
v =
ψ = mole equivalent
Ψ = molar equivalent